扶正化瘀方对肝硬化小鼠模型肝细胞消亡与再生的影响
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240417
伦理学声明:本研究方案于2020年6月19日经由上海中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会审批,批号:2020-618-45-07,符合实验室动物管理与使用准则。
利益冲突声明:本研究不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:朱亭亭、刘洪亮、李正鑫负责课题设计、资料分析、撰写论文;齐婧姝、郭亚楠参与收集数据、修改论文;陶艳艳、赵志敏负责指导撰写,修改论文;李正鑫、刘成海负责拟定写作思路、指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Effect of Fuzheng Huayu prescription on hepatocyte extinction and regeneration in a mouse model of liver cirrhosis
-
摘要:
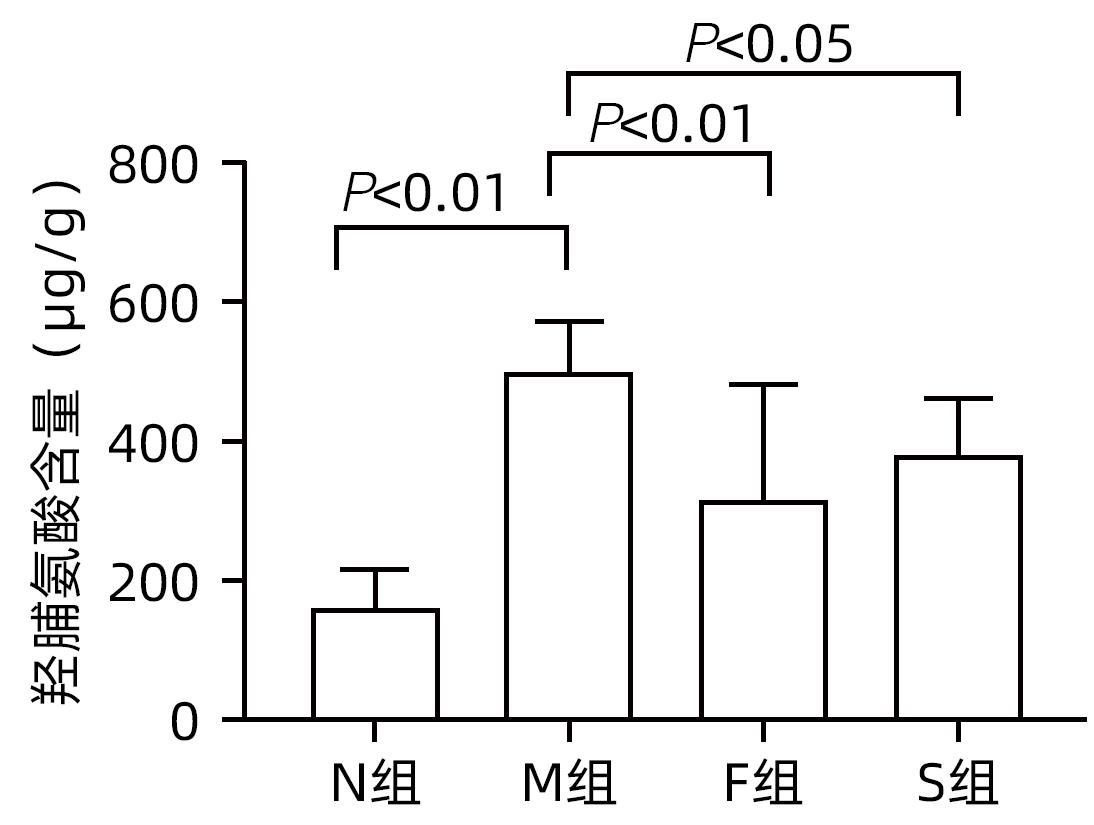
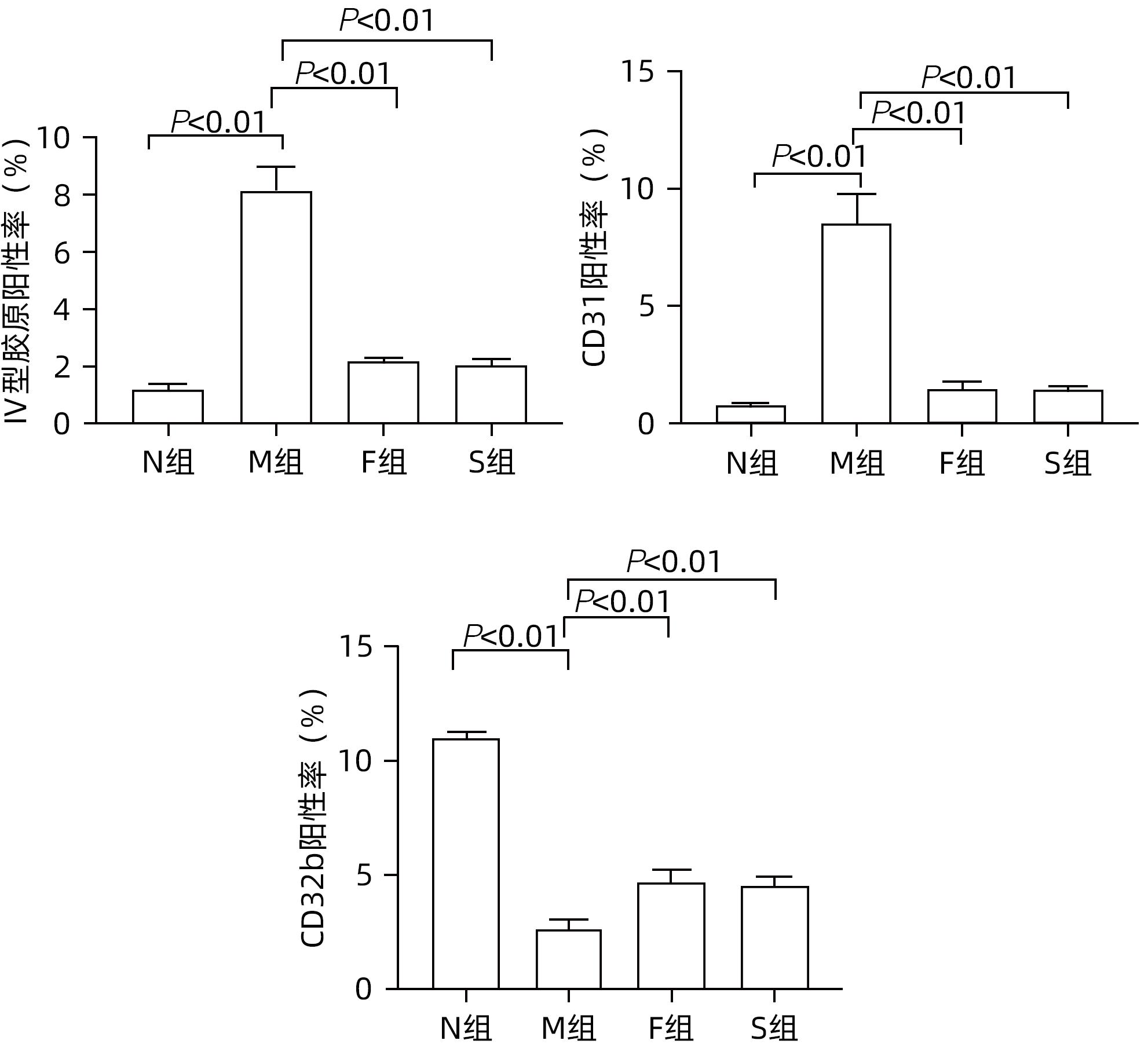
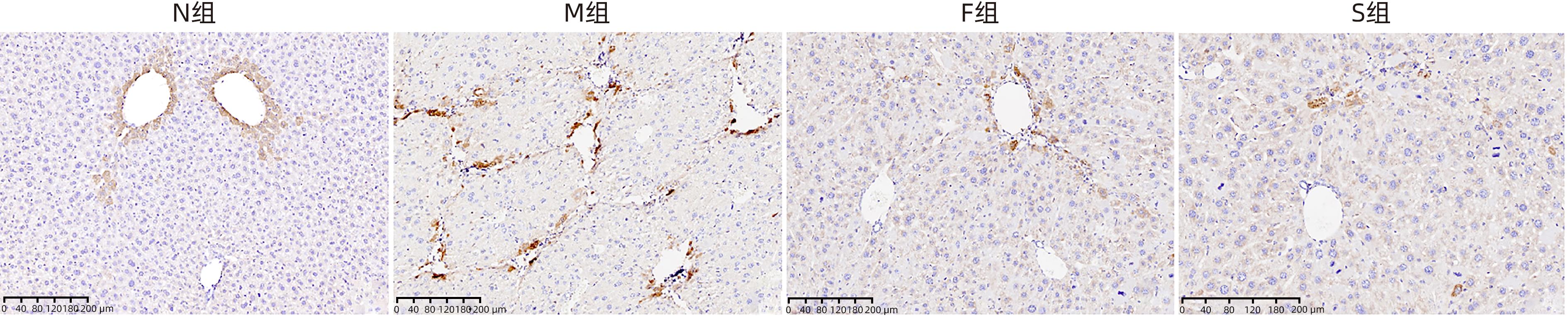
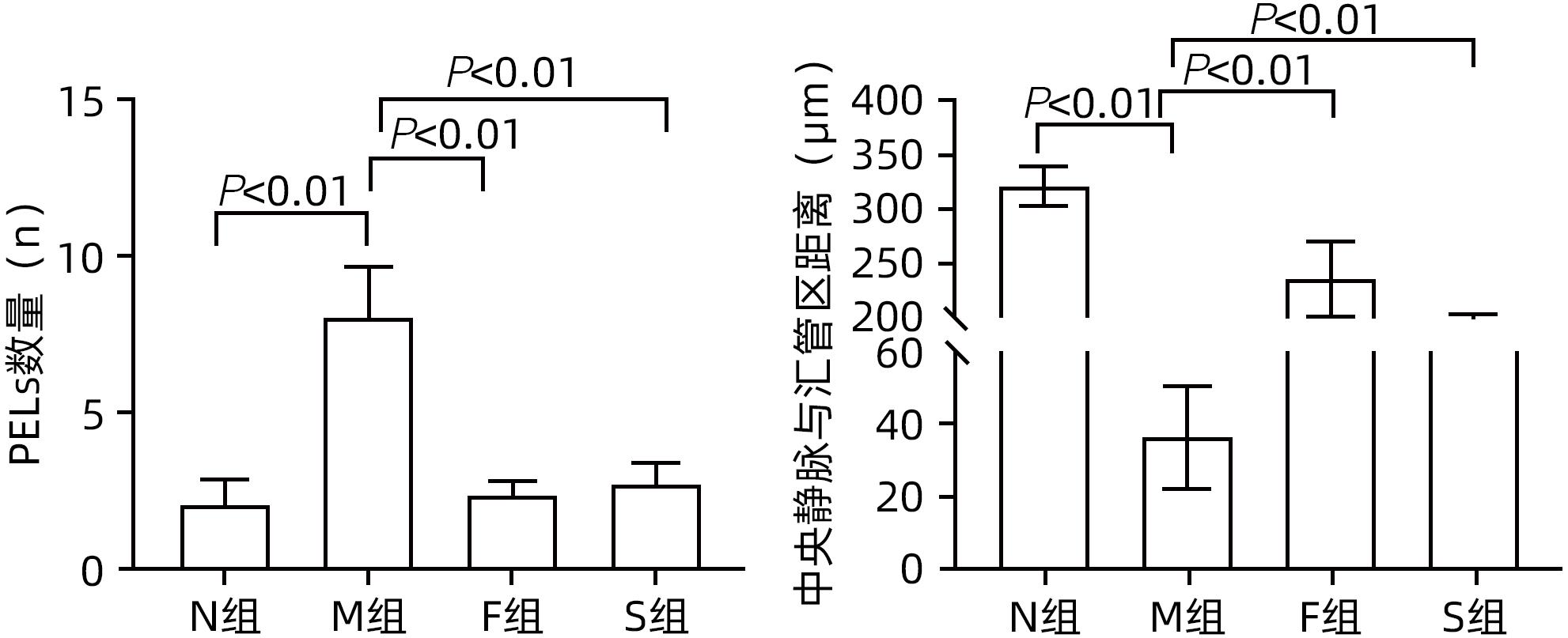
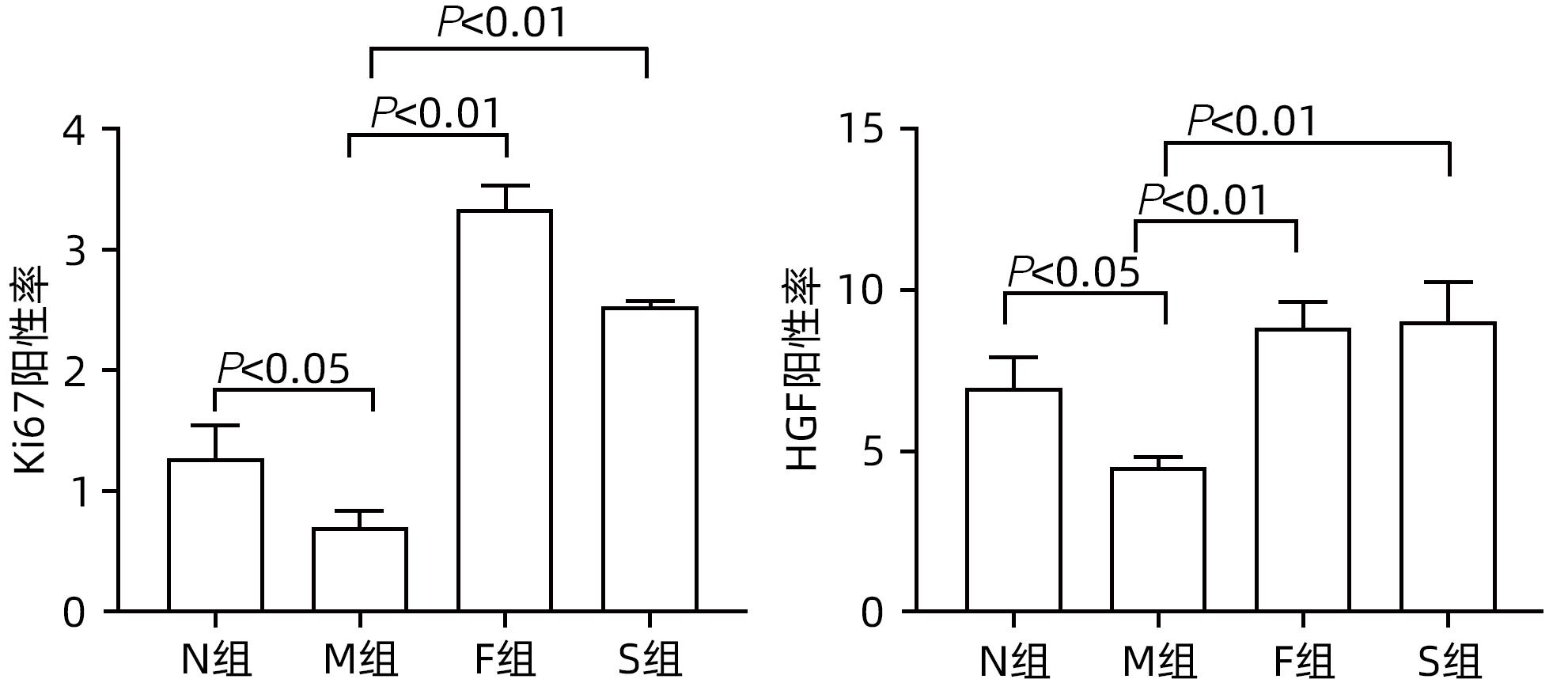
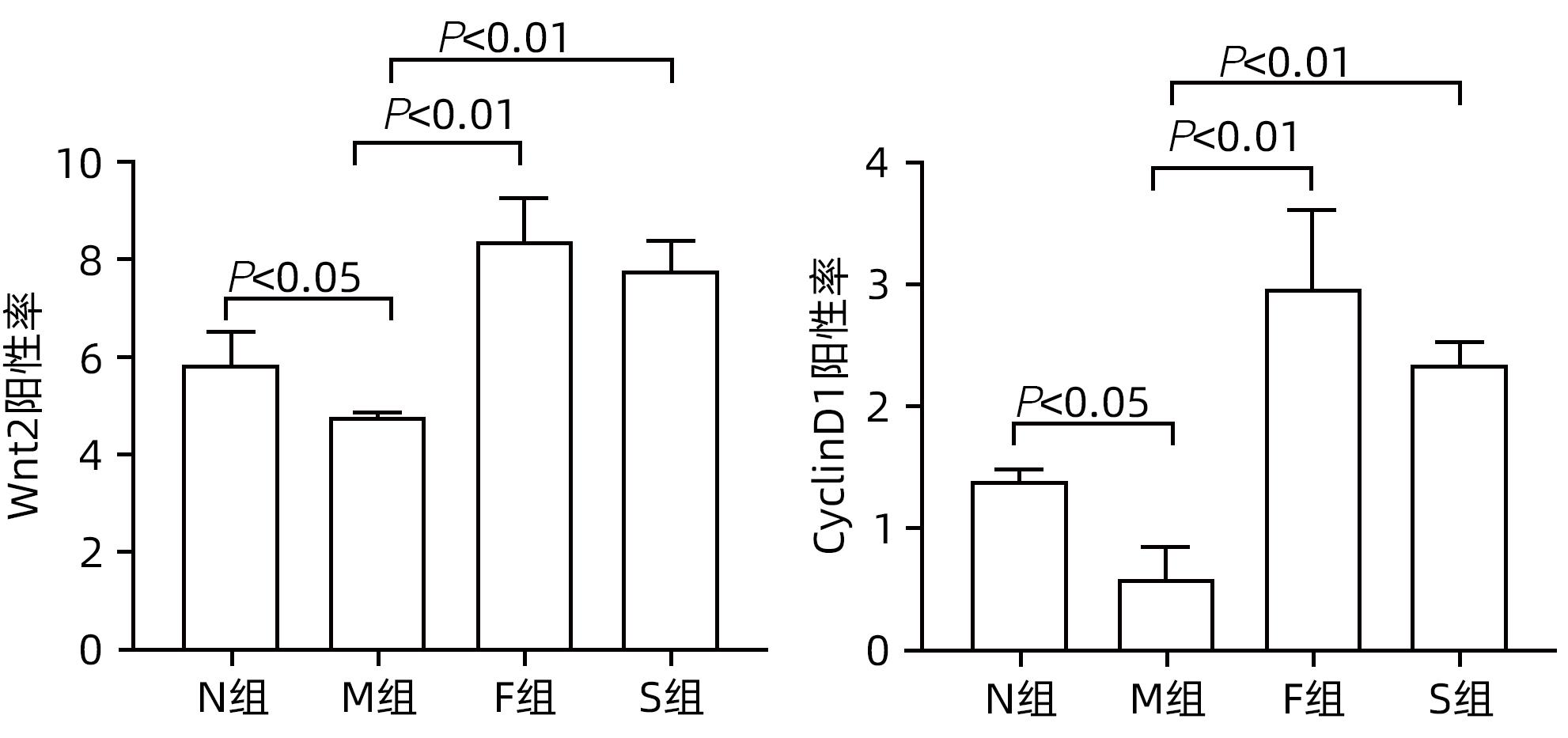
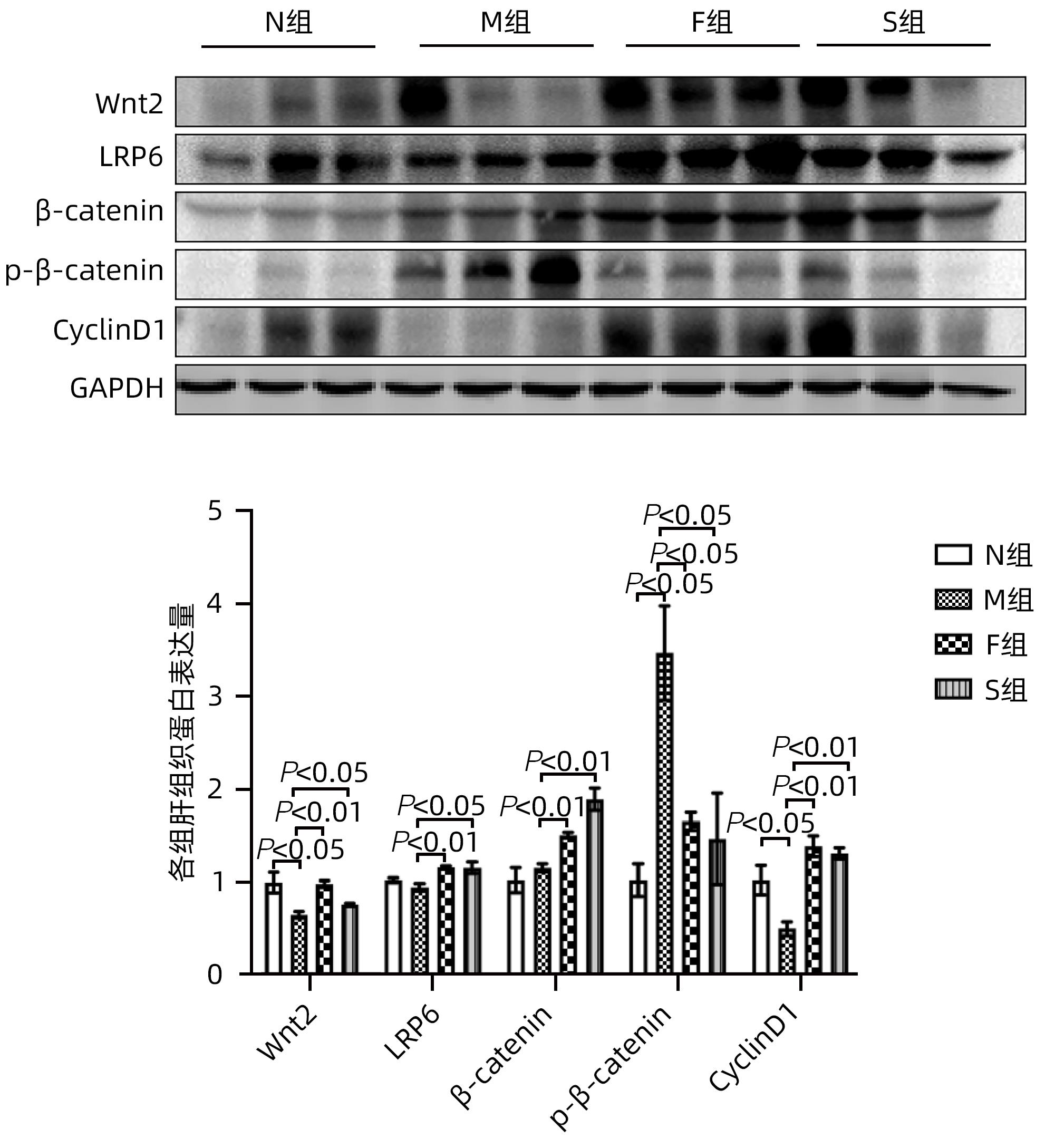
目的 探讨扶正化瘀方对纤维化肝脏肝细胞消亡与再生的影响,及其药物促进肝细胞再生的作用机制。 方法 以CCl4腹腔注射6周诱导建立肝硬化小鼠模型。正常对照组9只,模型组10只,索拉非尼组10只,扶正化瘀方组10只。自造模第4周起,扶正化瘀方组、索拉非尼组分别给予4.8 g/kg、4 mg/kg小鼠体质量相应药物灌胃,连续3周;正常组和模型组给予等体积羧甲基纤维素钠。检测血清肝功能;METAVIR评分系统评价肝组织炎症及纤维化分期;天狼星红染色和肝组织羟脯氨酸含量评价胶原沉积量;免疫组化检测Ⅳ型胶原、CD31与CD32b、Ki67、CyclinD1、谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)、Wnt2以及HGF蛋白的表达;Western Blot检测肝组织Wnt2、LRP6、β-catenin、p-β-catenin、CyclinD1表达。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。 结果 与模型组比较,扶正化瘀方组和索拉非尼组血清ALT、AST水平和肝组织羟脯氨酸含量均降低(P值均<0.01),METAVIR评分减低(P值均<0.05);Ⅳ型胶原、CD31表达减少(P值均<0.05),CD32b表达增加(P<0.01);肝组织实质病变消亡数量减少,Ki67、CyclinD1表达上升(P值均<0.01);Wnt2、LRP6、β-catenin、CyclinD1蛋白表达水平上调、p-β-catenin表达显著下调(P值均<0.05);肝组织CD32b与Wnt2共染阳性细胞显著增多。 结论 扶正化瘀方可通过抑制肝窦毛细血管化,改善肝窦内皮细胞Wnt2外分泌功能,激活肝细胞再生相关Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,最终逆转肝硬化。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of Fuzheng Huayu prescription on hepatocyte extinction and regeneration in fibrotic liver and its mechanism of action in promoting hepatocyte regeneration. Methods Mice were given intraperitoneal injection of CCl4 for 6 weeks to establish a model of liver cirrhosis, and there were 10 mice in the model group, 10 in the sorafenib group, 10 in the Fuzheng Huayu prescription group, and 9 in the normal control group. Since week 4 of modeling, the mice in the Fuzheng Huayu prescription group and the sorafenib group were given the corresponding drug by gavage at a dose of 4.8 g/kg and 4 mg/kg, respectively, for three consecutive weeks, and those in the normal group and the model group were given an equal volume of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. Serum liver function parameters were measured; the METAVIR scoring system was used to evaluate liver inflammation and fibrosis stage; Sirius Red staining and hydroxyproline (Hyp) content in liver tissue were used to evaluate collagen deposition; immunohistochemistry was used to measure the protein expression levels of type IV collagen, CD31, CD32b, Ki67, CyclinD1, glutamine synthetase, Wnt2, and HGF, and Western blot was used to measure the expression levels of Wnt2, LRP6, β-catenin, p-β-catenin, and CyclinD1 in liver tissue. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the model group, the Fuzheng Huayu prescription group and the sorafenib group showed the following changes: significant reductions in the serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase and the content of Hyp in liver tissue (all P<0.01); a significant reduction in METAVIR score; significant reductions in the expression levels of type Ⅳ collagen and CD31 (all P<0.05) and a significant increase in the expression level of CD32b (P<0.01); significant reductions in the number of parenchymal extinction lesions and significant increases in the expression levels of Ki67 and CyclinD1 in liver tissue (all P<0.01); significant increases in the protein expression levels of Wnt2, LRP6, β-catenin, and CyclinD1 and a significant reduction in the protein expression level of p-β-catenin (all P<0.05); significant increases in the number of cells stained positive for both CD32b and Wnt2. Conclusion Fuzheng Huayu prescription can inhibit hepatic sinusoidal capillarization, improve the Wnt2 exocrine function of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway associated with hepatocyte regeneration, and finally reverse liver cirrhosis. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Liver Regeneration /
- Fuzheng Huayu Recipe
-
-
[1] XU XY, DING HG, LI WG, et al. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006.徐小元, 丁惠国, 李文刚, 等. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. [2] MAGDALENO F, TREBICKA J. Selective LOXL2 inhibition: potent antifibrotic effects in ongoing fibrosis and fibrosis regression[J]. Gut, 2017, 66( 9): 1540- 1541. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313621. [3] HARRISON SA, ABDELMALEK MF, CALDWELL S, et al. Simtuzumab is ineffective for patients with bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis caused by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 155( 4): 1140- 1153. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro. 2018.07.006. [4] QI JS, HU XD, LIU CH. Reversal mechanism of hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2022, 30( 6): 577- 582. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220504-00239.齐婧姝, 胡旭东, 刘成海. 肝纤维化的逆转机制[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2022, 30( 6): 577- 582. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220504-00239. [5] LIU CH, ZHAO ZM, LYU J, et al. Advances in the understanding and treatment of liver fibrosis in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 4): 728- 733. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.04.006.刘成海, 赵志敏, 吕靖. 中医对肝纤维化逆转的认识与治疗[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 4): 728- 733. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.04.006. [6] CHENG Q, LI N, CHEN M, et al. Fuzheng Huayu inhibits carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice through activating hepatic NK cells[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013, 145( 1): 175- 181. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.047. [7] PAN Q, WANG YQ, LI GM, et al. Fuzheng Huayu recipe ameliorates liver fibrosis by restoring balance between epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015: 935903. DOI: 10.1155/2015/935903. [8] ZHANG M, LIU HL, HUANG K, et al. Fuzheng Huayu recipe prevented and treated CCl4-induced mice liver fibrosis through regulating polarization and chemotaxis of intrahepatic macrophages via CCL2 and CX3CL1[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2020, 2020: 8591892. DOI: 10.1155/2020/8591892. [9] LIU HL, LV J, ZHAO ZM, et al. Fuzhenghuayu Decoction ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by attenuating experimental sinusoidal capillarization and liver angiogenesis[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 18719. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-54663-4. [10] YANG T, SHEN DP, WANG QL, et al. Investigation of the absorbed and metabolized components of Danshen from Fuzheng Huayu recipe and study on the anti-hepatic fibrosis effects of these components[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2013, 148( 2): 691- 700. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.031. [11] JAMALL IS, FINELLI VN, QUE HS. A simple method to determine nanogram levels of 4-hydroxyproline in biological tissues[J]. Anal Biochem, 1981, 12( 1): 70- 75. DOI: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90261-x. [12] WANLESS IR, NAKASHIMA E, SHERMAN M. Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2000, 124( 11): 1599- 607. DOI: 10.5858/2000-124-1599-ROHC. [13] STUECK AE, WANLESS IR. Hepatocyte buds derived from progenitor cells repopulate regions of parenchymal extinction in human cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 5): 1696- 707. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27706. [14] WANLESS IR. The role of vascular injury and congestion in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis: the congestive escalator and the parenchymal extinction sequence[J]. Curr Hepatology Rep, 2020, 19: 40- 53. DOI: 10.1007/s11901-020-00508-y. [15] HYTIROGLOU P, THEISE ND. Regression of human cirrhosis: an update, 18 years after the pioneering article by Wanless et al[J]. Virchows Arch, 2018, 473( 1): 15- 22. DOI: 10.1007/s00428-018-2340-2. [16] XU XJ, LU LG. Basic and clinical studies on reversal of liver fibrosis after hepatitis C virus eradication[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2021, 26( 8): 840- 842. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2021.08.005.徐贤军, 陆伦根. 丙型肝炎病毒根除后肝纤维化逆转基础和临床研究[J]. 肝脏, 2021, 26( 8): 840- 842. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2021.08.005. [17] XU Y, ZHANG YG, WANG X, et al. Long-term antiviral efficacy of entecavir and liver histology improvement in Chinese patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21( 25): 7869- 7876. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7869. [18] MARCELLIN P, GANE E, BUTI M, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study[J]. Lancet, 2013, 381( 9865): 468- 475. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61425-1. [19] DING BS, NOLAN DJ, BUTLER JM, et al. Inductive angiocrine signals from sinusoidal endothelium are required for liver regeneration[J]. Nature, 2010, 468( 7321): 310- 315. DOI: 10.1038/nature09493. [20] ZHAO L, JIN Y, DONAHUE K, et al. Tissue repair in the mouse liver following acute carbon tetrachloride depends on injury-induced Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69( 6): 2623- 2635. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30563. [21] HU S, MONGA SP. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and liver regeneration: Circuit, biology, and opportunities[J]. Gene Expr, 2021, 20( 3): 189- 199. DOI: 10.3727/105221621X16111780348794. [22] RUSSELL JO, MONGA SP. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in liver development, homeostasis, and pathobiology[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2018, 13: 351- 378. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-044010. [23] XU LM, LIU P, SHEN XZ, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis in integrative medicine practice(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 7): 1444- 1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007.徐列明, 刘平, 沈锡中, 等. 肝纤维化中西医结合诊疗指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 7): 1444- 1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007. [24] CHENG J, Modern molecular biology of the extracellular matrix·Extracellular matrix and clinical medicine[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012: 696- 711.成军. 现代细胞外基质分子生物学·细胞外基质与临床医学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 696- 711. -



 PDF下载 ( 4131 KB)
PDF下载 ( 4131 KB)


 下载:
下载: