超重人群中健康者与非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者的临床特征及血清脂质组学分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240211
Clinical features and serum lipidomic profile of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and healthy individuals in the overweight population
-
摘要:
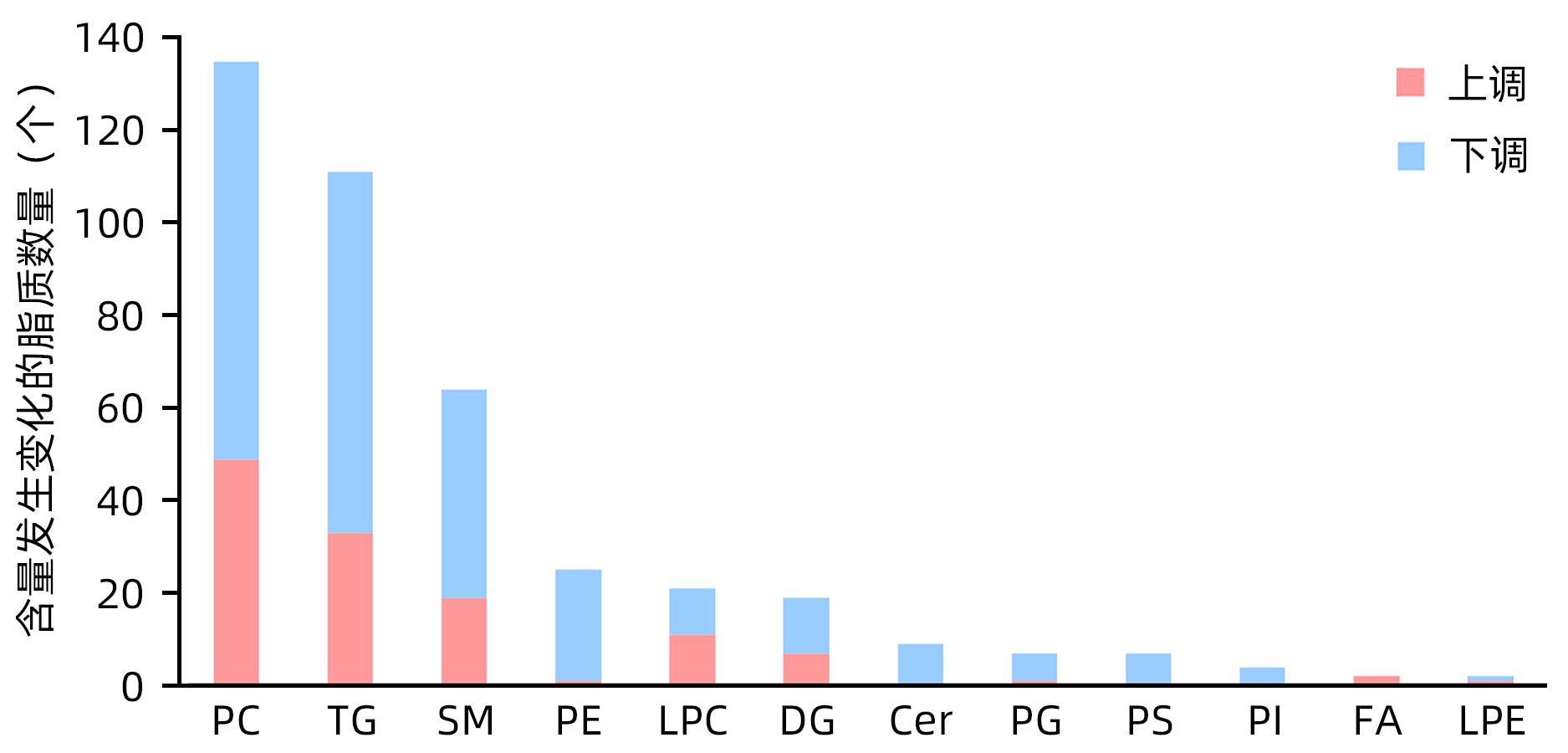
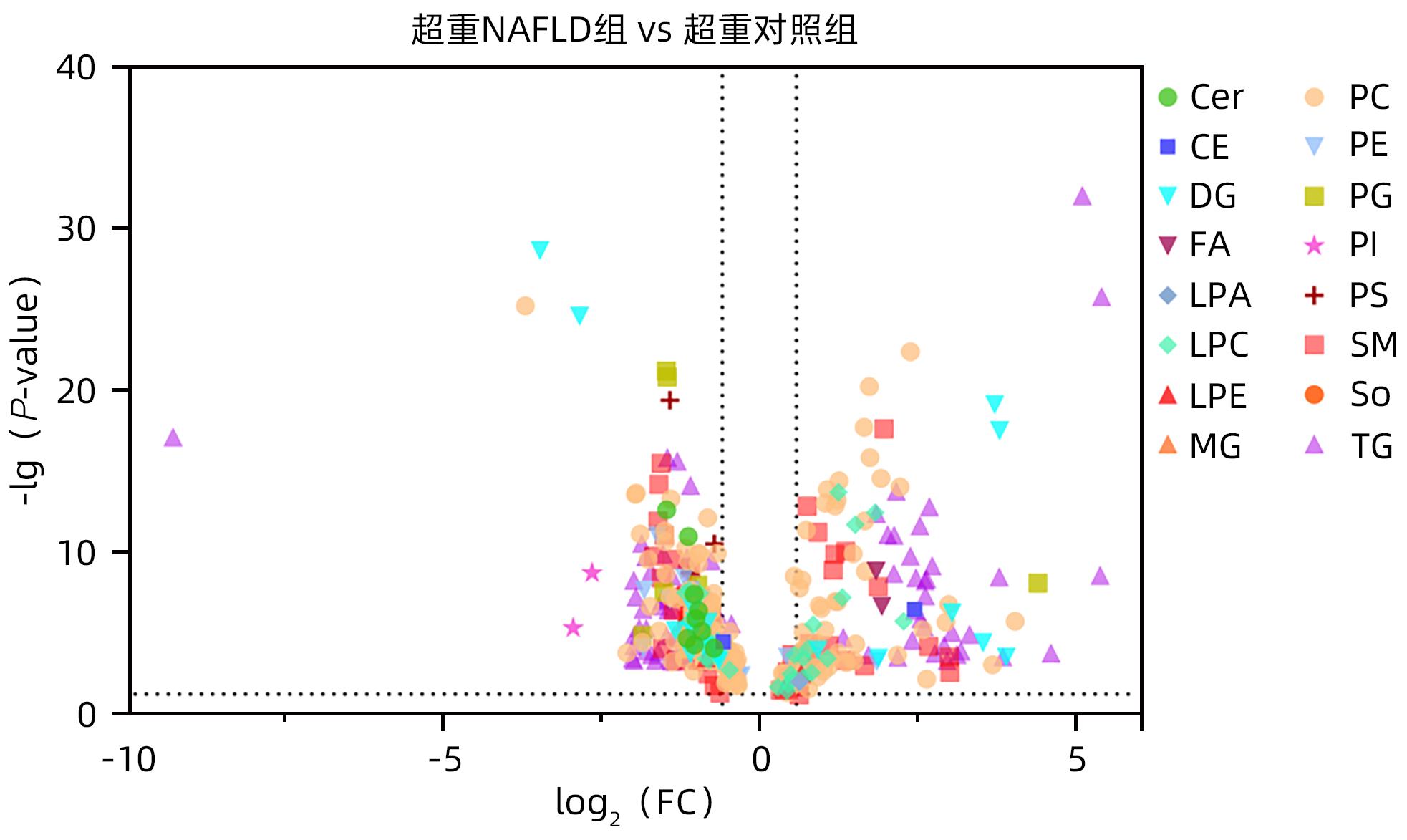
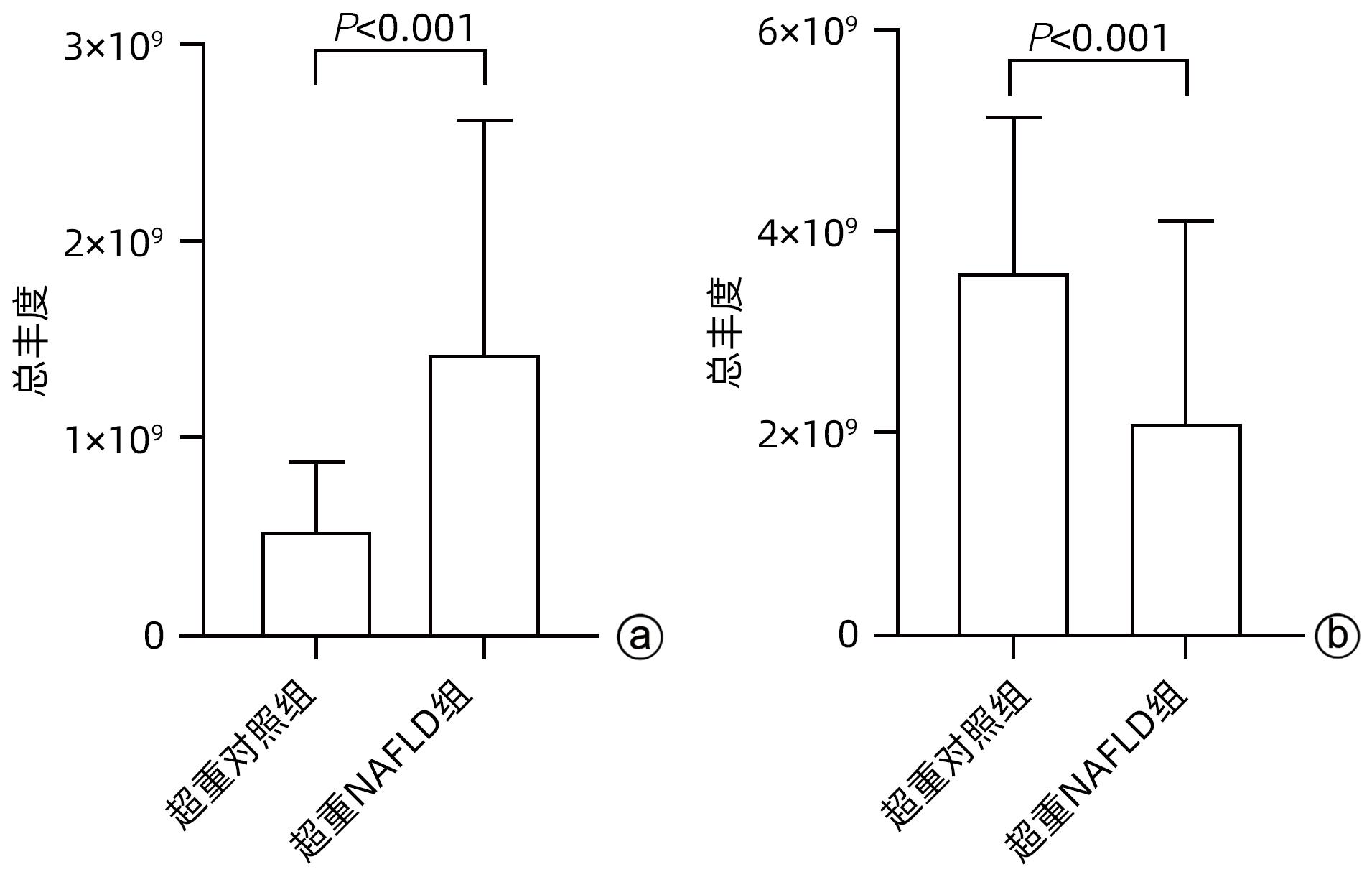
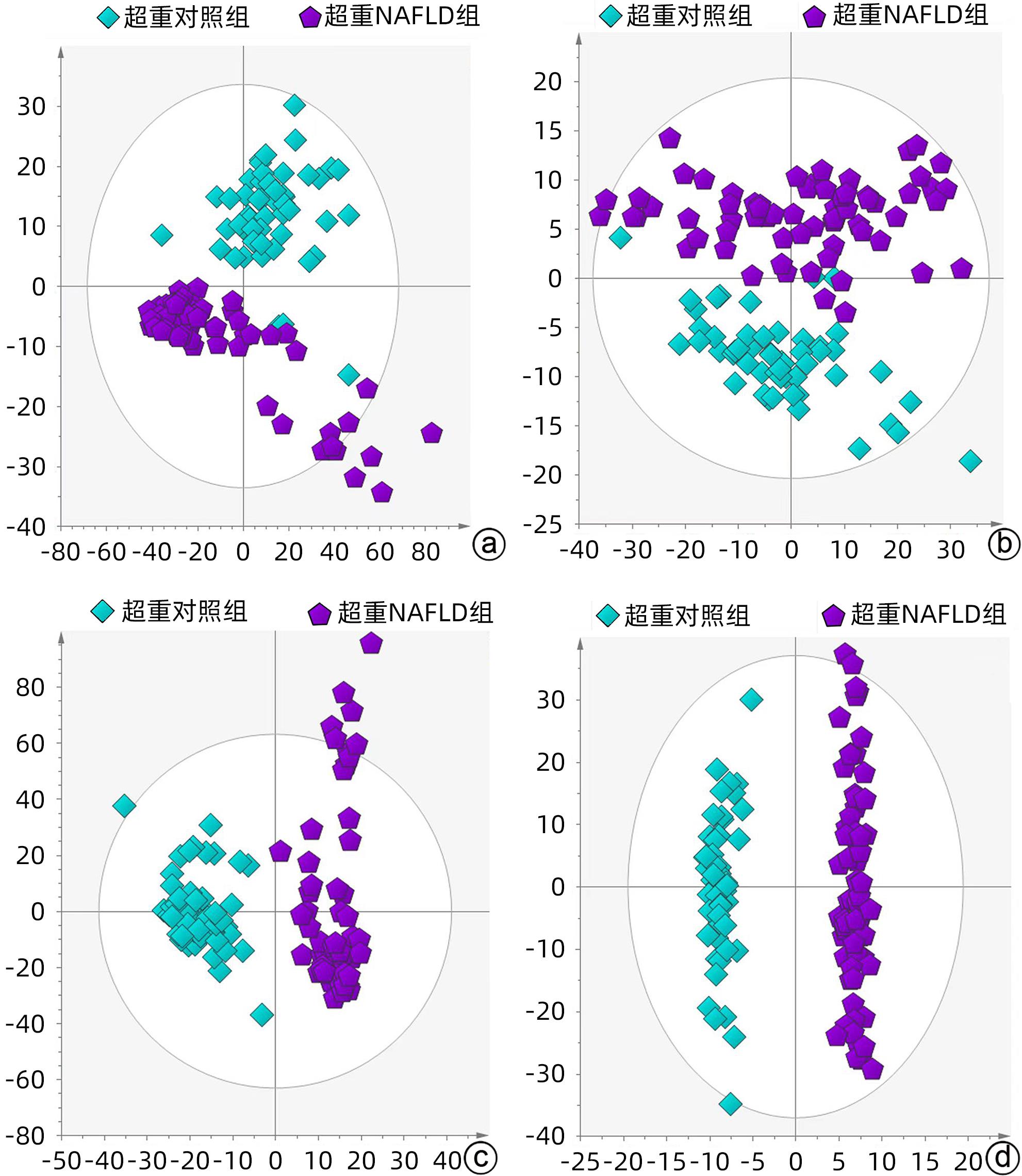
目的 探究超重人群中,非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)患者与健康人的临床指标与脂质代谢差异。 方法 本研究将体质量指数(BMI)>23 kg/m2定义为超重人群,选取2020年8月—2021年4月上海中医药大学附属普陀医院收治的62例超重NAFLD患者纳入超重NAFLD组,另选取同期超重健康体检者50例作为对照。记录所有受试者的临床信息以及血液生化指标数据。应用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法(UPLC-MS/MS)进行血清脂质组学分析;使用主成分分析法和正交偏最小二乘法判别分析对脂质组学数据进行多元统计分析。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验或Wilcoxon秩和检验。 结果 超重NAFLD组BMI显著高于超重对照组(Z=-2.365,P=0.018)。血清学指标中,超重NAFLD组红细胞、血红蛋白、红细胞比容、尿酸、总蛋白、球蛋白、ALP、GGT、ALT、AST、胆碱酯酶、低密度脂蛋白、总胆固醇、甘油三酯、载脂蛋白B、血糖水平均显著高于超重对照组(P值均<0.05)。脂质组学分析结果显示两组间脂质代谢具有明显差异,共鉴定出差异性脂质(VIP值>1,P<0.05)493个,其中超重NAFLD组中有143个脂质显著上调,350个脂质显著下调。超重NAFLD组的平均脂肪酸总量是超重对照组的3.6倍。超重NAFLD组不饱和键数>3的甘油三酯含量较超重对照组降低(P<0.001),而不饱和键数≤3的甘油三酯含量较超重对照组增多(P<0.001)。 结论 超重NAFLD患者的部分生化指标及脂质代谢产物明显异于超重健康人,血液内脂肪酸明显升高,甘油三酯中的含饱和脂肪链的种类显著升高。 Abstract:objective To investigate the differences in clinical indices and lipid metabolism between the patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and healthy individuals in the overweight population. Methods In this study, body mass index (BMI)>23 kg/m2 was defined as overweight. A total of 62 overweight patients with NAFLD who were admitted to Putuo Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from August 2020 to April 2021 were enrolled as overweight NAFLD group, and 50 overweight individuals who underwent physical examination during the same period of time were enrolled as control group. Clinical information and blood biochemical parameters were recorded for all subjects. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was used to analyze serum lipidomic profile, and principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis were used to perform the multivariate statistical analysis of lipidomic data. The chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups, and the independent-samples t test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups. Results The overweight NAFLD group had a significantly higher BMI than the overweight control group (Z=-2.365, P=0.018). As for serological markers, compared with the overweight control group, the overweight NAFLD group had significantly higher levels of red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, uric acid, total protein, globulin, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, cholinesterase, low-density lipoprotein, total cholesterol, triglyceride, apolipoprotein B, and blood glucose (all P<0.05). The lipidomic analysis showed that there was a significant difference in lipid metabolism between the two groups, and a total of 493 differentially expressed lipids were identified (VIP value>1, P<0.05), among which 143 lipids were significantly upregulated and 350 lipids were significantly downregulated in the overweight NAFLD group. The mean total fatty acid content in the overweight NAFLD group was 3.6 times that in the overweight control group. Compared with the overweight control group, the overweight NAFLD group had a significant reduction in the content of triglyceride with>3 unsaturated bonds (P<0.001) and a significant increase in the content of triglyceride with ≤3 unsaturated bonds (P<0.001). Conclusion Compared with healthy overweight individuals, overweight NAFLD patients tend to have significant abnormalities in some biochemical parameters and lipid metabolites, with significant increases in the content of fatty acid in blood and the types of saturated fat chains in triglycerides. -
Key words:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease /
- Overweight /
- Signs and Symptoms /
- Lipidomics
-
表 1 超重NAFLD组与超重对照组一般资料及血液生化指标比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data and blood biochemical indexes between NAFLD group and healthy control group in overweight people
临床指标 超重NAFLD组(n=62) 超重对照组(n=50) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 42/20 28/22 χ2=1.628 0.202 年龄(岁) 43.73±14.63 49.48±14.72 t=-2.064 0.041 身高(cm) 168.60±8.32 164.66±9.77 t=2.302 0.023 体质量(kg) 75.56±10.64 69.24±9.45 t=3.285 0.001 BMI(kg/m2) 26.15(24.90~27.73) 25.30(23.68~26.95) Z=-2.365 0.018 WBC(×109/L) 6.3(5.2~7.2) 5.9(5.1~6.9) Z=-1.016 0.310 RBC(%) 4.84(4.56~5.13) 4.59(4.33~4.83) Z=-3.348 0.001 Hb(g/L) 150.5(139.5~159.0) 143.0(127.0~150.8) Z=-2.916 0.004 Hct(%) 44.1(41.5~46.4) 41.9(38.4~44.6) Z=-3.085 0.002 MCV(fL) 90.9(88.0~93.4) 91.4(88.5~93.2) Z=-0.386 0.699 MCH(pg) 30.95(29.80~31.83) 30.75(30.08~31.50) Z=-0.018 0.986 MCHC(g/L) 338.00(331.75~345.25) 337.50(332.00~341.25) Z=-0.346 0.730 PLT(×109/L) 234.55±61.66 222.08±58.89 t=1.085 0.280 RDW(×1012/L) 12.5(12.1~13.2) 12.4(12.0~12.9) Z=-1.035 0.301 MPV(fL) 10.69±1.31 10.60±1.31 t=0.371 0.711 中性粒细胞(%) 57.01±8.70 56.87±9.60 t=0.080 0.936 淋巴细胞(%) 32.48±8.43 32.72±8.56 t=-0.145 0.885 单核细胞(%) 7.4(6.1~8.6) 6.8(6.0~8.3) Z=-0.480 0.631 嗜酸性粒细胞(%) 2.1(1.4~3.3) 1.8(1.2~3.8) Z=-0.659 0.510 嗜碱性粒细胞(%) 0.5(0.4~0.7) 0.6(0.4~0.8) Z=-0.186 0.853 尿素(mmol/L) 5.4(4.5~6.2) 5.1(4.1~6.1) Z=-1.243 0.214 肌酐(μmol/L) 74.0(68.0~83.3) 71.0(60.8~78.0) Z=-1.722 0.085 尿酸(μmol/L) 401.0(336.3~483.0) 356.0(289.5~422.8) Z=-2.519 0.012 GFR(mL/min) 94.90(80.26~105.43) 96.89(84.84~113.68) Z=-0.914 0.360 TBil(μmol/L) 14.5(11.0~19.3) 15.0(9.0~20.0) Z=-0.708 0.479 DBil(μmol/L) 2.7(1.9~3.8) 2.6(1.7~3.4) Z=-0.514 0.607 ALP(U/L) 79(69~89) 71(57~87) Z=-2.008 0.045 TP(g/L) 75(72~77) 72(69~74) Z=-3.074 0.002 Alb(g/L) 44(42~46) 44(42~45) Z=-1.198 0.231 Glb(g/L) 30(28~32) 29(26~31) Z=-2.353 0.019 GGT(U/L) 33(23~42) 26(15~40) Z=-2.186 0.029 ChE(U/L) 9 030.50(8 058.25~10 146.25) 8 102.00(7 276.50~8 879.00) Z=-3.894 0.001 ALT(U/L) 17(13~27) 14(10~22) Z=-2.195 0.028 AST(U/L) 26(21~31) 22(18~29) Z=-2.066 0.039 HDL(μmol/L) 1.11(0.99~1.25) 1.16(1.02~1.43) Z=-1.448 0.148 LDL(μmol/L) 3.51(3.12~3.97) 3.11(2.62~3.76) Z=-2.476 0.013 TC(μmol/L) 5.08(4.76~6.09) 4.66(4.06~5.67) Z=-2.510 0.012 TG(μmol/L) 1.78(1.28~2.58) 1.36(0.97~1.87) Z=-2.700 0.007 ApoA1(g/L) 1.34(1.24~1.44) 1.31(1.19~1.46) Z=-0.445 0.656 ApoB(g/L) 1.04(0.89~1.17) 0.89(0.73~1.06) Z=-3.178 0.001 Glu(mmol/L) 5.4(4.9~6.1) 5.0(4.6~5.3) Z=-3.238 0.001 注:WBC,白细胞;RBC,红细胞;Hb,血红蛋白;Hct,红细胞比容;MCV,平均红细胞体积;MCH,平均红细胞血红蛋白量;MCHC,红细胞平均血红蛋白浓度;PLT,血小板;RDW,红细胞体积分布宽度;MPV,平均血小板体积;GFR,肾小球滤过率;TBil,总胆红素;DBil,直接胆红素;ALP,碱性磷酸酶;TP,总蛋白;Alb,白蛋白;Glb,球蛋白;GGT,γ-谷氨酰基转移酶;ChE,胆碱酯酶;ALT,谷丙转氨酶;AST,谷草转氨酶;HDL,高密度脂蛋白;LDL,低密度脂蛋白;TC,总胆固醇;ApoA1,载脂蛋白A1;ApoB,载脂蛋白B;Glu,血糖。 -
[1] LI L, LIU DW, YAN HY, et al. Obesity is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies[J]. Obes Rev, 2016, 17( 6): 510- 519. DOI: 10.1111/obr.12407. [2] FAN JG, KIM SU, WONG VW. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67( 4): 862- 873. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.003. [3] IACOBINI C, PUGLIESE G, BLASETTI FANTAUZZI C, et al. Metabolically healthy versus metabolically unhealthy obesity[J]. Metabolism, 2019, 92: 51- 60. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.009. [4] OLIVEIRA DT, CHAVES-FILHO AB, YOSHINAGA MY, et al. Liver lipidome signature and metabolic pathways in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-sugar diet[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2021, 87: 108519. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108519. [5] MASOODI M, GASTALDELLI A, HYÖTYLÄINEN T, et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics in NAFLD: Biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18( 12): 835- 856. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00502-9. [6] TIAN JY, DU SN, GAO JJ, et al. Study on serum lipidomics of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients based on UPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS technology[J]. China Med Herald, 2022, 19( 19): 5- 11.田继云, 杜晟楠, 高静静, 等. 基于UPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS技术对非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者的血清脂质组学研究[J]. 中国医药导报, 2022, 19( 19): 5- 11. [7] ESLAM M, SARIN SK, WONG VW, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatol Int, 2020, 14( 6): 889- 919. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2. [8] National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007.中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组, 中国医师协会脂肪性肝病专家委员会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病防治指南(2018年更新版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 5): 947- 957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. [9] DING QP, ZHOU YB, ZHANG S, et al. Association between hemoglobin levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with young-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Endocr J, 2020, 67( 11): 1139- 1146. DOI: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0071. [10] LI GL, HU H, SHI W, et al. Elevated hematocrit in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A potential cause for the increased risk of cardiovascular disease?[J]. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc, 2012, 51( 1): 59- 68. DOI: 10.3233/CH-2011-1509. [11] JIANG YZ, ZENG J, CHEN B. Hemoglobin combined with triglyceride and ferritin in predicting non-alcoholic fatty liver[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 29( 7): 1508- 1514. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12580. [12] KIM K, KANG K, SHEOL H, et al. The association between serum uric acid levels and 10-year cardiovascular disease risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19( 3): 1042. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19031042. [13] ZHOU MM, YANG N, XING X, et al. Obesity interacts with hyperuricemia on the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21( 1): 43. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-021-01615-w. [14] SOUZA-MELLO V, GREGÓRIO BM, CARDOSO-DE-LEMOS FS, et al. Comparative effects of telmisartan, sitagliptin and metformin alone or in combination on obesity, insulin resistance, and liver and pancreas remodelling in C57BL/6 mice fed on a very high-fat diet[J]. Clin Sci(Lond), 2010, 119( 6): 239- 250. DOI: 10.1042/CS20100061. [15] GAGGINI M, MORELLI M, BUZZIGOLI E, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease[J]. Nutrients, 2013, 5( 5): 1544- 1560. DOI: 10.3390/nu5051544. [16] WANG TY, WANG RF, BU ZY, et al. Association of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease with kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2022, 18( 4): 259- 268. DOI: 10.1038/s41581-021-00519-y. [17] TONG C, LI YN, GU D, et al. The association between obesity measurement indices and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 10): 2465- 2468. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.10.044.童聪, 李亚年, 顾达, 等. 人体肥胖测量指标与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 10): 2465- 2468. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.10.044. [18] WANG WT, REN JP, ZHOU WZ, et al. Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(Lean-NAFLD) and the development of metabolic syndrome: A retrospective study[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12( 1): 10977. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14701-0. [19] MOCCIARO G, ALLISON M, JENKINS B, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is characterised by a reduced polyunsaturated fatty acid transport via free fatty acids and high-density lipoproteins(HDL)[J]. Mol Metab, 2023, 73: 101728. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101728. [20] BARR J, CABALLERÍA J, MARTÍNEZ-ARRANZ I, et al. Obesity-dependent metabolic signatures associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression[J]. J Proteome Res, 2012, 11( 4): 2521- 2532. DOI: 10.1021/pr201223p. [21] OREŠIČ M, HYÖTYLÄINEN T, KOTRONEN A, et al. Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty-liver disease and liver fat content by serum molecular lipids[J]. Diabetologia, 2013, 56( 10): 2266- 2274. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-013-2981-2. [22] DONNELLY KL, SMITH CI, SCHWARZENBERG SJ, et al. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115( 5): 1343- 1351. DOI: 10.1172/JCI23621. [23] SHIMOMURA I, BASHMAKOV Y, HORTON JD. Increased levels of nuclear SREBP-1c associated with fatty livers in two mouse models of diabetes mellitus[J]. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274( 42): 30028- 30032. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.42.30028. -



 PDF下载 ( 1229 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1229 KB)

 下载:
下载: