嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌在非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240326
-
摘要: 非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)已成为全球最常见的慢性肝病,同时也是发生肝硬化和肝细胞癌的主要原因之一,因此及时遏止NAFLD的发生发展尤为重要,但由于其复杂的发病机制,目前尚无有效的根治手段。嗜黏蛋白阿克曼菌(Akk菌)作为新一代益生菌,能够改善机体代谢紊乱。越来越多的研究表明,Akk菌对代谢性疾病,尤其是NAFLD有潜在的治疗作用。因此,本文就Akk菌在NAFLD中的作用机制作简要综述,旨在为NAFLD的治疗改进和开创新疗法提供新思路。Abstract: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the most common chronic liver disease in the world, and it is also one of the main causes of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, so it is particularly important to curb the development and progression of NAFLD in a timely manner. However, due to its complex pathogeneses, there are currently no effective methods for radical treatment. As a new generation of probiotics, Akkermansia muciniphila (Akk bacteria) can improve metabolic disorders of the body, and more and more studies have shown that Akk bacteria have a potential therapeutic effect on metabolic diseases, especially NAFLD. Therefore, this article briefly reviews the mechanism of action of Akk bacteria in NAFLD, in order to provide new ideas for improving the treatment of NAFLD and creating new therapies.
-
Key words:
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease /
- Akkermansia /
- Therapeutics
-
表 1 Akk菌在多种疾病中的作用
Table 1. The role of Akkermansia muciniphila in various diseases
-
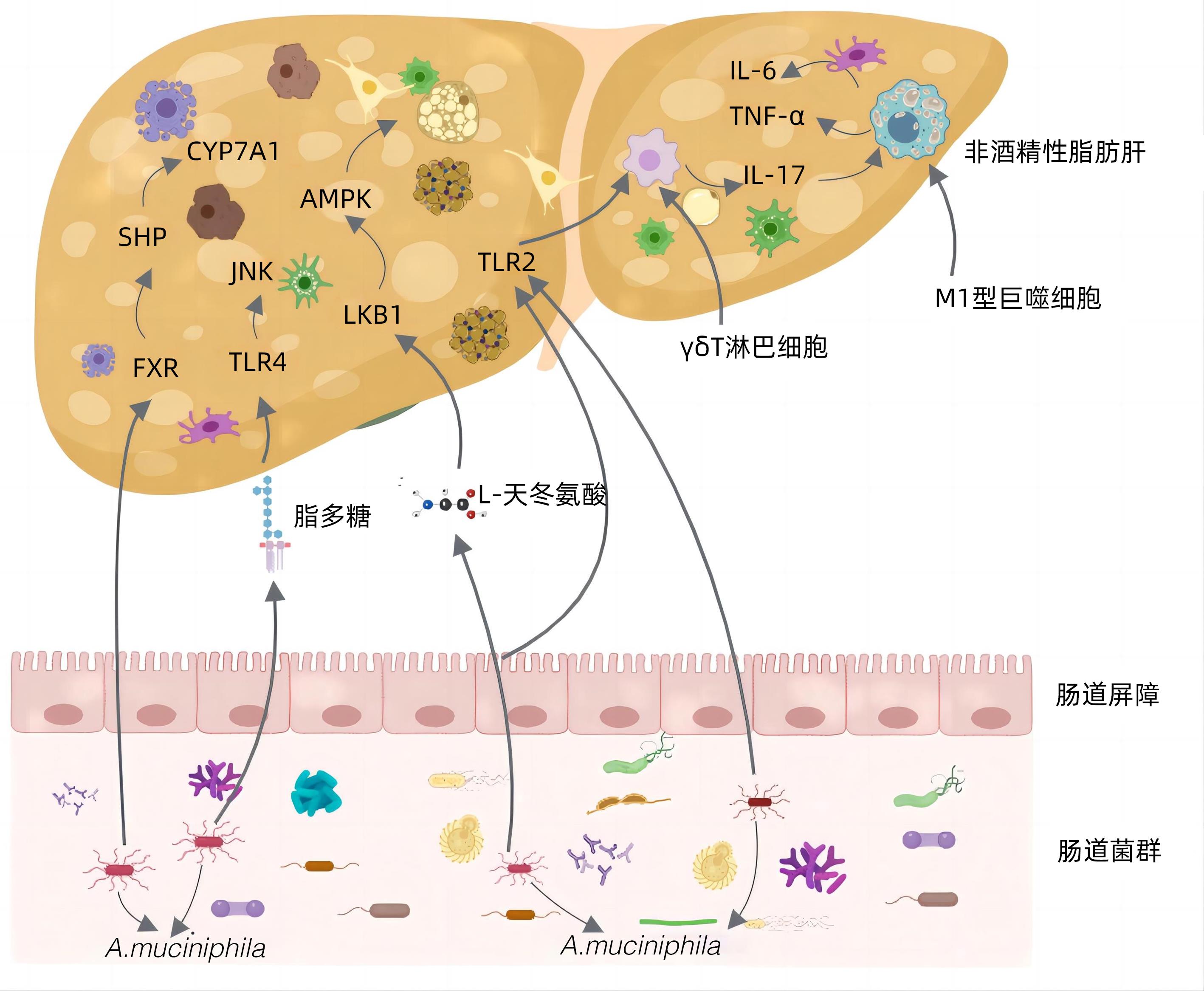
[1] RIAZI K, AZHARI H, CHARETTE JH, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7( 9): 851- 861. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. [2] WU CM, ZHANG CY, XU HL, et al. Epidemiological research and diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in China[J]. China Med Herald, 2023, 20( 11): 158- 161. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.11.36.吴车敏, 张从玉, 徐慧丽, 等. 我国非酒精性脂肪性肝病的流行病学研究和诊断现状分析[J]. 中国医药导报, 2023, 20( 11): 158- 161. DOI: 10.20047/j.issn1673-7210.2023.11.36. [3] JIN R, WANG XX, LIU F, et al. Research advances in pharmacotherapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 7): 1634- 1640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.033.靳睿, 王晓晓, 刘峰, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的药物治疗进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 7): 1634- 1640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.033. [4] ZHAO Q, YU J, HAO Y, et al. Akkermansiamuciniphila plays critical roles in host health[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 2023, 49( 1): 82- 100. DOI: 10.1080/1040841X.2022.2037506. [5] SHEN K, SINGH AD, MODARESI ESFEH J, et al. Therapies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2022 update[J]. World J Hepatol, 2022, 14( 9): 1718- 1729. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i9.1718. [6] LI YQ, TANG WJ, ZHOU YJ. Role of intestinal microbiota and metabolites in the development, progression, and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 8): 1805- 1810. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.006.李永强, 唐文娟, 周永健. 肠道菌群及其代谢产物在非酒精性脂肪性肝病发生发展及治疗中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 8): 1805- 1810. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.006. [7] BELKAID Y, HARRISON OJ. Homeostatic immunity and the microbiota[J]. Immunity, 2017, 46( 4): 562- 576. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.008. [8] CANI PD, DEPOMMIER C, DERRIEN M, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila: paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19( 10): 625- 637. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-022-00631-9. [9] SI J, KANG H, YOU HJ, et al. Revisiting the role of Akkermansia muciniphila as a therapeutic bacterium[J]. Gut Microbes, 2022, 14( 1): 2078619. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2078619. [10] BAE M, CASSILLY CD, LIU X, et al. Akkermansia muciniphilaphospholipid induces homeostatic immune responses[J]. Nature, 2022, 608( 7921): 168- 173. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04985-7. [11] KESHAVARZ AZIZI RAFTAR S, ASHRAFIAN F, YADEGAR A, et al. The protective effects of live and pasteurized akkermansiamuciniphila and its extracellular vesicles against HFD/CCl4-induced liver injury[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2021, 9( 2): e0048421. DOI: 10.1128/Spectrum.00484-21. [12] KIM S, SHIN YC, KIM TY, et al. Mucin degrader Akkermansiamuciniphila accelerates intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial development[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13( 1): 1- 20. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1892441. [13] QU S, FAN L, QI Y, et al. Akkermansiamuciniphila Alleviates Dextran Sulfate Sodium(DSS)-induced acute colitis by NLRP3 activation[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2021, 9( 2): e0073021. DOI: 10.1128/Spectrum.00730-21. [14] REUNANEN J, KAINULAINEN V, HUUSKONEN L, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila adheres to enterocytes and strengthens the integrity of the epithelial cell layer[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2015, 81( 11): 3655- 3662. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.04050-14. [15] LOPETUSO LR, QUAGLIARIELLO A, SCHIAVONI M, et al. Towards a disease-associated common trait of gut microbiota dysbiosis: The pivotal role of Akkermansia muciniphila[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2020, 52( 9): 1002- 1010. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.020. [16] SUN XW, HE JH, JIANG XZ, et al. Probiotics A. muciniphila improving diarrhea induced by ETEC in mice[J]. Acta Univ Med Nanjing(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 43( 1): 27- 33. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20230104.孙学伟, 何君花, 姜新泽, 等. 益生菌A. muciniphila改善大肠杆菌诱导的小鼠腹泻[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43( 1): 27- 33. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20230104. [17] ŠEŠELJA K, BAZINA I, VRECL M, et al. TFF3 deficiency protects against hepatic fat accumulation after prolonged high-fat diet[J]. Life(Basel), 2022, 12( 8): 1288. DOI: 10.3390/life12081288. [18] BARCENA C, VALDES-MAS R, MAYORAL P, et al. Healthspan and lifespan extension by fecal microbiota transplantation into progeroid mice[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25( 8): 1234- 1242. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0504-5. [19] van der LUGT B, van BEEK AA, AALVINK S, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates the age-related decline in colonic mucus thickness and attenuates immune activation in accelerated aging Ercc1-/Δ7 mice[J]. Immun Ageing, 2019, 16: 6. DOI: 10.1186/s12979-019-0145-z. [20] GRANDER C, GRABHERR F, SPADONI I, et al. The role of gut vascular barrier in experimental alcoholic liver disease and A. muciniphila supplementation[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 12( 1): 1851986. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1851986. [21] BI M, LIU C, WANG Y, et al. Therapeutic prospect of new probiotics in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11( 6): 1527. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11061527. [22] OU Z, DENG L, LU Z, et al. Protective effects of Akkermansiamuciniphila on cognitive deficits and amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Nutr Diabetes, 2020, 10( 1): 12. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116505. [23] LIU J, LIU H, LIU H, et al. Live and pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila decrease susceptibility to Salmonella Typhimurium infection in mice[J]. J Adv Res, 2023, 52: 89- 102. DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.03.008. [24] LI J, YANG G, ZHANG Q, et al. Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in type 2 diabetes and related diseases[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1172400. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1172400. [25] HOYLES L, FERNÁNDEZ-REAL JM, FEDERICI M, et al. Molecular phenomics and metagenomics of hepatic steatosis in non-diabetic obese women[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24( 7): 1070- 1080. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0061-3. [26] TSAI HJ, TSAI YC, HUNG WW, et al. Gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease severity in type 2 diabetes patients[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11( 3). DOI: 10.3390/jpm11030238. [27] ÖZKUL C, YALıNAY M, KARAKAN T, et al. Determination of certain bacterial groups in gut microbiota and endotoxin levels in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2017, 28( 5): 361- 369. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2017.17033. [28] LIANG T, LI D, ZUNONG J, et al. Interplay of lymphocytes with the intestinal microbiota in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14( 21): 4641. DOI: 10.3390/nu14214641. [29] PAN X, KAMINGA AC, LIU A, et al. Gut microbiota, glucose, lipid, and water-electrolyte metabolism in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 683743. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.683743. [30] KIM S, LEE Y, KIM Y, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila prevents fatty liver disease, decreases serum triglycerides, and maintains gut homeostasis[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2020, 86( 7): e03004-19. DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03004-19. [31] SHI Z, LEI H, CHEN G, et al. Impaired intestinal Akkermansia muciniphila and Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands contribute to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice[J]. mSystems, 2021, 6( 1): e00985-20. DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00985-20. [32] YE JZ, LI YT, WU WR, et al. Dynamic alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolome during the development of methionine-choline-deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24( 23): 2468- 2481. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i23.2468. [33] CHOPYK DM, GRAKOUI A. Contribution of the intestinal microbiome and gut barrier to hepatic disorders[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159( 3): 849- 863. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.077. [34] CARPINO G, DEL BEN M, PASTORI D, et al. Increased liver localization of lipopolysaccharides in human and experimental NAFLD[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 2): 470- 485. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31056. [35] ZHAO S, LIU W, WANG J, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila improves metabolic profiles by reducing inflammation in chow diet-fed mice[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2017, 58( 1): 1- 14. DOI: 10.1530/JME-16-0054. [36] WU W, LV L, SHI D, et al. Protective effect of Akkermansia muciniphila against immune-mediated liver injury in a mouse model[J]. Front Microbiol, 2017, 8: 1804. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01804. [37] CLIFFORD BL, SEDGEMAN LR, WILLIAMS KJ, et al. FXR activation protects against NAFLD via bile-acid-dependent reductions in lipid absorption[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33( 8): 1671- 1684. e 4. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.06.012. [38] YAN N, YAN T, XIA Y, et al. The pathophysiological function of non-gastrointestinal farnesoid X receptor[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 226: 107867. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107867. [39] NIAN F, WU L, XIA Q, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and bifidobacterium bifidum prevent NAFLD by regulating FXR expression and gut microbiota[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2023, 11( 4): 763- 776. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00415. [40] LENG W, LIU Y, SHI H, et al. Aspartate alleviates liver injury and regulates mRNA expressions of TLR4 and NOD signaling-related genes in weaned pigs after lipopolysaccharide challenge[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2014, 25( 6): 592- 599. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.01.010. [41] RAO Y, KUANG Z, LI C, et al. Gut Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease by regulating the metabolism of L-aspartate via gut-liver axis[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13( 1): 1- 19. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1927633. [42] KAZANKOV K, JØRGENSEN S, THOMSEN KL, et al. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16( 3): 145- 159. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0082-x. [43] HAN Y, LING Q, WU L, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila inhibits nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by orchestrating TLR2-activated γδT17 cell and macrophage polarization[J]. Gut Microbes, 2023, 15( 1): 2221485. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2221485. [44] NEGI CK, BABICA P, BAJARD L, et al. Insights into the molecular targets and emerging pharmacotherapeutic interventions for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Metabolism, 2022, 126: 154925. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154925. [45] MOREIRA GV, AZEVEDO FF, RIBEIRO LM, et al. Liraglutide modulates gut microbiota and reduces NAFLD in obese mice[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2018, 62: 143- 154. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.07.009. [46] DU J, ZHANG P, LUO J, et al. Dietary betaine prevents obesity through gut microbiota-drived microRNA-378a family[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13( 1): 1- 19. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1862612. [47] ZHANG Y, YANG L, ZHAO N, et al. Soluble polysaccharide derived from Laminaria japonica attenuates obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with gut microbiota regulation[J]. Mar Drugs, 2021, 19( 12): 699. DOI: 10.3390/md19120699. [48] PÉREZ-MONTER C, ÁLVAREZ-ARCE A, NUÑO-LAMBARRI N, et al. Inulin improves diet-induced hepatic steatosis and increases intestinal akkermansia genus level[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 2): 991. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020991. [49] ZHANG WJ, LI T. Akkermansia muciniphila suppresses non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated liver cancer in mice by recovering intestinal barrier function[J]. Cancer Res Prevent Treat, 2023, 50( 5): 463- 469. DOI: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2023.22.1259.张武剑, 李桃. 嗜蛋白阿克曼菌通过保护肠道屏障功能抑制小鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝炎相关肝癌[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2023, 50( 5): 463- 469. DOI: 10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2023.22.1259. [50] HIGARZA SG, ARBOLEYA S, ARIAS JL, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila and environmental enrichment reverse cognitive impairment associated with high-fat high-cholesterol consumption in rats[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13( 1): 1- 20. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1880240. [51] AGUZZI A, BARRES BA, BENNETT ML. Microglia: scapegoat, saboteur, or something else?[J]. Science, 2013, 339( 6116): 156- 161. DOI: 10.1126/science.1227901. [52] YANG Y, ZHONG Z, WANG B, et al. Early-life high-fat diet-induced obesity programs hippocampal development and cognitive functions via regulation of gut commensal Akkermansia muciniphila[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2019, 44( 12): 2054- 2064. DOI: 10.1038/s41386-019-0437-1. -



 PDF下载 ( 867 KB)
PDF下载 ( 867 KB)

 下载:
下载:


