B型尼曼-皮克病及其肝脏受累的异质性表现1例报告
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240221
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:阳乔负责病例收集,撰写论文;沈轶负责信息收集,文献检索;史悦、王进负责数据和病理图谱收集;吕芳芳负责诊治策略和论文审阅及修改。
Niemann-Pick disease type B and heterogeneous manifestations of its liver involvement: A case report
-
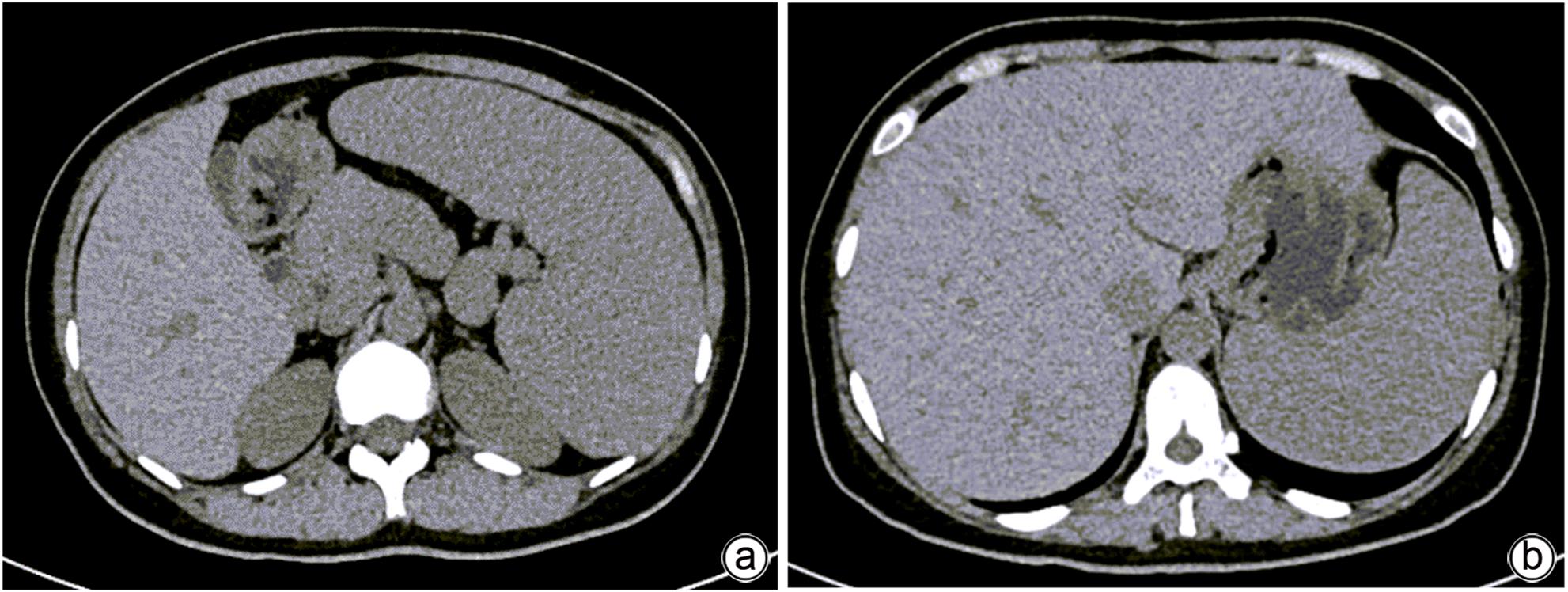
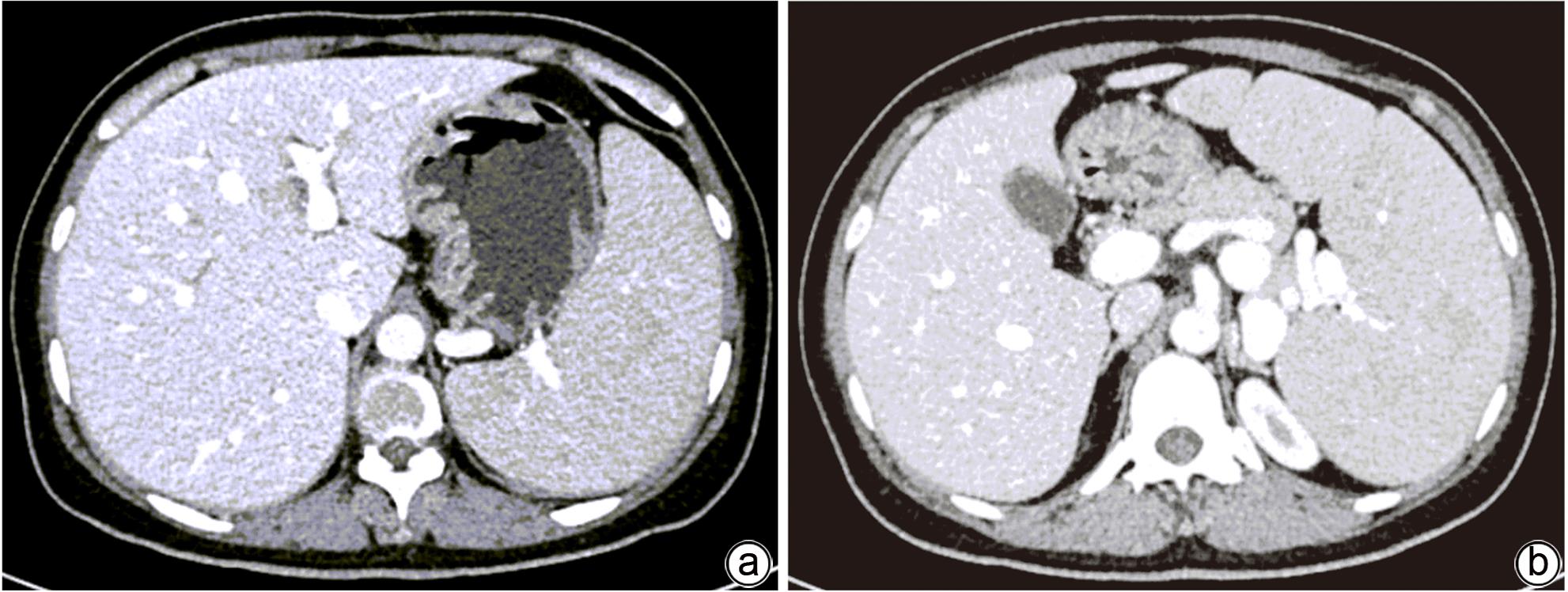
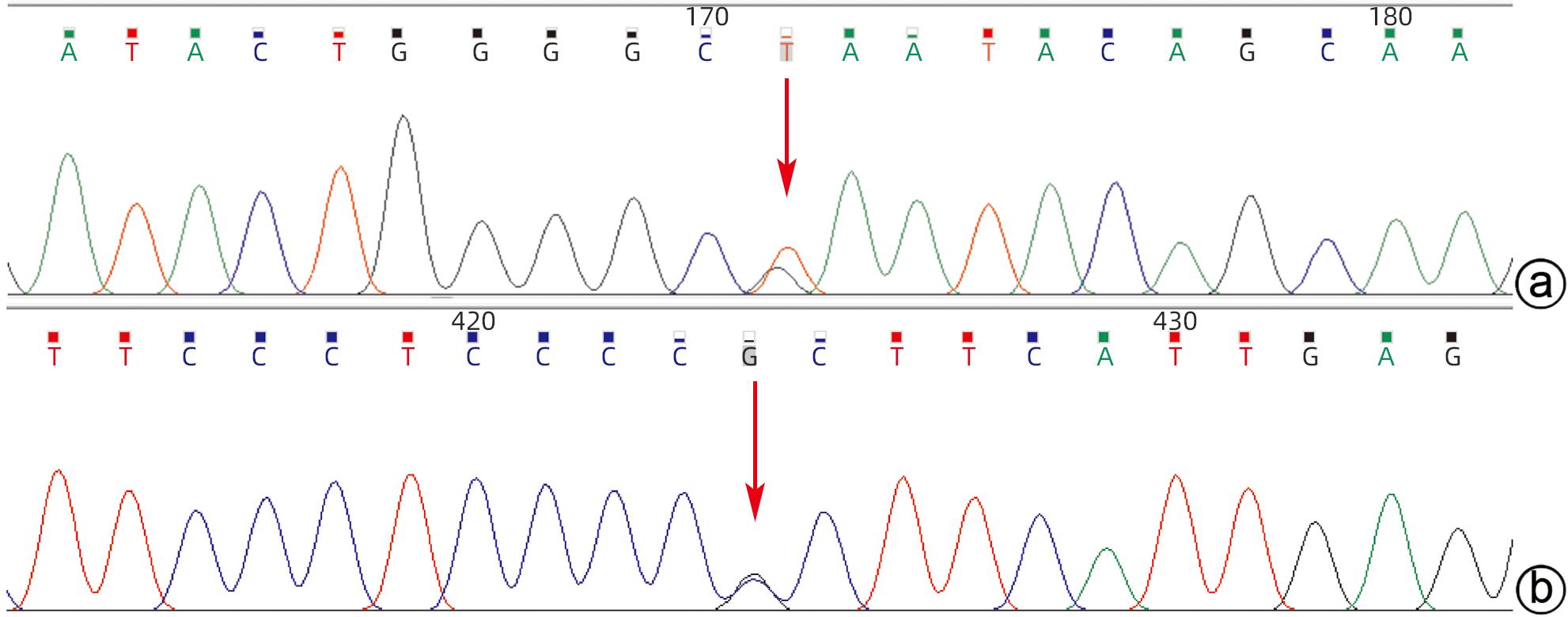
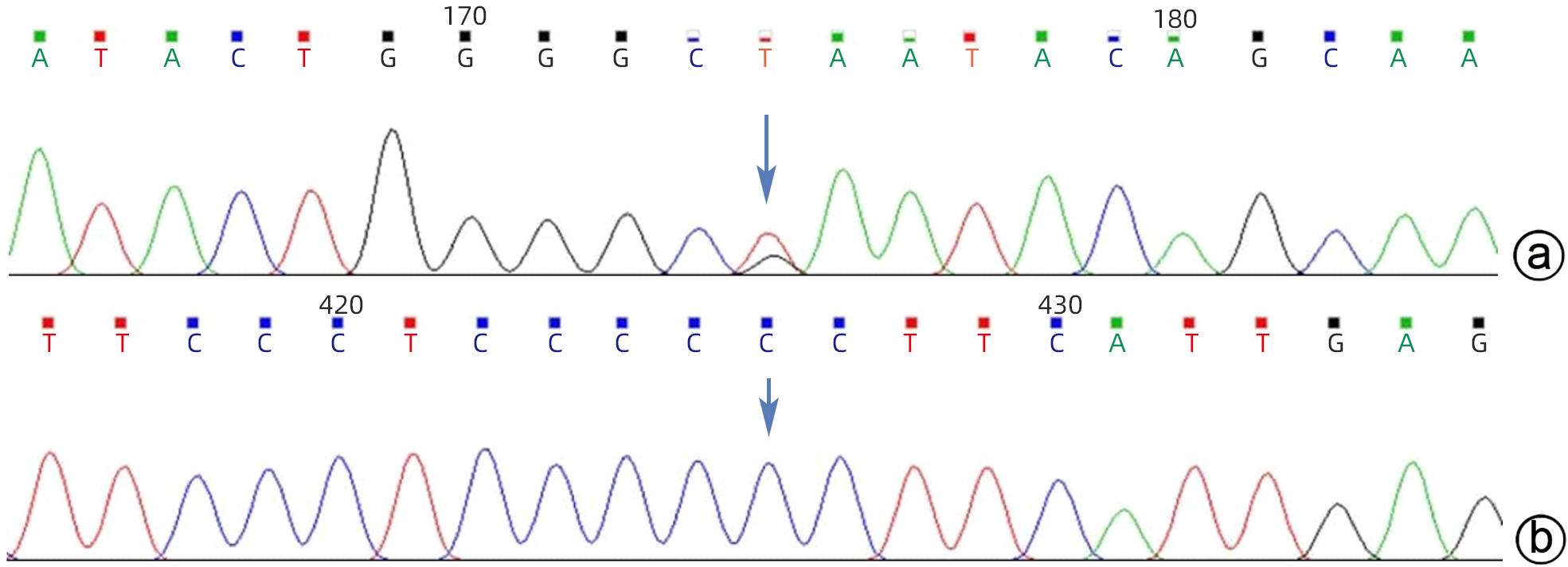
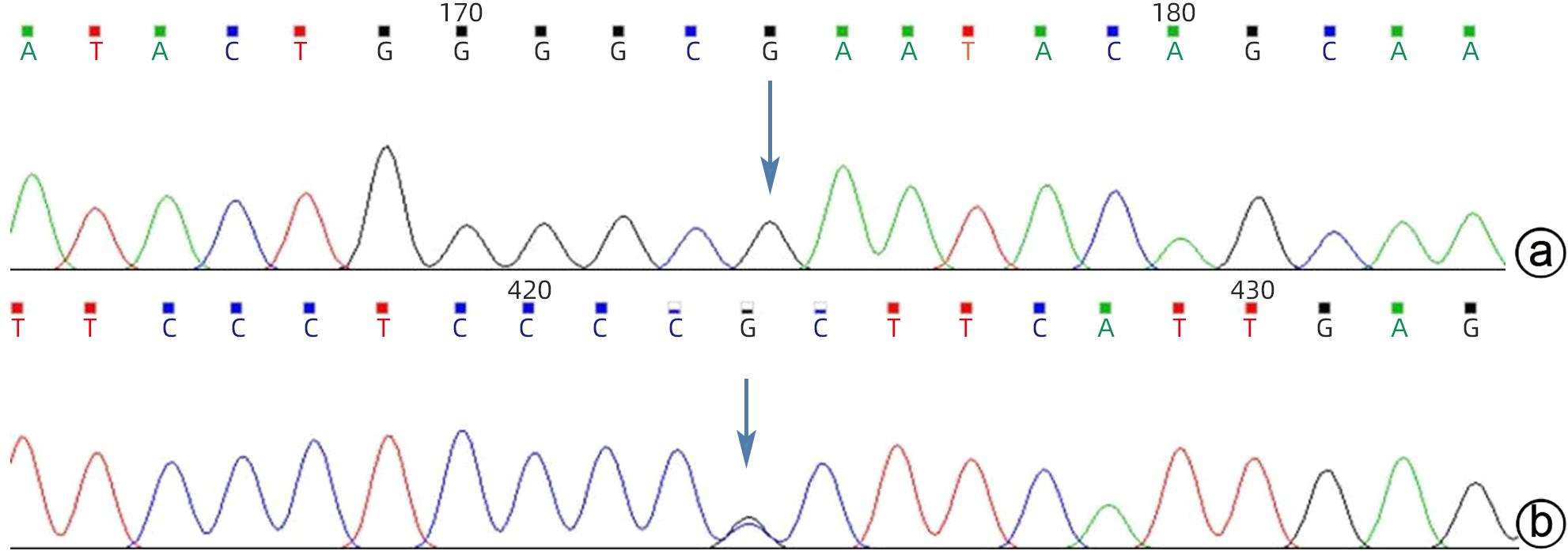
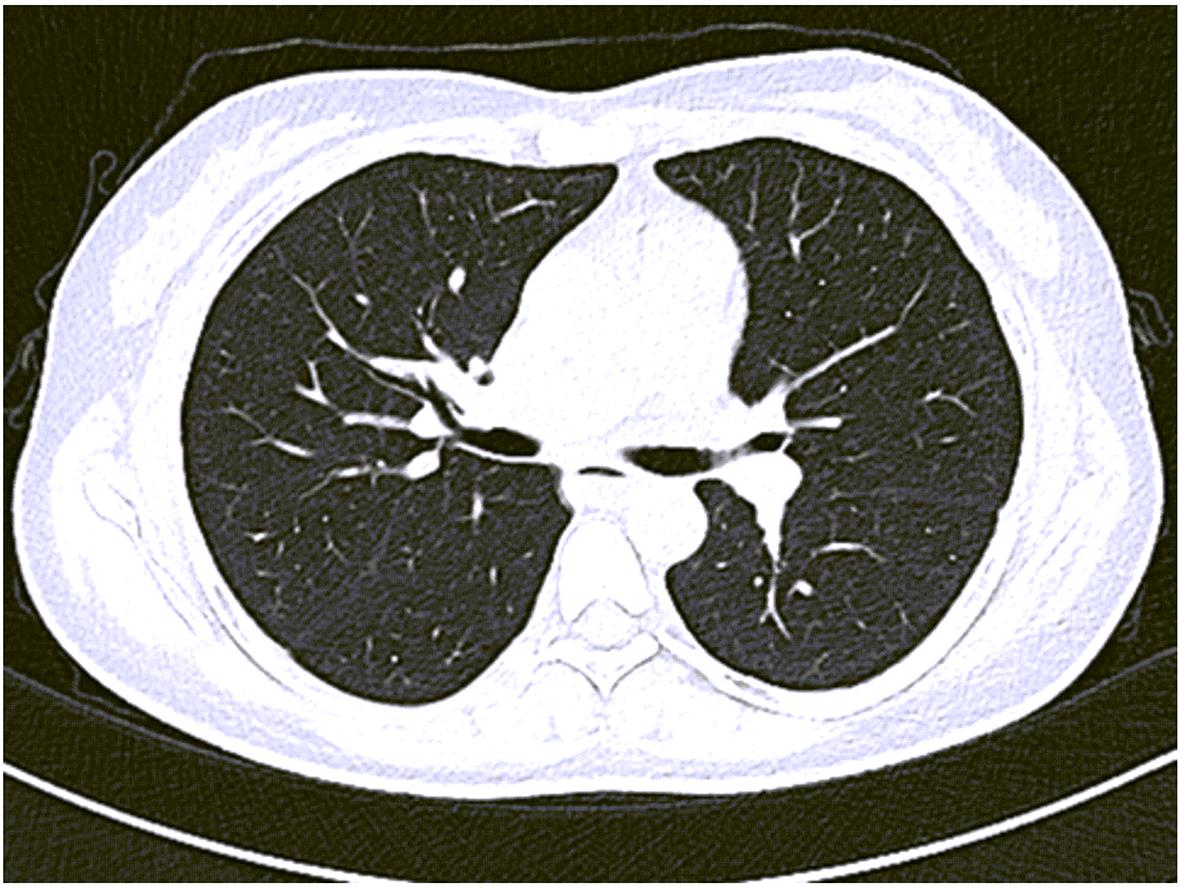
摘要: 本文报道以“肝脾肿大待查”为主诉,经各项检查确诊为B型尼曼-皮克病的案例,并通过文献复习,总结B型尼曼-皮克病肝脏受累的异质性表现,旨在提高疑难罕见肝脏疾病的临床诊治水平。
-
关键词:
- 尼曼-皮克病, B型 /
- 肝肿大 /
- 遗传性疾病, 先天性 /
- 基因检测
Abstract: This article reports a case with the chief complaint of “hepatosplenomegaly to be investigated” and a confirmed diagnosis of Niemann-Pick disease type B after various tests, and a literature review was conducted to summarize the heterogeneous manifestations of liver involvement in type B Niemann-Pick disease, in order to improve the clinical management of difficult and rare liver diseases.-
Key words:
- Niemann-Pick Disease, Type B /
- Hepatomegaly /
- Genetic Diseases, Inborn /
- Genetic Testing
-
-
[1] PINTO C, SOUSA DA, GHILAS V, et al. Acid sphingomyelinase deficiency: A clinical and immunological perspective[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 23): 12870. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222312870. [2] SCHUCHMAN EH, DESNICK RJ. Types A and B Niemann-Pick disease[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2017, 120( 1-2): 27- 33. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.12.008. [3] VÉLEZ PINOS PJ, SAAVEDRA PALACIOS MS, COLINA ARTEAGA PA, et al. Niemann-Pick disease: A case report and literature review[J]. Cureus, 2023, 15( 1): e33534. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33534. [4] COLOGNA SM, PATHMASIRI KC, PERGANDE MR, et al. Alterations in cholesterol and phosphoinositides levels in the intracellular cholesterol trafficking disorder NPC[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2023, 1422: 143- 165. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-21547-6_5. [5] ZHANG HW, WANG Y, GONG ZW, et al. Identification of a distinct mutation spectrum in the SMPD1 gene of Chinese patients with acid sphingomyelinase-deficient Niemann-Pick disease[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2013, 8: 15. DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-8-15. [6] LAN MY, LIN SJ, CHEN YF, et al. A novel missense mutation of the SMPD1 gene in a Taiwanese patient with type B Niemann-Pick disease[J]. Ann Hematol, 2009, 88( 7): 695- 697. DOI: 10.1007/s00277-008-0648-8. [7] CHEEMA HA, RASOOL IG, ANJUM MN, et al. Mutational spectrum of SMPD1 gene in Pakistani Niemann-Pick disease patients[J]. Pak J Med Sci, 2020, 36( 3): 479- 484. DOI: 10.12669/pjms.36.3.467. [8] WASSERSTEIN MP, DESNICK RJ, SCHUCHMAN EH, et al. The natural history of type B Niemann-Pick disease: Results from a 10-year longitudinal study[J]. Pediatrics, 2004, 114( 6): e672- e677. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2004-0887. [9] LIPIŃSKI P, KUCHAR L, ZAKHAROVA EY, et al. Chronic visceral acid sphingomyelinase deficiency(Niemann-Pick disease type B) in 16 Polish patients: Long-term follow-up[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2019, 14( 1): 55. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-019-1029-1. [10] MCGOVERN MM, POHL-WORGALL T, DECKELBAUM RJ, et al. Lipid abnormalities in children with types A and B Niemann Pick disease[J]. J Pediatr, 2004, 145( 1): 77- 81. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.02.048. [11] CASSIMAN D, PACKMAN S, BEMBI B, et al. Cause of death in patients with chronic visceral and chronic neurovisceral acid sphingomyelinase deficiency(Niemann-Pick disease type B and B variant): Literature review and report of new cases[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2016, 118( 3): 206- 213. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.05.001. [12] LAN MY, KANG TW, LAN SC, et al. Spontaneous splenic rupture as the first clinical manifestation of Niemann-Pick disease type B: A case report and review of the literature[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2022, 16( 4): 434- 437. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacl.2022.06.002. [13] MCGOVERN MM, WASSERSTEIN MP, GIUGLIANI R, et al. A prospective, cross-sectional survey study of the natural history of Niemann-Pick disease type B[J]. Pediatrics, 2008, 122( 2): e341- e349. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2007-3016. [14] ADIN ME, ONDER H, ALABALıK U. Echogenic splenic lesions in a child with type B Niemann-Pick disease[J]. J Clin Ultrasound, 2013, 41( Suppl 1): 32- 34. DOI: 10.1002/jcu.22009. [15] THURBERG BL, WASSERSTEIN MP, SCHIANO T, et al. Liver and skin histopathology in adults with acid sphingomyelinase deficiency(Niemann-Pick disease type B)[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2012, 36( 8): 1234- 1246. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31825793ff. [16] MOLES A, TARRATS N, FERNÁNDEZ-CHECA JC, et al. Cathepsin B overexpression due to acid sphingomyelinase ablation promotes liver fibrosis in Niemann-Pick disease[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287( 2): 1178- 1188. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.272393. [17] WANG RS, QIN ZY, HUANG L, et al. SMPD1 expression profile and mutation landscape help decipher genotype-phenotype association and precision diagnosis for acid sphingomyelinase deficiency[J]. Hereditas, 2023, 160( 1): 11. DOI: 10.1186/s41065-023-00272-1. [18] PATTERSON MC, DI BISCEGLIE AM, HIGGINS JJ, et al. The effect of cholesterol-lowering agents on hepatic and plasma cholesterol in Niemann-Pick disease type C[J]. Neurology, 1993, 43( 1): 61- 64. DOI: 10.1212/wnl.43.1_part_1.61. [19] WASSERSTEIN MP, DIAZ GA, LACHMANN RH, et al. Olipudase Alfa for treatment of acid sphingomyelinase deficiency(ASMD): Safety and efficacy in adults treated for 30 months[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2018, 41( 5): 829- 838. DOI: 10.1007/s10545-017-0123-6. [20] MIRANDA SR, ERLICH S, FRIEDRICH VL Jr, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy leads to marked visceral organ improvements and a delayed onset of neurological abnormalities in the acid sphingomyelinase deficient mouse model of Niemann-Pick disease[J]. Gene Ther, 2000, 7( 20): 1768- 1776. DOI: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301300. [21] LIU Y, LUO Y, XIA L, et al. The effects of liver transplantation in children with niemann-pick disease type B[J]. Liver Transpl, 2019, 25( 8): 1233- 1240. DOI: 10.1002/lt.25457. [22] GASPERINI S, D’ANTIGA L. Liver transplantation for lysosomal storage disorders: A novel option to pick[J]. Liver Transpl, 2019, 25( 8): 1140- 1141. DOI: 10.1002/lt.25578. [23] GEBERHIWOT T, WASSERSTEIN M, WANNINAYAKE S, et al. Consensus clinical management guidelines for acid sphingomyelinase deficiency(Niemann-Pick disease types A, B and A/B)[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2023, 18( 1): 85. DOI: 10.1186/s13023-023-02686-6. -



 PDF下载 ( 1123 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1123 KB)

 下载:
下载: