NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎性小体在肝细胞癌发生发展中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240229
Role of NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要: 近年来,关于NOD样受体蛋白3(NLRP3)炎性小体在肿瘤中的研究已成为热点话题,尤其是在黑色素瘤、结直肠癌、肺癌、乳腺癌等肿瘤中,越来越多的证据表明炎症在促进肿瘤的发生发展、血管生成和肿瘤侵袭中具有重要的作用。肝细胞癌(HCC)是原发性肝癌中最常见的类型,而关于NLRP3炎性小体在HCC发生发展中的作用仍争议不断。因此,本文就NLRP3炎性小体在HCC进展过程中的潜在影响以及在抗癌治疗中的作用机制作一综述,认为NLRP3炎性小体可以作为HCC患者的有效治疗靶点。
-
关键词:
- 癌, 肝细胞 /
- NLR家族, 热蛋白结构域包含蛋白3 /
- 细胞焦亡
Abstract: In recent years, NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in tumors has become a research hotspot, especially in melanoma, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, and breast cancer, and more and more evidence has shown that inflammation plays a role in the development, progression, angiogenesis, and invasion of cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer, and there are still controversies over the role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the development and progression of HCC. Therefore, this article reviews the potential impact of NLRP3 inflammasome in the progression of HCC and its mechanism of action in anticancer therapy, and it is believed that NLRP3 inflammasome can be used as an effective therapeutic target for HCC patients. -
在全球范围内,癌症被认为是主要的公共卫生事件之一,肝细胞癌(HCC)是我国第四位常见的恶性肿瘤及癌症死亡的第二大病因[1-2],其发病率在发达国家和发展中国家均呈上升趋势。尽管目前在HCC的诊断和治疗方面取得了显著进步,但由于其转移及复发率高,预后仍较差,严重威胁人类的生命和健康。有文献[3]表明,激活细胞焦亡可促进HCC细胞死亡,从而发挥抗癌特性,炎性小体在促进细胞焦亡的过程中发挥至关重要的作用。近些年来,NOD样受体蛋白3(NOD-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)炎性小体引起了广大学者的关注[4-5],有证据[6]表明其在不同类型的癌症中既有保护性的抗肿瘤作用又有促肿瘤作用。目前尚不清楚NLRP3炎性小体在肝癌进展过程中对肝实质细胞的作用是有益还是有害,本文主要对NLRP3炎性小体发生机制及其在HCC发生发展中的作用机制作一综述,明确NLRP3炎性小体在肿瘤增殖、扩散中的作用, 以及寻找合适的治疗肝癌的炎性小体靶点,为肿瘤治疗和抗癌药物的筛选提供新的参考。
1. NLRP3炎性小体的结构及激活过程
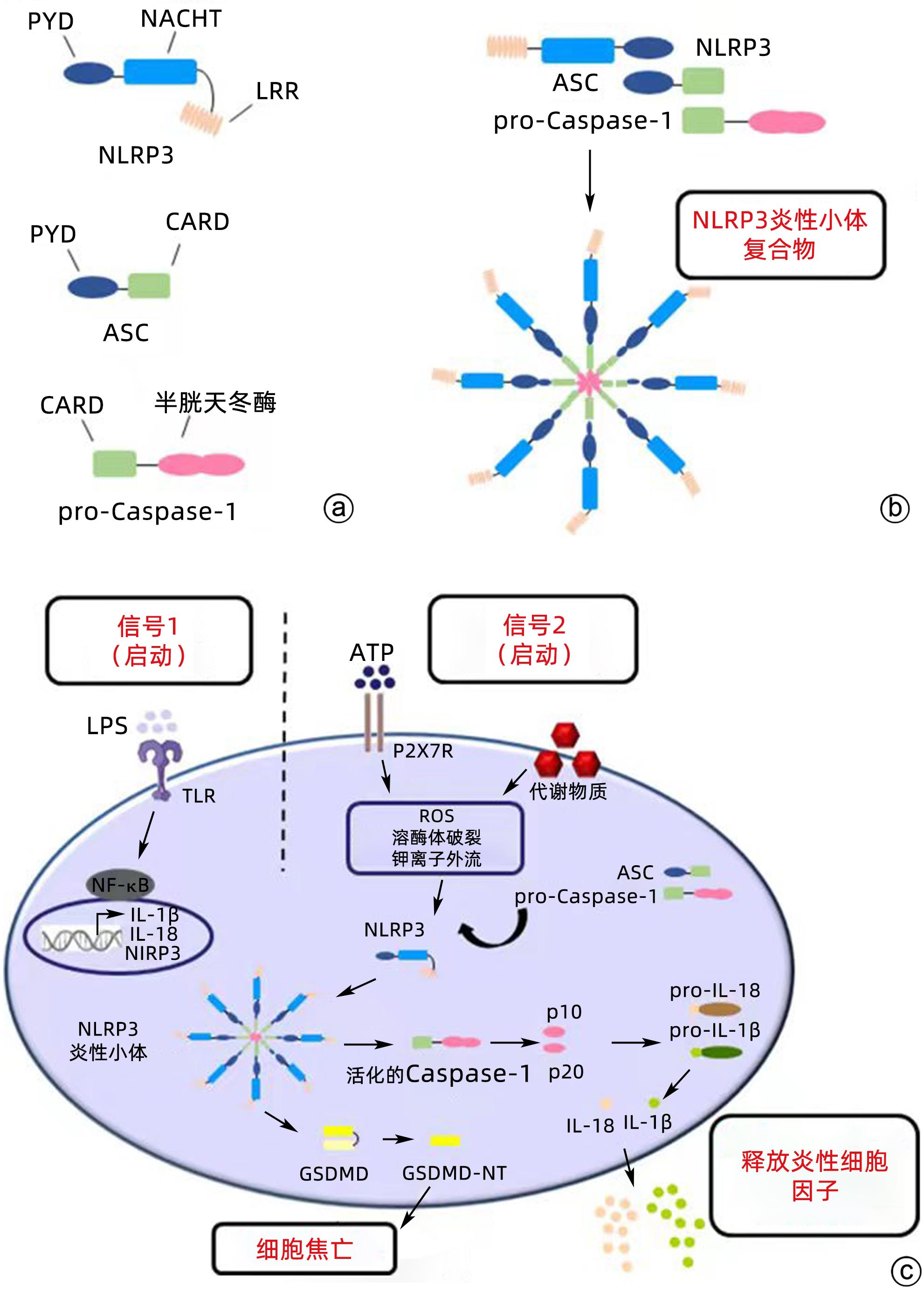
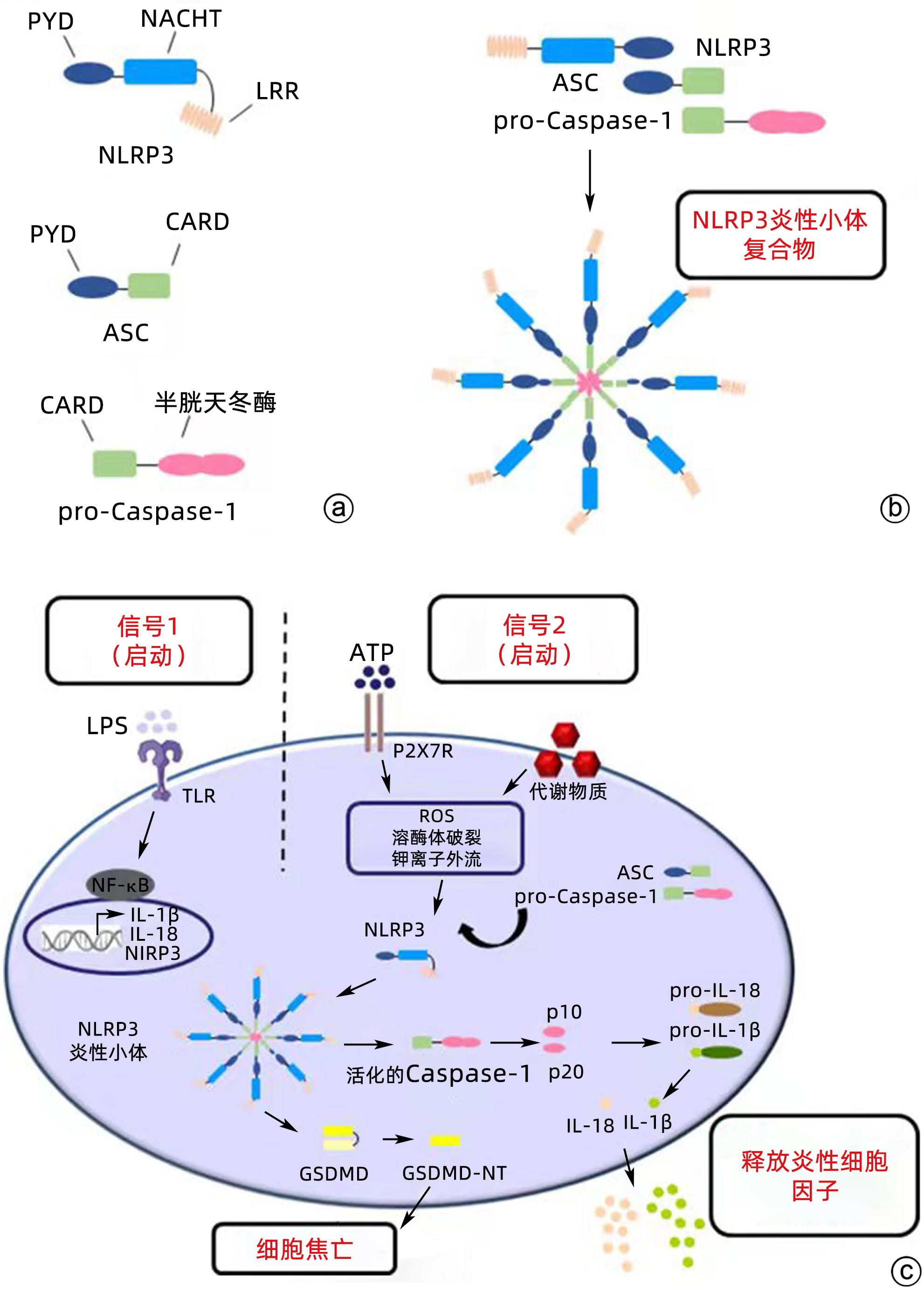
炎性小体是一种由胞浆内模式识别受体识别病原体相关分子模式和损伤相关分子模式后组装的多聚体蛋白复合物,是先天性免疫反应的一部分[7]。研究最多的炎性小体是由NLRP3受体蛋白、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(apoptosis speck protein,ASC)和效应分子半胱氨酸蛋白酶-1前体(pro-Caspase-1)经同型相互作用进行寡聚化形成的NLRP3炎性小体(图1a、b),是NLR家族的一员[8-9]。NLRP3炎性小体发挥作用需要经过启动和激活两个阶段[10-12]。启动阶段主要是由Toll样受体(Toll-like receptor,TLR)配体或内源性分子提供炎症刺激,诱导NF-κB的表达。激活过程是由病原体相关分子模式和损伤相关分子模式促进,引起K+、Ca2+外排以及活性氧(ROS)的产生,从而转录和表达NLRP3炎性小体成分及其他前体炎症因子,组装成NLRP3炎性小体,具体机制目前仍存在争议。
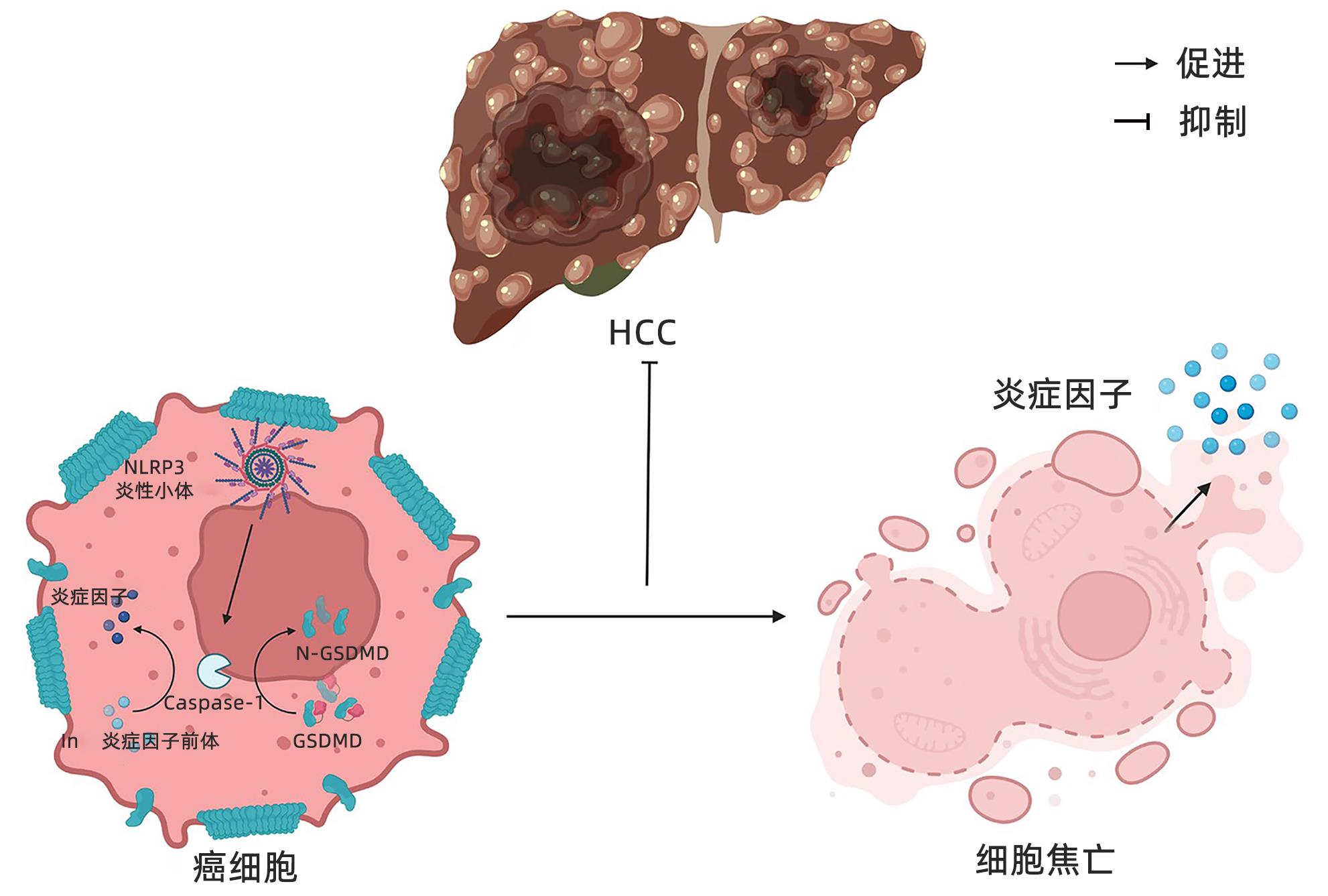
NLRP3炎性小体的激活可出现两种效应。首先,可以引起细胞焦亡。细胞焦亡是程序性细胞死亡的一种炎症形式,病理特征包括细胞肿胀、穿孔、破裂、溶解、核浓缩以及释放炎症因子IL-1β和IL-18,穿孔破裂的细胞失去细胞膜结构的完整性和控制物质进出细胞的功能[13]。细胞焦亡的信号通路主要依赖于Caspase⁃1的激活,是细胞焦亡的关键标志,在该通路中细胞内的NLRP3、AIM2和Pyrin等炎性小体在外源性病原体和内源性损伤信号的刺激下被激活,活化的炎性小体通过识别pro⁃Caspase⁃1后与下游含有Caspase⁃1激活结构域ASC结合而激活Caspase⁃1,形成多蛋白复合物[14]。其次,NLRP3炎性小体自裂解形成活性Caspase-1和p10/p20四聚体,孔隙形成蛋白(gasdermin D,GSDMD)作为活化的Caspase⁃1的蛋白底物,是焦亡的执行分子,可促进胞浆内容物IL⁃1β和IL⁃18等释放,从而影响多种自身免疫性疾病或诱导炎症反应,并可能导致癌症[15-16](图1c)。
2. HCC
HCC是原发性肝癌中最常见的类型,起源于肝细胞,与病毒性肝炎、肝硬化、酗酒、黄曲霉毒素摄入、肥胖、糖尿病和吸烟等因素密切相关[17-18]。在过去的几年里,原发性肝癌在全球范围内的发病率仍居高不下,中国每年大约有35万人死于肝癌,占全世界肝癌死亡人数一半以上,死亡率仅次于肺癌[19]。超声、甲胎蛋白(AFP)检测、计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振成像(MRI)以及病理组织学检查是诊断HCC的主要方法,截至2022年,中国肝癌的诊断率在所有肿瘤中仅排名第四,诊断率仍然较低[1]。即使是小肝癌(<5 cm),根治性切除或肝移植后3年内的复发率也>50%,术后5年的复发率为70%[20-21]。HCC预后不良,易复发,对患者生命造成严重威胁[22]。因此,肝癌作为典型的消化系统恶性肿瘤,以手术治疗为主,结合放疗、化疗等综合治疗尤为重要。
3. NLRP3炎性小体与HCC的关系
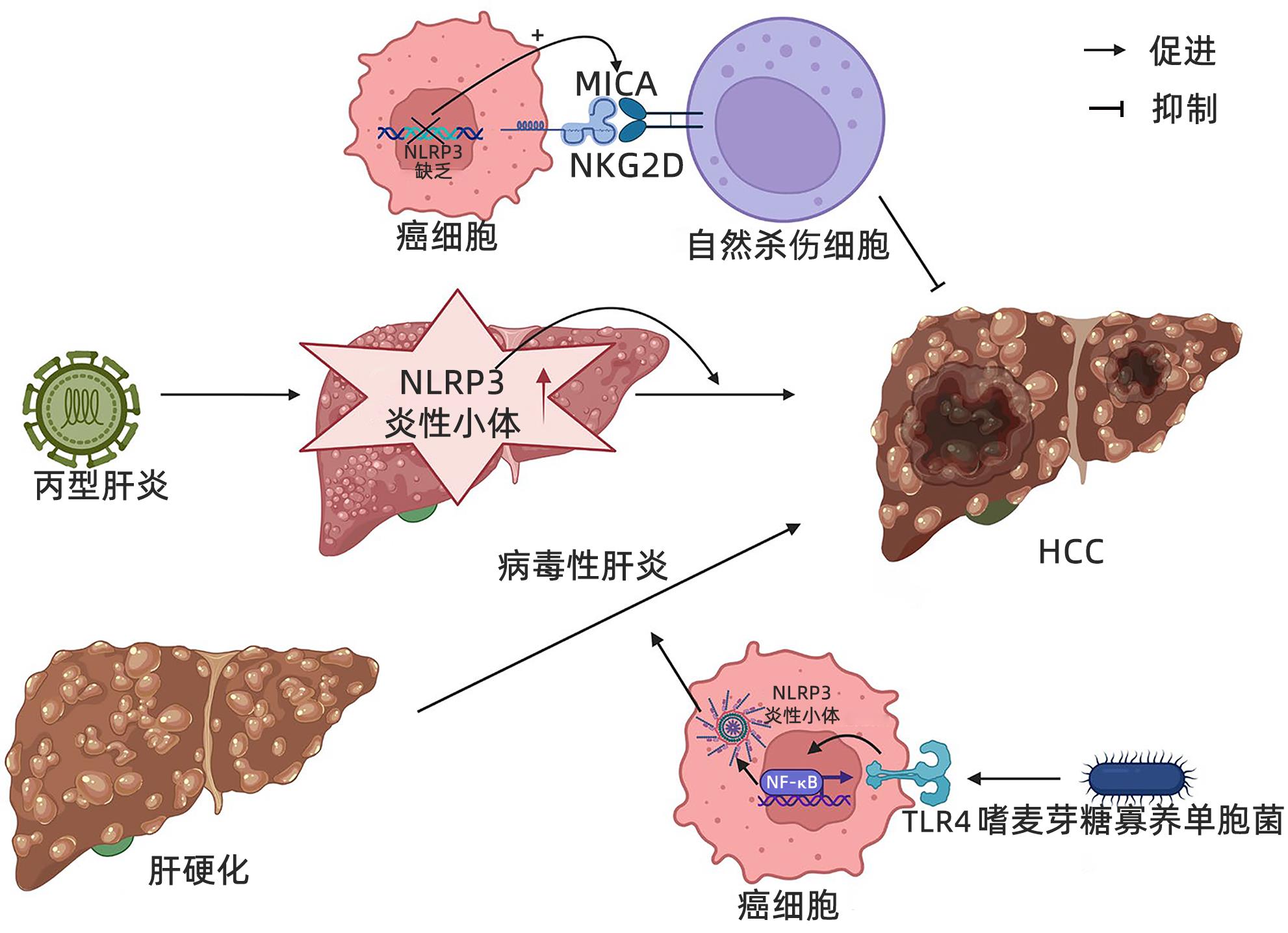
炎症是机体应对外界刺激作出的保护性反应,炎症与肿瘤发生密切相关,是癌症发生发展的标志[4]。当不同病原体(细菌、病毒)或其他刺激激活NLRP3炎性小体时,大量前体炎症细胞因子、生长因子、趋化因子、促血管生成因子和先天免疫细胞被释放,形成的肿瘤微环境在肿瘤的发生上起着关键作用[5]。慢性病毒性肝炎会损害肝细胞,引起肝纤维化或肝硬化,最终导致HCC的发生,这也被称作“肝癌进展三部曲”。
然而,在过去十年中,NLRP3炎性小体在肿瘤发生和抗肿瘤免疫中的不同作用已经出现[4]。当前,关于NLRP3炎性小体在HCC中的作用研究较少,且意见尚不统一。NLRP3炎性小体既可以通过相关的炎症信号通路促进HCC进展,又能够通过引起癌细胞焦亡抑制HCC进展,并且在HCC发生发展的不同时期,NLRP3炎性小体的作用也不同。
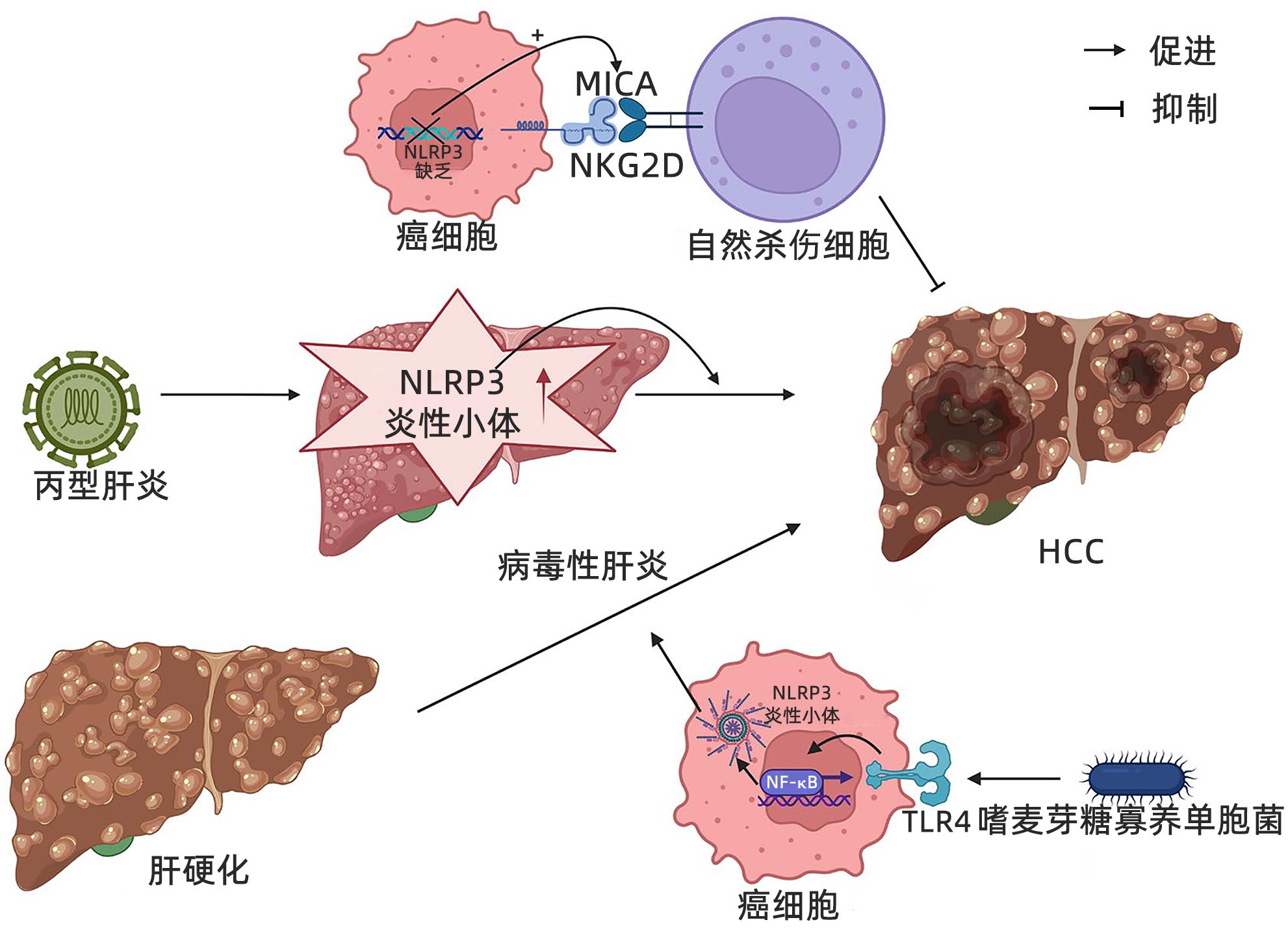
3.1 NLRP3炎性小体在HCC的发生过程中起促进作用
Wei等[23]研究发现NLRP3炎性小体的数量在HCC发生发展过程中处于动态变化,在正常肝组织中表达较低,当出现炎症性疾病(肝炎、肝硬化)时会升高,加剧肝硬化向HCC转变,再于HCC期降低,与癌旁正常肝组织相比,癌组织中NLRP3炎性小体的分子成分丢失或明显减少,NLRP3炎性小体各成分的mRNA表达水平与之变化同步,并且NLRP3各成分含量与HCC临床分期和病理分化程度呈负相关。据报道[24],HCC患者肿瘤微生物群中存在大量嗜麦芽糖寡养单胞菌,可激活TLR4/NF-κB通路,诱导NLRP3炎性小体组装形成,促进纤维化标志物α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的释放,导致肝纤维化,并在肝脏中分泌多种细胞因子、炎症因子加速肝硬化,从而形成有利于肿瘤细胞生长的微环境,促进细胞增殖和HCC进展[14,25](图2)。有体外实验研究[26]发现,细胞外ATP可以通过P2X7激活肝内NLRP3炎症小体,使肝星状细胞活化增强,也促进α-SMA和Ⅰ型胶原等纤维化标志物的释放从而导致肝纤维化;此外,抗P2X7R的siRNA能够抑制NLRP3和α-SMA蛋白的表达,抑制Ⅰ型胶原的沉积和分泌,P2X7R介导的NLRP3炎症小体激活参与肝星状细胞产生IL-1β可能与细胞外基质沉积有关,提示阻断P2X7R-NLRP3炎性小体轴可能减缓肝纤维化、限制HCC细胞的增殖和转移,是降低肝癌风险的潜在治疗靶点。
木犀草苷是一种存在于大叶龙胆中的黄酮类化合物,其可以减少细胞内ROS的产生,阻止NLRP3炎症小体的激活,降低NLRP3炎性小体的含量,同时降低IL-1β和Caspase-1的水平,减轻炎症和肝纤维化,抑制肝硬化,有效预防HCC的发生[27]。另外有研究[28-29]发现NLRP3失活可抑制免疫检查点LAG-3和PD-L1等蛋白的表达,从而降低HCC细胞免疫逃逸功能,促进T淋巴细胞对癌细胞的杀伤作用。此外,下调NLRP3炎性小体可诱导HCC细胞系Hep3B的凋亡,提示激活NLRP3炎性小体通路可触发致癌过程,并且与植入HCC细胞的正常小鼠相比,NLRP3炎性小体缺陷小鼠肿瘤进展速度明显缓慢,转移率更低[30]。NLRP3炎性小体缺失可促进HCC细胞表面MICA分子与自然杀伤细胞表面NKDG2D分子结合,使自然杀伤细胞识别并杀伤HCC细胞。有报道[31]称HCC根治性切除术后患者,肝脏中NLRP3表达升高与预后不良显著相关。
因此,上述研究证实NLRP3炎性小体通过多种方式促进HCC的发生和进展,NLRP3的高表达表明疾病处于活动期或恶化状态。然而,NLRP3的表达在HCC晚期逐渐下降,不代表病情好转,而是与临床分期密切相关。
3.2 NLRP3炎性小体引起的细胞焦亡抑制HCC的进展
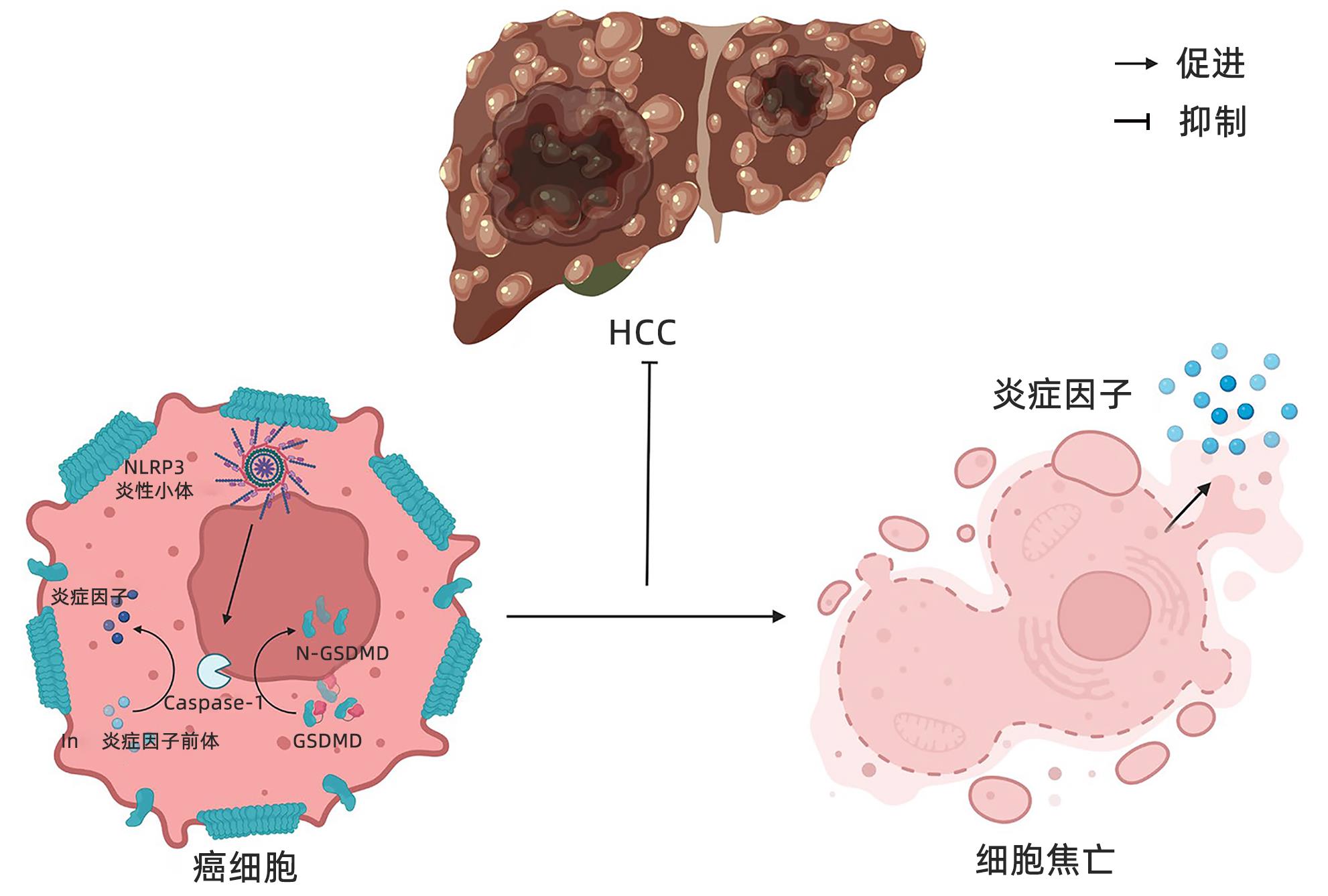
细胞焦亡是程序性死亡的一种,但与其他死亡(自噬、凋亡、坏死等)存在差别,焦亡过程涉及的信号通路主要是以Caspase⁃1激活为主要特征的经典型通路和依赖于Caspase⁃4/5/11的非经典型通路[32-33]。近些年关于NLRP3炎性小体介导的细胞焦亡在多种癌症的发生发展中发挥重要作用的报道较多[17],包括黑色素瘤、皮肤癌、结直肠癌等,并且发现细胞焦亡主要抑制肿瘤进展,因而,有望从细胞焦亡角度发现治疗肿瘤的新靶点。然而,细胞焦亡是否在HCC的发展过程中发挥作用仍需要进一步研究。
先前有研究[34]专门评估了细胞焦亡在HCC发展过程中的作用,发现与癌旁组织相比,癌组织中Caspase-1、IL⁃1β和IL⁃18的mRNA显著降低,表明肝癌组织中细胞焦亡受到抑制。有细胞模型[35]显示,减少或抑制NLRP3炎性小体激活而下调细胞焦亡现象会促进HCC的进展。17-β-雌二醇(E2)通过E2/ER/MAPK通路诱导NLRP3炎性小体激活引发HCC细胞焦亡增加,抑制了HCC的恶性增殖和转移,这也是男性发生HCC的风险是女性的2~7倍的主要原因之一[36]。NEK7是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,通过有丝分裂纺锤体形成和细胞分裂参与细胞周期进程[37]。Yan等[38]通过生物信息学、体外细胞实验和临床肿瘤标本研究发现,与肝癌周围正常组织相比,癌组织中NEK7表达明显上调,在肝癌细胞中敲低NEK7可显著提高NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD等细胞焦亡标志物的浓度,通过触发癌细胞焦亡来抑制肿瘤-基质的相互作用,从而显著降低肿瘤细胞迁移、侵袭和增殖,这也有效地减缓了HCC的发展速度,具体机制如图3所示。
这些研究充分表明,NLRP3炎性小体介导的癌细胞焦亡可能是HCC一种有效的治疗手段,以上调炎性小体相关基因或促进炎性小体的激活为策略,促进肝癌细胞焦亡,可起到肿瘤免疫的作用,这为以后抗肿瘤研究及肿瘤治疗开辟出新的方向。
4. 总结与展望
综上所述,NLRP3炎性小体在HCC发生发展过程中的功能具有双向性,这种双重作用一方面是由于NLRP3炎性小体被激活,释放多种炎性细胞因子,形成肿瘤细胞发生和发展的炎性微环境,最终促进肝炎、肝硬化向HCC转变,也促进HCC的增殖和转移;另一方面,NLRP3炎性小体可介导细胞焦亡途径抑制HCC的恶性进展。
因而,靶向NLRP3炎性小体可能是一种潜在治疗HCC的新策略,靶向NLRP3炎性小体的药物在HCC中的作用主要取决于以上两种机制中哪种受主要影响,但如何充分利用炎性小体的双向性作用,使其既能达到抗肿瘤效应,又能保持有利于这种效应的动态平衡状态仍值得探索。准确分析不同中药及其提取物通过NLRP3炎性小体介导细胞焦亡而发挥抗癌作用,降低化疗耐药,对延长肝癌患者生存周期具有积极意义,未来还需要进一步实验和临床研究来探索。
-
-
[1] LI Z, ZHU JY. Interpretation of standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 5): 1027- 1029. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.010.李照, 朱继业.《原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)》解读[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 5): 1027- 1029. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.010. [2] YANG JD, HAINAUT P, GORES GJ, et al. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16( 10): 589- 604. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y. [3] HUANG XY, CHAO X, HUANG F. Research progress on role of pyroptosis in progress of primary liver cancer[J]. Drug Eval Res, 2021, 44( 7): 1535- 1540. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2021.07.026.黄鑫悦, 晁旭, 黄峰. 细胞焦亡在原发性肝癌进展中的作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2021, 44( 7): 1535- 1540. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2021.07.026. [4] KARKI R, KANNEGANTI TD. Diverging inflammasome signals in tumorigenesis and potential targeting[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2019, 19( 4): 197- 214. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-019-0123-y. [5] KANTONO M, GUO BC. Inflammasomes and cancer: The dynamic role of the inflammasome in tumor development[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 1132. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01132. [6] XIA XJ, WANG X, CHENG Z, et al. The role of pyroptosis in cancer: Pro-cancer or pro-“host”?[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10( 9): 650. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1883-8. [7] DAGENAIS M, SKELDON A, SALEH M. The inflammasome: In memory of Dr. Jurg Tschopp[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2012, 19( 1): 5- 12. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.159. [8] SCHRODER K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasomes[J]. Cell, 2010, 140( 6): 821- 832. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.040. [9] MISSIROLI S, PERRONE M, BONCOMPAGNI C, et al. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome as a new therapeutic option for overcoming cancer[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13( 10): 2297. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13102297. [10] MALIK A, KANNEGANTI TD. Inflammasome activation and assembly at a glance[J]. J Cell Sci, 2017, 130( 23): 3955- 3963. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.207365. [11] PATEL MN, CARROLL RG, GALVÁN-PEÑA S, et al. Inflammasome priming in sterile inflammatory disease[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2017, 23( 2): 165- 180. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.12.007. [12] MOOSSAVI M, PARSAMANESH N, BAHRAMI A, et al. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17( 1): 158. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0900-3. [13] TSAI YM, CHIANG KH, HUNG JY, et al. Der f1 induces pyroptosis in human bronchial epithelia via the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41( 2): 757- 764. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3310. [14] TANG YL, TAO Y, ZHU L, et al. Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatocellular carcinoma: A double-edged sword[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 118: 110107. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110107. [15] SHI JJ, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death[J]. Nature, 2015, 526( 7575): 660- 665. DOI: 10.1038/nature15514. [16] HAMARSHEH S, ZEISER R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in cancer: A double-edged sword[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1444. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01444. [17] MAMUN A AL, MIMI AA, AZIZ MA, et al. Role of pyroptosis in cancer and its therapeutic regulation[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 910: 174444. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174444. [18] INCHINGOLO R, POSA A, MARIAPPAN M, et al. Locoregional treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current evidence and future directions[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25( 32): 4614- 4628. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4614. [19] CHEN WQ, ZHENG RS, BAADE PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66( 2): 115- 132. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21338. [20] ZENG HM, CHEN WQ, ZHENG RS, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2018, 6( 5): e555- e567. DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30127-X. [21] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [22] VOGEL A, MEYER T, SAPISOCHIN G, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400( 10360): 1345- 1362. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01200-4. [23] WEI Q, MU K, LI T, et al. Deregulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in hepatic parenchymal cells during liver cancer progression[J]. Lab Invest, 2014, 94( 1): 52- 62. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2013.126. [24] LIU BY, ZHOU ZW, JIN Y, et al. Hepatic stellate cell activation and senescence induced by intrahepatic microbiota disturbances drive progression of liver cirrhosis toward hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2022, 10( 1): e003069. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003069. [25] THI HTH, HONG S. Inflammasome as a therapeutic target for cancer prevention and treatment[J]. J Cancer Prev, 2017, 22( 2): 62- 73. DOI: 10.15430/JCP.2017.22.2.62. [26] JIANG S, ZHANG Y, ZHENG JH, et al. Potentiation of hepatic stellate cell activation by extracellular ATP is dependent on P2X7R-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2017, 117: 82- 93. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.040. [27] FAN SH, WANG YY, LU J, et al. Luteoloside suppresses proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9( 2): e89961. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089961. [28] DALEY D, MANI VR, MOHAN N, et al. NLRP3 signaling drives macrophage-induced adaptive immune suppression in pancreatic carcinoma[J]. J Exp Med, 2017, 214( 6): 1711- 1724. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20161707. [29] DING Y, YAN YL, DONG YH, et al. NLRP3 promotes immune escape by regulating immune checkpoints: A pan-cancer analysis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 104: 108512. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108512. [30] WAN LF, YUAN X, LIU MT, et al. miRNA-223-3p regulates NLRP3 to promote apoptosis and inhibit proliferation of hep3B cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 15( 3): 2429- 2435. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5667. [31] SONOHARA F, INOKAWA Y, KANDA M, et al. Association of inflammasome components in background liver with poor prognosis after curatively-resected hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Anticancer Res, 2017, 37( 1): 293- 300. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.11320. [32] WANG L, QIN XW, LIANG JM, et al. Induction of pyroptosis: A promising strategy for cancer treatment[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 635774. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.635774. [33] CHEN YF, LI S, SHI Y, et al. Research progress on atherosclerosis induced by clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential and the therapeutic effect of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. China Med Herald, 2023, 20( 21): 40- 44. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.21.08.陈雅芳, 李思, 史洋, 等. 潜质未定克隆性造血致动脉粥样硬化及NLRP3炎性小体治疗作用研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2023, 20( 21): 40- 44. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.21.08. [34] CHU Q, JIANG YN, ZHANG W, et al. Pyroptosis is involved in the pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7( 51): 84658- 84665. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12384. [35] CHEN YF, QI HY, WU FL. Euxanthone exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-invasive activities in hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing pyroptosis: Preliminary results[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22( 23): 8186- 8196. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_201812_16511. [36] WEI Q, ZHU R, ZHU JY, et al. E2-induced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome triggers pyroptosis and inhibits autophagy in HCC cells[J]. Oncol Res, 2019, 27( 7): 827- 834. DOI: 10.3727/096504018X15462920753012. [37] SHARIF H, WANG L, WANG WL, et al. Structural mechanism for NEK7-licensed activation of NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Nature, 2019, 570( 7761): 338- 343. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1295-z. [38] YAN ZL, DA QG, LI ZF, et al. Inhibition of NEK7 suppressed hepatocellular carcinoma progression by mediating cancer cell pyroptosis[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 812655. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.812655. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 周青青,潘陈为. MicroRNA-375低水平表达与乙肝肝细胞癌预后相关性分析. 中国药物滥用防治杂志. 2025(01): 46-50 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 段淑文,魏亚君,武天凯,王晓辉,丁照然,刘灿,戴恩来. 基于NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD通路对泼尼松联合淫羊藿苷提高激素抵抗型肾病综合征疗效的机制研究. 中国临床药理学与治疗学. 2024(10): 1081-1090 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 沈赞,王冠尹,张镒,裴航,韦新士,王子月,陈志远,何帮剑. 激素性股骨头坏死中多重细胞死亡方式作用的研究进展. 中国骨质疏松杂志. 2024(12): 1832-1837 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-




 PDF下载 ( 942 KB)
PDF下载 ( 942 KB)


 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术