Hedgehog信号通路在肝细胞癌中的作用及其与肿瘤微环境的关系
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240429
Role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment
-
摘要: Hedgehog(Hh)信号通路在肝细胞癌的发生发展和肿瘤微环境中发挥重要作用。Hh信号异常激活可加速肿瘤的生长。Hh信号通路和肿瘤微环境之间的相互串扰与肿瘤的生长和抑制性肿瘤微环境的形成密切相关。有证据表明,抑制Hh信号在抑制肝细胞癌生长中发挥重要作用。本文就Hh信号异常激活在肝细胞癌和肝癌肿瘤微环境中作用及机制的研究现状与潜在的治疗意义作一综述,为肝癌的治疗提供新的思路。
-
关键词:
- 癌, 肝细胞 /
- 肿瘤微环境 /
- Hedgehog信号通路
Abstract: The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway plays an important role in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment, and abnormal activation of Hh signal can accelerate the growth of tumor. The crosstalk between the Hh signaling pathway and TME is closely associated with tumor growth and the formation of inhibitory tumor microenvironment. Evidence shows that inhibition of Hh signal plays an important role in inhibiting the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. This article reviews the current research status of the role, mechanism, and potential therapeutic significance of abnormal activation of Hh signal in hepatocellular carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment, so as to provide new ideas for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. -
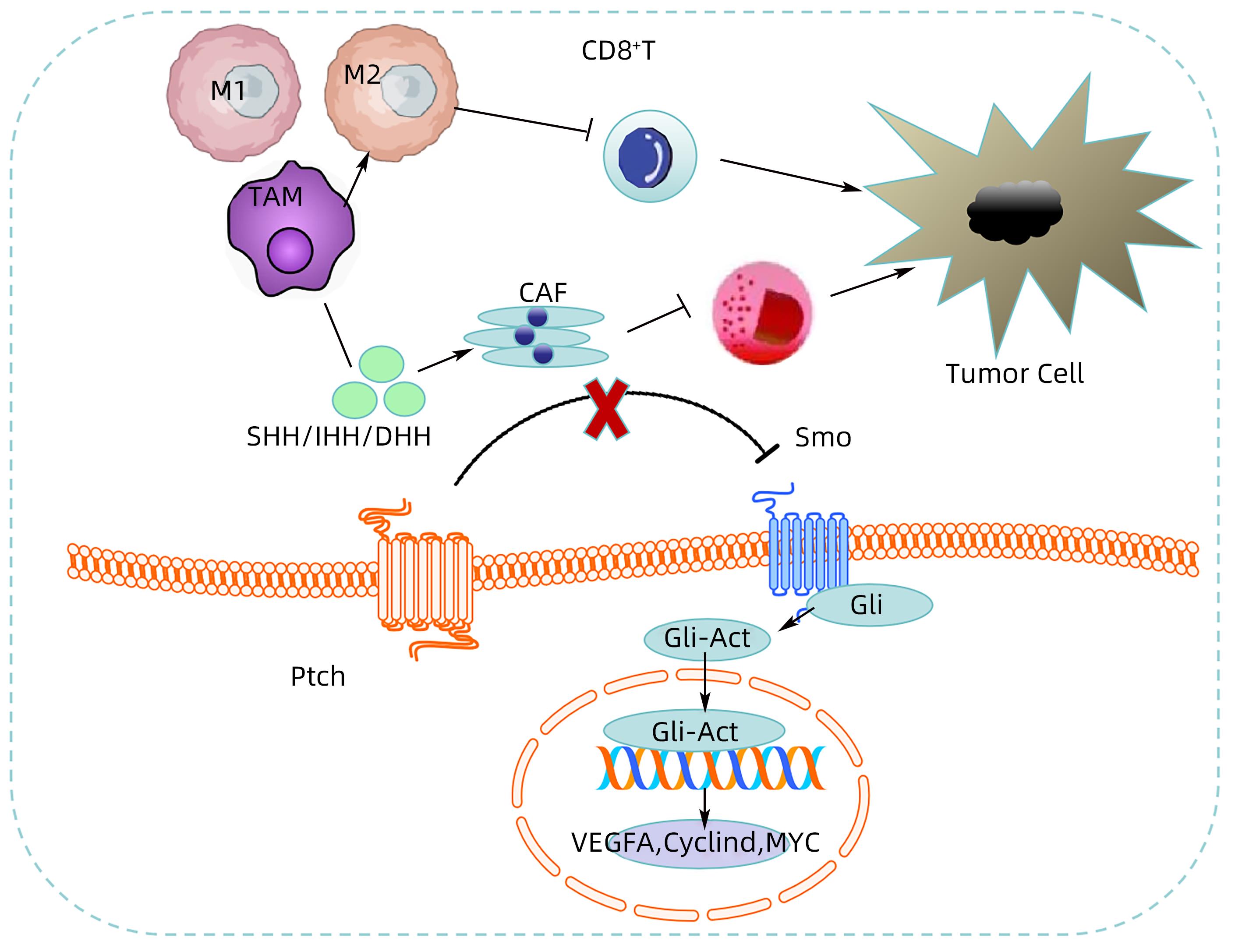
注: 当没有Hh配体蛋白时,Ptch能释放抑制Smo活性的蛋白,从而阻滞Smo的激活,使得Hh信号通路关闭。而当Hh配体蛋白(SHH、IHH或DHH)与Ptch结合后,Ptch停止分泌,Smo解除抑制,Hh信号系统被激活,最终导致Gli转录因子成员的激活、向细胞核转移,上调Hh通路下游靶基因如VEGF、Myc、Cyclin D等,从而促进肿瘤增殖、侵袭、转移等;细胞中的Hh信号能驱动肿瘤间质中肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAM)的M2极化,抑制CD8+T淋巴细胞功能,从而促进肿瘤的生长;细胞中异常激活的Hh信号和肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(CAF)相互作用并协同促进肿瘤的发展。
图 1 肝癌TME中的Hh信号转导
Figure 1. Hh signal transduction in TME of hepatocellular carcinoma
-
[1] LLOVET JM, KELLEY RK, VILLANUEVA A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7( 1): 6. DOI: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3. [2] KHANAM A, KOTTILIL S. New therapeutics for HCC: Does tumor immune microenvironment matter?[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 24( 1): 437. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24010437. [3] WU T, DAI Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 387: 61- 68. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.043. [4] AMAKYE D, JAGANI Z, DORSCH M. Unraveling the therapeutic potential of the Hedgehog pathway in cancer[J]. Nat Med, 2013, 19( 11): 1410- 1422. DOI: 10.1038/nm.3389. [5] PETTY AJ, LI A, WANG XY, et al. Hedgehog signaling promotes tumor-associated macrophage polarization to suppress intratumoral CD8+ T cell recruitment[J]. J Clin Invest, 2019, 129( 12): 5151- 5162. DOI: 10.1172/JCI128644. [6] ZHANG JH, FAN JJ, ZENG X, et al. Hedgehog signaling in gastrointestinal carcinogenesis and the gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11( 3): 609- 620. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.022. [7] NÜSSLEIN-VOLHARD C, WIESCHAUS E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila[J]. Nature, 1980, 287( 5785): 795- 801. DOI: 10.1038/287795a0. [8] JIANG J. Hedgehog signaling mechanism and role in cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 85: 107- 122. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.04.003. [9] PORTER JA, EKKER SC, PARK WJ, et al. Hedgehog patterning activity: Role of a lipophilic modification mediated by the carboxy-terminal autoprocessing domain[J]. Cell, 1996, 86( 1): 21- 34. DOI: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80074-4. [10] BRISCOE J, THÉROND PP. The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2013, 14( 7): 416- 429. DOI: 10.1038/nrm3598. [11] RYAN KE, CHIANG C. Hedgehog secretion and signal transduction in vertebrates[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287( 22): 17905- 17913. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R112.356006. [12] GAO LL, ZHANG ZY, ZHANG P, et al. Role of canonical Hedgehog signaling pathway in liver[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14( 12): 1636- 1644. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.28089. [13] OCHOA B, SYN WK, DELGADO I, et al. Hedgehog signaling is critical for normal liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51( 5): 1712- 1723. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23525. [14] ZHU CY, TABAS I, SCHWABE RF, et al. Maladaptive regeneration-the reawakening of developmental pathways in NASH and fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18( 2): 131- 142. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00365-6. [15] HUANG SH, HE J, ZHANG XL, et al. Activation of the hedgehog pathway in human hepatocellular carcinomas[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2006, 27( 7): 1334- 1340. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgi378. [16] KIM Y, YOON JW, XIAO XK, et al. Selective down-regulation of glioma-associated oncogene 2 inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67( 8): 3583- 3593. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3040. [17] JENG KS, SHEEN IS, JENG WJ, et al. High expression of patched homolog-1 messenger RNA and glioma-associated oncogene-1 messenger RNA of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway indicates a risk of postresection recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2013, 20( 2): 464- 473. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-012-2593-y. [18] CHEN JS, HUANG XH, WANG Q, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway induces cell migration and invasion through focal adhesion kinase/AKT signaling-mediated activation of matrix metalloproteinase(MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in liver cancer[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2013, 34( 1): 10- 19. DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs274. [19] HE J, ZUO QZ, HU B, et al. A novel, liver-specific long noncoding RNA LINC01093 suppresses HCC progression by interaction with IGF2BP1 to facilitate decay of GLI1 mRNA[J]. Cancer Lett, 2019, 450: 98- 109. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.02.033. [20] HUANG XH, CHEN JS, WANG Q, et al. miR-338-3p suppresses invasion of liver cancer cell by targeting smoothened[J]. J Pathol, 2011, 225( 3): 463- 472. DOI: 10.1002/path.2877. [21] CHOI SS, OMENETTI A, WITEK RP, et al. Hedgehog pathway activation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions during myofibroblastic transformation of rat hepatic cells in culture and cirrhosis[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2009, 297( 6): G1093- G1106. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00292.2009. [22] GU Y, WANG YY, HE LY, et al. Circular RNA circIPO11 drives self-renewal of liver cancer initiating cells via Hedgehog signaling[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20( 1): 132. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-021-01435-2. [23] BEACHY PA, HYMOWITZ SG, LAZARUS RA, et al. Interactions between Hedgehog proteins and their binding partners come into view[J]. Genes Dev, 2010, 24( 18): 2001- 2012. DOI: 10.1101/gad.1951710. [24] ANDERSON NM, SIMON MC. The tumor microenvironment[J]. Curr Biol, 2020, 30( 16): R921- R925. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.06.081. [25] XIAO Y, YU DH. Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 221: 107753. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107753. [26] LIU TY, HAN CC, WANG SW, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: An emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12( 1): 86. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-019-0770-1. [27] CHEN XM, SONG EW. Turning foes to friends: Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019, 18( 2): 99- 115. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-018-0004-1. [28] KALLURI R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2016, 16( 9): 582- 598. DOI: 10.1038/nrc.2016.73. [29] BU LK, BABA H, YOSHIDA N, et al. Biological heterogeneity and versatility of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Oncogene, 2019, 38( 25): 4887- 4901. DOI: 10.1038/s41388-019-0765-y. [30] WILL AJ, COVA G, OSTERWALDER M, et al. Composition and dosage of a multipartite enhancer cluster control developmental expression of Ihh(Indian hedgehog)[J]. Nat Genet, 2017, 49( 10): 1539- 1545. DOI: 10.1038/ng.3939. [31] GONG X, QIAN HW, CAO PP, et al. Structural basis for the recognition of Sonic Hedgehog by human Patched1[J]. Science, 2018, 361( 6402): eaas8935. DOI: 10.1126/science.aas8935. [32] HUANG PX, ZHENG SD, WIERBOWSKI BM, et al. Structural basis of smoothened activation in hedgehog signaling[J]. Cell, 2018, 175( 1): 295- 297. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.09.003. [33] ZHANG Y, FU L, QI XL, et al. Structural insight into the mutual recognition and regulation between suppressor of fused and Gli/Ci[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2608. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3608. [34] INFANTE P, FAEDDA R, BERNARDI F, et al. Itch/β-arrestin2-dependent non-proteolytic ubiquitylation of SuFu controls Hedgehog signalling and medulloblastoma tumorigenesis[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9( 1): 976. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03339-0. [35] LEX RK, JI ZC, FALKENSTEIN KN, et al. GLI transcriptional repression regulates tissue-specific enhancer activity in response to Hedgehog signaling[J]. eLife, 2020, 9: e50670. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.50670. [36] MILENKOVIC L, SCOTT MP. Not lost in space: Trafficking in the hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Sci Signal, 2010, 3( 117): pe14. DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.3117pe14. [37] VON AHRENS D, BHAGAT TD, NAGRATH D, et al. The role of stromal cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10( 1): 76. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0448-5. [38] SAITO RA, MICKE P, PAULSSON J, et al. Forkhead box F1 regulates tumor-promoting properties of cancer-associated fibroblasts in lung cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70( 7): 2644- 2654. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3644. [39] VALENTI G, QUINN HM, HEYNEN GJJE, et al. Cancer stem cells regulate cancer-associated fibroblasts via activation of hedgehog signaling in mammary gland tumors[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77( 8): 2134- 2147. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3490. [40] CAZET AS, HUI MN, ELSWORTH BL, et al. Targeting stromal remodeling and cancer stem cell plasticity overcomes chemoresistance in triple negative breast cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9( 1): 2897. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05220-6. [41] JIANG NX, XIA JW, JIANG B, et al. Retraction notice to“TUG1 alleviates hypoxia injury by targeting miR-124 in H9c2 cells”[Biomed. Pharmacother. 103(2018) 1669-1677][J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2022, 150: 112856. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112856. [42] LIU J, CHEN S, WANG W, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through chemokine-activated hedgehog and TGF-β pathways[J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 379( 1): 49- 59. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.05.022. [43] ATHAR M, LI CX, TANG XW, et al. Inhibition of smoothened signaling prevents ultraviolet B-induced basal cell carcinomas through regulation of Fas expression and apoptosis[J]. Cancer Res, 2004, 64( 20): 7545- 7552. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1393. [44] THAYER SP, DI MAGLIANO MP, HEISER PW, et al. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis[J]. Nature, 2003, 425( 6960): 851- 856. DOI: 10.1038/nature02009. [45] PATIL MA, ZHANG J, HO C, et al. Hedgehog signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2006, 5( 1): 111- 117. DOI: 10.4161/cbt.5.1.2379. [46] VITALE I, MANIC G, COUSSENS LM, et al. Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cell Metab, 2019, 30( 1): 36- 50. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.001. [47] MAZZONE M, MENGA A, CASTEGNA A. Metabolism and TAM functions-it takes two to tango[J]. FEBS J, 2018, 285( 4): 700- 716. DOI: 10.1111/febs.14295. [48] ANDREJEVA G, RATHMELL JC. Similarities and distinctions of cancer and immune metabolism in inflammation and tumors[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 26( 1): 49- 70. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.06.004. [49] MOVAHEDI K, LAOUI D, GYSEMANS C, et al. Different tumor microenvironments contain functionally distinct subsets of macrophages derived from Ly6C(high) monocytes[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70( 14): 5728- 5739. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4672. [50] WANG XC, LU XJ, SUN BC. The pros and cons of dying tumour cells in adaptive immune responses[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2017, 17( 9): 591. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.87. [51] PHILIP M, SCHIETINGER A. CD8+ T cell differentiation and dysfunction in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 22( 4): 209- 223. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-021-00574-3. [52] PETTY AJ, DAI R, LAPALOMBELLA R, et al. Hedgehog-induced PD-L1 on tumor-associated macrophages is critical for suppression of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cell function[J]. JCI Insight, 2021, 6( 6): e146707. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.146707. [53] TAN JZ, FAN WZ, LIU T, et al. TREM2+ macrophages suppress CD8+ T-cell infiltration after transarterial chemoembolisation in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 1): 126- 140. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.02.032. [54] MULLOR JL, SÁNCHEZ P, ALTABA ARI. Pathways and consequences: Hedgehog signaling in human disease[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2002, 12( 12): 562- 569. DOI: 10.1016/S0962-8924(02)02405-4. [55] LEE J, PLATT KA, CENSULLO P, et al. Gli1 is a target of Sonic hedgehog that induces ventral neural tube development[J]. Development, 1997, 124( 13): 2537- 2552. DOI: 10.1242/dev.124.13.2537. [56] CHEN JS, LI HS, HUANG JQ, et al. Down-regulation of Gli-1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2014, 393( 1-2): 283- 291. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-014-2071-x. [57] QUAGLIO D, INFANTE P, DI MARCOTULLIO L, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors: An updated patent review(2015-present)[J]. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 2020, 30( 4): 235- 250. DOI: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1730327. [58] LORUSSO PM, RUDIN CM, REDDY JC, et al. Phase I trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib(GDC-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2011, 17( 8): 2502- 2511. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2745. [59] RUDIN CM, HANN CL, LATERRA J, et al. Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 361( 12): 1173- 1178. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0902903. [60] SEKULIC A, MIGDEN MR, ORO AE, et al. Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 366( 23): 2171- 2179. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113713. [61] PINTER M, SIEGHART W, SCHMID M, et al. Hedgehog inhibition reduces angiogenesis by downregulation of tumoral VEGF-A expression in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2013, 1( 4): 265- 275. DOI: 10.1177/2050640613496605. [62] WANG Y, HAN C, LU L, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58( 3): 995- 1010. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26394. -



 PDF下载 ( 860 KB)
PDF下载 ( 860 KB)

 下载:
下载:


