慢性乙型肝炎患者血清HBV RNA水平与核苷(酸)类似物治疗时间的关系
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240111
Correlation between serum HBV RNA and duration of treatment with nucleos(t)ide analogues in patients with chronic hepatitis B
-
摘要:
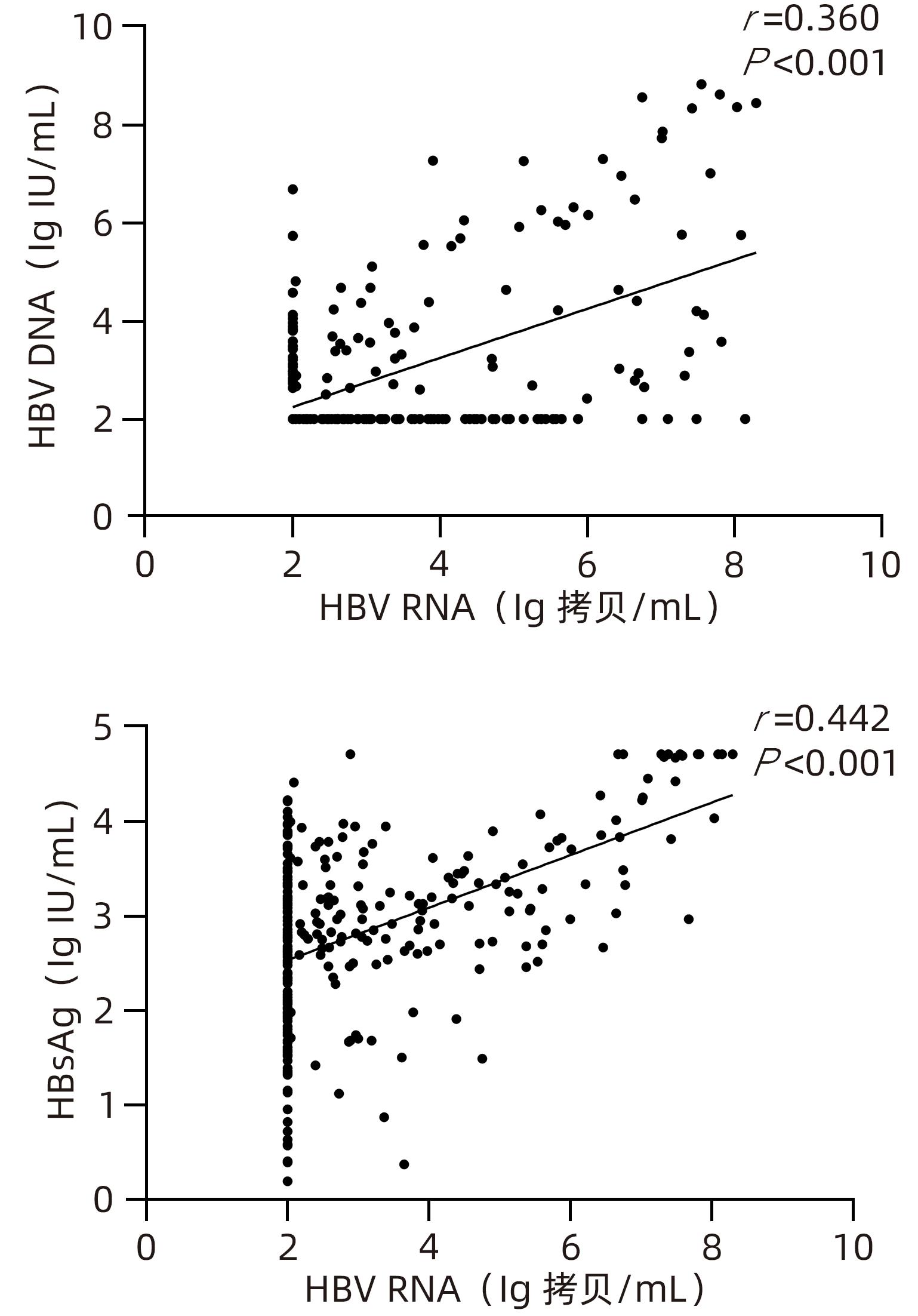
目的 检测未治疗和经过治疗的慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者血清HBV RNA水平,并分析血清HBV RNA水平与核苷(酸)类似物(NAs)抗病毒治疗时间的关系。 方法 选取2022年2月—2022年7月间就诊于石河子大学医学院第一附属医院感染科门诊患者中的300例CHB患者为研究对象。收集患者临床资料,根据患者抗病毒治疗时间不同分为未治疗组(n=73)、治疗时间≤1年组(n=91)、治疗时间>1年组(n=136),检测患者血清HBV RNA和HBV DNA载量及HBsAg浓度。计量资料两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验,多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni校正法;计数资料用χ2检验,采用Spearman相关分析比较各指标间相关程度。 结果 HBeAg阳性率18.3%,在HBV DNA阴性者中HBV RNA阳性者占比44.1%(86/195)。HBeAg阳性组和HBeAg阴性组患者血清HBV RNA、HBV DNA、HBsAg水平分布差异均具有统计学意义(Z值分别为10.740、6.300、7.280,P值均<0.05)。未治疗组与治疗时间≤1年组仅有DNA水平分布情况有统计学差异(P<0.05),未治疗组与治疗时间>1年组HBV RNA、HBV DNA水平分布差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05),治疗时间≤1年与治疗时间>1年组中HBV RNA、HBV DNA、HBsAg水平分布情况差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。抗病毒治疗时间与HBV RNA、HBsAg水平呈极弱负相关(r值分别为-0.247、-0.138,P值均<0.05),与HBV DNA水平呈强负相关(r=-0.771,P<0.001)。血清HBV RNA与HBV DNA、HBsAg水平呈低度相关(r值分别为0.360、0.442,P值均<0.001),进一步分层分析显示,在未治疗组中,HBV RNA与HBV DNA水平呈强正相关(r=0.752,P<0.001),与HBsAg水平呈中度正相关(r=0.559,P<0.001);在治疗时间≤1年组中,HBV RNA与HBV DNA、HBsAg水平呈低度正相关(r值分别为0.396、0.388,P值均<0.001);在治疗时间>1年组中,HBV RNA与HBsAg水平呈低度正相关(r=0.352,P<0.001)。 结论 血清HBV RNA与NAs治疗时间呈负相关,与HBV DNA、HBsAg水平的相关性随着治疗时间的延长逐渐下降,可以在一定程度上作为CHB患者病毒学水平监测的补充指标,尤其在未治疗患者中反映病毒复制水平准确性较高。 Abstract: Objective To investigate the serum level of HBV RNA in untreated or treatment-experienced patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and the correlation between serum HBV RNA level and the duration of antiviral therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues (NAs). Methods A total of 300 patients with CHB who attended Department of Infectious Diseases in The First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University School of Medicine from February to July, 2022, were enrolled as subjects. Related clinical data were collected, and according to the duration of antiviral therapy, they were divided into untreated group with 73 patients, treatment duration ≤1 year group with 91 patients, and treatment duration >1 year group with 136 patients. Serum HBV RNA load, HBV DNA load, and HBsAg concentration were measured for all patients. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison between multiple groups, further pairwise comparison using Bonferroni method; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data; a Spearman correlation analysis was used to investigate the degree of correlation between various indicators. Results The positive rate of HBeAg was 18.3%, and among the patients with negative HBV DNA, the patients with positive HBV RNA accounted for 44.1% (86/195). There was a significant difference in the distribution of the serum levels of HBV RNA, HBV DNA, and HBsAg between the positive HBeAg group and the negative HBeAg group (Z=10.740, 6.300, and 7.280, all P<0.05). There was a significant difference in the distribution of DNA level between the untreated group and the treatment duration ≤1 year group (P<0.05); there was a significant difference in the distribution of HBV RNA and HBV DNA levels between the untreated group and the treatment duration >1 year group (P<0.05); there was a significant difference in the distribution of HBV RNA, HBV DNA, and HBsAg levels between the treatment duration ≤1 year group and the treatment duration >1 year group (P<0.05). The correlation analysis between the duration of antiviral therapy and the levels of HBV RNA, HBV DNA, and HBsAg showed that the duration of antiviral therapy had an extremely weak negative correlation with the levels of HBV RNA and HBsAg (r=-0.247 and -0.138, both P<0.05) and a strong negative correlation with the level of HBV DNA (r=-0.771, P<0.001). There was a low degree of correlation between the serum level of HBV RNA and the serum levels of HBV DNA and HBsAg (r=0.360 and 0.442, both P<0.001). Further stratified analysis showed that in the untreated group, there was a strong positive correlation between HBV RNA and HBV DNA (r=0.752, P<0.001) and a moderate positive correlation between HBV RNA and HBsAg (r=0.559, P<0.001); in the treatment duration ≤1 year group, there was a low degree of positive correlation between HBV RNA and HBV DNA/HBsAg (r=0.396 and r=0.388, both P<0.001); in the treatment duration >1 year group, there was a low degree of positive correlation between HBV RNA and HBsAg (r=0.352, P<0.001). Conclusion Serum HBV RNA is negatively correlated with the duration of treatment with NAs, and the correlation of HBV RNA with HBV DNA and HBsAg gradually decreases with the increase in the duration of treatment. Therefore, it can be used as a supplementary indicator for monitoring the level of virologic response in CHB patients to a certain extent, with a relatively high accuracy in reflecting the level of viral replication in untreated patients. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- Nucleosides /
- Nucleotides
-
表 1 一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data
指标 HBeAg阳性组(n=55) HBeAg阴性组(n=245) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 46(35~53) 51(45~56) Z=-3.116 0.002 性别[例(%)] χ2=0.615 0.433 男 34(61.8) 165(67.3) 女 21(38.2) 80(32.7) HBV RNA(lg 拷贝/mL) 6.02(4.50~7.33) 2.00(2.00~2.75) Z=10.831 <0.001 HBV DNA(lg IU/mL) 3.58(2.00~6.48) 2.00(2.00~2.75) Z=6.298 <0.001 HBsAg(lg IU/mL) 3.64(3.19~4.28) 2.77(2.09~3.21) Z=7.282 <0.001 ALT(U/L) 24.60(16.40~53.40) 19.80(14.60~26.30) Z=3.563 <0.001 AST(U/L) 24.60(20.20~33.90) 19.90(16.95~24.55) Z=3.703 <0.001 表 2 不同的抗病毒药物对各指标的影响
Table 2. Effects of different antiviral drugs on various indicators
指标 恩替卡韦组(n=180) 替诺福韦组(n=46) 统计值 P值 HBV DNA检出率[例(%)] 28(15.6) 4(8.7) χ2=1.418 0.234 HBV RNA检出率[例(%)] 85(47.2) 23(50.0) χ2=0.113 0.736 HBV DNA(lg IU/mL) 2.00(2.00~2.00) 2.00(2.00~2.00) Z=-1.334 0.182 HBV RNA(lg 拷贝/mL) 2.00(2.00~3.20) 2.09(2.00~4.20) Z=0.861 0.389 HBsAg(lg IU/mL) 2.88(2.28~3.38) 2.92(2.50~3.57) Z=0.539 0.590 表 3 抗病毒治疗时间不同HBV RNA、HBV DNA、HBsAg水平差异
Table 3. Differences in HBV RNA, HBV DNA, and HBsAg levels at different times of antiviral treatment
组别 例数 HBV RNA(lg 拷贝/mL) HBV DNA(lg IU/mL) HBsAg(lg IU/mL) 未治疗组 73 2.73(2.00~5.11) 3.96(3.33~6.00) 2.86(2.11~3.70) 治疗时间≤1年组 91 2.47(2.00~4.71) 2.00(2.00~2.71)1) 3.25(2.63~3.84) 治疗时间>1年组 136 2.00(2.00~2.94)1)2) 2.00(2.00~2.00)1)2) 2.78(2.20~3.13)2) H值 19.301 206.390 13.693 P值 <0.001 <0.001 0.001 注:与未治疗组比较,1)P<0.05;与治疗时间≤1年组比较,2)P<0.05。 -
[1] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. [2] LIU J, LIANG WN, JING WZ, et al. Countdown to 2030: Eliminating hepatitis B disease, China[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2019, 97( 3): 230- 238. DOI: 10.2471/BLT.18.219469. [3] PETERSEN J, THOMPSON AJ, LEVRERO M. Aiming for cure in HBV and HDV infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65( 4): 835- 848. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.043. [4] TIAN Y, REN F. Advances in the detection and clearance of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA(cccDNA)[J]. Chin J Microbiol Immunol, 2019, 39( 11): 875- 879. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5101.2019.11.011.田原, 任锋. 乙型肝炎病毒共价闭合环状DNA(cccDNA)检测和清除的研究进展[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2019, 39( 11): 875- 879. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-5101.2019.11.011. [5] ZAI WJ, CHEN JL, YUAN ZH. Regulatory mechanisms of the transcription and metabolism of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA and strategies for silencing and elimination[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 5): 983- 988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05.006.宰文静, 陈捷亮, 袁正宏. HBV cccDNA转录代谢调控机制及沉默清除策略[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 5): 983- 988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05.006. [6] ZHANG Y, ZHAO JM. Clinical application of covalently closed circular DNA detection techniques[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 10): 2140- 2144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.002.张宇, 赵景民. HBV cccDNA检测技术与临床应用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 10): 2140- 2144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.002. [7] LEVRERO M, TESTONI B, ZOULIM F. HBV cure: Why, how, when?[J]. Curr Opin Virol, 2016, 18: 135- 143. DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.06.003. [8] WANG J, SHEN T, HUANG XB, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA is encapsidated pregenome RNA that may be associated with persistence of viral infection and rebound[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65( 4): 700- 710. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.029. [9] XIA MY, CHI H, WU YB, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA level is associated with biochemical relapse in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection who discontinue nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 54( 5): 709- 714. DOI: 10.1111/apt.16538. [10] LU FM, WANG J, CHEN XM, et al. The potential use of serum HBV RNA to guide the functional cure of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2017, 25( 2): 105- 110. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.02.005.鲁凤民, 王杰, 陈香梅, 等. 乙型肝炎病毒RNA病毒样颗粒的发现及其对抗病毒治疗临床实践的潜在影响[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2017, 25( 2): 105- 110. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.02.005. [11] KÖCK J, THEILMANN L, GALLE P, et al. Hepatitis B virus nucleic acids associated with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells do not originate from replicating virus[J]. Hepatology, 1996, 23( 3): 405- 413. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510230303. [12] TAO YC, WANG ML, LIAO J, et al. Dynamics of serum pregenome RNA in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving 96-month nucleos(t)ide analog therapy[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 787770. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.787770. [13] ZHANG X, AN XC, SHI L, et al. Baseline quantitative HBcAb strongly predicts undetectable HBV DNA and RNA in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with entecavir for 10 years[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 13389. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92757-0. [14] SHEN S, XIE ZL, CAI DW, et al. Biogenesis and molecular characteristics of serum hepatitis B virus RNA[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2020, 16( 10): e1008945. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008945. [15] PRAKASH K, RYDELL GE, LARSSON SB, et al. High serum levels of pregenomic RNA reflect frequently failing reverse transcription in hepatitis B virus particles[J]. Virol J, 2018, 15( 1): 86. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-018-0994-7. [16] TSUKUDA S, WATASHI K. Hepatitis B virus biology and life cycle[J]. Antiviral Res, 2020, 182: 104925. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104925. [17] LI H, XU WT, DENG BC, et al. Research progress of nucleoside(acid) analogues combined with pegylated interferon in functional treatment of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 890- 893. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.04.李卉, 许文涛, 邓宝成, 等. 核苷(酸)类似物联合聚乙二醇干扰素功能性治愈慢性乙型肝炎研究进展[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2022, 50( 9): 890- 893. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.04. [18] GIERSCH K, ALLWEISS L, VOLZ T, et al. Serum HBV pgRNA as a clinical marker for cccDNA activity[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 66( 2): 460- 462. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.028. [19] WANG Y, LIU YN, LIAO H, et al. Serum HBV DNA plus RNA reflecting cccDNA level before and during NAs treatment in HBeAg positive CHB patients[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2022, 19( 5): 858- 866. DOI: 10.7150/ijms.71737. [20] PENG YM, YUAN H, ZHOU YF, et al. Serum hepatitis B virus RNA level in chronic hepatitis B with low level of hepatitis B virus DNA and its influential factors[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2019, 22( 18): 2217- 2222. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.020.彭亚梦, 袁浩, 周毅峰, 等. 低水平乙型肝炎病毒DNA慢性乙型肝炎患者血清乙型肝炎病毒RNA水平及其影响因素研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22( 18): 2217- 2222. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.020. [21] WANG CK, LIU SR. Expression level of serum HBV RNA in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients at different periods and its value of measurement[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 12): 2798- 2801. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.12.014.王成康, 刘寿荣. 血清HBV RNA在HBeAg阳性慢性乙型肝炎患者不同时期的表达水平及检测价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 12): 2798- 2801. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.12.014. [22] LING XZ, WANG RM, SU MH, et al. Clinical significance of dynamic monitoring of serum HBV pgRNA in CHB patients treated with NAs[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2022, 42( 5): 404- 408. DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2022050112.零小樟, 王荣明, 苏明华, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎患者核苷酸类似物治疗中动态监测血清乙型肝炎病毒前基因组RNA的临床意义[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2022, 42( 5): 404- 408. DOI: 10.19538/j.nk2022050112. [23] ZHU Y, LUO YX, GUO FX, et al. Predictive value of serum HBV RNA for therapeutic effect of entecavir in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J South Med Univ, 2022, 42( 8): 1250- 1255. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.08.19.朱莹, 罗园香, 郭凤霞, 等. 血清HBV RNA预测恩替卡韦治疗慢性乙型肝炎患者疗效的价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42( 8): 1250- 1255. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.08.19. [24] JIANG B, DAI QH, LIU YM, et al. Levels of HBV RNA in chronic HBV infected patients during first-line nucleos(t)ide analogues therapy[J]. Infect Agent Cancer, 2022, 17( 1): 61. DOI: 10.1186/s13027-022-00473-9. -



 PDF下载 ( 721 KB)
PDF下载 ( 721 KB)

 下载:
下载:


