胰腺内副脾误诊2例报告
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240223
伦理学声明:本例报告已获得患者及家属知情同意。
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:张孟哲负责收集病例资料,撰写文章并最后定稿;饶洁参与收集病例资料,资料分析;张正乐负责拟定写作思路,修改论文。
-
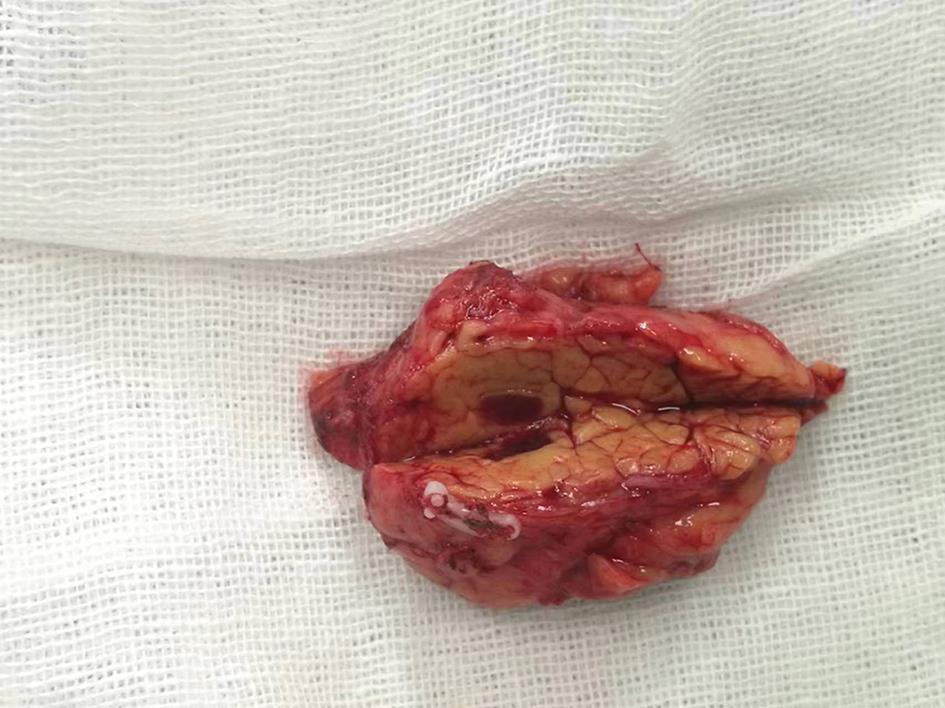
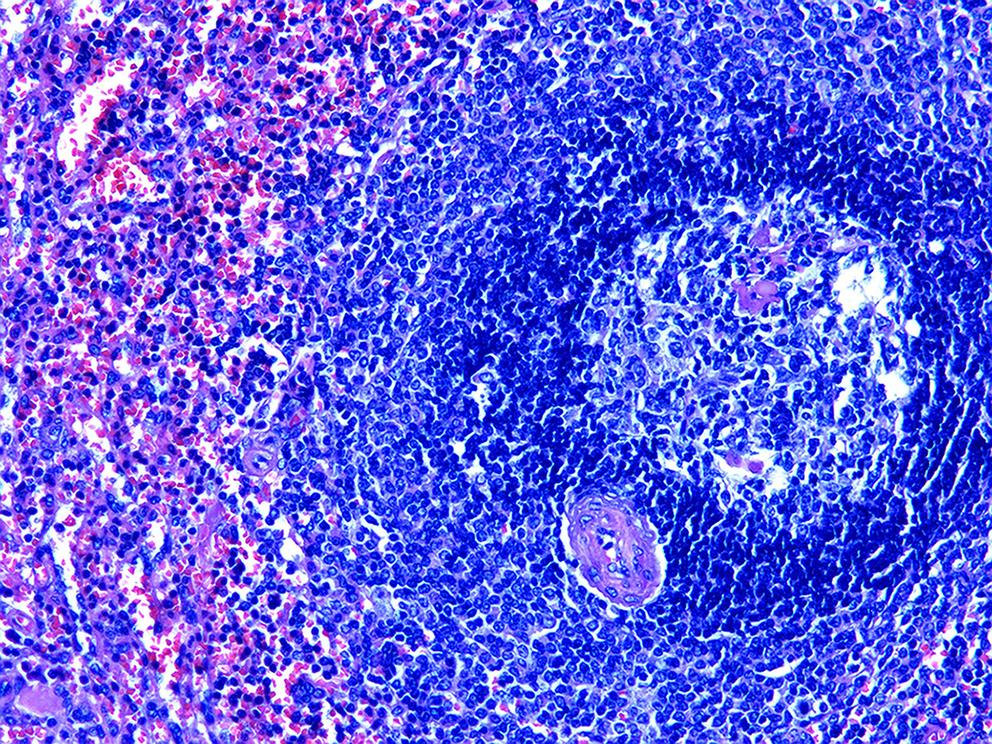
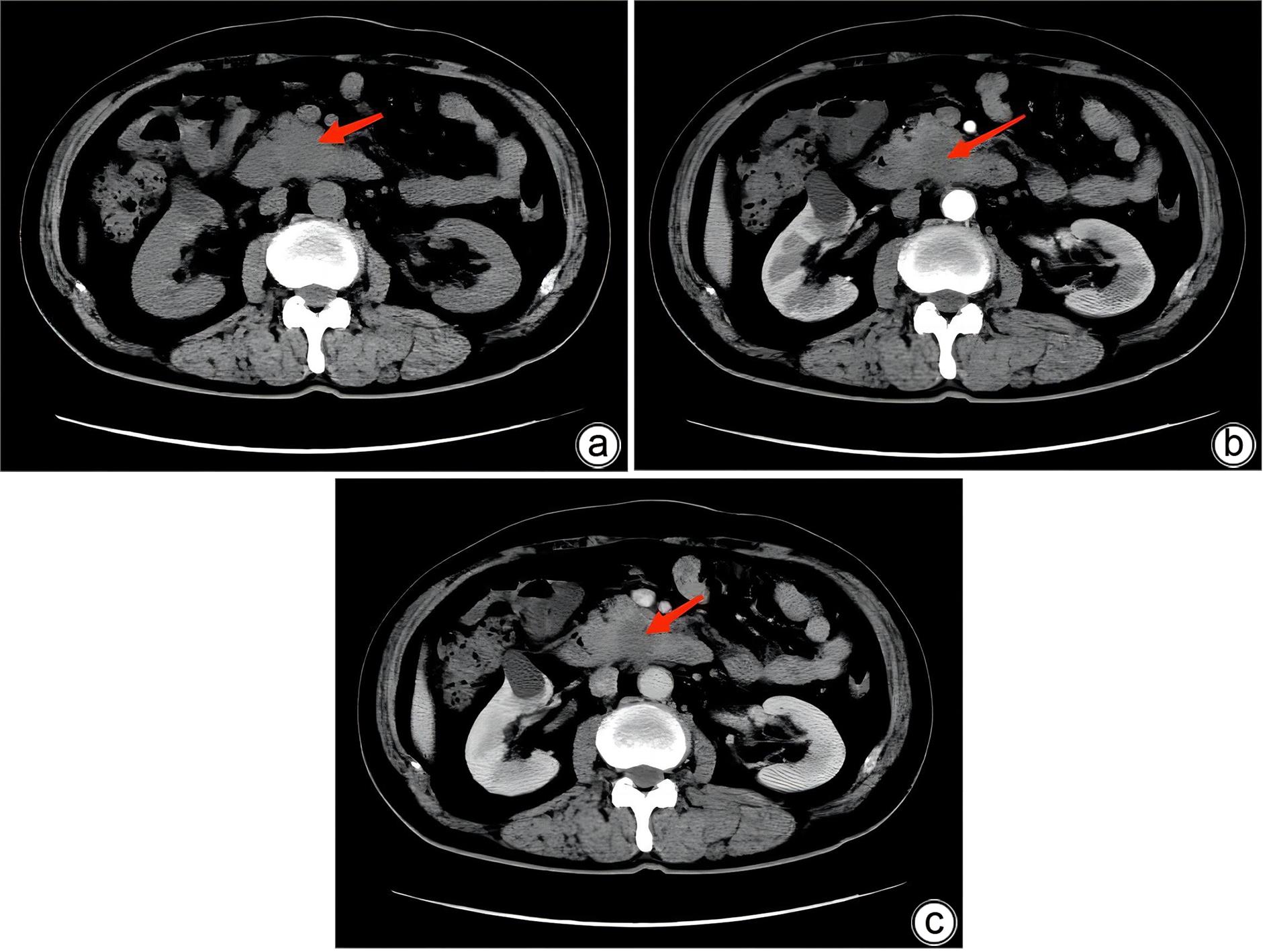
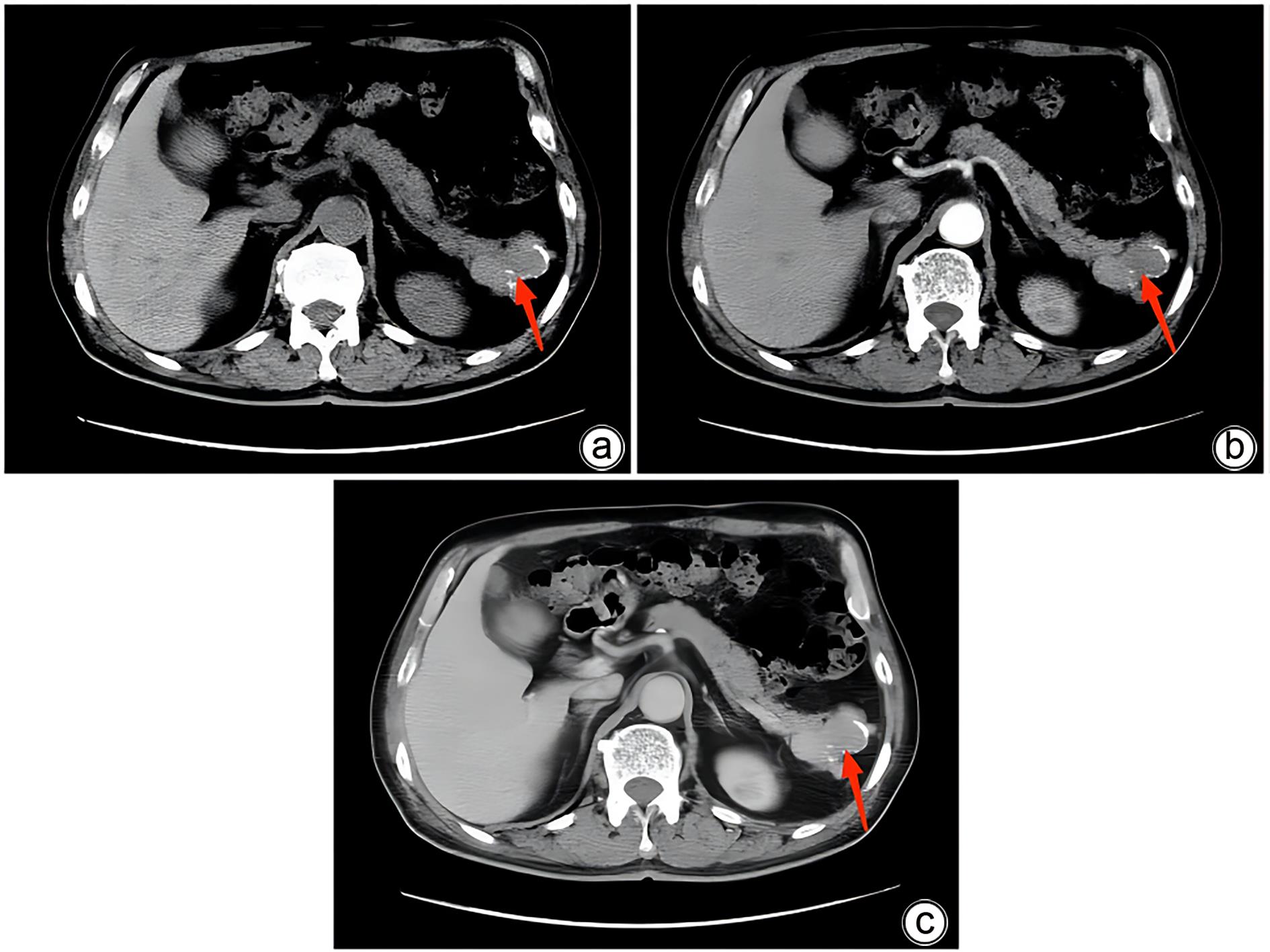
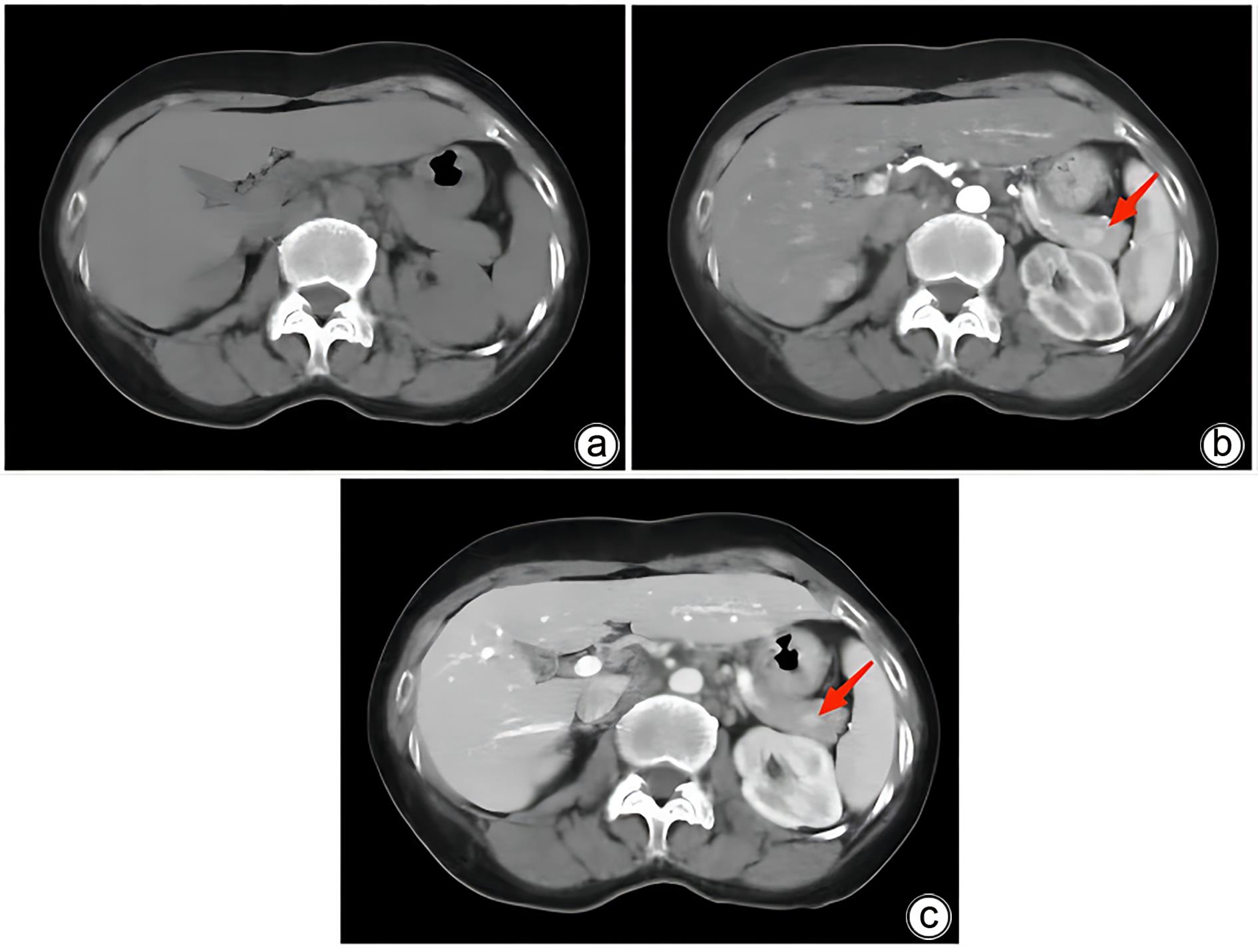
摘要: 副脾是指正常脾脏以外存在的,与主脾结构相似,有一定功能的脾脏组织,其中完全被胰腺包裹的胰腺内副脾(IPAS)发生率仅为2%,因其临床症状不典型,影像学特征与胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤、胰腺实性假乳头状瘤以及其他胰腺占位性病变较为相似,临床上容易误诊。本文报道了2例分别被误诊为胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤和胰腺实性假乳头状瘤的IPAS患者,并分析误诊原因,总结诊疗经验,以期提升临床对IPAS明确鉴别诊断的认识。Abstract: Accessory spleen refers to the spleen tissue that exists outside of the normal spleen, with a similar structure to the main spleen and certain functions. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen (IPAS) completely enveloped by the pancreas has an incidence rate of only 2%, and it is easily misdiagnosed in clinical practice due to its atypical clinical symptoms and similar radiological features to pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, pancreatic solid pseudopapillary tumor, and other pancreatic space-occupying lesions. This article reports the clinical data of two patients with IPAS who were misdiagnosed as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and pancreatic solid pseudopapillary tumor, respectively, analyzes the reasons for misdiagnosis, and summarizes the experience in diagnosis and treatment, in order to improve the ability for the differential diagnosis of IPAS in clinical practice.
-
Key words:
- Splenic Diseases /
- Pancreas /
- Diagnostic Errors /
- Neuroendocrine Tumors /
- Papilloma
-
-
[1] TIPTON SG, SMYRK T, SARR MG, et al. Malignant potential of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas[J]. Br J Surg, 2006, 93( 6): 733- 737. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.5334. [2] MOVITZ D. Accessory spleens and experimental splenosis. Principles of growth[J]. Chic Med Sch Q, 1967, 26( 4): 183- 187. [3] HALPERT B, GYORKEY F. Lesions observed in accessory spleens of 311 patients[J]. Am J Clin Pathol, 1959, 32( 2): 165- 168. DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/32.2.165. [4] RADOJKOVIC M, RADOJKOVIC D, PREMOVIC N. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen[J]. Med Clínica, 2021, 157( 3): 153- 154. DOI: 10.1016/j.medcli.2020.05.031. [5] ZHAO X, ZHOU ZQ, XIANG K, et al. CT diagnosis of intrapancreatic accessory spleen(a report of 2 cases)[J]. Radiol Pract, 2013, 28( 10): 1046- 1048. DOI: 10.13609/j.cnki.1000-0313.2013.10.015.赵旭, 周志强, 项鹍, 等. 胰腺内异位副脾的CT诊断(附2例报道)[J]. 放射学实践, 2013, 28( 10): 1046- 1048. DOI: 10.13609/j.cnki.1000-0313.2013.10.015. [6] KIM SH, LEE JM, HAN JK, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Findings on MR Imaging, CT, US and scintigraphy, and the pathologic analysis[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2008, 9( 2): 162- 174. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.2.162. [7] JANG KM, KIM SH, LEE SJ, et al. Differentiation of an intrapancreatic accessory spleen from a small(<3-cm) solid pancreatic tumor: Value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 2013, 266( 1): 159- 167. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.12112765. [8] PENG HF, GONG J, LI Q. A case of epidermoid cyst of intrapancreatic accessory spleen[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 11): 2413- 2414. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.11.032.彭翰斐, 龚瑾, 李强. 胰腺尾部副脾上皮样囊肿1例报告[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 11): 2413- 2414. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.11.032. [9] NI X, HU XM, JIANG H. Clinicopathologic analysis of epidermoid cyst in intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A report of 12 cases[J]. Chin J Pancreatol, 2022, 22( 3): 201- 204. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115667-20210829-00156.倪响, 胡小木, 蒋慧. 胰腺内副脾伴表皮样囊肿12例临床病理特征分析[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2022, 22( 3): 201- 204. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115667-20210829-00156. [10] OTA T, TEI M, YOSHIOKA A, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen diagnosed by technetium-99m heat-damaged red blood cell SPECT[J]. J Nucl Med, 1997, 38( 3): 494- 495. [11] SCHMID-TANNWALD C, SCHMID-TANNWALD CM, MORELLI JN, et al. Comparison of abdominal MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging to 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in detection of neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2013, 40( 6): 897- 907. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-013-2371-5. [12] MAKINO Y, IMAI Y, FUKUDA K, et al. Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of an intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A case report[J]. J Clin Ultrasound, 2011, 39( 6): 344- 347. DOI: 10.1002/jcu.20798. [13] PENG N, MI JW, ZHAO DQ. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors[J]. Chin J Ultrason, 2020( 1): 87- 90. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2020.01.017.彭娜, 秘建威, 赵东强. 超声内镜在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤诊治中的进展[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2020( 1): 87- 90. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2020.01.017. [14] XIA XX, LYU GY, QIU XT, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen misdiagnosed as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: A case report[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 436- 438. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.036.夏旭翔, 吕国悦, 仇晓桐, 等. 胰腺内副脾误诊为胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤1例报告[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 2): 436- 438. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.036. [15] TATSAS AD, OWENS CL, SIDDIQUI MT, et al. Fine-needle aspiration of intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Cytomorphologic features and differential diagnosis[J]. Cancer Cytopathol, 2012, 120( 4): 261- 268. DOI: 10.1002/cncy.21185. [16] BASTIDAS AB, HOLLOMAN D, LANKARANI A, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided needle-based probe confocal laser endomicroscopy(nCLE) of intrapancreatic ectopic spleen[J]. ACG Case Rep J, 2016, 3( 3): 196- 198. DOI: 10.14309/crj.2016.48. -



 PDF下载 ( 1188 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1188 KB)

 下载:
下载: