高频不可逆电穿孔消融猪胰腺组织的效果观察
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240523
Effect of high-frequency irreversible electroporation in the ablation of porcine pancreatic tissue
-
摘要:
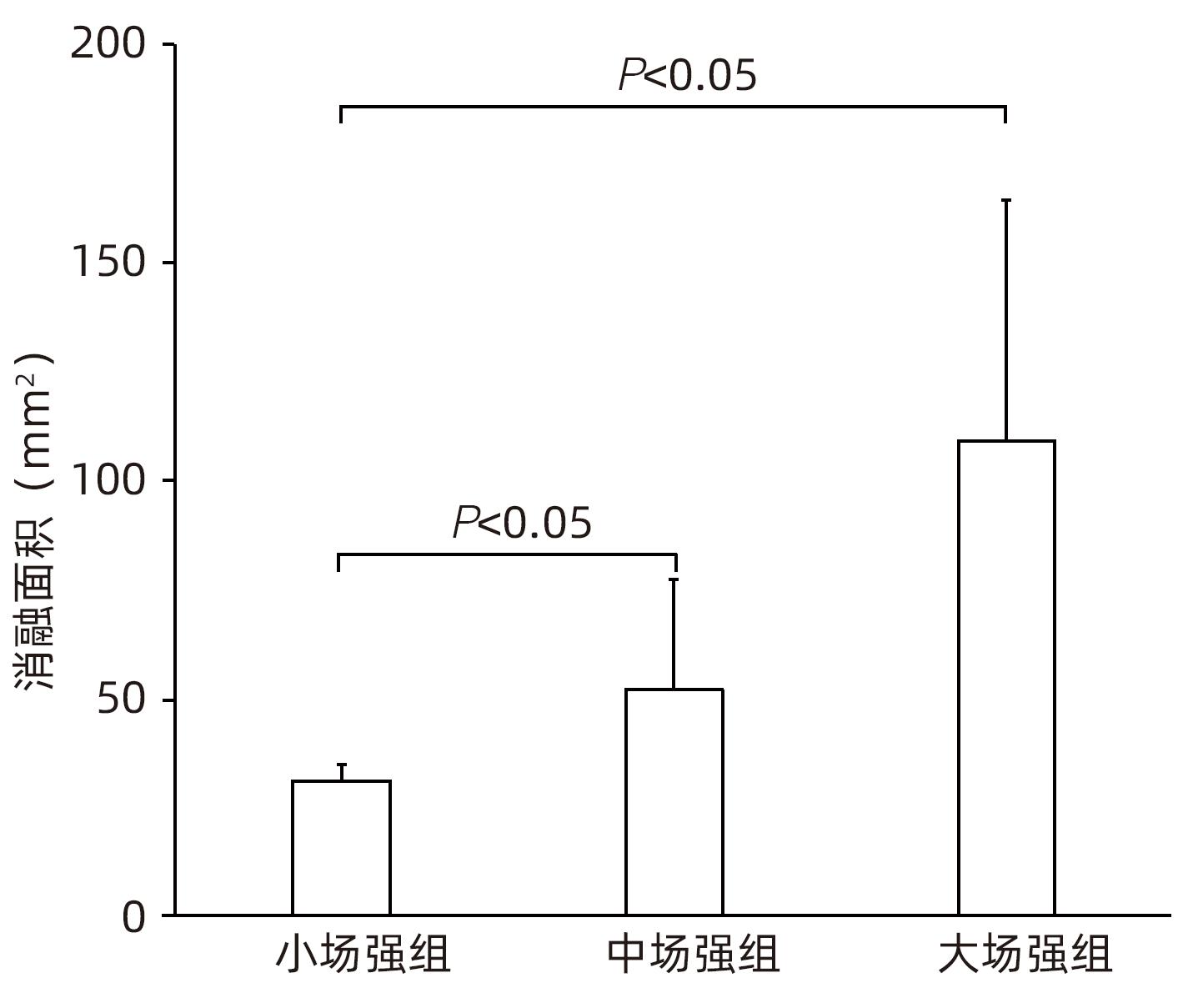
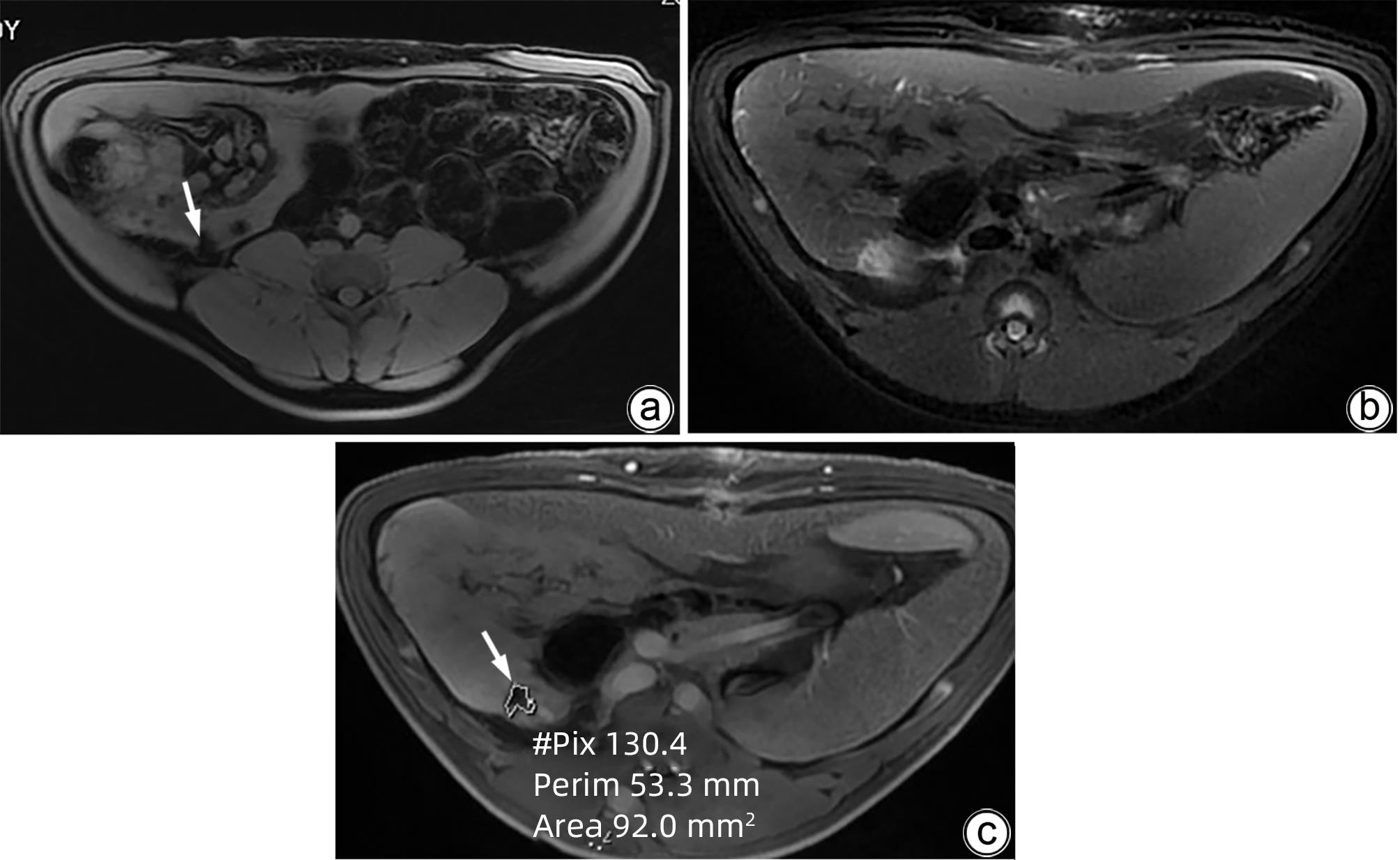
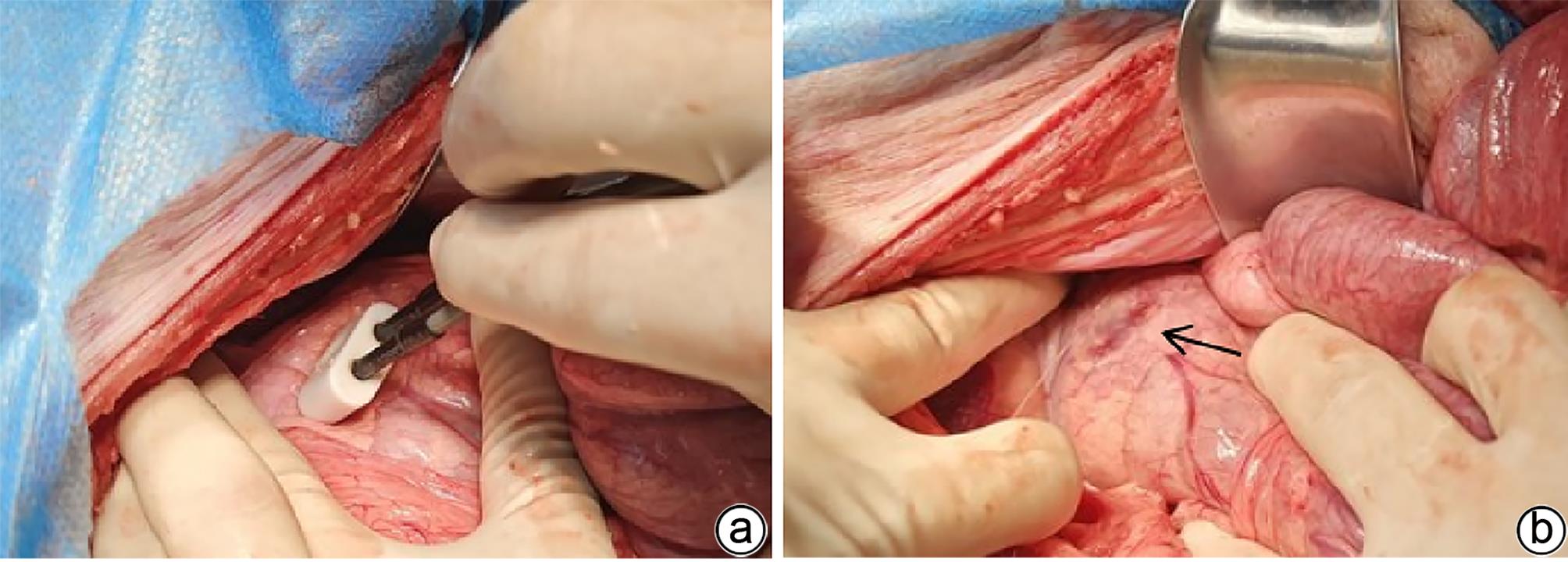
目的 探索高频不可逆电穿孔(H-FIRE)消融猪胰腺组织的效果。 方法 采用开腹手术,借助针式电极对12只猪释放电脉冲,按照场强数值小、中、大设置三组参数(1 000 V/cm、1 500 V/cm、2 500 V/cm)进行消融。通过比较各组术后恢复情况、消融面积、组织病理学表现等数据验证H-FIRE消融猪胰腺组织的安全性、有效性。计量资料两组间比较使用配对t检验。 结果 所有实验猪均存活,且获得明确的消融效果,各组组织病理学均提示,消融有效彻底,消融区与正常组织区分界明显,小场强组、中场强组、大场强组平均消融面积分别为(30.96±3.73)mm2、(51.93±25.26)mm2、(108.90±55.23)mm2,大、中场强组消融面积均显著大于小场强组(P值均<0.05),中场强组与大场强组消融面积差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 在特定的消融参数下,对猪胰腺进行H-FIRE消融安全、有效。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of high-frequency irreversible electroporation (H-FIRE) in the ablation of pig pancreatic tissue. Methods Laparotomy was conducted in this study, and needle electrodes were used to release electric pulses in 12 pigs. Three sets of parameters were established for ablation at the low, medium, and high values of field strength (1 000 V/cm, 1 500 V/cm, and 2 500 V/cm). The groups were compared in terms of the data including postoperative recovery, ablation area, and histopathological features to validate the safety and efficacy of H-FIRE in the ablation of porcine pancreatic tissue. The paired t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups. Results All pigs in the experiment survived and showed a good effect of ablation. The histopathological analysis of all groups showed thorough and effective ablation, with a clear boundary between the ablated area and the normal tissue area. The mean ablation area in the low, medium, and high field strength groups was 30.96±3.73 mm2, 51.93±25.26 mm2, and 108.90±55.23 mm2, respectively, and the high and medium field strength groups had a significantly larger ablation area than the low field strength group (both P<0.05), while there was no significant difference in ablation area between the medium and high field strength groups (P>0.05). Conclusion H-FIRE ablation is safe and effective for porcine pancreatic tissue under specific ablation parameters. -
Key words:
- Pancreatic Neoplasms /
- Electroporation /
- Ablation Techniques /
- Animal Experimentation
-
表 1 实验室检查结果
Table 1. Laboratory test results
指标 术前(n=12) 术后第7天(n=12) t值 P值 红细胞计数(×1012/L) 6.86±1.09 6.81±1.16 0.11 0.915 血红蛋白(g/L) 121.00±5.73 119.00±9.31 0.59 0.568 白细胞计数(×109/L) 15.22±1.40 20.50±2.02 10.63 <0.001 血小板计数(×109/L) 388.00±109.01 438.67±84.06 1.31 0.216 血清淀粉酶(U/L) 3 170.67±1 235.67 2 988.00±1 403.83 0.41 0.688 -
[1] TORRE LA, SIEGEL RL, WARD EM, et al. Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends: An update[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2016, 25( 1): 16- 27. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0578. [2] KWON W, THOMAS A, KLUGER MD. Irreversible electroporation of locally advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Semin Oncol, 2021, 48( 1): 84- 94. DOI: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2021.02.004. [3] ZHANG ZH, HE SL, WANG P, et al. The efficacy and safety of gemcitabine-based combination therapy vs. gemcitabine alone for the treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 13( 4): 1967- 1980. DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-624. [4] SPRINGFELD C, JÄGER D, BÜCHLER MW, et al. Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer[J]. Presse Med, 2019, 48( 3 Pt 2): e159- e174. DOI: 10.1016/j.lpm.2019.02.025. [5] GEBOERS B, SCHEFFER HJ, GRAYBILL PM, et al. High-voltage electrical pulses in oncology: Irreversible electroporation, electrochemotherapy, gene electrotransfer, electrofusion, and electroimmunotherapy[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295( 2): 254- 272. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020192190. [6] LIU CP, YE P, ZHANG MY. Research progress in irreversible electroporation ablation for tumors[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2023, 32( 5): 498- 502. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2023.05.018.刘春苹, 叶萍, 张明悦. 不可逆电穿孔对肿瘤消融的研究进展[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2023, 32( 5): 498- 502. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2023.05.018. [7] GARCIA PA, KOS B, ROSSMEISL JH Jr, et al. Predictive therapeutic planning for irreversible electroporation treatment of spontaneous malignant glioma[J]. Med Phys, 2017, 44( 9): 4968- 4980. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12401. [8] LATOUCHE EL, SANO MB, LORENZO MF, et al. Irreversible electroporation for the ablation of pancreatic malignancies: A patient-specific methodology[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2017, 115( 6): 711- 717. DOI: 10.1002/jso.24566. [9] QASRAWI R, SILVE L, BURDÍO F, et al. Anatomically realistic simulations of liver ablation by irreversible electroporation: Impact of blood vessels on ablation volumes and undertreatment[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2017, 16( 6): 783- 792. DOI: 10.1177/1533034616687477. [10] MARTIN RC, SCHWARTZ E, ADAMS J, et al. Intra-operative anesthesia management in patients undergoing surgical irreversible electroporation of the pancreas, liver, kidney, and retroperitoneal tumors[J]. Anesth Pain Med, 2015, 5( 3): e22786. DOI: 10.5812/aapm.22786. [11] MEROLA G, FUSCO R, DI BERNARDO E, et al. Design and characterization of a minimally invasive bipolar electrode for electroporation[J]. Biology(Basel), 2020, 9( 9): 303. DOI: 10.3390/biology9090303. [12] LEE EW, SHAHROUKI P, PETERSON S, et al. Safety of irreversible electroporation ablation of the pancreas[J]. Pancreas, 2021, 50( 9): 1281- 1286. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001916. [13] AGNASS P, van VELDHUISEN E, VOGEL JA, et al. Thermodynamic profiling during irreversible electroporation in porcine liver and pancreas: A case study series[J]. J Clin Transl Res, 2020, 5( 3): 109- 132. [14] SOROKIN I, CANVASSER N, JOHNSON B, et al. Irreversible electroporation for renal ablation does not cause significant injury to adjacent ureter or bowel in a porcine model[J]. J Endourol, 2021, 35( 6): 873- 877. DOI: 10.1089/end.2020.0856. [15] MA XY, XIAO YY, ZHANG X, et al. Comparison of irreversible electroporation with cryotherapyablation in porcine liver tissue[J]. Chin J Interv Imag Ther, 2015, 12( 5): 267- 270. DOI: 10.13929/j.1672-8475.2015.05.004.马旭阳, 肖越勇, 张欣, 等. 不可逆电穿孔与冷冻治疗消融猪肝脏组织对比分析[J]. 中国介入影像与治疗学, 2015, 12( 5): 267- 270. DOI: 10.13929/j.1672-8475.2015.05.004. [16] MIZRAHI JD, SURANA R, VALLE JW, et al. Pancreatic cancer[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395( 10242): 2008- 2020. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30974-0. [17] GUGENHEIM J, CROVETTO A, PETRUCCIANI N. Neoadjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer[J]. Updates Surg, 2022, 74( 1): 35- 42. DOI: 10.1007/s13304-021-01186-1. [18] ZHANG BL, ZHOU FY, HONG JZ, et al. The role of FOLFIRINOX in metastatic pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19( 1): 182. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-021-02291-6. [19] PASSARDI A, RAPPOSELLI IG, SCARPI E, et al. Multimodal treatment with GEMOX plus helical tomotherapy in unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis of two phase 2 studies[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11( 8): 1200. DOI: 10.3390/biom11081200. [20] General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 5): 1006- 1030. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.007.国家卫生健康委办公厅. 胰腺癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 5): 1006- 1030. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.007. [21] TASU JP, TOUGERON D, ROLS MP. Irreversible electroporation and electrochemotherapy in oncology: State of the art[J]. Diagn Interv Imaging, 2022, 103( 11): 499- 509. DOI: 10.1016/j.diii.2022.09.009. [22] LIANG B, NIU LZ, ZENG JY, et al. Irreversible electroporation ablation of the hepatic region close to the gallbladder: Pathological observation in experimental rabbits[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2014, 23( 4): 320- 324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2014.04.012.梁冰, 牛立志, 曾健滢, 等. 不可逆电穿孔消融兔胆囊侧肝脏病理学观察[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2014, 23( 4): 320- 324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2014.04.012. [23] NIU LZ, ZENG JY, ZHANG YS, et al. Irreversible electroporation ablation therapy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Observation of its safety and short-term effect[J]. J Interv Radiol, 2016, 25( 3): 225- 230.牛立志, 曾健滢, 张怡湜, 等. 不可逆电穿孔消融治疗胰腺癌的安全性及近期疗效观察[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2016, 25( 3): 225- 230. [24] MEIJERINK MR, RUARUS AH, VROOMEN LGPH, et al. Irreversible electroporation to treat unresectable colorectal liver metastases(COLDFIRE-2): A phase II, two-center, single-arm clinical trial[J]. Radiology, 2021, 299( 2): 470- 480. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2021203089. [25] RUARUS AH, VROOMEN LGPH, GEBOERS B, et al. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation in locally advanced and recurrent pancreatic cancer(PANFIRE-2): A multicenter, prospective, single-arm, phase II study[J]. Radiology, 2020, 294( 1): 212- 220. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2019191109. [26] WAH TM, LENTON J, SMITH J, et al. Irreversible electroporation(IRE) in renal cell carcinoma(RCC): A mid-term clinical experience[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31( 10): 7491- 7499. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-021-07846-5. [27] WANG HF, XUE W, YAN WG, et al. Extended focal ablation of localized prostate cancer with high-frequency irreversible electroporation: A nonrandomized controlled trial[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157( 8): 693- 700. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2022.2230. [28] Chinese Society of Interventional and Minimally Invasive Therapy, China Medicine Education Association. Expert consensus on image-guided irreversible electroporation ablation for pancreatic cancer(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 2): 299- 302. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.02.011.中国医药教育协会介入微创治疗专业委员会. 影像学引导胰腺癌不可逆电穿孔消融治疗专家共识2018版[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 2): 299- 302. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.02.011. [29] RASHID MF, HECHT EM, STEINMAN JA, et al. Irreversible electroporation of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a primer for the radiologist[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY), 2018, 43( 2): 457- 466. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-017-1349-3. -



 PDF下载 ( 1263 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1263 KB)

 下载:
下载: