乙型肝炎肝硬化异型增生结节患者中医体质类型分布及临床特点分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240515
TCM constitution distribution and clinical features of patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis and dysplastic nodules
-
摘要:
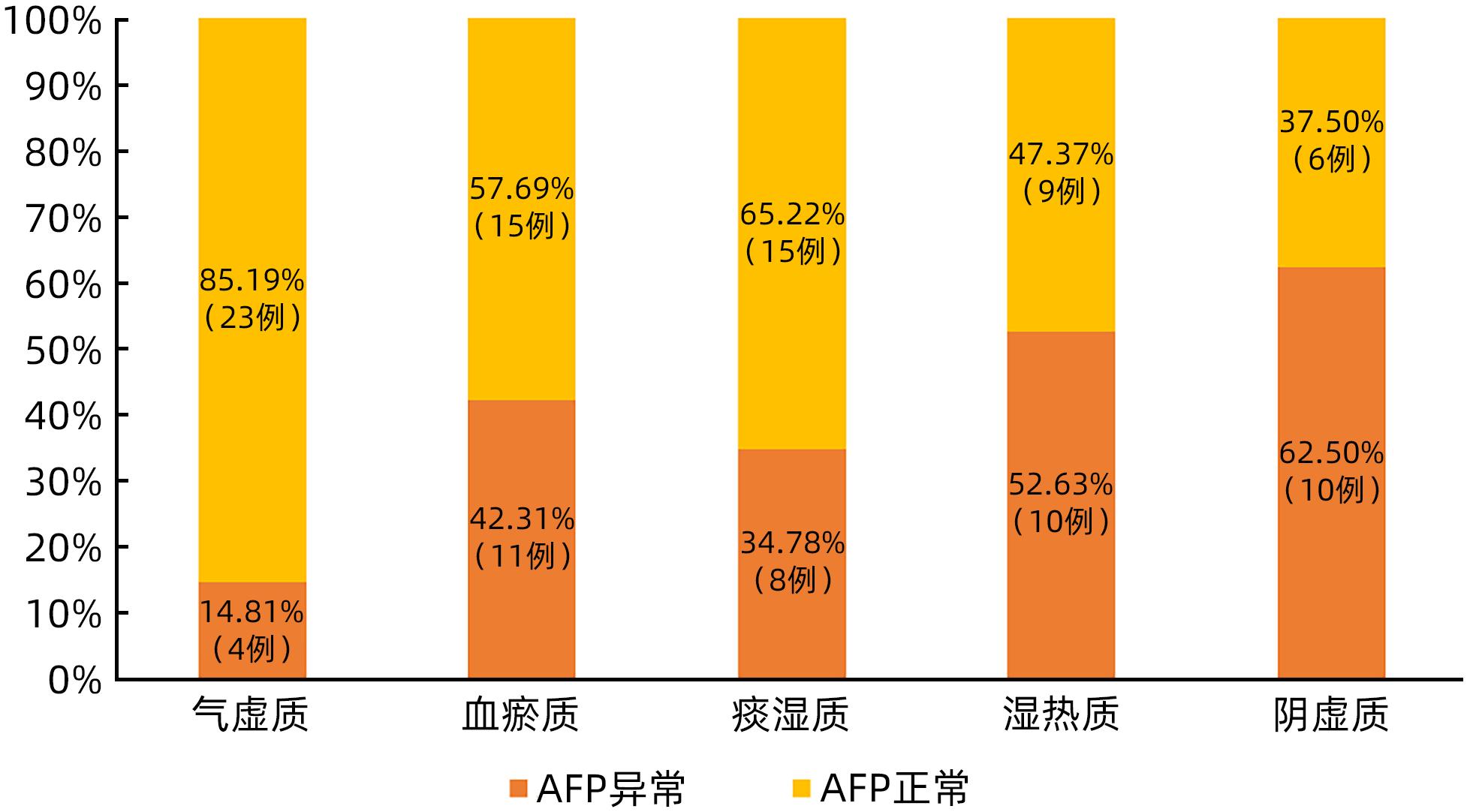
目的 探讨乙型肝炎肝硬化异型增生结节(DN)患者中医体质分布特征,为肝癌癌前病变的防治提供依据。 方法 选取2015年5月—2023年3月在广东省中医院住院治疗的乙型肝炎肝硬化DN患者113例、乙型肝炎肝硬化再生结节(RN)患者105例、乙型肝炎肝硬化小肝癌(sHCC)患者70例。收集患者的年龄、性别、肝功能Child-Pugh分级、中医体质类型、实验室指标等资料。正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析及LSD-t法;非正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验;计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验,进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni校正法。 结果 乙型肝炎肝硬化DN患者以气虚质(27例,23.89%)、血瘀质(26例,23.01%)、痰湿质(23例,20.35%)为主。3组患者在痰湿质、湿热质占比方面比较差异有统计学意义(χ2值分别为6.822、6.383,P值均<0.05),从肝硬化RN患者、肝硬化DN患者到sHCC患者,痰湿质占比逐渐降低(30.48% vs 20.35% vs 14.29%),而湿热质占比逐渐升高(12.38% vs 16.81% vs 27.14%)。部分中医体质类型肝硬化DN患者在性别、Child-Pugh分级、前白蛋白、Alb、AST、TBil、总胆汁酸、甲胎蛋白上差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05),其中女性肝硬化DN患者气虚质占比高于男性患者(χ2=4.895,P=0.027);气虚质患者Child-Pugh A级占比低于Child-Pugh B级(χ2=6.380,P=0.012),而痰湿质患者Child-Pugh A级占比高于Child-Pugh B级(χ2=8.515,P=0.004);痰湿质患者前白蛋白、Alb水平高于其他4种体质患者(P值均<0.05),同时痰湿质患者TBil、总胆汁酸水平低于湿热质患者(P值均<0.05);阴虚质患者Alb水平低于气虚质、血瘀质、痰湿质患者(P值均<0.05);阴虚质患者甲胎蛋白异常比例显著高于非阴虚质患者(χ2=4.448,P=0.035)。 结论 乙型肝炎肝硬化DN患者以气虚质、血瘀质、痰湿质多见,痰湿质患者癌变可能性小,而湿热质、阴虚患者癌变风险较大。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the characteristics of TCM constitution distribution in hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with dysplastic nodules (DN), and to provide a basis for the prevention and treatment of precancerous lesions of liver cancer. Methods This study was conducted among 113 hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with DN, 105 hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with regenerative nodules (RN), and 70 hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma (sHCC) who were hospitalized in Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from May 2015 to March 2023. Related data were collected, including age, sex, liver function Child-Pugh class, TCM constitution type, and laboratory markers. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups; the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between groups, and the Bonferroni correction method was used for further comparison between two groups. Results The main TCM constitution types of hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with DN were Qi-deficiency constitution (27 patients, 23.89%), blood-stasis constitution (26 patients, 23.01%), and phlegm-dampness constitution (23 patients, 20.35%). There were significant differences between the three groups in the proportion of patients with phlegm-dampness constitution or damp-heat constitution (χ2=6.822 and 6.383, both P<0.05); the hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with RN had the highest proportion of patients with phlegm-dampness constitution (30.48%), followed by those with DN (20.35%) and those with sHCC (14.29%), while the hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with sHCC had the highest proportion of patients with damp-heat constitution (27.14%), followed by those with DN (16.81%) and those with RN (12.38%). There were significant differences between the hepatitis B cirrhosis DN patients with different TCM constitution types in sex, age, Child-Pugh class, prealbumin, albumin (Alb), aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin (TBil), total bile acid, and alpha-fetoprotein (all P<0.05). Compared with the male hepatitis B cirrhosis DN patients, female patients showed a significantly higher proportion of patients with Qi-deficiency constitution (χ2=4.895, P=0.027). Among the patients with Qi-deficiency constitution, the patients with Child-Pugh class A liver function accounted for a significantly lower proportion than those with Child-Pugh class B liver function (χ2=6.380, P=0.012), while among the patients with phlegm-dampness constitution, the patients with Child-Pugh class A liver function accounted for a significantly higher proportion than those with Child-Pugh class B liver function (χ2=8.515, P=0.004). The patients with phlegm-dampness constitution had significantly higher levels of prealbumin and Alb than those with the other four constitutions (all P<0.05), as well as significantly lower levels of TBil and total bile acid than those with damp-heat constitution (P<0.05); the patients with Yin-deficiency constitution had a significantly lower level of Alb than those with qi-deficiency constitution, blood-stasis constitution, or phlegm-dampness constitution (all P<0.05); the patients with Yin-deficiency constitution had a significantly lower proportion of patients with abnormal alpha-fetoprotein than those with non-Yin-deficiency constitutions (χ2=4.448, P=0.035). Conclusion Hepatitis B cirrhosis patients with DN mainly have the TCM constitution types of Qi deficiency, blood stasis, and phlegm dampness. The patients with phlegm-dampness constitution seem to have a low probability of carcinogenesis, while those with damp-heat constitution and Yin-deficiency constitution have a relatively high risk of carcinogenesis. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Dysplasia Nodules /
- Constitutional Type (TCM)
-
表 1 3组患者基线特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline characteristics among the three groups of patients
指标 肝硬化RN(n=105) 肝硬化DN(n=113) sHCC(n=70) 统计值 P值 性别[例(%)] χ2=4.505 0.105 男 75(71.43) 78(69.03) 58(82.86) 女 30(28.57) 35(30.97) 12(17.14) 年龄段[例(%)] 青年 20(19.05) 16(14.16) 7(10.00) χ2=2.794 0.247 中年 44(41.90)1) 66(58.41) 24(34.29)1) χ2=11.528 0.003 老年 41(39.05) 31(27.43) 39(55.71) χ2=3.341 0.188 Child-Pugh分级[例(%)] A级 59(56.19) 62(54.87) 42(60.00) χ2=0.475 0.789 B级 38(36.19) 36(31.86) 24(34.29) χ2=0.458 0.795 C级 8(7.62) 15(13.27) 4(5.71) χ2=3.507 0.173 PA(mg/L) 150.00(90.00~200.00) 139.00(82.50~203.00) 151.00(78.75~208.50) H=0.090 0.956 Alb(g/L) 37.56±7.25 37.47±7.32 37.27±6.56 F=0.035 0.966 ALT(U/L) 30.00(17.50~47.00) 29.00(19.00~44.00) 31.00(20.00~50.75) H=1.185 0.553 AST(U/L) 34.00(26.00~48.00) 35.00(25.00~50.00) 38.00(28.00~56.00) H=1.522 0.467 ALP(U/L) 88.00(70.00~116.50) 86.00(66.50~132.50) 82.50(69.50~119.50) H=0.467 0.792 GGT(U/L) 47.00(24.50~94.50) 48.00(27.50~76.50) 40.50(31.00~89.00) H=0.097 0.953 TBil(μmol/L) 18.10(12.45~26.30) 19.30(12.85~31.65) 19.00(11.75~31.33) H=1.019 0.601 TBA(μmol/L) 12.40(6.15~35.80) 21.60(6.10~50.50) 15.70(7.00~37.38) H=1.983 0.371 PLT(×109/L) 95.00(67.00~151.50) 94.00(64.00~140.50) 110.50(79.75~155.50) H=4.261 0.119 AFP(ng/mL) 4.82(2.45~12.42) 2) 4.52(2.87~10.81) 2) 8.92(3.92~51.75) H=11.655 0.003 注:1)与肝硬化DN比较,P<0.05;2)与sHCC比较,P<0.05。年龄段:青年,<45岁;中年,45~59岁;老年,≥60岁。 表 2 3组患者体质分布及构成比
Table 2. Physical distribution and composition ratio of three groups of patients
体质类型 肝硬化RN(n=105) 肝硬化DN(n=113) sHCC(n=70) χ2值 P值 气虚质[例(%)] 29(27.62) 27(23.89) 13(18.57) 1.888 0.389 血瘀质[例(%)] 21(20.00) 26(23.01) 14(20.00) 0.372 0.830 痰湿质[例(%)] 32(30.48)1) 23(20.35) 10(14.29) 6.822 0.033 湿热质[例(%)] 13(12.38)1) 19(16.81) 19(27.14) 6.383 0.041 阴虚质[例(%)] 9(8.57) 16(14.16) 11(15.71) 2.427 0.297 气郁质[例(%)] 1(0.95) 2(1.77) 1(1.43) 阳虚质[例(%)] 0(0.00) 0(0.00) 2(2.86) 注:1)与sHCC比较,P<0.05。 表 3 不同性别、年龄的肝硬化DN患者体质分布及构成比
Table 3. Physical distribution and composition ratio of patients with cirrhosis DN in different genders and ages
体质类型 例数 性别 年龄 男(n=78) 女(n=35) χ2值 P值 青年(n=16) 中年(n=66) 老年(n=31) χ2值 P值 气虚质[例(%)] 27 14(17.95) 13(37.14) 4.895 0.027 4(25.00) 13(19.70) 10(32.26) 1.843 0.398 血瘀质[例(%)] 26 21(26.92) 5(14.29) 2.178 0.140 2(12.50) 17(25.76) 7(22.58) 1.282 0.527 痰湿质[例(%)] 23 17(21.79) 6(17.14) 0.323 0.570 4(25.00) 17(25.76) 2(6.45) 5.098 0.078 湿热质[例(%)] 19 15(19.23) 4(11.43) 1.051 0.305 4(25.00) 10(15.15) 5(16.13) 0.907 0.635 阴虚质[例(%)] 16 9(11.54) 7(20.00) 1.423 0.233 1(6.25) 8(12.12) 7(22.58) 2.858 0.240 表 4 不同Child-Pugh分级肝硬化DN患者体质分布及构成比
Table 4. Physical distribution and composition ratio of patients with cirrhosis DN in different Child-Pugh grades
体质类型 例数 Child-Pugh A(n=62) Child-Pugh B(n=36) Child-Pugh C(n=15) χ2值 P值 气虚质[例(%)] 27 10(16.13)1) 14(38.89) 3(20.00) 6.632 0.036 血瘀质[例(%)] 26 15(24.19) 9(25.00) 2(13.33) 0.922 0.631 痰湿质[例(%)] 23 19(30.65)1) 2(5.56) 2(13.33) 9.370 0.009 湿热质[例(%)] 19 11(17.74) 4(11.11) 4(26.67) 1.916 0.384 阴虚质[例(%)] 16 6(9.68) 6(16.67) 4(26.67) 3.141 0.208 注:与Child-Pugh B比较,P<0.05。 表 5 不同中医体质类型肝硬化DN患者生化指标比较
Table 5. Comparison of biochemical indicators in patients with cirrhosis DN of different TCM constitution types
指标 气虚质(n=27) 血瘀质(n=26) 痰湿质(n=23) 湿热质(n=19) 阴虚质(n=16) 统计值 P值 PA(mg/L) 122.00 (83.00~179.00)1) 146.00 (70.75~189.00)1) 220.00 (176.00~296.00) 113.00 (67.00~166.00)1) 125.50 (48.25~146.00)1) H=21.665 <0.001 Alb(g/L) 36.42±7.291)2) 38.62±5.551)2) 40.86±8.06 35.84±6.021) 33.88±7.621) F=3.032 0.021 ALT(U/L) 25.00 (18.00~33.00) 27.00 (14.75~39.00) 29.00 (18.00~45.00) 29.00 (19.00~74.00) 36.00 (19.50~69.00) H=4.764 0.312 AST(U/L) 31.00 (22.00~45.00) 35.00 (23.00~50.00) 30.00 (20.00~40.00) 38.00 (29.00~88.00) 42.50 (33.00~84.75) H=10.986 0.027 ALP(U/L) 82.00 (67.00~123.00) 88.00 (77.75~150.75) 74.00 (64.00~107.00) 98.00 (68.00~145.00) 108.00 (77.50~157.25) H=5.066 0.281 GGT(U/L) 43.00 (18.00~70.00) 60.00 (36.50~125.00) 39.00 (21.00~73.00) 55.00 (40.00~129.00) 50.00 (37.75~65.75) H=7.132 0.129 TBil(μmol/L) 19.60 (12.10~26.70) 19.40 (15.73~31.20) 14.10 (10.20~17.90) 31.70 (19.50~46.50) 1) 24.30 (12.28~41.78) H=14.586 0.006 TBA(μmol/L) 17.30 (8.10~39.60) 28.90 (10.30~53.33) 5.80 (3.20~15.30) 30.50 (17.80~68.10) 1) 25.95 (8.75~46.88) H=13.265 0.010 PLT(×109/L) 90.00 (63.00~116.00) 98.50 (48.75~139.25) 134.00 (92.00~180.00) 86.00 (56.00~122.00) 88.00 (63.50~106.50) H=8.838 0.065 AFP(ng/mL) 3.58 (2.65~5.08) 4.38 (3.04~24.52) 3.11 (2.49~8.62) 10.07 (3.02~42.80) 8.50 (4.01~20.32) H=12.967 0.011 注:1)与痰湿质比较,P<0.05;2)与阴虚质比较,P<0.05。 -
[1] General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009.国家卫生健康委办公厅. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. [2] Chinese Journal of Hepatology; Liver Cancer Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of precancerous lesions of hepatocellular carcinoma(2020 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 3): 514- 518. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.003.007.《中华肝脏病杂志》编辑委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会肝癌学组. 肝细胞癌癌前病变的诊断和治疗多学科专家共识(2020版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 3): 514- 518. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.003.007. [3] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2023, 41( 1): 3- 28. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20230220-00050.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2023, 41( 1): 3- 28. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20230220-00050. [4] SONG B, YAN FH. Chinese imaging medicine-hepatobiliary pancreatic spleen volume[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2019: 78- 80.宋彬, 严福华. 中华影像医学·肝胆胰脾卷[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019: 78- 80. [5] FAN XL, LING Q, FANG Z, et al. Clinical value of MRI in the diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma with disodium gadolinium sephate in the context of liver cirrhosis[J]. Imag Sci Photochem, 2020, 38( 6): 1038- 1042. DOI: 10.7517/issn.1674-0475.200410.范晓黎, 凌茜, 方正, 等. MRI在肝硬化背景下诊断小肝癌中联用钆塞酸二钠的临床价值分析[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2020, 38( 6): 1038- 1042. DOI: 10.7517/issn.1674-0475.200410. [6] WANG Q, SHENG ZX. Constitution theory of traditional Chinese medicine[M]. Nanjing: Phoenix Science Press, 1982: 15.王琦, 盛增秀. 中医体质学说[M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1982: 15. [7] TENG X, JIN T, LIU Y, et al. Research progress in the relationship between genetic mechanisms of vestibular migraine and constitution of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2023, 39( 1): 108- 112. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.01.024.滕鑫, 荆涛, 刘寅, 等. 前庭性偏头痛遗传学机制与中医体质关系的研究进展[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2023, 39( 1): 108- 112. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.01.024. [8] YAO XX, HAO YK, XIAO Z, et al. Distribution of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types and elements in liver cirrhosis patients with dysplastic nodules: An analysis of 138 cases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 2): 352- 358. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.02.015.姚肖肖, 郝尧坤, 肖准, 等. 138例肝硬化不典型增生结节患者中医证型证素分布分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 2): 352- 358. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.02.015. [9] HUANG Q, LI JT, ZHANG HB, et al. Li Jingtao’s experience in diagnosis and treatment of precancerous lesions of liver cancer[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2020, 30( 3): 246- 248. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2020.03.018.黄倩, 李京涛, 张海博, 等. 李京涛诊治肝癌癌前病变经验探析[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2020, 30( 3): 246- 248. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2020.03.018. [10] HUANG JJ, CHEN SL, PAN Z, et al. Treatment of precancerous lesions of liver cancer with toxic turbidity and blood stasis[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2014, 24( 1): 59- 60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2013.06.018.黄晶晶, 陈松林, 潘哲, 等. 毒浊瘀论治肝癌癌前病变[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2014, 24( 1): 59- 60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2013.06.018. [11] GONG PQ, CHI XL, JIANG YY. Chi xiaoling’s experience on diagnosis and treatment of liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 36( 12): 2996- 2999. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2018.12.046.公培强, 池晓玲, 蒋元烨. 池晓玲教授对肝硬化的证治经验[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2018, 36( 12): 2996- 2999. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2018.12.046. [12] XIAO HM, LI S, XIE YB, et al. Discussion on the theory and application of soothing liver and strengthening spleen in the treatment of chronic liver disease[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2021, 31( 7): 651- 653. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2021.07.020.萧焕明, 黎胜, 谢玉宝, 等. 疏肝健脾法治疗慢性肝病的理论与应用探讨[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2021, 31( 7): 651- 653. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2021.07.020. [13] ZHOU L. Physical analysis of patients with family history of hepatitis B cirrhosis[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013.周浪. 具有乙肝肝硬化家族史的患者的体质分析[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2013. [14] NG CH, CHAN SW, LEE WK, et al. Hepatocarcinogenesis of regenerative and dysplastic nodules in Chinese patients[J]. Hong Kong Med J, 2011, 17( 1): 11- 19. [15] CHO HJ, KIM B, LEE JD, et al. Development of risk prediction model for hepatocellular carcinoma progression of indeterminate nodules in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhotic liver[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2017, 112( 3): 460- 470. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2016.480. [16] PAPATHEODORIDIS G, DALEKOS G, SYPSA V, et al. PAGE-B predicts the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B on 5-year antiviral therapy[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64( 4): 800- 806. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.035. [17] YU JH, SUH YJ, JIN YJ, et al. Prediction model for hepatocellular carcinoma risk in treatment-naive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving entecavir/tenofovir[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31( 7): 865- 872. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001357. [18] WANG Y, ZHOU YT, CHEN RX, et al. The prognostic value of total bile acid for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Clin Med, 2019, 26( 4): 594- 597. DOI: 10.12025/j.issn.1008-6358.2019.20190519.王妍, 周颖婷, 陈荣新, 等. 血清总胆汁酸水平对肝细胞肝癌患者预后的影响[J]. 中国临床医学, 2019, 26( 4): 594- 597. DOI: 10.12025/j.issn.1008-6358.2019.20190519. [19] CHIANG HH, LEE CM, HU TH, et al. A combination of the on-treatment FIB-4 and alpha-foetoprotein predicts clinical outcomes in cirrhotic patients receiving entecavir[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38( 11): 1997- 2005. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13889. -



 PDF下载 ( 775 KB)
PDF下载 ( 775 KB)

 下载:
下载:


