巨大胆囊腺瘤误诊为胆囊癌1例报告
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240424
伦理学声明:本例报告已获得患者知情同意。
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王悦华、江华负责病例诊疗及文章的撰写;滕梁红、段焕利负责病理分析;崔壁霄负责影像资料分析;王冬梅负责病例随诊及文献整理。
Giant adenoma of the gallbladder misdiagnosed as gallbladder carcinoma: A case report
-
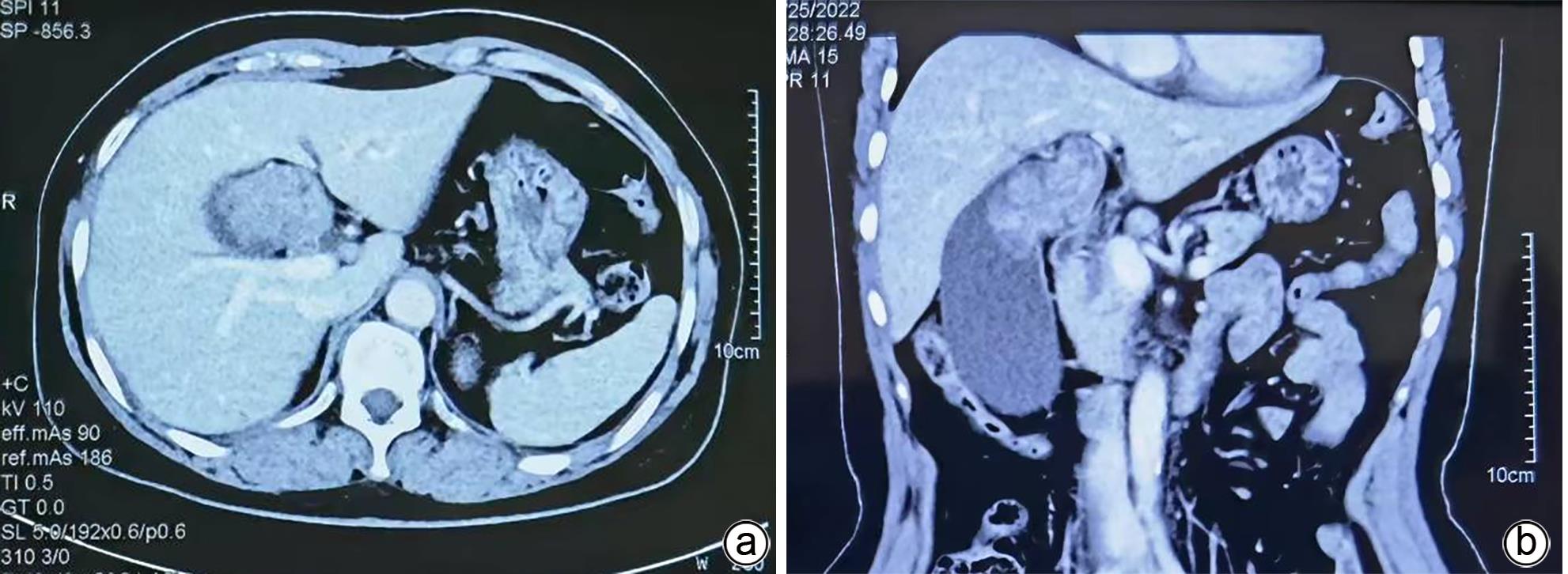
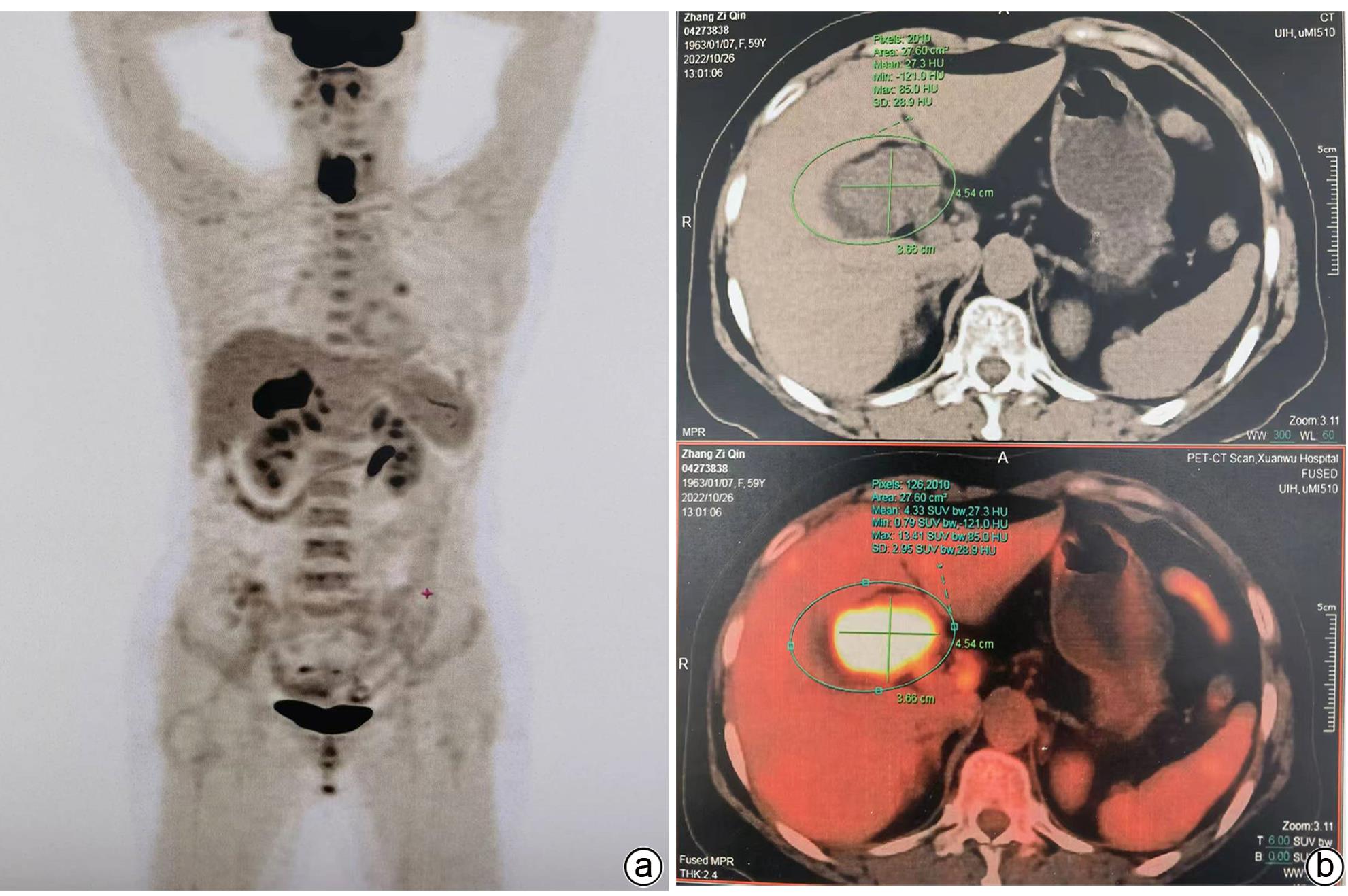
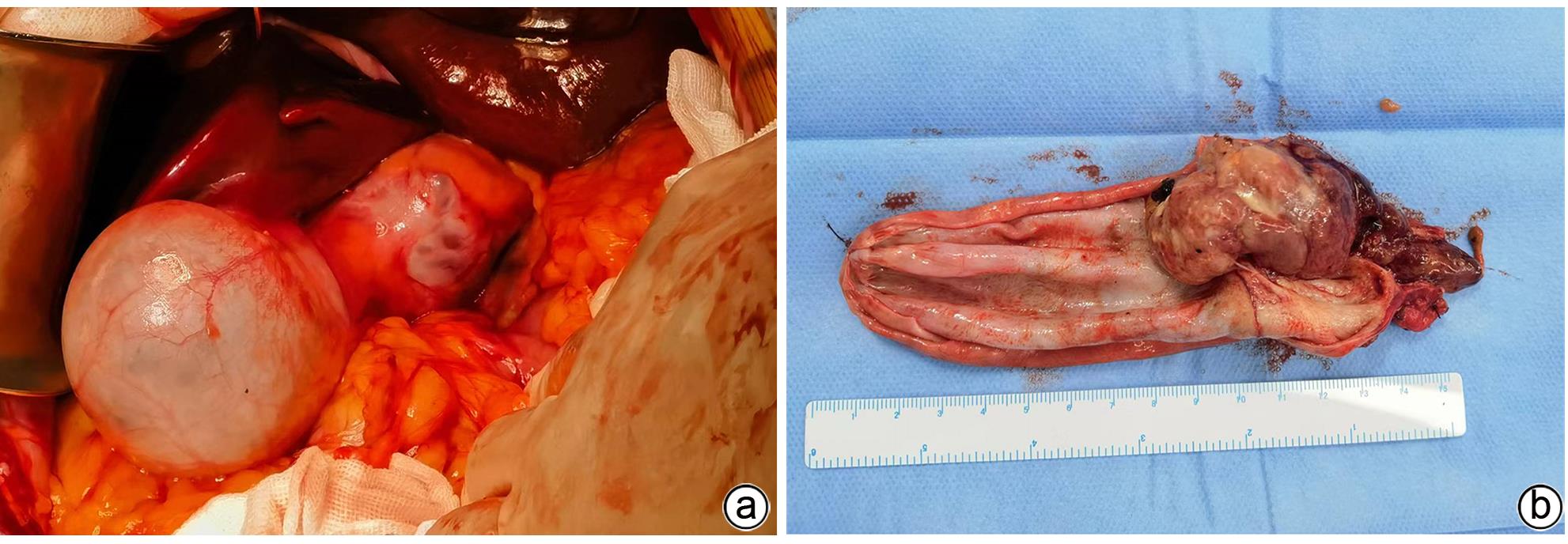
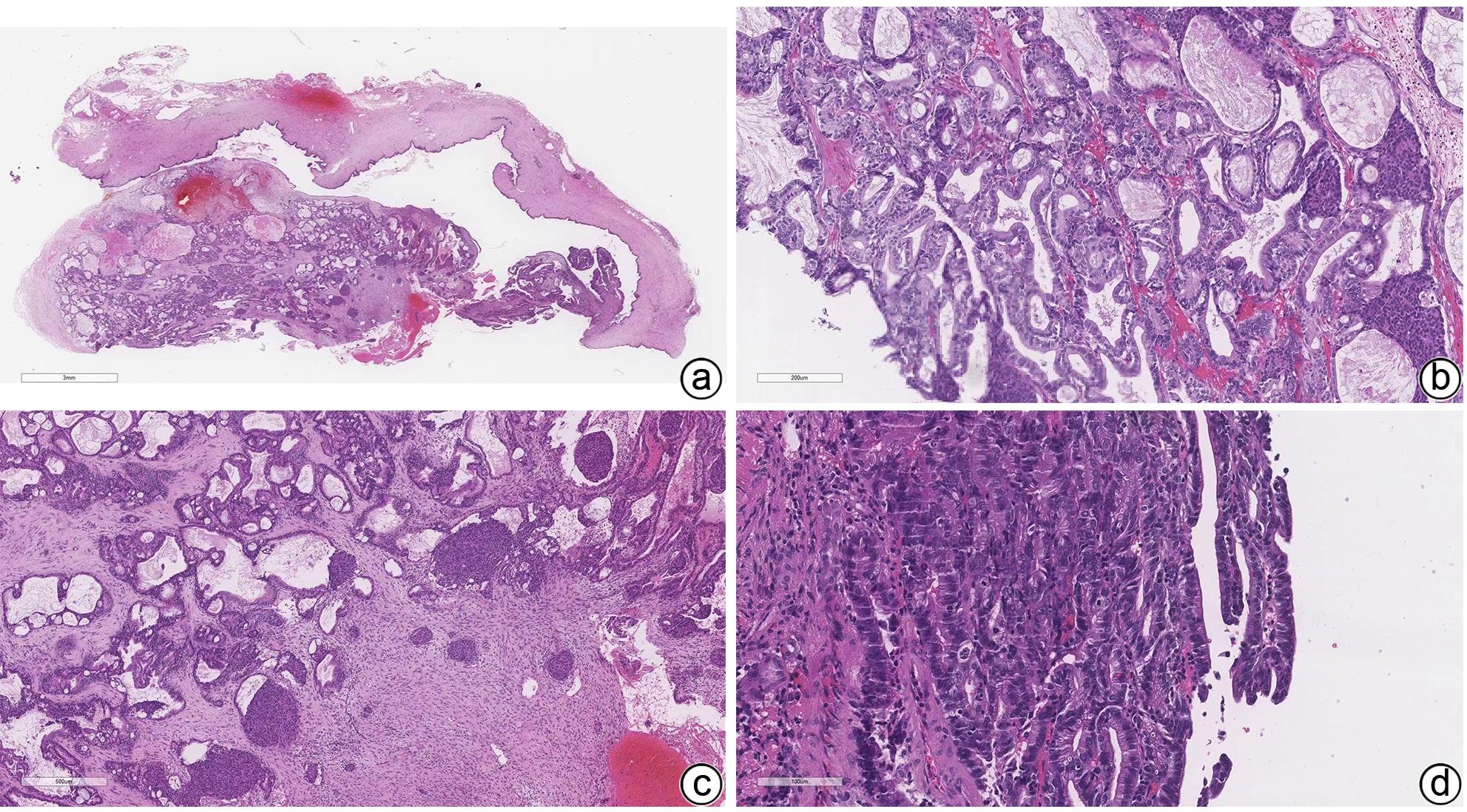
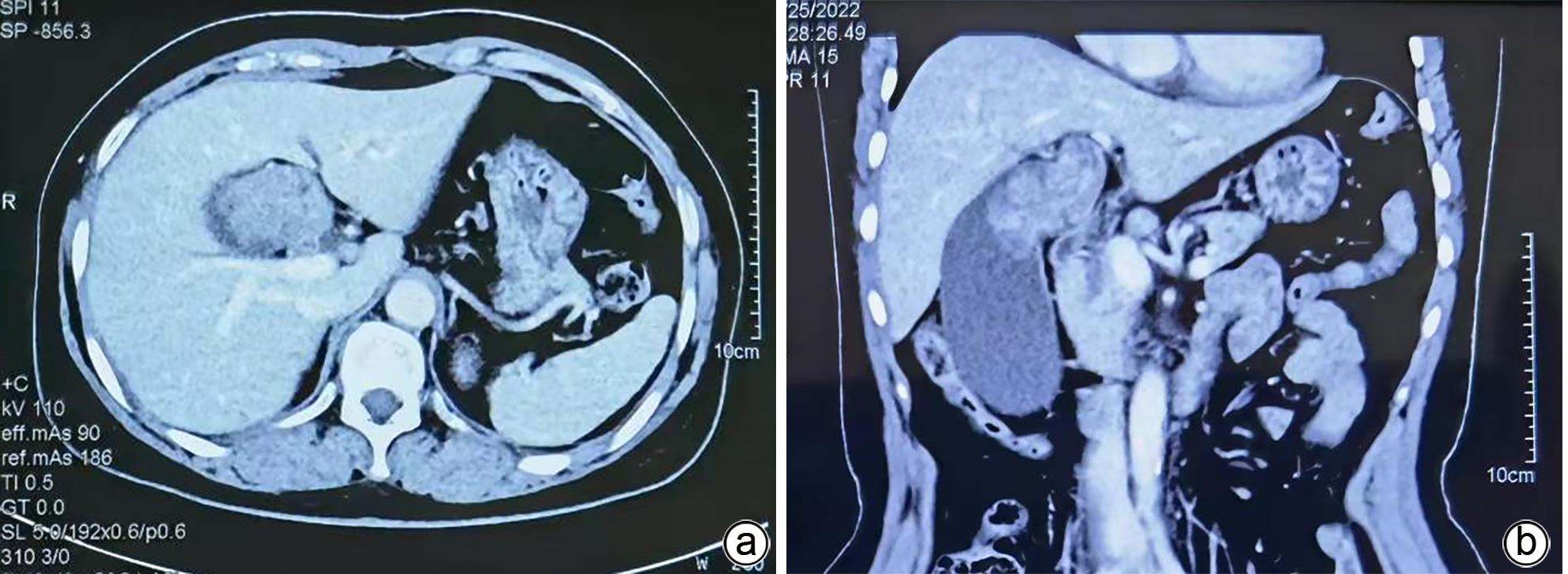
摘要: 1例胆囊肿物患者,曾出现一过性黄疸,经腹部超声、增强CT、MRCP及PET-CT检查,均诊断为胆囊癌。手术探查见胆囊增大,胆囊颈部肿物挤压肝门部,但没有肿瘤侵犯表现,肝脏未见肿瘤转移征象,仅为患者行胆囊切除术。病理诊断为胆囊管状腺瘤,未见癌变。本病例特点是胆囊肿瘤巨大,影像未见肿瘤边缘浸润,病理未见恶变。Abstract: One patient with gallbladder mass had transient jaundice and was diagnosed with gallbladder carcinoma by abdominal ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced CT, MRCP, and PET-CT. Surgical exploration showed enlarged gallbladder and a mass in the neck of the gallbladder pressing against the hilum of the liver, with no manifestation of tumor invasion, and there were no signs of liver metastasis. Only cholecystectomy was performed for the patient. The pathological diagnosis was tubular adenoma of the gallbladder without carcinogenesis. This case is characterized by a large gallbladder tumor, without marginal infiltration on imaging or malignant transformation based on pathology.
-
Key words:
- Gallbladder Neoplasms /
- Adenoma /
- Cholecystectomy /
- Diagnostic Errors
-
[1] FOLEY KG, LAHAYE MJ, THOENI RF, et al. Management and follow-up of gallbladder polyps: updated joint guidelines between the ESGAR, EAES, EFISDS and ESGE[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32( 5): 3358- 3368. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-021-08384-w. [2] TASKIN OC, BASTURK O, REID MD, et al. Gallbladder polyps: Correlation of size and clinicopathologic characteristics based on updated definitions[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15( 9): e0237979. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237979. [3] VALIBOUZE C, AMRANI M EL, TRUANT S, et al. The management of gallbladder polyps[J]. J Visc Surg, 2020, 157( 5): 410- 417. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2020.04.008. [4] HUANG JX, WANG Y, PANG Z. Research progress on risk factors and treatment strategies of malignant transformation of gallbladder polyps[J]. Int J Dig Dis, 2022, 42( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn. 1673-7083.2022.01.004.黄军祥, 王允, 庞智. 胆囊息肉恶变危险因素及治疗策略的研究进展[J]. 国际消化病杂志, 2022, 42( 1): 13- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7083.2022.01.004. [5] ADSAY V, JANG KT, ROA JC, et al. Intracholecystic papillary-tubular neoplasms(ICPN) of the gallbladder(neoplastic polyps, adenomas, and papillary neoplasms that are ≥1.0 cm): clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 123 cases[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2012, 36( 9): 1279- 1301. DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e318262787c. [6] YU MH, KIM YJ, PARK HS, et al. Benign gallbladder diseases: Imaging techniques and tips for differentiating with malignant gallbladder diseases[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26( 22): 2967- 2986. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.2967. [7] SHI Y, LIU HT. CT and MRI diagnosis of gallbladder adenoma[J]. Chin J CT and MRI, 2020, 18( 8): 97- 100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2020.08.030.石岩, 刘海涛. 胆囊腺瘤的CT、MRI诊断[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18( 8): 97- 100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2020.08.030. [8] NISHIYAMA Y, YAMAMOTO Y, FUKUNAGA K, et al. Dual-time-point 18F-FDG PET for the evaluation of gallbladder carcinoma[J]. J Nucl Med, 2006, 47( 4): 633- 638. [9] LEE J, YUN M, KIM KS, et al. Risk stratification of gallbladder polyps(1-2 cm) for surgical intervention with 18F-FDG PET/CT[J]. J Nucl Med, 2012, 53( 3): 353- 358. DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.111.093948. [10] PEDERSEN MR, DAM C, RAFAELSEN SR. Ultrasound follow-up for gallbladder polyps less than 6 mm may not be necessary[J]. Dan Med J, 2012, 59( 10): A4503. [11] METMAN M, OLTHOF PB, van der WAL J, et al. Clinical relevance of gallbladder polyps; is cholecystectomy always necessary?[J]. HPB(Oxford), 2020, 22( 4): 506- 510. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.08.006. -



 PDF下载 ( 1133 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1133 KB)

 下载:
下载: