《2024年世界卫生组织慢性乙型肝炎患者的预防、诊断、关怀和治疗指南》推荐意见要点
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240510
Key recommendations in guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, care and treatment for people with chronic hepatitis B infection released by the World Health Organization in 2024
-
摘要: 2024年3月世界卫生组织(WHO)发布了最新版《慢性乙型肝炎患者的预防、诊断、关怀和治疗指南》。该指南在以下方面进行了更新:扩大并简化慢性乙型肝炎治疗适应证,增加可选的抗病毒治疗方案,扩大抗病毒治疗预防母婴传播的适应证,提高乙型肝炎病毒诊断,增加合并丁型肝炎病毒的检测等。本文对指南中的推荐意见进行归纳及摘译。Abstract: In March 2024, the World Health Organization released the latest version of guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, care and treatment for people with chronic hepatitis B infection. The guidelines were updated in several aspects, including expanding and simplifying the indications for chronic hepatitis B treatment, adding alternative antiviral treatment regimens, broadening the indications for antiviral therapy to prevent mother-to-child transmission, improving the diagnosis of hepatitis B virus, and adding hepatitis D virus (HDV) testing. This article summarizes and gives an excerpt of the recommendations in the guidelines.
-
Key words:
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- Prevention /
- Diagnosis /
- Therapeutics /
- World Health Organization /
- Practice Guideline
-
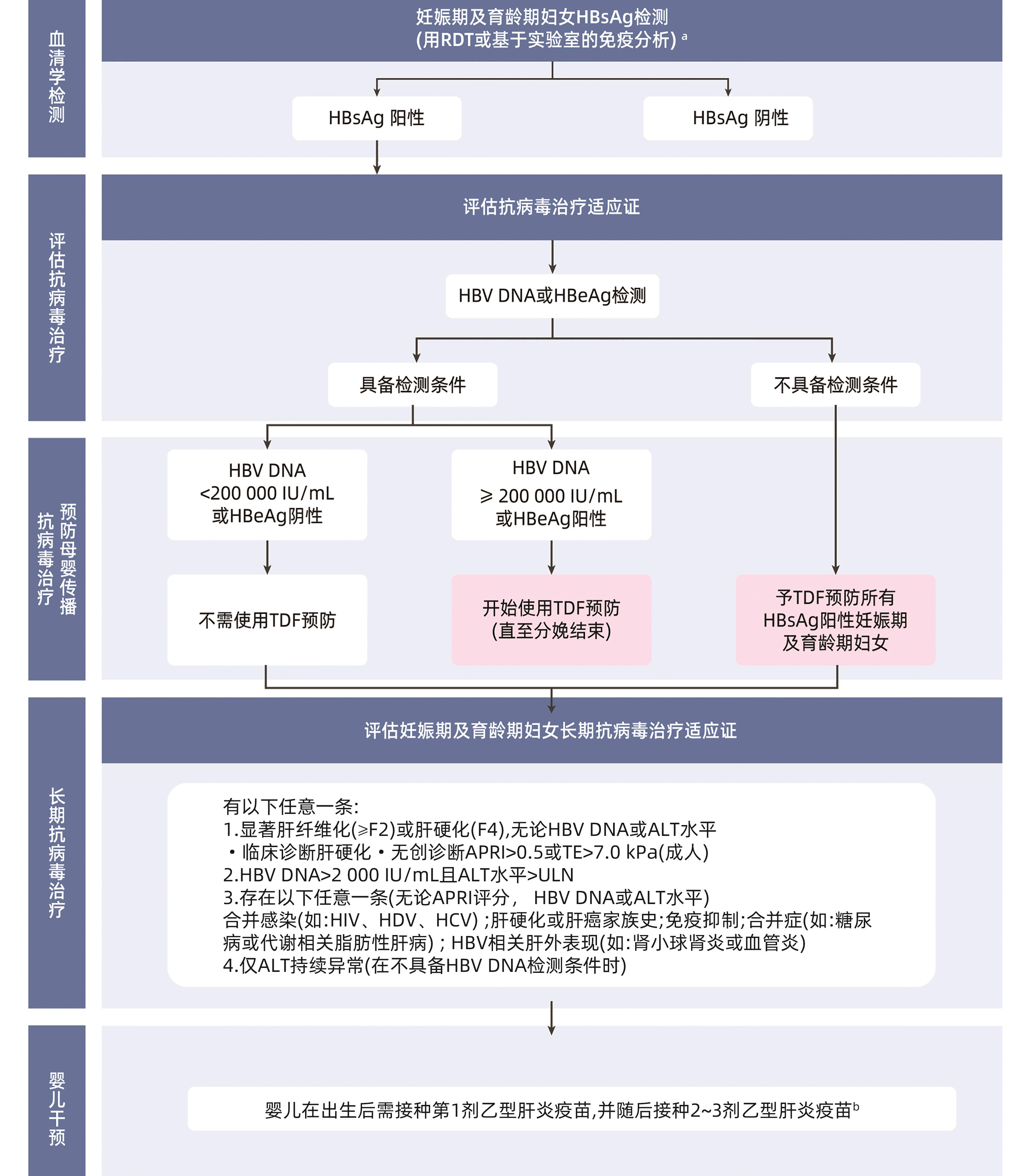
注: TDF,富马酸替诺福韦酯;3TC,拉米夫定;ETV,恩替卡韦;FTC,恩曲他滨;TAF,富马酸丙酚替诺福韦。a,慢性HBV感染者定义为成人HBsAg阳性,青少年或儿童HBsAg持续阳性6个月及以上;b,在治疗开始前,应考虑评估肾功能(如血清肌酐水平、肾小球滤过率、尿蛋白、尿糖)及肾功能损伤的高风险因素[包括失代偿期肝硬化、肌酐清除率(creatinine clearance,CrCl)<50 mL/min,年龄>60岁,BMI<18.5 kg/m2(体质量<50 kg)、控制不佳的高血压、蛋白尿、控制不佳的糖尿病、活动性肾小球肾炎、同时使用肾毒性药物或HIV增强型蛋白酶抑制剂和实体器官移植];对于有肾功能损伤高风险的人群应更频繁监测;c,年龄分组: 本指南中成人定义为≥18岁,青少年定义为12~17岁(包括17岁),儿童定义为2~11岁。各国法律对年龄段定义可能不同;d,失代偿期肝硬化的临床特征有:门静脉高压,表现为腹水、静脉曲张出血和肝性脑病;凝血功能障碍;肝功能不全(黄疸)。其他晚期肝病或肝硬化的临床特征有:肝大、脾大、皮肤瘙痒、乏力、关节痛、肝掌和水肿;e,APRI和TE等无创纤维化检测尚未在儿童及青少年中验证;f,ALT ULN定义为男性30 U/L, 女性19 U/L。ALT持续正常或异常可定义为6~12个月内任意时间间隔内两次ALT都低于或高于ULN。CHB患者ALT水平常波动,需要长期监测其变化趋势;g,ALT升高是妊娠期妇女正常表现,不适合作为该人群长期抗病毒治疗的指征。妊娠期妇女应在分娩后重新检测ALT;h,所有CHB患者应定期监测疾病活动度及进展情况、肝细胞癌(HCC)和停止治疗后HBV再激活;应更频繁地监测那些处于晚期肝病阶段的患者,抗病毒治疗第1年内患者以及怀疑治疗依从性不佳的患者。
图 1 慢性HBV感染者筛查、治疗、监测流程图a
Figure 1. Algorithm for assessment, treatment and monitoring of people with chronic hepatitis B infectiona
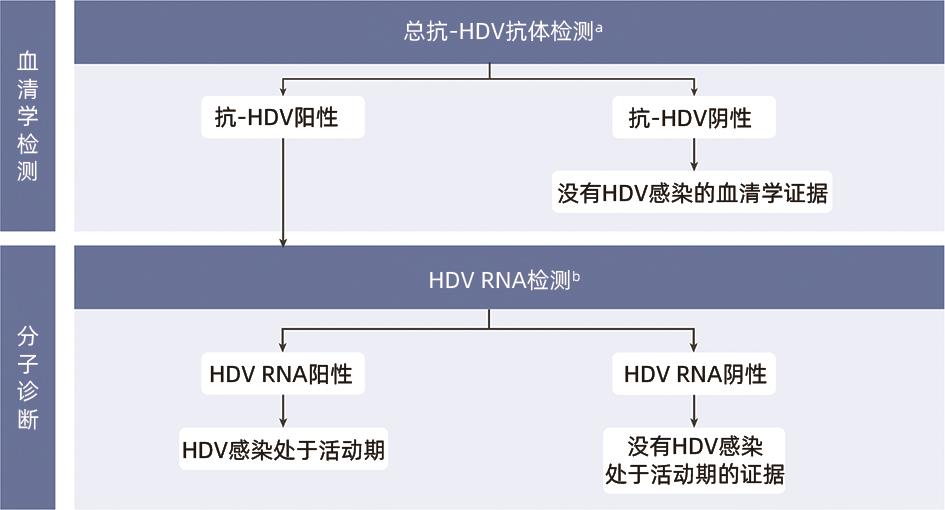
注: RDT,快速诊断检测;a,所有孕妇在妊娠期间应至少检测一次HIV、梅毒及HBsAg,并应尽早检测;b,无论孕妇HBsAg状态,婴儿出生后应立即(24 h内)接种乙型肝炎疫苗并随后接种2~3剂乙型肝炎疫苗。在高收入地区,对HBsAg阳性(尤其是HBV DNA高水平)母亲所生的婴儿,也需要注射乙型肝炎免疫球蛋白。
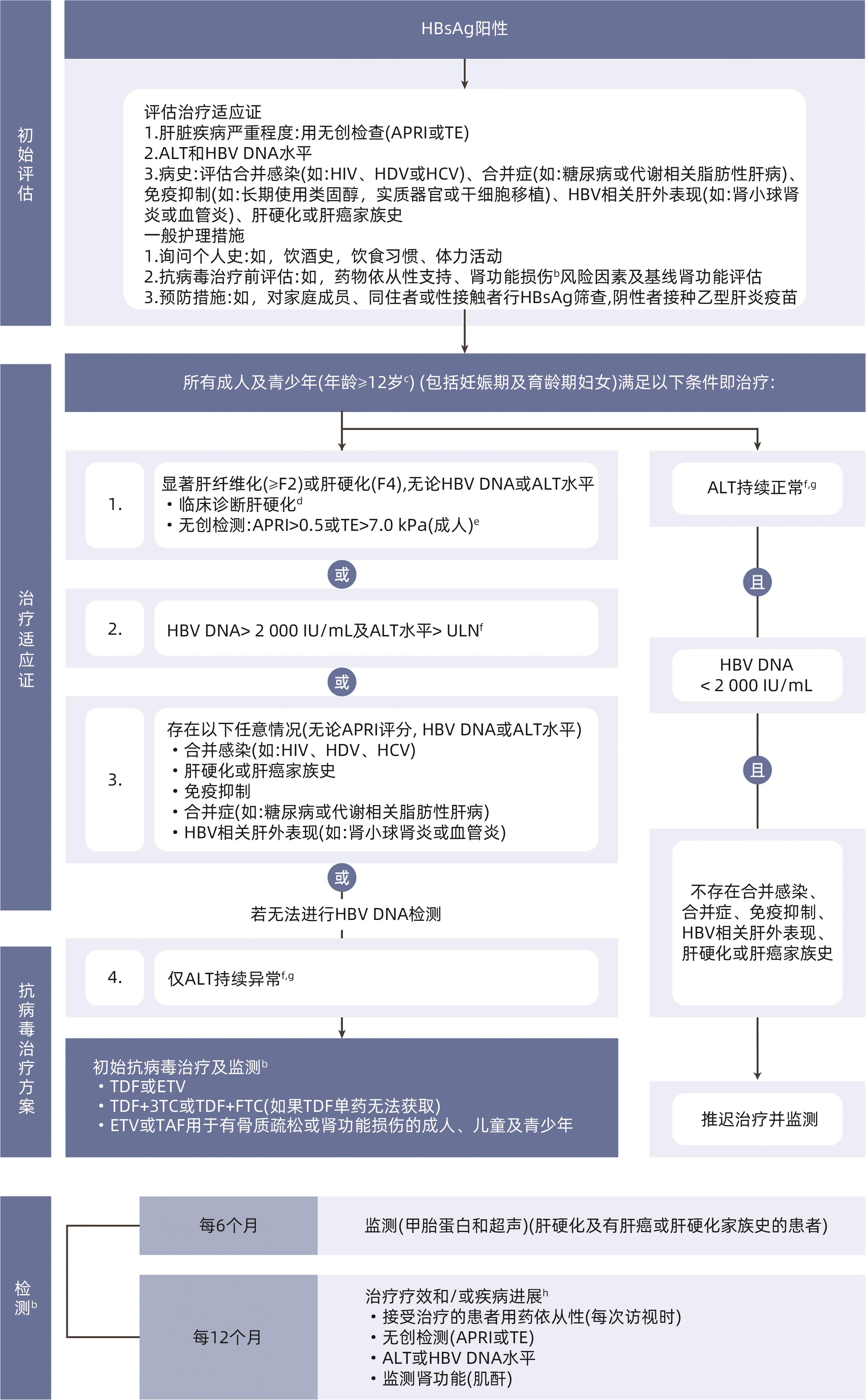
图 2 妊娠期及育龄期妇女以预防母婴传播和管理其自身健康为目的评估制定抗病毒治疗策略
Figure 2. Algorithm on use of antiviral prophylaxis for prevention of mother-to-child transmission in pregnant women and adolescent girls with CHB and assessment of treatment eligibility for their own health
表 1 首选及替代一线抗病毒治疗方案汇总
Table 1. Summary of preferred and alternative first-line antiviral regimens
人群 首选一线方案 替代一线方案 特殊情况 成人 TDF ETV TDF+3TC TDF+FTC (当TDF单药无法获得时) ETV TAF (对有骨质疏松和/或肾功能损伤患者) 青少年 (12~17岁) TDF ETV TDF+3TC TDF+FTC (当TDF单药无法获得时) TAF 儿童 (2~11岁) TDF1) ETV 注:1)TDF低剂量制剂可能无法广泛获取。 -
[1] World Health Organization. Guidelines for the prevention, diagnosis, care and treatment for people with chronic hepatitis B infection[R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2024. -



 PDF下载 ( 2084 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2084 KB)

 下载:
下载: