邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(DEHP)诱发小鼠胆汁淤积和肝损伤的作用机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240521
Mechanism of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in inducing cholestasis and liver injury in mice
-
摘要:
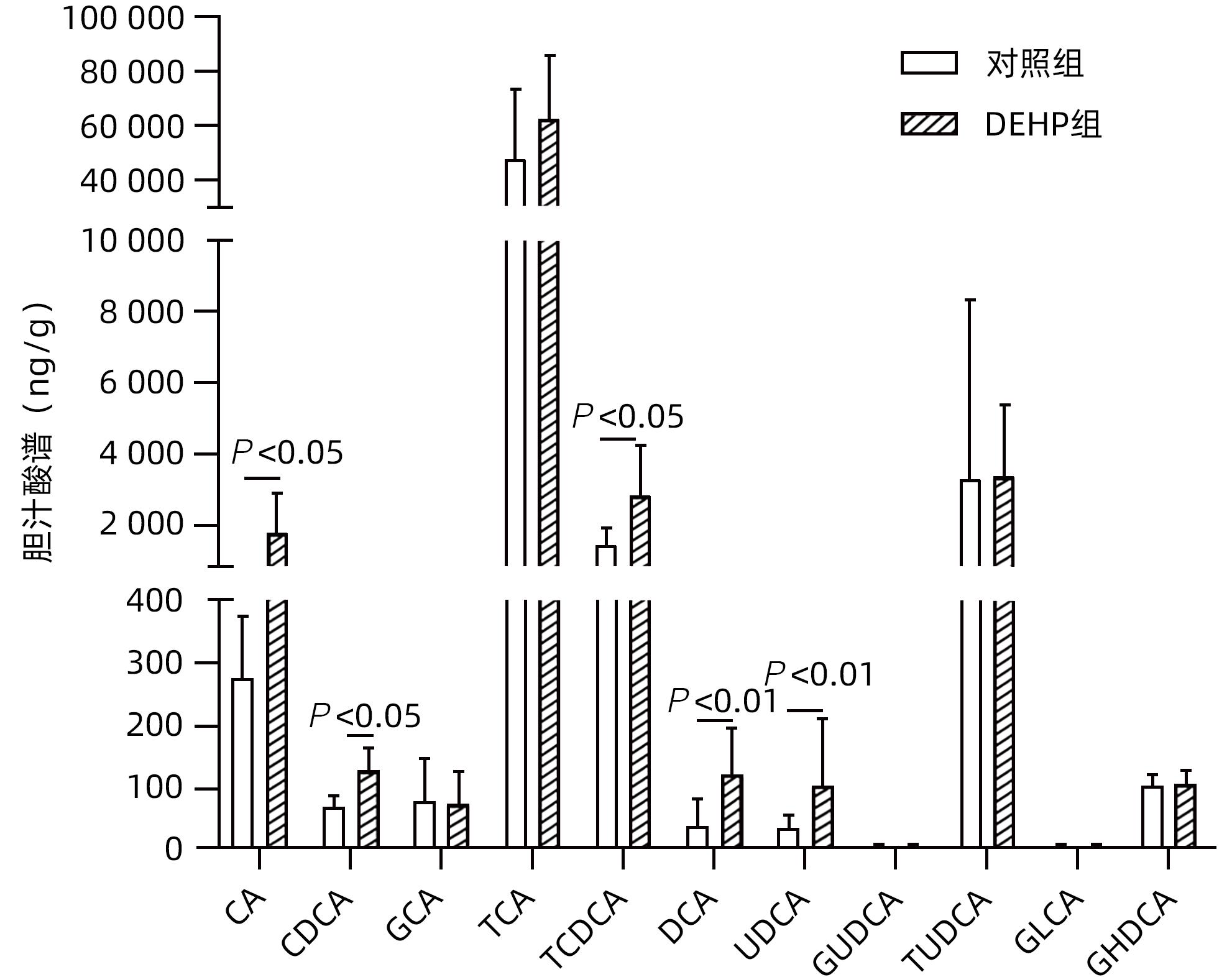
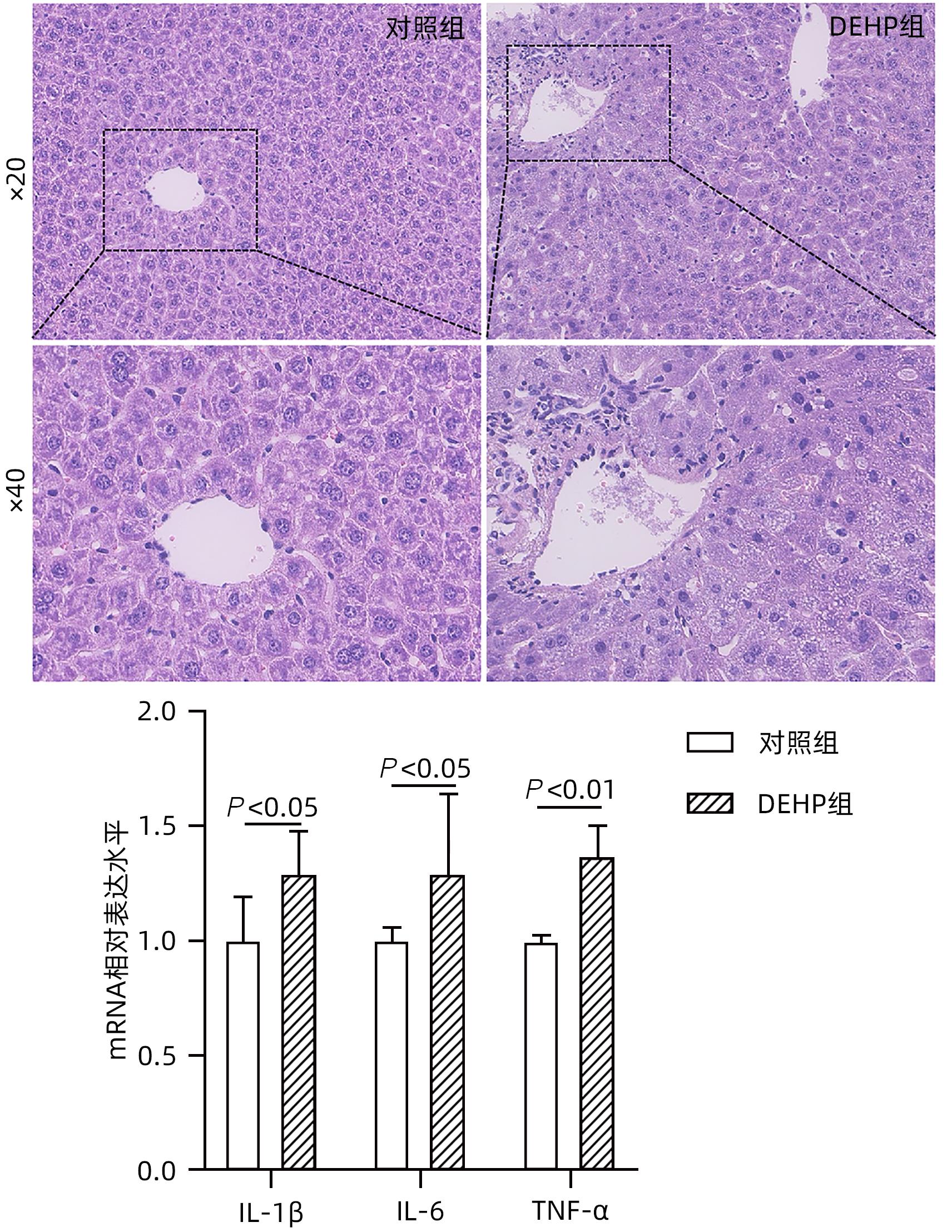
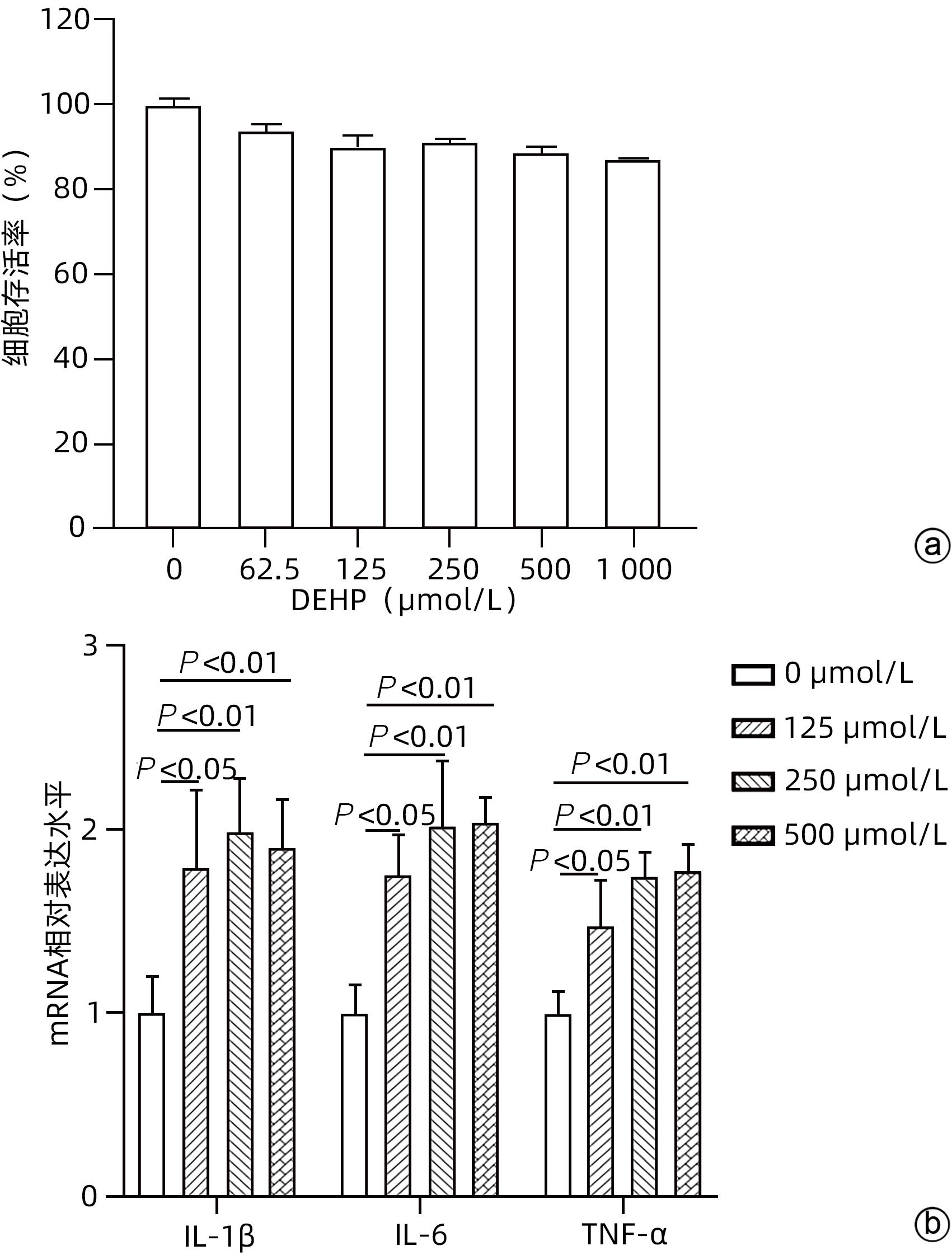
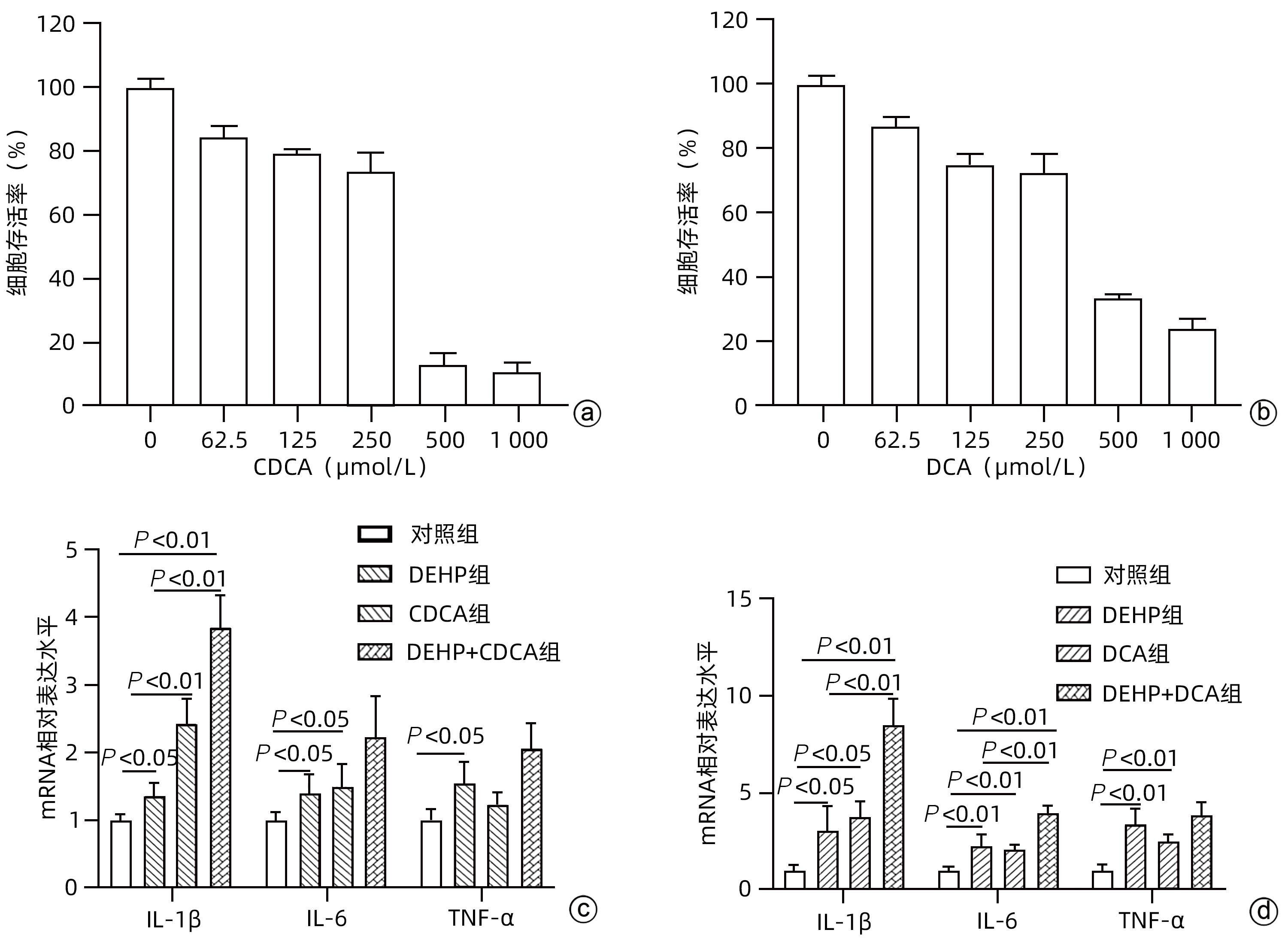
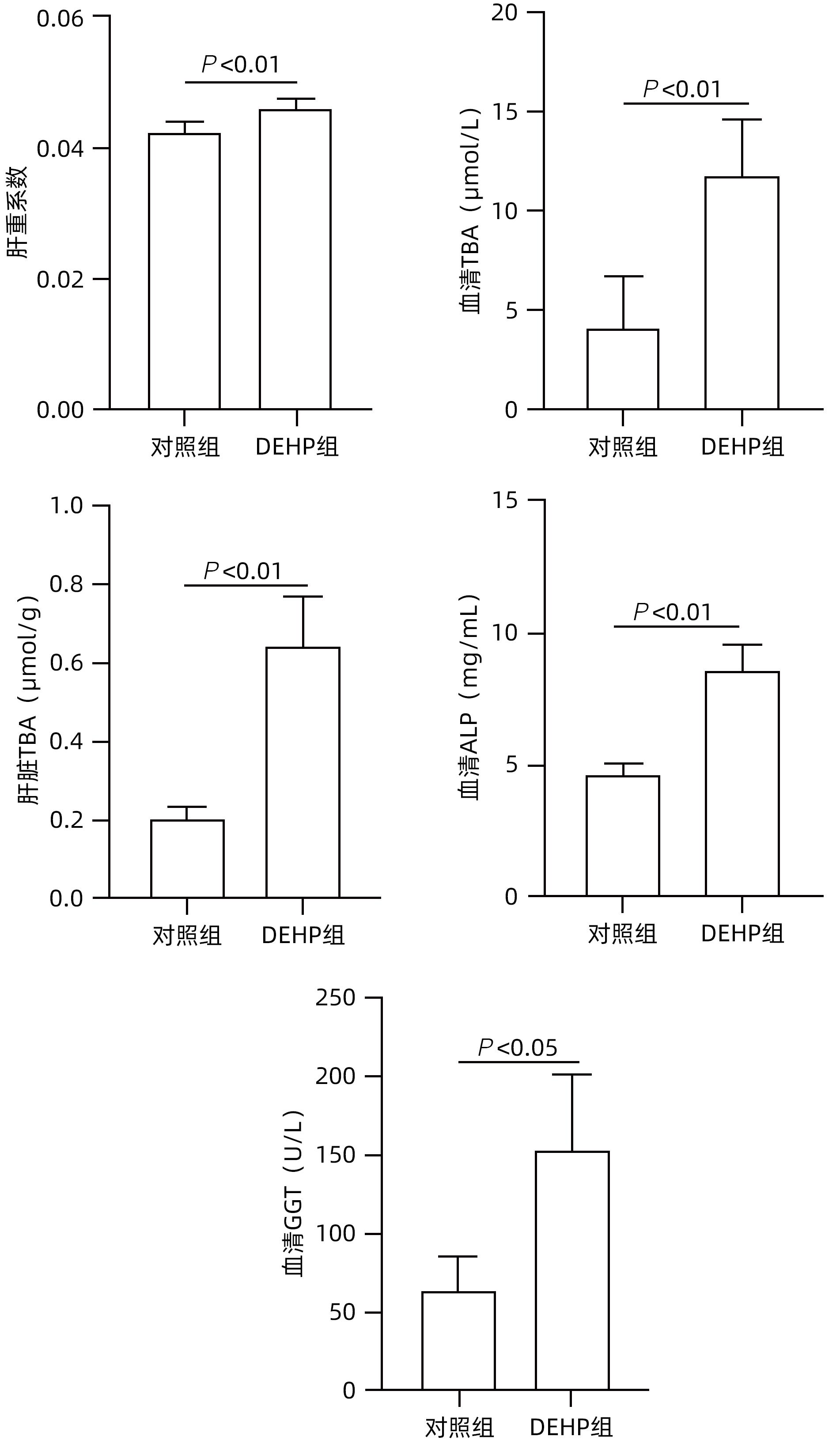
目的 探讨邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(DEHP)诱发小鼠胆汁淤积和肝损伤机制研究。 方法 体内实验:将成年雌性ICR小鼠随机分为对照组(玉米油)、DEHP组(200 mg·kg-1·d-1),共灌胃4周,建立胆汁淤积模型。收集所有小鼠血液与肝组织,生化仪检测血清、肝脏总胆汁酸(TBA)水平,酶标仪检测ALP、GGT;HE染色观察肝组织病理变化;实时定量PCR检测肝脏炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α的表达水平;液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱仪(LC-MS/MS)检测小鼠肝脏胆汁酸谱。体外实验:培养小鼠肝细胞AML-12,使用DEHP(250 µmol/L)以及去氧胆酸(DCA)(125 µmol/L)和鹅去氧胆酸(CDCA)(125 µmol/L)处理细胞24 h,实时定量PCR检测细胞炎性因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α的mRNA水平。计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。 结果 体内实验显示:与对照组相比,DEHP组小鼠肝体比,血清TBA、ALP、GGT及肝脏TBA均显著升高(t值分别为-4.396、-5.109、-8.504、-3.792和-7.974,P值均<0.05)。与对照组相比,肝脏胆汁酸谱中胆酸(CA)、CDCA、牛磺鹅去氧胆酸(TCDCA)、DCA及熊去氧胆酸(UDCA)均显著升高(t值分别为-2.802、-3.177、-2.633、-2.874和-2.311,P值均<0.05)。DEHP组小鼠肝脏HE染色显示为汇管区扩大、胆管变形、胆管周围伴有炎性细胞浸润,且肝脏炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α mRNA水平均显著升高(t值分别为-2.539、-2.823和-4.636,P值均<0.05)。体外实验显示:0~1 000 µmol/L DEHP处理后肝细胞活力实际数值相差不超过15%,分别使用125、250以及500 µmol/L的DEHP刺激后,肝细胞的炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α mRNA水平均明显升高(P值均<0.05)。与单独使用DEHP刺激相比,CDCA联合DEHP刺激上调了细胞炎症因子IL-1β mRNA水平(P<0.01);DCA与DEHP联合刺激可显著增加细胞炎症因子IL-1β和IL-6的mRNA水平(P值均<0.01)。 结论 DEHP暴露导致小鼠胆汁淤积肝病的发生并诱发肝脏炎症,这可能与其促进有毒胆汁酸的产生进而加剧炎性因子分泌有关。 -
关键词:
- 邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯 /
- 环境污染物 /
- 胆汁淤积 /
- 胆汁酸类
Abstract:Objective To investigate the mechanism of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in inducing cholestasis and liver injury in mice. Methods In the in vivo experiment, adult female ICR mice were randomly divided into control group (corn oil) and DEHP group (200 mg/kg/d), and a model of cholestasis was established by intragastric administration for 4 weeks. After blood and liver tissue samples were collected from all mice, a biochemical analyzer was used to measure the level of total bile acid (TBA) in serum and the liver, and a microplate reader was used to measure alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT); HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of the liver; RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of the inflammatory factors interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the liver; liquid chromatography/triple quadrupole mass spectrometry was used to measure the bile acid profile in the liver of mice. In the in vitro experiment, AML-12 mouse hepatocytes were cultured and treated with DEHP (250 µmol/L), DCA (125 µmol/L), and CDCA (125 µmol/L) for 24 hours, and RT-PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups; a one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison between multiple groups, and the LSD-t test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results The in vivo experiment showed that compared with the control group, the DEHP group had significant increases in the serum levels of TBA, ALP, and GGT and the level of TBA in the liver (the t values are respectively -4.396, -5.109, -8.504, -3.792 and -7.974, all P<0.05,). Compared with the control group, the DEHP group had significant increases in cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid, taurocholic acid, deoxycholic acid, and ursodeoxycholic acid (the t values are respectively -2.802, -3.177, -2.633, -2.874 and -2.311, all P<0.05). HE staining of the liver showed that the mice in the DEHP group had enlargement of the portal area, bile duct deformation, inflammatory cell infiltration around the bile duct, and significant increases in the mRNA expression levels of the inflammatory factors IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the liver (the t values are respectively -2.539, -2.823 and -4.636, all P<0.05). The in vitro experiment showed that the actual difference in hepatocyte viability after 0-1 000 µmol/L DEHP treatment does not exceed 15%, but there were significant increases in the mRNA expression levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α after treatment with DEHP at different concentrations of 125 µmol/L, 250 µmol/L, and 500 µmol/L (all P<0.05). Compared with DEHP stimulation alone, the combined stimulation of CDCA and DEHP upregulates the cytokine in hepatocyte IL-1β mRNA levels (P<0.01); the combined stimulation of DCA and DEHP can significantly increase the cytokine in hepatocyte IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA levels (all P<0.01). Conclusion DEHP exposure can cause cholestasis and induce liver inflammation in mice, possibly by promoting the production of toxic bile acids and the secretion of inflammatory factors. -
Key words:
- Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate /
- Environmental Pollutants /
- Cholestasis /
- Bile Acid
-
表 1 基因的引物序列
Table 1. Primers sequence of genes
基因名称 引物序列(5'-3') 18S F:GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT R:CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG IL-1β F:AACTGCACTACAGGCTCCGAG R:TGCTTGGTTCTCCTTGTACAAAGC TNF-α F:AAAAGATGGGGGGCTTCCAGAA R:CCATTTGGGAACTTCTCATCCCTT IL-6 F:TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA R:GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT -
[1] CHIANG JYL, FERRELL JM. Discovery of farnesoid X receptor and its role in bile acid metabolism[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2022, 548: 111618. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111618. [2] FANG D, LI PY. The treatment of cholestasis[J]. J Crit Care Intern Med, 2020, 26( 1): 22- 24. DOI: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20200106.方丹, 黎培员. 胆汁淤积的治疗[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2020, 26( 1): 22- 24. DOI: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20200106. [3] LI X, HAN XX, VOGT RD, et al. Polyethylene terephthalate and di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in surface and core sediments of Bohai Bay, China: Occurrence and ecological risk[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 286( Pt 3): 131904. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131904. [4] BAGEL S, DESSAIGNE B, BOURDEAUX D, et al. Influence of lipid type on bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate(DEHP) leaching from infusion line sets in parenteral nutrition[J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2011, 35( 6): 770- 775. DOI: 10.1177/0148607111414021. [5] GAITANTZI H, HAKENBERG P, THEOBALD J, et al. Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and its role in developing cholestasis: An in vitro study on different liver cell types[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2018, 66( 2): e28- e35. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001813. [6] QU MC, ZHAO F, ZHANG C, et al. Protective effect of obeticholic acid on cholestasis induced by subacute exposure to DEHP in mice[J]. Acta Univ Med Anhui, 2022, 57( 10): 1608- 1613. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2022.10.018.屈明超, 赵凡, 张程, 等. 奥贝胆酸对DEHP亚急性暴露导致小鼠胆汁淤积的保护作用[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2022, 57( 10): 1608- 1613. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2022.10.018. [7] PREECE AS, SHU H, KNUTZ M, et al. Indoor phthalate exposure and contributions to total intake among pregnant women in the SELMA study[J]. Indoor Air, 2021, 31( 5): 1495- 1508. DOI: 10.1111/ina.12813. [8] ZHANG YX, HUANG B, HE H, et al. Urinary phthalate metabolites among workers in plastic greenhouses in Western China[J]. Environ Pollut, 2021, 289: 117939. DOI: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117939. [9] ZHANG JY, WANG JQ. Research advances in the impact of phthalates on cholestatic liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 1): 226- 230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.01.035.张佳怡, 王建青. 邻苯二甲酸酯对胆汁淤积性肝病影响的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 1): 226- 230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.01.035. [10] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of cholestasis liver diseases(2015)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31( 12): 1989- 1999.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 胆汁淤积性肝病诊断和治疗共识(2015)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31( 12): 1989- 1999. [11] GOURLAY T, SAMARTZIS I, STEFANOU D, et al. Inflammatory response of rat and human neutrophils exposed to di-(2-ethyl-hexyl)-phthalate-plasticized polyvinyl chloride[J]. Artif Organs, 2003, 27( 3): 256- 260. DOI: 10.1046/j.1525-1594.2003.07107.x. [12] SONG PZ, ZHANG YC, KLAASSEN CD. Dose-response of five bile acids on serum and liver bile Acid concentrations and hepatotoxicty in mice[J]. Toxicol Sci, 2011, 123( 2): 359- 367. DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr177. -



 PDF下载 ( 1455 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1455 KB)

 下载:
下载: