二维剪切波弹性成像和血清学模型在慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化分期中的应用价值
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240312
Application value of two-dimensional shear wave elastography and serological models in the staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B
-
摘要:
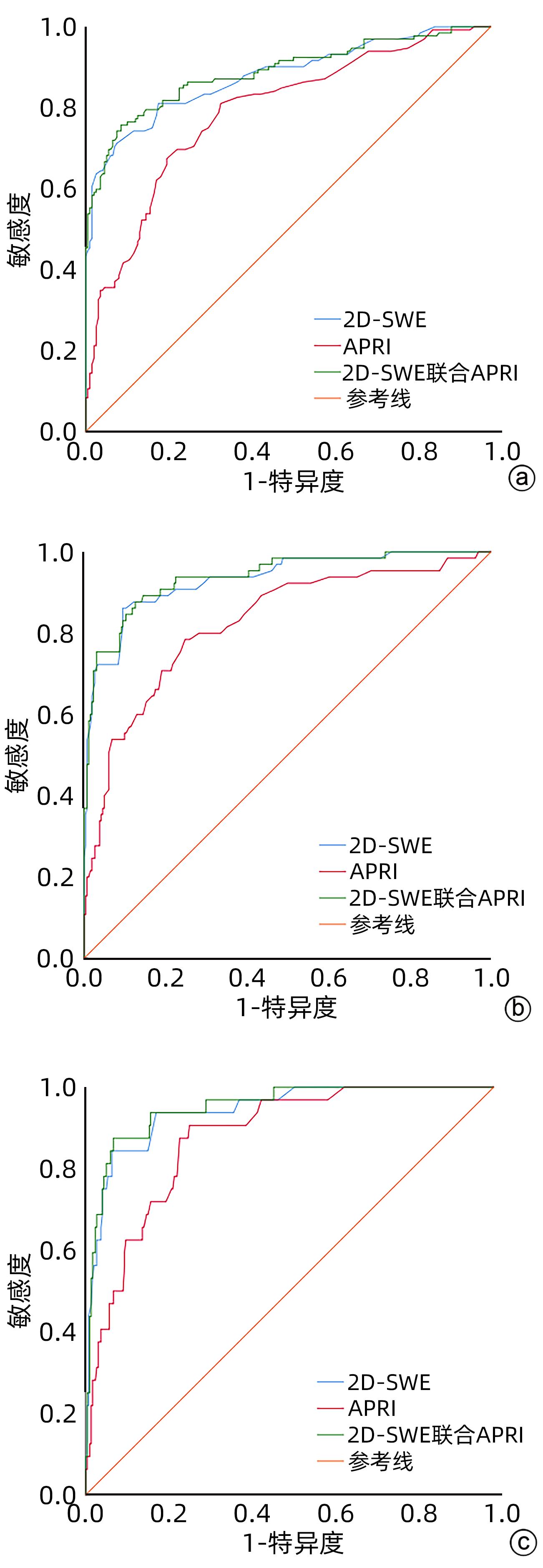
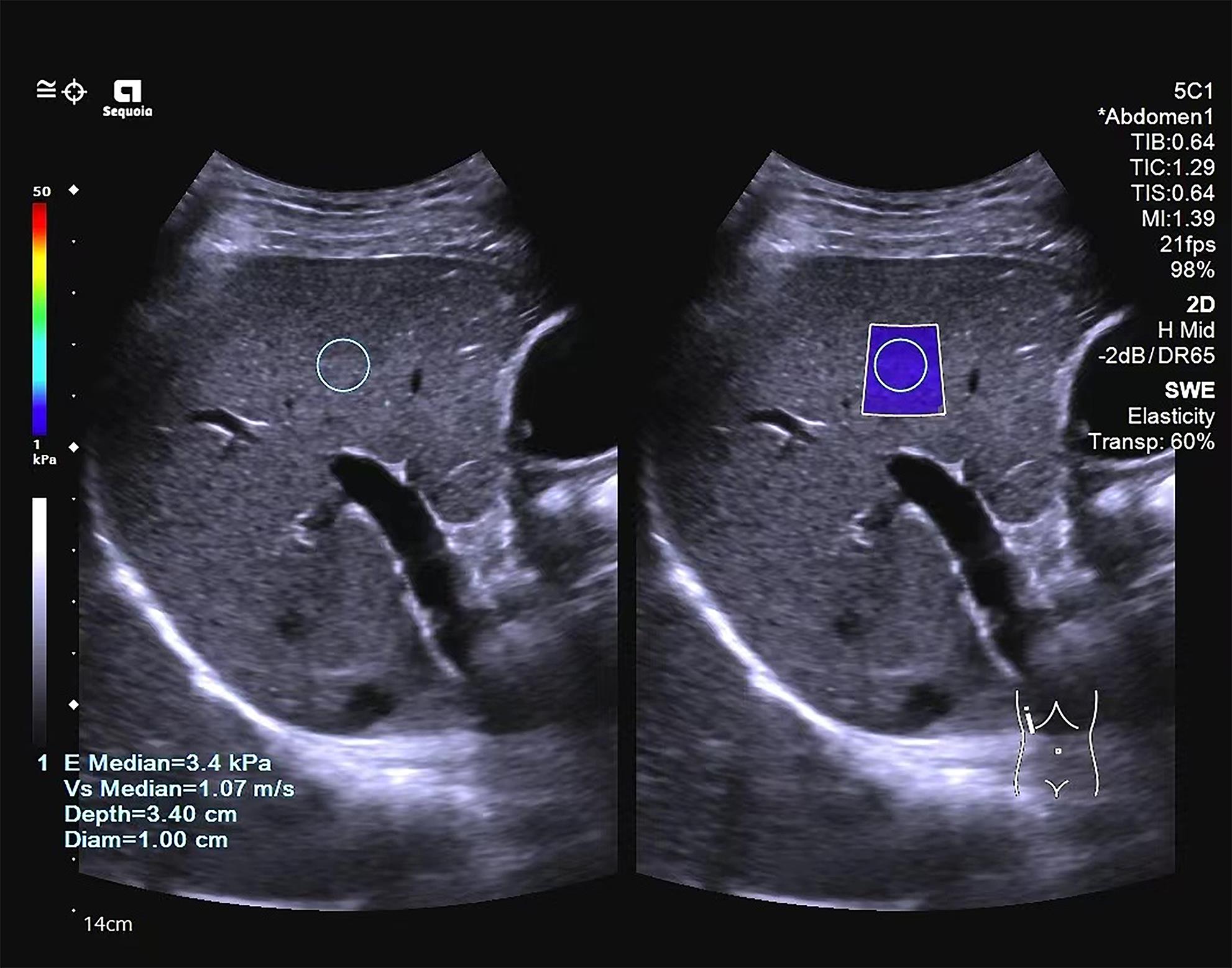
目的 探讨二维剪切波弹性成像和血清学模型及其联合应用在慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化分期中的诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析2020年8月—2022年8月在福建医科大学孟超肝胆医院进行过二维剪切波弹性成像(2D-SWE)与肝组织病理学检查的327例慢性乙型肝炎患者的临床资料,提取患者的性别、年龄、血清学指标和2D-SWE结果,根据肝纤维化程度分为S0~S1组、S≥2组、S≥3组和S=4组,根据血清学指标计算血清学模型。采用Spearman相关分析法对2D-SWE和血清学模型与肝纤维化分期进行相关分析,以肝组织病理结果为标准,绘制受试者工作特征曲线,比较各参数及其联合应用诊断肝纤维化分期的效能,并采用Delong检验比较不同方法间的差异。 结果 2D-SWE检测LSM值与肝纤维化分期呈强相关性(r=0.741,P<0.001),血清学模型中除了AAR外的其他6种(APRI、FIB-4、GPR、GP、RPR、S指数)与肝纤维化分期均存在正相关(P值均<0.001)。2D-SWE诊断S≥2、S≥3和S=4肝纤维化的AUC值分别为0.878、0.932、0.942,显著高于血清学模型(P值均<0.001),其最佳截断值分别为6.9 kPa、7.9 kPa、9.4 kPa。血清学模型中APRI在诊断S≥2、S=4的AUC值最高(0.788、0.875),S指数在诊断S≥3的AUC值最高(0.846)。在诊断S≥2、S≥3、S=4时2D-SWE和APRI联合能将AUC值分别提高到0.887、0.938、0.950,诊断S≥2、S≥3、S=4时2D-SWE和S指数联合诊断的AUC值分别为0.879、0.935、0.941;但单独使用2D-SWE与上述联合诊断并无统计学差异(P值均>0.05)。 结论 2D-SWE对肝纤维化分期的诊断效能显著优于7种血清学模型;血清学模型具有一定的诊断价值,其中APRI、S指数的价值较高;单独使用2D-SWE与指标联合并无明显差异,联合并不能显著提高诊断效能,新的联合诊断方法仍有待探索。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) or serological models used alone or in combination in determining the stage of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 327 patients with chronic hepatitis B who were admitted to Mengchao Hepatobiliary Hospital of Fujian Medical University from August 2020 to August 2022 and underwent 2D-SWE and liver histopathological examination, including sex, age, serological markers, and 2D-SWE results. According to the degree of liver fibrosis, they were divided into S0-S1, S≥2, S≥3, and S=4 groups, and the serological models were calculated based on serological markers. A Spearman correlation analysis was used to investigate the correlation of 2D-SWE and serological models with liver fibrosis stage; the receiver operating characteristic curve was plotted with the results of liver histopathology as the standard to compare the efficiency of each parameter used alone or in combination in determining the stage of liver fibrosis; the Delong test was used to investigate the difference between different methods. Results Liver stiffness measurement measured by 2D-SWE was strongly correlated with the stage of liver fibrosis (r=0.741, P<0.001), and as for the serological model, six markers (APRI, FIB-4, GPR, GP, RPR, and S index), other than AAR, were positively correlated with the stage of liver fibrosis (all P<0.001). 2D-SWE had an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.878, 0.932, and 0.942, respectively, in the diagnosis of S≥2, S≥3, and S=4 liver fibrosis (all P<0.001), with an optimal cut-off value of 6.9 kPa, 7.9 kPa, and 9.4 kPa, respectively. Among the serological models, APRI had the largest AUC of 0.788 and 0.875, respectively, in the diagnosis of S≥2 and S=4 liver fibrosis, and S index had the largest AUC of 0.846 in the diagnosis of S≥3 liver fibrosis. In the diagnosis of S≥2, S≥3, and S=4 liver fibrosis, 2D-SWE combined with APRI increased the AUC values to 0.887, 0.938, and 0.950, respectively, and 2D-SWE combined with S index increased the AUC values to 0.879, 0.935, and 0.941, respectively, while there were no significant differences between 2D-SWE and the above combinations (P>0.05). Conclusion 2D-SWE has a better diagnostic efficacy than the above seven serological models in determining liver fibrosis stage. The serological models have a certain diagnostic value, among which APRI and S index have a relatively high diagnostic value. There is no significant difference between 2D-SWE and 2D-SWE combined with serological models, and such combinations cannot significantly improve diagnostic efficiency. Therefore, further studies are needed to explore new combinations of diagnostic methods. -
Key words:
- Chronic Hepatitis B /
- Liver Fibrosis /
- Elasticity Imaging Techniques /
- Biopsy, Needle
-
表 1 患者基础情况
Table 1. Patient basic information table
项目 数值 性别(男/女,例) 199/128 年龄(岁) 37(31~46) LSM(kPa) 5.8(4.4~8.0) ALT(IU/L) 35(22~51) AST(IU/L) 28(22~39) GGT(U/L) 26(16~53) Alb(g/L) 43(40~45) Glo(g/L) 30(27~33) PLT(×109/L) 215(180~255) RDW 12.8(12.4~13.3) APRI 0.34(0.24~0.53) FIB-4 0.85(0.63~1.34) AAR 0.88(0.68~1.12) GPR 0.12(0.07~0.31) GP 13.73(11.81~17.26) PRP 0.06(0.05~0.07) S指数 0.07(0.04~0.18) 肝纤维化分期[例(%)] S0~1 195(59.6) S2 67(20.5) S3 33(10.1) S4 32(9.8) 表 2 2D-SWE、各血清学模型与肝纤维化分期的相关性
Table 2. Correlation between 2D-SWE、serological models and hepatic fibrosis stage
项目 r值 P值 LSM 0.741 <0.001 APRI 0.498 <0.001 FIB-4 0.493 <0.001 GPR 0.348 <0.001 GP 0.509 <0.001 RPR 0.285 <0.001 S指数 0.329 <0.001 AAR 0.012 0.835 表 3 2D-SWE和各血清学模型单独诊断肝纤维化S≥2的效能比较
Table 3. Comparison of the efficacy of 2D-SWE and each serological model in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis S≥2
项目 最佳截断值 AUC 95%CI 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 2D-SWE 6.90 kPa 0.878 0.838~0.919 71.2 92.3 APRI 0.32 0.788 0.738~0.839 81.1 66.7 FIB-4 0.96 0.710 0.650~0.769 61.4 75.9 AAR 0.83 0.454 0.391~0.517 54.5 58.5 GPR 0.10 0.778 0.727~0.828 84.1 61.0 GP 15.4 0.735 0.677~0.792 61.4 79.0 PRP 0.07 0.694 0.635~0.753 40.9 88.2 S指数 0.08 0.776 0.725~0.826 66.7 76.4 表 4 2D-SWE和各血清学模型单独诊断肝纤维化S≥3的效能比较
Table 4. Comparison of the efficacy of 2D-SWE and each serological model in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis S≥3
项目 最佳截断值 AUC 95%CI 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 2D-SWE 7.90 kPa 0.932 0.896~0.968 86.2 90.5 APRI 0.42 0.825 0.765~0.885 78.5 75.2 FIB-4 1.13 0.801 0.737~0.866 70.8 77.5 AAR 1.63 0.516 0.436~0.596 12.3 96.6 GPR 0.16 0.841 0.793~0.890 83.1 72.5 GP 15.63 0.777 0.703~0.852 72.3 76.7 PRP 0.07 0.749 0.678~0.821 53.8 84.0 S指数 0.12 0.846 0.799~0.894 75.4 80.9 表 5 2D-SWE和各血清学模型单独诊断肝纤维化S=4的效能比较
Table 5. Comparison of the efficacy of 2D-SWE and each serological model in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis S=4
项目 最佳截断值 AUC 95%CI 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 2D-SWE 9.40 kPa 0.942 0.902~0.982 84.4 93.6 APRI 0.44 0.875 0.820~0.929 90.6 74.6 FIB-4 1.13 0.864 0.792~0.936 87.5 73.9 AAR 1.73 0.550 0.444~0.656 15.6 99.3 GPR 0.22 0.837 0.782~0.891 81.2 74.6 GP 15.79 0.885 0.819~0.952 90.6 74.9 PRP 0.09 0.844 0.767~0.920 78.1 82.4 S指数 0.12 0.835 0.779~0.891 81.2 75.3 表 6 2D-SWE联合血清学模型诊断肝纤维化的效能比较
Table 6. Comparison of efficacy of 2D-SWE combined serological model in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis
项目 肝纤维化分期 AUC 95%CI 2D-SWE联合APRI S≥2 0.887 0.847~0.927 S≥3 0.938 0.904~0.972 S=4 0.950 0.915~0.985 2D-SWE联合S指数 S≥2 0.879 0.838~0.919 S≥3 0.935 0.900~0.971 S=4 0.941 0.902~0.980 -
[1] SEKIBA K, OTSUKA M, OHNO M, et al. Hepatitis B virus pathogenesis: Fresh insights into hepatitis B virus RNA[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 21): 2261- 2268. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i21.2261. [2] ROEHLEN N, CROUCHET E, BAUMERT TF. Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 4). DOI: 10.3390/cells9040875. [3] LI YP, LI CY, CAO D, et al. New progress in non-invasive diagnostic models of chronic hepatitis B liver fibrosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2017, 22( 12): 1144- 1146. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2017.12.023.李艳平, 李春艳, 曹丹, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化无创诊断模型研究新进展[J]. 肝脏, 2017, 22( 12): 1144- 1146. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2017.12.023. [4] WANG K, LU X, ZHOU H, et al. Deep learning radiomics of shear wave elastography significantly improved diagnostic performance for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B: a prospective multicentre study[J]. Gut, 2019, 68( 4): 729- 741. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316204. [5] HERRMANN E, de LÉDINGHEN V, CASSINOTTO C, et al. Assessment of biopsy-proven liver fibrosis by two-dimensional shear wave elastography: An individual patient data-based meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67( 1): 260- 272. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29179. [6] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. [7] SONNEVELD MJ, BROUWER WP, CHAN HL, et al. Optimisation of the use of APRI and FIB-4 to rule out cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: results from the SONIC-B study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4( 7): 538- 544. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30087-1. [8] XU XL, JIANG LS, WU CS, et al. The role of fibrosis index FIB-4 in predicting liver fibrosis stage and clinical prognosis: A diagnostic or screening tool?[J]. J Formos Med Assoc, 2022, 121( 2): 454- 466. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.07.013. [9] ZHOU L, WANG SB, CHEN SG, et al. Prognostic value of ALT, AST, and AAR in hepatocellular carcinoma with B-type hepatitis-associated cirrhosis after radical hepatectomy[J]. Clin Lab, 2018, 64( 10): 1739- 1747. DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.180532. [10] DING R, LU W, ZHOU X, et al. A novel non-invasive model based on GPR for the prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2021, 8: 727706. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.727706. [11] LI Q, LU C, LI W, et al. Globulin-platelet model predicts significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in CHB patients with high HBV DNA and mildly elevated alanine transaminase levels[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2018, 18( 1): 71- 78. DOI: 10.1007/s10238-017-0472-3. [12] YUYUN D, ZHIHUA T, HAIJUN W, et al. Predictive value of the red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio for hepatic fibrosis[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2019, 54( 1): 81- 86. DOI: 10.1080/00365521.2018.1558786. [13] TAG-ADEEN M, OMAR MZ, ABD-ELSALAM FM, et al. Assessment of liver fibrosis in Egyptian chronic hepatitis B patients: A comparative study including 5 noninvasive indexes[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2018, 97( 6): e9781. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009781. [14] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of hepatic fibrosis(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 10): 2163- 2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 10): 2163- 2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007. [15] DESMET VJ, GERBER M, HOOFNAGLE JH, et al. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging[J]. Hepatology, 1994, 19( 6): 1513- 1520. [16] DONG M, WU J, YU X, et al. Validation and comparison of seventeen noninvasive models for evaluating liver fibrosis in Chinese hepatitis B patients[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38( 9): 1562- 1570. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13688. [17] TAO ZZ, WANG YL, SUN YH, et al. Comparison of different Young’s modulus determination by two-dimensional shear wave elastography in predicting liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B.[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2023, 26( 3): 328- 331. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2023.03.007.陶贞贞, 王永莉, 孙红艳, 等. 二维剪切波弹性成像诊断慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化价值研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2023, 26( 3): 328- 331. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2023.03.007. [18] OSMAN AM, SHIMY A EL, AZIZ MM ABD EL. 2D shear wave elastography(SWE) performance versus vibration-controlled transient elastography(VCTE/fibroscan) in the assessment of liver stiffness in chronic hepatitis[J]. Insights Imaging, 2020, 11( 1): 38. DOI: 10.1186/s13244-020-0839-y. [19] GUO H, LIAO M, JIN J, et al. How intrahepatic cholestasis affects liver stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a study of 1197 patients with liver biopsy[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30( 2): 1096- 1104. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06451-x. [20] EKIN N, UCMAK F, EBIK B, et al. GPR, King’s Score and S-Index are superior to other non-invasive fibrosis markers in predicting the liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2022, 85( 1): 62- 68. DOI: 10.51821/85.1.9156. [21] KAVAK S, KAYA S, SENOL A, et al. Evaluation of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients with 2D shear wave elastography with propagation map guidance: a single-centre study[J]. BMC Med Imaging, 2022, 22( 1): 50. DOI: 10.1186/s12880-022-00777-7. [22] ZHUANG Y, DING H, ZHANG Y, et al. Two-dimensional shear-wave elastography performance in the noninvasive evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Comparison with serum fibrosis indexes[J]. Radiology, 2017, 283( 3): 873- 882. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2016160131. -



 PDF下载 ( 1188 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1188 KB)

 下载:
下载: