松果菊苷对雨蛙素诱导的急性胰腺炎大鼠模型胰腺及肝损伤的影响与机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240422
Effect of echinacoside intervention on liver and pancreas injury in rats with acute pancreatitis and its mechanism
-
摘要:
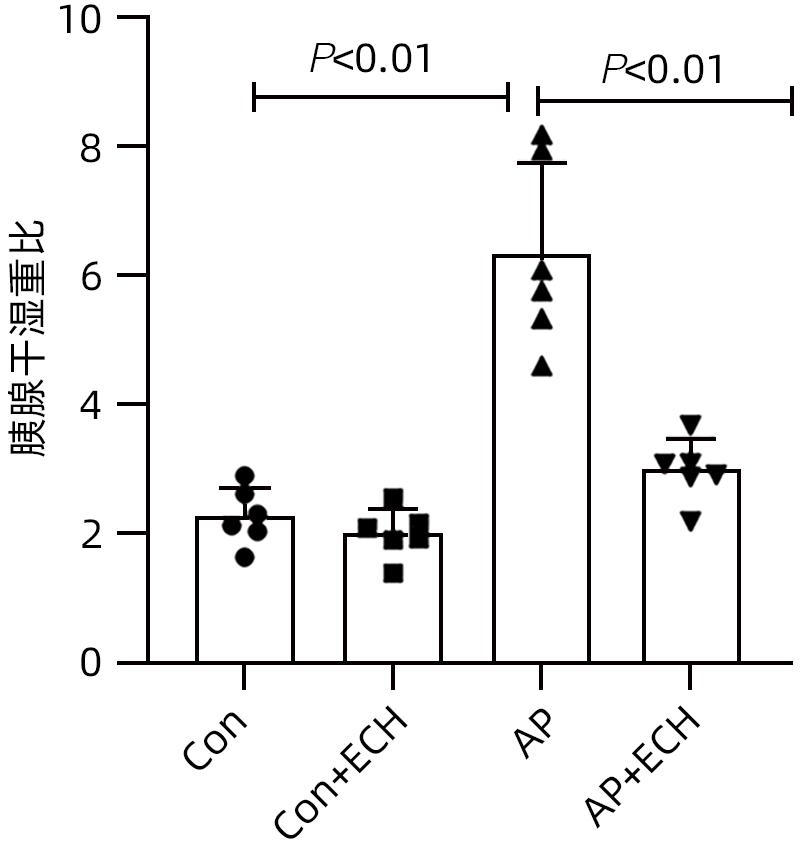
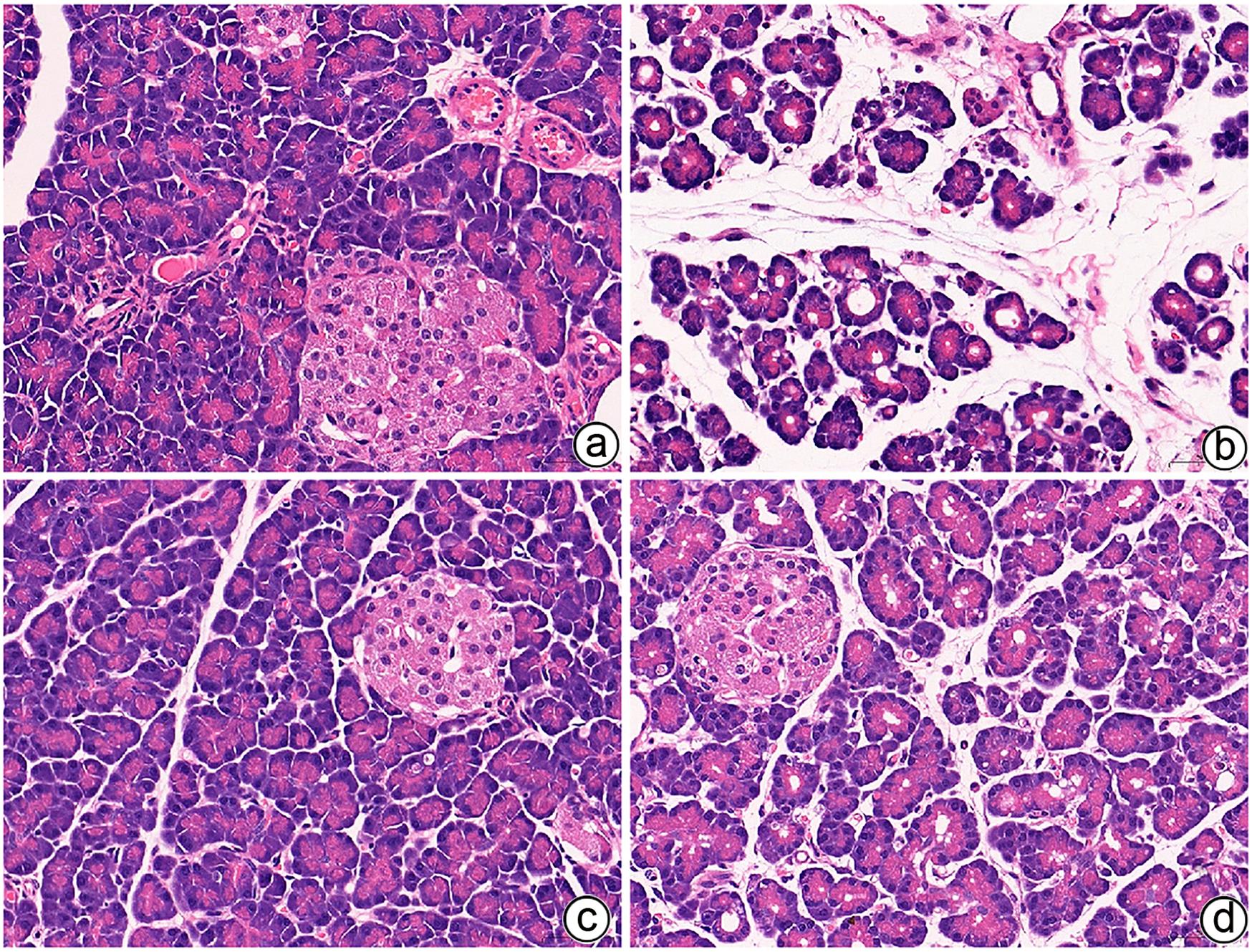
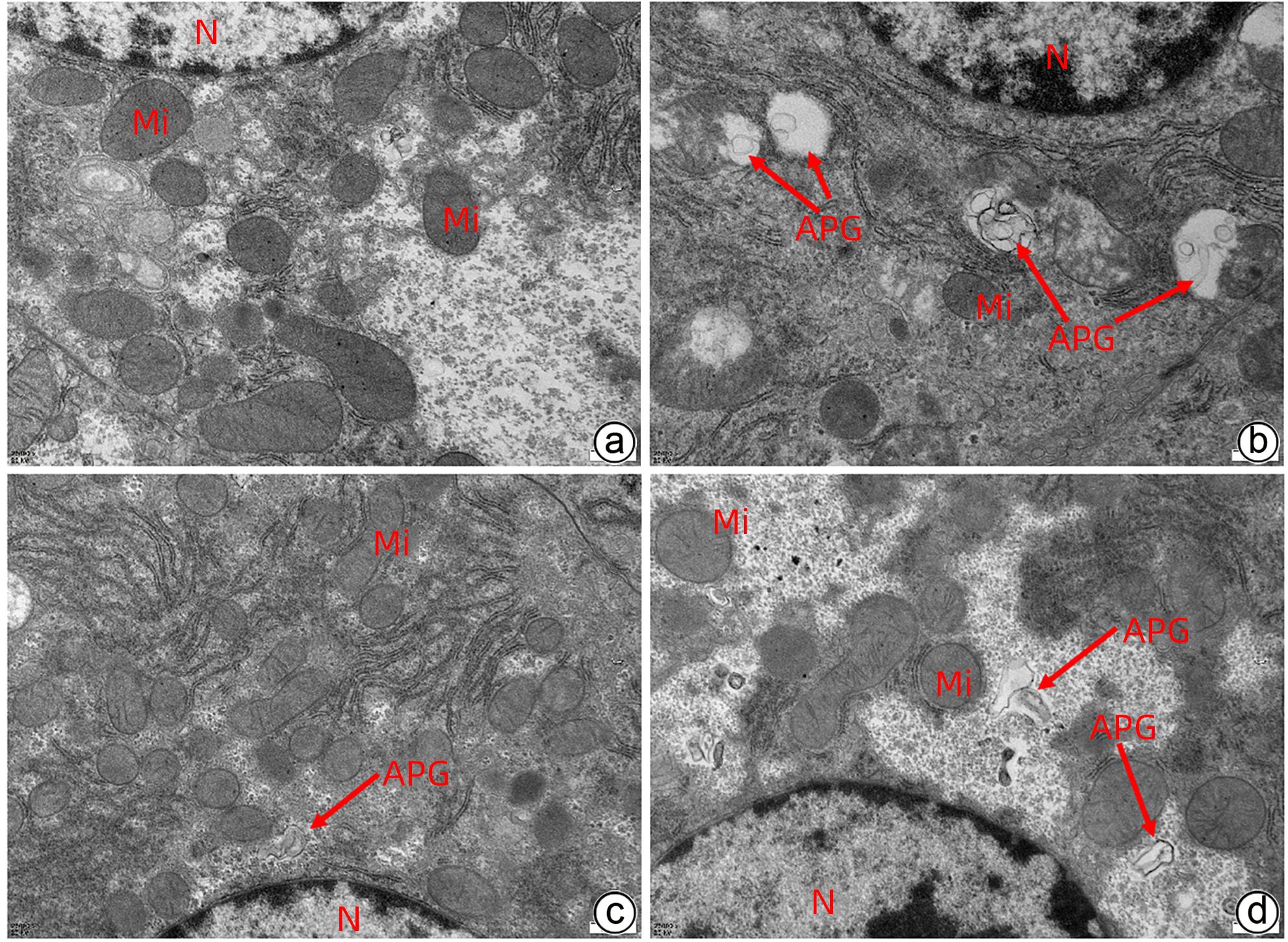
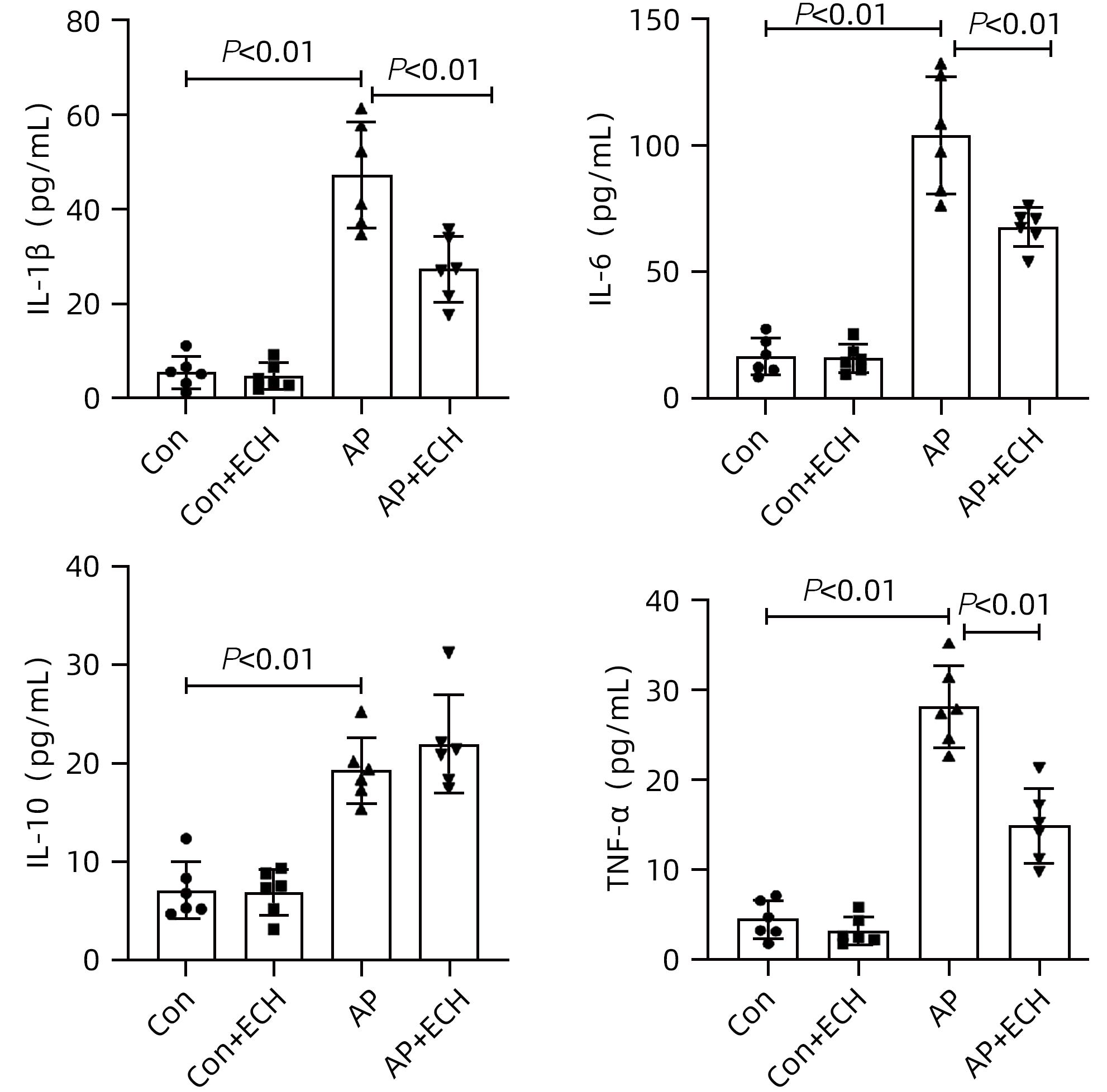
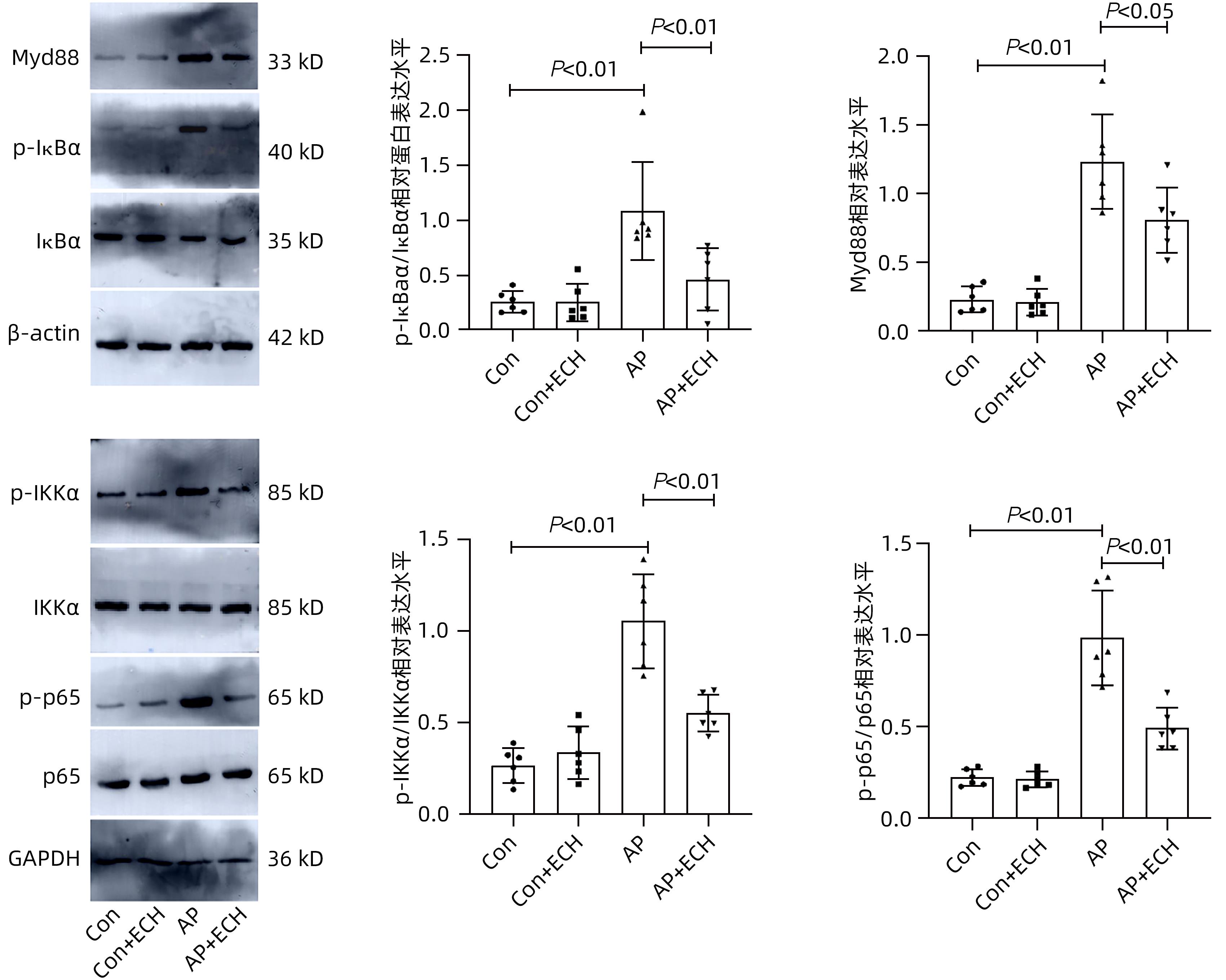
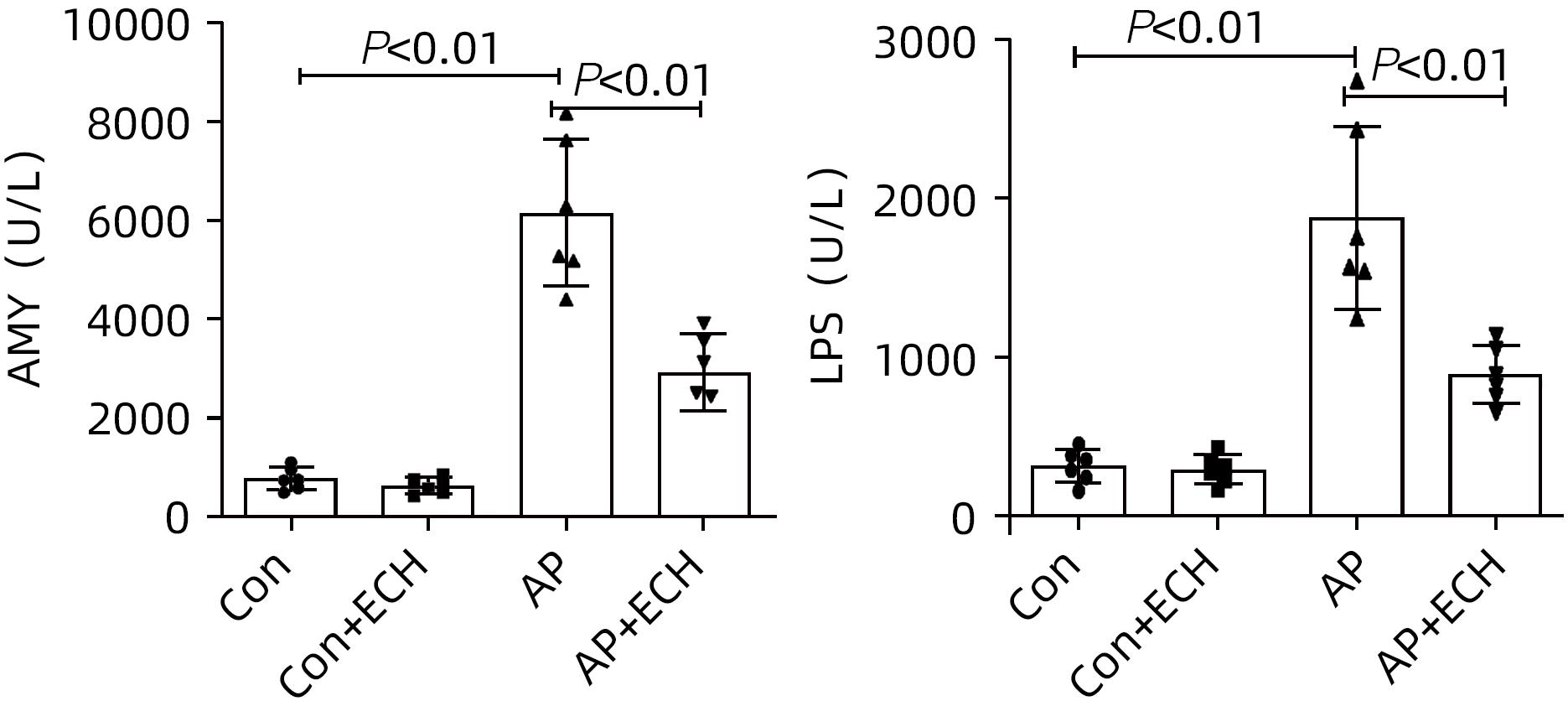
目的 通过建立急性胰腺炎(AP)大鼠模型,研究松果菊苷(ECH)对雨蛙素诱导的AP大鼠模型胰腺及肝损伤的改善作用及机制。 方法 24只SD大鼠随机分为空白组(Con组)、对照组(Con+ECH组)、AP组和AP+ECH组4组,每组各6只。AP模型构建前7 d给予10 mg/kg ECH腹腔注射,雨蛙素末次给药24 h后,腹主动脉取血,分离血清行ALT、AST、乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)、GGT、ALP、Alb、TBil、胆碱酯酶(ChE)、血淀粉酶(Amy)、脂肪酶(LPS)等生化检测;HE染色检测胰腺和肝组织病理学改变;透射电镜观察胰腺和肝组织微观结构改变;ELISA检测肝组织匀浆中IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、IL-10水平;免疫组化分析胰腺和肝组织中TNF-α和p-p65 NF-κB水平;Western Blot检测肝组织中NF-κB通路蛋白表达水平。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用SNK-q或Dunnett’s T3检验。 结果 与Con组相比,AP组大鼠ALT、AST、GGT、LDH、ALP、TBil、AMY、LPS指标均明显增高(P值均<0.01);肝组织匀浆液IL-1β、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α水平均增加(P值均<0.01)。ECH干预降低AP大鼠ALT、AST、GGT、LDH、ALP、TBil、AMY、LPS水平,并能抑制IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α的分泌。HE染色观察可见ECH干预后胰腺组织中腺泡细胞空泡变性和炎性细胞浸润较AP组减轻,肝细胞坏死较AP组减轻。透射电镜检查镜下见ECH干预后肝和胰腺细胞内线粒体肿胀程度较AP组减轻。ECH干预后能部分逆转AP大鼠胰腺和肝组织中p-p65 NF-κB、TNF-α的表达增加。此外,AP大鼠肝组织中MyD88、p-IκBα、p-IKKα、p-p65表达上调,而ECH干预后能部分逆转。 结论 松果菊苷可通过抑制TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB途径来改善AP诱发的胰腺和肝损伤。 -
关键词:
- 松果菊苷 /
- 胰腺炎 /
- 大鼠, Sprague-Dawley /
- NF-κB
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect and mechanism of echinacoside (ECH) in improving liver injury in rats with acute pancreatitis by establishing a rat model of acute pancreatitis and liver injury. Methods A total of 24 Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into blank group (Con group), control group (Con+ECH group), acute pancreatitis group (AP group), and acute pancreatitis+ECH intervention (AP+ECH group). The rats were given intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg ECH on day 7 before the establishment of the model of acute pancreatitis; at 24 hours after the last administration of cerulein, blood samples were collected via the abdominal aorta, and serum was separated for biochemical analysis including alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), albumin (Alb), total bilirubin (TBil), cholinesterase, blood amylase (Amy), and lipase (LPS). HE staining was used to observe the histopathological changes of the pancreas and the liver; transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to observe the microstructural changes of pancreas and liver tissue; ELISA was used to measure the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-16 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in liver tissue homogenate; immunohistochemistry was used to measure the levels of TNF-α and p-p65 NF-κB in pancreas and liver tissue; Western blot was used to measure the expression levels of NF-κB pathway proteins in liver tissue. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the SNK test or the Dunnett’s T3 method was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Compared with the Con group, the AP group had significant increases in ALT, AST, GGT, LDH, ALP, TBil, Amy, and LPS (all P<0.01), as well as significant increases in the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α in liver tissue homogenate (all P<0.01). ECH intervention reduced the levels of ALT, AST, GGT, LDH, ALP, TBil, AMY, and LPS and inhibited the secretion of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in rats with acute pancreatitis. HE staining showed that ECH intervention alleviated the vacuolar degeneration of acinar cells, inflammatory cell infiltration in pancreatic tissue, and the necrosis of hepatocytes compared with the AP group. TEM showed that compared with the AP group, there was a reduction in the degree of mitochondrial swelling in liver and pancreatic cells after ECH intervention. ECH intervention partially reversed the elevated expression levels of p-p65 NF-κB and TNF-α in liver and pancreatic tissue. In addition, the expression levels of MyD88, p-IκBα, p-IKKα, and p-p65 were upregulated in liver tissue of rats with acute pancreatitis, which could be partially reversed after ECH intervention. Conclusion Echinacoside can alleviate liver and pancreatic injury induced by acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. -
Key words:
- Echinacoside /
- Pancreatitis /
- Rats, Sprague-Dawley /
- NF-kappa B
-
表 1 ECH对雨蛙素诱导AP大鼠肝酶水平的影响
Table 1. The effects of Echinacoside on hepatic enzyme in rats with Cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis
项目 Con组(n=6) Con+ECH组(n=6) AP组(n=6) AP+ECH组(n=6) F值 P值 ALT(U/L) 37.35±11.04 32.95±9.90 185.07±33.581) 101.05±21.883) 66.53 <0.01 AST(U/L) 138.67±45.21 155.72±52.61 588.58±91.761) 329.28±85.663) 50.93 <0.01 GGT(U/L) 27.13±5.98 27.92±5.35 74.78±22.351) 43.80±11.653) 17.03 <0.01 Alb(U/L) 38.05±2.66 38.72±1.80 15.40±3.821) 27.82±3.343) 79.53 <0.01 ChE(U/L) 114.60±19.36 117.87±21.63 58.35±12.251) 93.95±8.193) 16.96 <0.01 LDH(U/L) 389.72±125.35 381.48±120.51 642.20±155.95 440.87±120.55 5.17 <0.01 ALP(U/L) 26.43±4.56 26.70±5.22 55.88±14.371) 35.77±7.333) 14.88 <0.01 TBil(μmol/L) 5.02±1.00 5.46±1.17 11.56±2.731) 6.25±1.723) 17.34 <0.01 注:与Con组比较,1)P<0.01,2)P<0.05;与AP组比较,3)P<0.01。 -
[1] MASAMUNE A, HAMADA S, KIKUTA K. Implementation of pancreatitis bundles is associated with reduced mortality in patients with severe acute pancreatitis in Japan[J]. Pancreas, 2021, 50( 2): e24- e25. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001750. [2] XIAO AY, TAN MLY, WU LM, et al. Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 1( 1): 45- 55. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30004-8. [3] KONG LJ, ZHANG HW, LU CS, et al. AICAR, an AMP-activated protein kinase activator, ameliorates acute pancreatitis-associated liver injury partially through Nrf2-mediated antioxidant effects and inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 724514. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.724514. [4] FU ZF, FAN X, WANG XY, et al. Cistanches Herba: An overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, and pharmacokinetics property[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 219: 233- 247. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.015. [5] SONG YL, ZENG KW, JIANG Y, et al. Cistanches Herba, from an endangered species to a big brand of Chinese medicine[J]. Med Res Rev, 2021, 41( 3): 1539- 1577. DOI: 10.1002/med.21768. [6] WANG NQ, JI SZ, ZHANG H, et al. Herba cistanches: Anti-aging[J]. Aging Dis, 2017, 8( 6): 740- 759. DOI: 10.14336/AD.2017.0720. [7] WANG YH, XUAN ZH, TIAN S, et al. Echinacoside protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammatory responses in PC12 cells via reducing ROS production[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2015, 2015: 189239. DOI: 10.1155/2015/189239. [8] LU CW, HSIEH HL, LIN TY, et al. Echinacoside, an active constituent of Cistanche herba, exerts a neuroprotective effect in a kainic acid rat model by inhibiting inflammatory processes and activating the akt/GSK3β pathway[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2018, 41( 11): 1685- 1693. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00407. [9] YANG L, ZHANG X, LIAO M, et al. Echinacoside improves diabetic liver injury by regulating the AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway in db/db mice[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 271: 119237. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119237. [10] LI W, ZHOU J, ZHANG YJ, et al. Echinacoside exerts anti-tumor activity via the miR-503-3p/TGF-β1/Smad aixs in liver cancer[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21( 1): 304. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-01890-3. [11] CHEN XT, YANG YS, CHEN K, et al. Advances in the research of experimental animal models of acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2017, 15( 5): 857- 860. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.05.039.陈杏田, 杨元生, 陈垦, 等. 急性胰腺炎实验动物模型的研究进展[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15( 5): 857- 860. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2017.05.039. [12] HYUN JJ, LEE HS. Experimental models of pancreatitis[J]. Clin Endosc, 2014, 47( 3): 212- 216. DOI: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.3.212. [13] MCGILL MR, JAESCHKE H. Animal models of drug-induced liver injury[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2019, 1865( 5): 1031- 1039. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.037. [14] BARBALAT R, LAU L, LOCKSLEY RM, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 on inflammatory monocytes induces type I interferon in response to viral but not bacterial ligands[J]. Nat Immunol, 2009, 10( 11): 1200- 1207. DOI: 10.1038/ni.1792. [15] FUREY C, BUXBAUM J, CHAMBLISS AB. A review of biomarker utilization in the diagnosis and management of acute pancreatitis reveals amylase ordering is favored in patients requiring laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J]. Clin Biochem, 2020, 77: 54- 56. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2019.12.014. [16] HOESEL B, SCHMID JA. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2013, 12: 86. DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-86. [17] ZHANG H, SHAN Y, WU Y, et al. Berberine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation through modulating Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2017, 52: 93- 100. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.08.032. [18] LAPIERRE P, BÉLAND K, ALVAREZ F. Pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis: From break of tolerance to immune-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis[J]. Transl Res, 2007, 149( 3): 107- 113. DOI: 10.1016/j.trsl.2006.11.010. [19] LAN DT, HE L, LI MD, et al. Echinacoside improves liver damage and inflammatory response in septic rats by activating Nrf pathway[J]. Chin J Immunol, 2020, 36( 4): 428- 432, 438. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.04.09.兰戴天, 何力, 李茂德, 等. 松果菊苷改善脓毒症大鼠的肝损伤和炎症反应与激活Nrf通路相关[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36( 4): 428- 432, 438. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.04.09. [20] WANG H, ZHANG XQ. Observation on Curative Effect of Huaxian Rougan Liquid Combined with Western Medicine in Treatment of Liver Fibrosis due to Hepatitis B and Effects on Serum IL-6, TNF-α and TGF-β1[J]. Chin J Tradit Med Sci Technol, 2022, 29( 4): 579- 581.王欢, 张晓强. 化纤柔肝饮辅助西药治疗乙型肝炎肝纤维化的效果观察及对血清IL-6、TNF-α及TGF-β1水平的影响[J]. 中国中医药科技, 2022, 29( 4): 579- 581. [21] FENG WW, WU AB, WANG HB. Effect of apigenin on the expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α in rats with hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2019, 17( 2): 183- 185. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000634.冯韦韦, 吴爱兵, 王宏宾. 芹菜素对肝缺血-再灌注大鼠IL-1β、IL-6及TNF-α表达的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17( 2): 183- 185. DOI: 10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.000634. [22] LIU JK, ZHAO WX, XU SC. Effects of Tuihuang mixture on endotoxin and levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in rats with acute liver failure[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2015, 26( 3): 587- 588. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2015.03.026.刘江凯, 赵文霞, 许顺畅. 退黄合剂对急性肝衰竭大鼠内毒素及TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6水平的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2015, 26( 3): 587- 588. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2015.03.026. [23] UEMATSU S, FUJIMOTO K, JANG MH, et al. Regulation of humoral and cellular gut immunity by Lamina propria dendritic cells expressing Toll-like receptor 5[J]. Nat Immunol, 2008, 9( 7): 769- 776. DOI: 10.1038/ni.1622. [24] YAROVINSKY F, ZHANG DK, ANDERSEN JF, et al. TLR11 activation of dendritic cells by a protozoan profilin-like protein[J]. Science, 2005, 308( 5728): 1626- 1629. DOI: 10.1126/science.1109893. [25] YAMAMOTO M, TAKEDA K. Current views of toll-like receptor signaling pathways[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2010, 2010: 240365. DOI: 10.1155/2010/240365. [26] TANIGUCHI K, KARIN M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18( 5): 309- 324. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.142. [27] JIN JL, YU XF, HU ZC, et al. Isofraxidin targets the TLR4/MD-2 axis to prevent osteoarthritis development[J]. Food Funct, 2018, 9( 11): 5641- 5652. DOI: 10.1039/c8fo01445k. [28] KUZMICH NN, SIVAK KV, CHUBAREV VN, et al. TLR4 signaling pathway modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis[J]. Vaccines, 2017, 5( 4): 34. DOI: 10.3390/vaccines5040034. [29] ZHANG XS, XUE CY, XU Q, et al. Caprylic acid suppresses inflammation via TLR4/NF-κB signaling and improves atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice[J]. Nutr Metab, 2019, 16: 40. DOI: 10.1186/s12986-019-0359-2. [30] WAN ZH, ZENG L, ZHOU H, et al. Protective effect of polyphyllin Ⅶ on acute lung injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. J Jilin Univ Med Ed, 2022, 48( 3): 668- 675. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220315.万朝辉, 曾良, 周辉, 等. 重楼皂苷Ⅶ通过抑制NF-κB信号通路对重症急性胰腺炎大鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48( 3): 668- 675. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220315. [31] SONG IJ, YANG YM, INOKUCHI-SHIMIZU S, et al. The contribution of toll-like receptor signaling to the development of liver fibrosis and cancer in hepatocyte-specific TAK1-deleted mice[J]. Int J Cancer, 2018, 142( 1): 81- 91. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31029. [32] ZOU M, YANG L, NIU L, et al. Baicalin ameliorates Mycoplasma gallisepticum-induced lung inflammation in chicken by inhibiting TLR6-mediated NF-κB signalling[J]. Br Poult Sci, 2021, 62( 2): 199- 210. DOI: 10.1080/00071668.2020.1847251. [33] ZHANG HL, JIA CX, LI HO, et al. Shenshao decoction improves myocardial inflammatory injury in diabetic rats by regulation of TLR4/MyD88 pathway[J]. Chin J Comp Med, 2017, 27( 8): 28- 33. DOI: 10.3969.j.issn.1671-7856.2017.08.006.张红利, 贾春新, 李海鸥, 等. 参芍口服液调控TLR4/MyD88通路改善糖尿病大鼠心肌炎症损伤[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2017, 27( 8): 28- 33. DOI: 10.3969.j.issn.1671-7856.2017.08.006. [34] LIU MJ, XIE JH, SUN YX. TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB-mediated inflammation contributes to cardiac dysfunction in rats of PTSD[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2020, 40( 6): 1029- 1035. DOI: 10.1007/s10571-020-00791-9. [35] DANG L, SONG L, ZHANG XQ, et al. Chaiqinchengqi decoction alleviates liver injury during severe acute pancreatitis in mice via inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2020, 36( 1): 134- 139. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.01.026.党琳, 宋亮, 张晓芹, 等. 柴芩承气汤通过抑制TLR4/NF-κB p65通路减轻小鼠重症急性胰腺炎并发肝损伤[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2020, 36( 1): 134- 139. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.01.026. [36] LU B, YU YQ, YIN JJ, et al. Effects of PPAR-γ agonists on liver cells in rats correlate with NF-kappa B/TLR4 signal pathway during acute pancreatitis[J]. China Mod Dr, 2016, 54( 33): 30- 33, 169.陆贝, 于源泉, 殷俊杰, 等. NF-κB/TLR4信号通路在急性胰腺炎大鼠肝损伤中的表达及PPAR-γ激动剂的保护作用[J]. 中国现代医生, 2016, 54( 33): 30- 33, 169. [37] ZHANG JS, ZHANG ZN, XIANG J, et al. Neuroprotective effects of echinacoside on regulating the stress-active p38MAPK and NF-κB p52 signals in the mice model of Parkinson’s disease[J]. Neurochem Res, 2017, 42( 4): 975- 985. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-016-2130-7. [38] ZHANG YF, WU QF, ZHONG LM, et al. Echinacoside promotes the proliferation of human renal tubular epithelial cells by blocking the HBX/TREM2-mediated NF-κB signalling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22( 2): 1137- 1144. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11201. -



 PDF下载 ( 3277 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3277 KB)

 下载:
下载: