鳖甲煎丸调控AKT/mTOR信号通路在肝癌细胞有氧糖酵解中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250216
Effect of Biejia Decoction Pill on aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway
-
摘要:
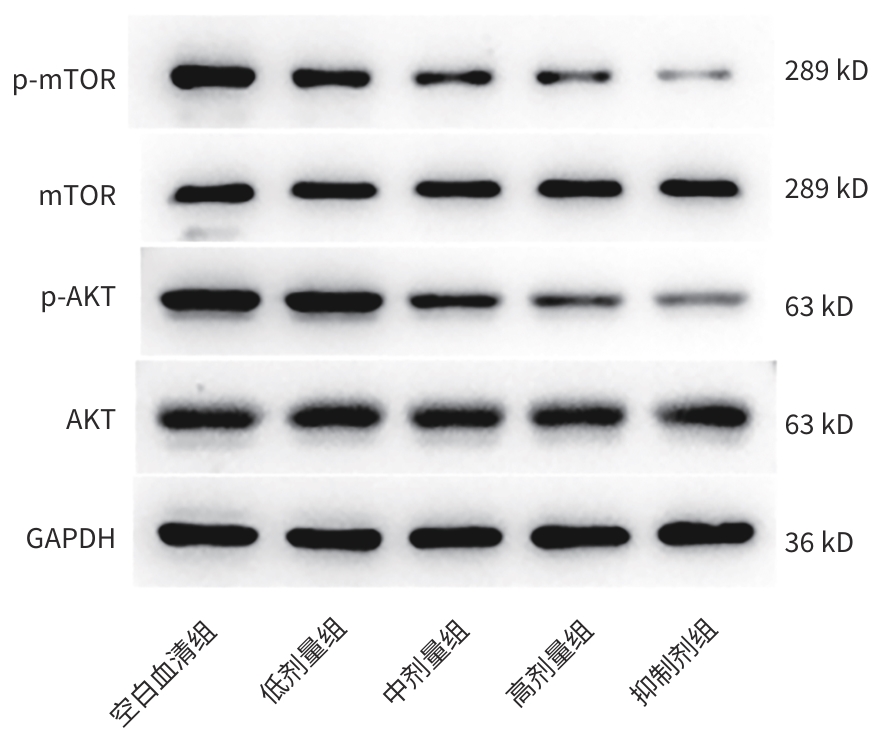
目的 利用细胞实验探索鳖甲煎丸对肝细胞癌增殖、迁移及有氧糖酵解的抑制作用,并探索其内在机制。 方法 选取人肝癌细胞株(Huh7)作为研究对象,随机将SD大鼠分为空白血清组、鳖甲煎丸高、中、低剂量组及抑制剂组,制备含药大鼠血清,用以孵育Huh7细胞。CCK-8、划痕实验探索鳖甲煎丸对肝癌细胞的增殖、迁移的影响,糖酵解限速酶及代谢产物检测探索鳖甲煎丸对肝癌细胞有氧糖酵解的影响,RT-qPCR、Western Blot实验探索鳖甲煎丸对AKT/mTOR信号通路的mRNA、相关蛋白及磷酸化的表达。多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t或Dunnettg T3检验。 结果 与空白血清组相比,鳖甲煎丸组的OD值、不同时间段的迁移率、糖酵解限速酶(己糖激酶、磷酸果糖激酶、丙酮酸激酶)及糖酵解代谢产物(丙酮酸、乳酸、ATP)检测均显著降低(P值均<0.05);RT-qPCR结果显示,与空白血清组比较,鳖甲煎丸高、中、低剂量组的mTOR mRNA表达水平均下调,高、低剂量组的AKT mRNA表达水平下调(P值均<0.05);Western Blot 结果显示,与空白血清组比较,鳖甲煎丸高、中、低剂量组的mTOR相关蛋白及磷酸化蛋白表达水平均下调,高、中剂量组的AKT相关蛋白及磷酸化蛋白表达水平均下调(P值均<0.05)。 结论 初步验证了鳖甲煎丸含药血清可以抑制人肝癌细胞Huh7细胞的有氧糖酵解,从而抑制其增殖、迁移,其机制可能与抑制AKT/mTOR信号通路的相关蛋白表达有关。 -
关键词:
- 鳖甲煎丸 /
- 肝肿瘤, 实验性 /
- 瓦尔堡效应, 肿瘤学
Abstract:Objective To investigate the inhibitory effect of Biejia Decoction Pill on the proliferation, migration, and aerobic glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using cell experiments, as well as related mechanisms. Methods Human liver cancer cell line Huh7 was selected, and Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into blank serum group, inhibitor group, and high-, middle-, and low-dose Biejia Decoction Pill groups. Rat serum containing the drug was prepared for the incubation of Huh7 cells. CCK8 assay and scratch assay were used to explore the effect of Biejia Decoction Pill on the proliferation and migration of HCC cells; glycolytic rate-limiting enzymes and metabolites were measured to explore the effect of Biejia Decoction Pill on aerobic glycolysis of liver cancer cells; RT-qPCR and Western blot were used to explore the effect of Biejia Decoction Pill on the mRNA expression, related proteins, and phosphorylation of the protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test or the Dunnett’s T3 test were used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the blank serum group, the Biejia Decoction Pill groups had significant reductions in OD value, migration rate during different periods of time, glycolytic rate-limiting enzymes (hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, pyruvate kinase), and glycolytic metabolites (pyruvate, lactic acid, ATP) (all P<0.05). RT-qPCR results showed that compared with the blank serum group, the high-, middle-, and low-dose Biejia Decoction Pill groups had a significant reduction in the mRNA expression level of mTOR, and the high- and low-dose Biejia Decoction Pill groups had a significant reduction in the mRNA expression level of AKT (all P<0.05). Western blot results showed that compared with the blank serum group, the high-, middle-, and low-dose Biejia Decoction Pill groups had significant reductions in the expression levels of mTOR-related proteins and phosphorylated proteins, and the high- and middle-dose Biejia Decoction Pill groups had significant reductions in the expression levels of AKT-related proteins and phosphorylated proteins (all P<0.05). Conclusion This study preliminarily verifies that the serum containing Bijia Decoction Pill can inhibit the aerobic glycolysis of human hepatoma Huh7 cells, thereby inhibiting their proliferation and migration, possibly by inhibiting the expression of the proteins related to the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. -
表 1 各组细胞OD值检测结果
Table 1. Test results of cell OD value in each group
组别 细胞增殖(OD值) 空白血清组 2.07±0.02 低剂量组 1.55±0.051) 中剂量组 1.22±0.081) 高剂量组 1.13±0.041) 抑制剂组 0.90±0.051) F值 332.81 P值 <0.001 注:与空白血清组比较,1)P<0.05。
表 2 各组细胞24、48 h的迁移率比较
Table 2. Comparison of 24 h and 48 h mobility of cells in each group
组别 24 h迁移率 48 h迁移率 空白血清组 0.385±0.017 0.891±0.009 低剂量组 0.311±0.0241) 0.850±0.0051) 中剂量组 0.301±0.0251) 0.774±0.0161) 高剂量组 0.129±0.0251) 0.740±0.0211) 抑制剂组 0.059±0.0351) 0.677±0.0051) F值 83.60 137.73 P值 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白血清组比较,1)P<0.05。
表 3 各组细胞糖酵解限速酶活性
Table 3. Cell glycolytic rate-limiting enzyme activities in each group
组别 HK活性
(μg/mL)
PFK活性
(U/mg)
PK活性
(U/mg)
空白血清组 13.62±0.42 36.43±2.02 628.57±23.98 低剂量组 12.29±0.691) 35.16±0.431) 582.52±21.601) 中剂量组 8.39±0.581) 26.22±0.981) 525.14±5.211) 高剂量组 10.23±0.821) 28.56±0.491) 527.28±13.361) 抑制剂组 5.43±0.581) 21.75±0.121) 472.42±24.121) F值 78.78 98.75 29.41 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白血清组比较,1)P<0.05。
表 4 各组细胞糖酵解代谢产物水平
Table 4. Levels of glycolytic metabolites in each group
组别 丙酮酸
(μmol/mg)
乳酸
(μmol/g)
ATP活性(μmol/106个) 空白血清组 0.451±0.009 3.709±0.113 0.083±0.003 低剂量组 0.366±0.0081) 2.818±0.0481) 0.072±0.0011) 中剂量组 0.188±0.0061) 2.062±0.0321) 0.057±0.0031) 高剂量组 0.178±0.0031) 1.781±0.0471) 0.053±0.0021) 抑制剂组 0.144±0.0061) 1.319±0.0211) 0.047±0.0021) F值 1 222.53 707.09 88.49 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白血清组比较,1)P<0.05。
表 5 AKT、mTOR的mRNA水平
Table 5. mRNA levels of AKT and mTOR
组别 AKT mTOR 空白血清组 0.98±0.03 1.06±0.21 低剂量组 0.74±0.111) 0.64±0.121) 中剂量组 0.86±0.10 0.53±0.081) 高剂量组 0.73±0.211) 0.54±0.111) 抑制剂组 0.33±0.091) 0.15±0.031) F值 12.10 19.73 P值 0.001 <0.001 注:与空白血清组比较,1)P<0.05。
表 6 p-AKT/AKT、p-mTOR/mTOR的表达水平
Table 6. Expression levels of P-AKT/AKT and P-mTOR/mTOR
组别 p-AKT/AKT p-mTOR/mTOR 空白血清组 1.09±0.15 1.29±0.16 低剂量组 1.07±0.13 0.95±0.141) 中剂量组 0.72±0.091) 0.71±0.081) 高剂量组 0.55±0.071) 0.51±0.061) 抑制剂组 0.37±0.051) 0.23±0.031) F值 124.00 82.98 P值 <0.001 <0.001 注:与空白血清组比较,1)P<0.05。
-
[1] WANG J, ZHANG CL, TANG KY, et al. Research advances in traditional Chinese medicine in regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transformation to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 11): 2636- 2642. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.040.王珏, 张春蕾, 汤凯悦, 等. 中医药调控上皮-间质转化抑制肝癌转移的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 11): 2636- 2642. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.040. [2] SEVER R, BRUGGE JS. Signal transduction in cancer[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2015, 5( 4): a006098. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006098. [3] LEE G, ZHENG YX, CHO S, et al. Post-transcriptional regulation of de novo lipogenesis by mTORC1-S6K1-SRPK2 signaling[J]. Cell, 2017, 171( 7): 1545- 1558. e 18. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.037. [4] PATRA T, MEYER K, RAY RB, et al. A combination of AZD5363 and FH5363 induces lethal autophagy in transformed hepatocytes[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11( 7): 540. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02741-1. [5] WANG HY, CHEN L. Tumor microenviroment and hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28( Suppl 1): 43- 48. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12091. [6] SUN C, LI B, LI L, et al. Effect of Huaier granules on patients with middle and advanced liver cancer[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2022, 38( 10): 1130- 1133. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2022.10.016.孙川, 李宾, 李磊, 等. 槐耳颗粒治疗中晚期肝癌[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2022, 38( 10): 1130- 1133. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2022.10.016. [7] SHI ZG, WANG WP. The transformation of the pathogenesis of tumor metastasis[J]. J Pract Tradit Chin Intern Med, 2013, 27( 8): 68- 70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7813.2013.04(x).34.史振广, 王文萍. 恶性肿瘤转移的病机转化[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2013, 27( 8): 68- 70. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7813.2013.04(x).34. [8] WU MS, LIU H, TAN NH, et al. The effect of Biejiajian Pills on regulating the EGFR/MAPK/ERK pathway in MHCC-97H liver cancer cells[J]. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med, 2024, 47( 3): 394- 406.伍梦思, 刘华, 谭年花, 等. 鳖甲煎丸调控EGFR/MAPK/ERK通路对MHCC-97H肝癌细胞的影响[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2024, 47( 3): 394- 406. [9] ZHONG XD, WEN B, SUN HT, et al. Mechanism of Biejiajian Wan against EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2022, 28( 1): 24- 32. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20212421.钟晓丹, 文彬, 孙海涛, 等. 鳖甲煎丸通过NF-κB信号通路抑制肝癌细胞上皮间质转化的作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28( 1): 24- 32. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20212421. [10] HUANG JJ, HUANG HN, ZHANG WF, et al. Bie Jia Jian pill combined with bone mesenchymal stem cells regulates microRNA-140 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells[J]. Int J Stem Cells, 2021, 14( 3): 275- 285. DOI: 10.15283/ijsc20157. [11] SHAO FL, CHEN QP, BI Q, et al. Intervention mechanism of Biejiajian Wan on primary liver cancer by regulating lncRNA SNHG5/miRNA-26a-5p/GSK-3β signal axis[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2024, 30( 4): 107- 113. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230730.邵范雷, 陈秋平, 毕倩, 等. 鳖甲煎丸调控lncRNA SNHG5/miRNA-26a-5p/GSK-3β信号轴干预原发性肝癌的作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024, 30( 4): 107- 113. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20230730. [12] TAO ZD, WU QY, LAN XH, et al. Effect of physcion on proliferation and glycolysis of liver cancer cells and its mechanism[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2022, 27( 9): 769- 775. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2022.09.001.陶正娣, 吴勤研, 蓝晓红, 等. 大黄素甲醚对人肝癌细胞增殖及糖酵解的调控作用及机制研究[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2022, 27( 9): 769- 775. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2022.09.001. [13] ZANOTELLI MR, ZHANG J, REINHART-KING CA. Mechanoresponsive metabolism in cancer cell migration and metastasis[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33( 7): 1307- 1321. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.04.002. [14] NIU YQ, LIU F, WANG XY, et al. miR-183-5p promotes HCC migration/invasion via increasing aerobic glycolysis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2021, 14: 3649- 3658. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S304117. [15] WEI YH, YANG CX, YANG GM, et al. Inhibitory effect of downregulating HMGB2 expression on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of liver cancer LM3 cells and its AKT/mTOR signaling pathway mechanism[J]. J Jilin Univ Med Ed, 2024, 50( 1): 143- 149. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240118.魏雁虹, 杨晨雪, 杨广民, 等. 下调HMGB2表达对肝癌LM3细胞上皮-间质转化的抑制作用及其AKT/mTOR信号通路机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2024, 50( 1): 143- 149. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240118. [16] DI SC, GONG M, LV JM, et al. Glycolysis-related biomarker TCIRG1 participates in regulation of renal cell carcinoma progression and tumor immune microenvironment by affecting aerobic glycolysis and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23( 1): 186. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-023-03019-0. [17] YU FY, ZHAO XY, LI MT, et al. SLITRK6 promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and Warburg effect[J]. Apoptosis, 2023, 28( 7-8): 1216- 1225. DOI: 10.1007/s10495-023-01838-0. [18] SHI Z, ZHOU LY, ZHAO GD, et al. Effect of micro-ribonucleic acid-21 on the malignant biological behavior of cholangiocarcinoma cells by targeting the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 9): 2091- 2098. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.026.施喆, 周丽媛, 赵国栋, 等. MiR-21靶向调控PTEN/PI3K/Akt通路对胆管癌细胞恶性生物学行为的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 9): 2091- 2098. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.026. [19] LI ZB, YE JX, WU Y, et al. Study on the mechanism of bezafibrate inhibiting glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma through AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. J Guangdong Pharm Univ, 2024, 40( 1): 101- 104. DOI: 10.16809/j.cnki.2096-3653.2023030703.李智斌, 叶锦霞, 巫艳, 等. 苯扎贝特通过AKT/mTOR通路抑制肺腺癌糖酵解机制研究[J]. 广东药科大学学报, 2024, 40( 1): 101- 104. DOI: 10.16809/j.cnki.2096-3653.2023030703. [20] QU YQ, ZHANG QY, TAN XY, et al. Effect of nuciferine against the proliferation of cholangiocarcinoma cells through Akt/mTOR/4EBP1-glycolytic pathway[J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2023, 35( 8): 1297- 1304, 1379. DOI: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2023.8.002.屈雅琴, 张倩玉, 谈相云, 等. 荷叶碱抑制Akt/mTOR/4EBP1-糖酵解通路抗胆管癌细胞增殖作用研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2023, 35( 8): 1297- 1304, 1379. DOI: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2023.8.002. [21] DENG DJ, LI L, TAN XY, et al. Effect and mechanism of icaritin on inhibiting proliferation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells by Akt/mTOR-mediated glycolysis[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2022, 53( 10): 3061- 3069. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.10.016.邓冬杰, 李励, 谈相云, 等. 淫羊藿素通过Akt/mTOR调控糖酵解抑制肝内胆管癌细胞增殖的作用机制研究[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53( 10): 3061- 3069. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.10.016. -




 PDF下载 ( 2065 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2065 KB)


 下载:
下载: