Wnt信号通路与肝再生的关系及其在肝脏疾病中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240529
The relationship between the Wnt signaling pathway and liver regeneration and its role in liver diseases
-
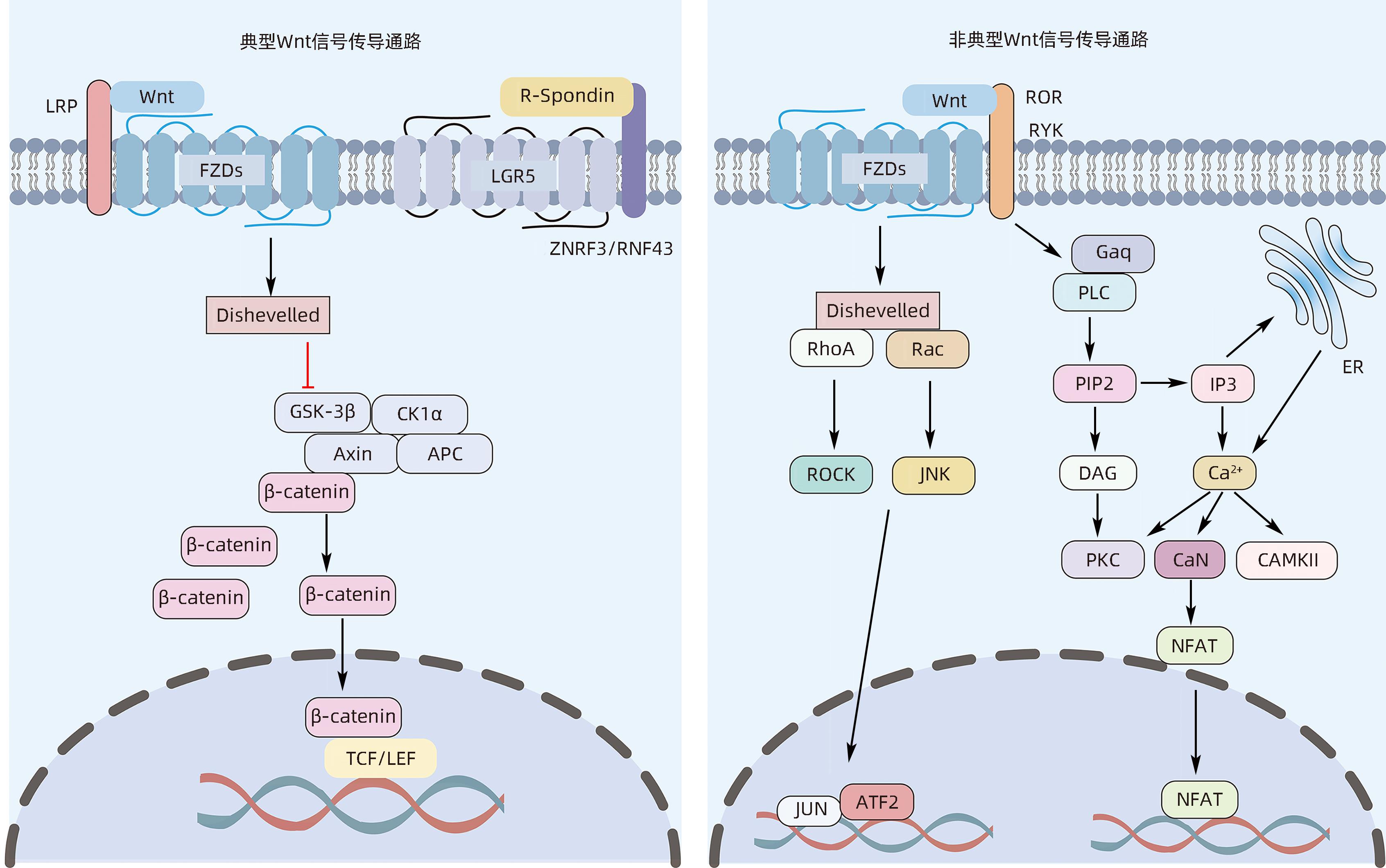
摘要: Wnt信号通路在维持肝脏内稳态和肝脏再生过程中扮演重要角色,在成熟的健康肝脏中,Wnt信号通路大多是不活跃的,但在细胞更新或再生过程中,以及在某些病理条件、疾病、癌前状态和癌症中,Wnt信号通路被持续过度激活。持续的肝细胞损伤常常会导致慢性肝病,如肝纤维化、肝硬化及肝癌等。本文概述了Wnt信号通路的基本结构特点,详细分析了其在多种肝脏疾病病理进展所扮演的重要角色,希望为临床防治肝脏疾病提供新思路。Abstract: The Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in maintaining liver homeostasis and liver regeneration. In healthy livers, the Wnt signaling pathway is mostly inactive, but it is continuously overactivated during cell renewal or regeneration processes, as well as in certain pathological conditions, diseases, precancerous states, and cancers. Persistent liver cell injury often leads to chronic liver diseases such as liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and liver cancer. This article summarizes the basic structural features of the Wnt signaling pathway and analyzes its important role in the pathological progression of various liver diseases, so as to provide new ideas for the prevention and treatment of liver diseases in clinical practice.
-
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- Liver Regeneration /
- Wnt Signaling Pathway /
- beta Catenin
-
表 1 针对Wnt/β-catenin信号传导的药物临床试验
Table 1. Clinical trials of agents targeting Wnt/β-catenin signalling
药物 类型 靶点 作用 阶段 临床试验记录 LGK974(WNT974) 融合蛋白 Wnt配体 FZD8融合蛋白与FZD8竞争结合Wnt配体 Ⅰ期 NCT01608867,NCT02050178, NCT02069145,NCT02092363 OMP-131R10 单抗 R-spondin 3 抑制 RSPO-LGR-ZNRF3/RNF43复合体 Ⅰ期 NCT02482441 OTSA101 单抗 FZD10 抗FZD10型单抗 Ⅰ期 NCT01469975 OMP-18R5 单抗 FZD受体 抗FZD受体型单抗 Ⅰ期 NCT01345201,NCT01957007, NCT01973309,NCT02005315 DKN-01 单抗 DKK1 抗DKK1型单抗,抑制非典型β-catenin传导途径 Ⅰ期, Ⅱ期 NCT01457417,NCT01711671, NCT02013154,NCT02375880 BHQ880 单抗 DKK1 抗DKK1型单抗,抑制非典型β-catenin传导途径 Ⅰ期, Ⅱ期 NCT00741377,NCT01302886, NCT01337752 Foxy-5 小肽 FZD受体 Wnt 5a类似物 Ⅰ期 NCT02020291,NCT02655952 PRI 724 小分子 β-catenin, CREB结合蛋白 下调β-catenin反应基因 Ⅰ期, Ⅱ期 NCT01302405,NCT01606579, NCT01764477,NCT02195440 SM08502 小分子 未知 抑制β-catenin传导途径 Ⅰ期 NCT03355066 -
[1] TREFTS E, GANNON M, WASSERMAN DH. The liver[J]. Curr Biol, 2017, 27( 21): R1147- R1151. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.09.019. [2] BAJAJ JS. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16( 4): 235- 246. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-018-0099-1. [3] MANDATO C, di NUZZI A, VAJRO P. Nutrition and liver disease[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 10( 1): 9. DOI: 10.3390/nu10010009. [4] XIAO J, WANG F, WONG NK, et al. Global liver disease burdens and research trends: Analysis from a Chinese perspective[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71( 1): 212- 221. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.004. [5] ASRANI SK, DEVARBHAVI H, EATON J, et al. Burden of liver diseases in the world[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70( 1): 151- 171. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.09.014. [6] NUSSE R, CLEVERS H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities[J]. Cell, 2017, 169( 6): 985- 999. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016. [7] LOH KM, van AMERONGEN R, NUSSE R. Generating cellular diversity and spatial form: Wnt signaling and the evolution of multicellular animals[J]. Dev Cell, 2016, 38( 6): 643- 655. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.08.011. [8] NAPOLITANO T, SILVANO S, AYACHI C, et al. Wnt pathway in pancreatic development and pathophysiology[J]. Cells, 2023, 12( 4): 565. DOI: 10.3390/cells12040565. [9] RASLAN AA, YOON JK. WNT signaling in lung repair and regeneration[J]. Mol Cells, 2020, 43( 9): 774- 783. DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2020.0059. [10] STEINHART Z, ANGERS S. Wnt signaling in development and tissue homeostasis[J]. Development, 2018, 145( 11): dev146589. DOI: 10.1242/dev.146589. [11] ZHAN T, RINDTORFF N, BOUTROS M. Wnt signaling in cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36( 11): 1461- 1473. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.304. [12] CLEVERS H, NUSSE R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease[J]. Cell, 2012, 149( 6): 1192- 1205. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012. [13] MONGA SP, PEDIADITAKIS P, MULE K, et al. Changes in WNT/beta-catenin pathway during regulated growth in rat liver regeneration[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 33( 5): 1098- 1109. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.23786. [14] CHEN TY, OH S, GREGORY S, et al. Single-cell omics analysis reveals functional diversification of hepatocytes during liver regeneration[J]. JCI Insight, 2020, 5( 22): e141024. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.141024. [15] APTE U, THOMPSON MD, CUI SS, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates oval cell response in rodents[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47( 1): 288- 295. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21973. [16] NELSEN CJ, RICKHEIM DG, TIMCHENKO NA, et al. Transient expression of cyclin D1 is sufficient to promote hepatocyte replication and liver growth in vivo[J]. Cancer Res, 2001, 61( 23): 8564- 8568. [17] TAN XP, BEHARI J, CIEPLY B, et al. Conditional deletion of beta-catenin reveals its role in liver growth and regeneration[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 131( 5): 1561- 1572. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.042. [18] PLANAS-PAZ L, ORSINI V, BOULTER L, et al. The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module controls liver zonation and size[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2016, 18( 5): 467- 479. DOI: 10.1038/ncb3337. [19] SUN TL, PIKIOLEK M, ORSINI V, et al. AXIN2+ pericentral hepatocytes have limited contributions to liver homeostasis and regeneration[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2020, 26( 1): 97- 107. e 6. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.10.011. [20] JHO EH, ZHANG T, DOMON C, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2002, 22( 4): 1172- 1183. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1172-1183.2002. [21] LUSTIG B, JERCHOW B, SACHS M, et al. Negative feedback loop of Wnt signaling through upregulation of conductin/axin2 in colorectal and liver tumors[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2002, 22( 4): 1184- 1193. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1184-1193.2002. [22] JUNG YS, JUN S, KIM MJ, et al. TMEM9 promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through vacuolar-ATPase-activated Wnt/β-catenin signalling[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2018, 20( 12): 1421- 1433. DOI: 10.1038/s41556-018-0219-8. [23] HENDERSON NC, RIEDER F, WYNN TA. Fibrosis: From mechanisms to medicines[J]. Nature, 2020, 587( 7835): 555- 566. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2938-9. [24] SEKI E, SCHWABE RF. Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 3): 1066- 1079. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27332. [25] GE WS, WANG YJ, WU JX, et al. β-catenin is overexpressed in hepatic fibrosis and blockage of Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 9( 6): 2145- 2151. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2099. [26] XIONG WJ, HU LJ, JIAN YC, et al. Wnt5a participates in hepatic stellate cell activation observed by gene expression profile and functional assays[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012, 18( 15): 1745- 1752. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i15.1745. [27] MYUNG SJ, YOON JH, GWAK GY, et al. Wnt signaling enhances the activation and survival of human hepatic stellate cells[J]. FEBS Lett, 2007, 581( 16): 2954- 2958. DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.05.050. [28] TOKUNAGA Y, OSAWA Y, OHTSUKI T, et al. Selective inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin/CBP signaling ameliorates hepatitis C virus-induced liver fibrosis in mouse model[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7( 1): 325. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00282-w. [29] IRVINE KM, CLOUSTON AD, GADD VL, et al. Deletion of Wntless in myeloid cells exacerbates liver fibrosis and the ductular reaction in chronic liver injury[J]. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, 2015, 8: 19. DOI: 10.1186/s13069-015-0036-7. [30] PREZIOSI ME, SINGH S, VALORE EV, et al. Mice lacking liver-specific β-catenin develop steatohepatitis and fibrosis after iron overload[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67( 2): 360- 369. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.012. [31] GEH D, ANSTEE QM, REEVES HL. NAFLD-associated HCC: Progress and opportunities[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2021, 8: 223- 239. DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S272213. [32] MONGA SP. β-catenin signaling and roles in liver homeostasis, injury, and tumorigenesis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2015, 148( 7): 1294- 1310. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.056. [33] SEO MH, LEE JM, HONG SW, et al. Exendin-4 inhibits hepatic lipogenesis by increasing β-catenin signaling[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11( 12): e0166913. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166913. [34] DEBEBE A, MEDINA V, CHEN CY, et al. Wnt/β-catenin activation and macrophage induction during liver cancer development following steatosis[J]. Oncogene, 2017, 36( 43): 6020- 6029. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2017.207. [35] LIU SG, YEH TH, SINGH VP, et al. β-catenin is essential for ethanol metabolism and protection against alcohol-mediated liver steatosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55( 3): 931- 940. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24766. [36] GO GW, SRIVASTAVA R, HERNANDEZ-ONO A, et al. The combined hyperlipidemia caused by impaired Wnt-LRP6 signaling is reversed by Wnt3a rescue[J]. Cell Metab, 2014, 19( 2): 209- 220. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.11.023. [37] CARPINO G, NOBILI V, RENZI A, et al. Macrophage activation in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) correlates with hepatic progenitor cell response via Wnt3a pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11( 6): e0157246. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157246. [38] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline on the management of cholestasis liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 1): 62- 69. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211112-00795.中华医学会肝病学分会. 胆汁淤积性肝病管理指南(2021年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 1): 62- 69. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20211112-00795. [39] YEH TH, KRAULAND L, SINGH V, et al. Liver-specific β-catenin knockout mice have bile canalicular abnormalities, bile secretory defect, and intrahepatic cholestasis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52( 4): 1410- 1419. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23801. [40] LEMBERGER UJ, FUCHS CD, KARER M, et al. Hepatocyte specific expression of an oncogenic variant of β-catenin results in cholestatic liver disease[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7( 52): 86985- 86998. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.13521. [41] SHACKEL NA, MCGUINNESS PH, ABBOTT CA, et al. Identification of novel molecules and pathogenic pathways in primary biliary cirrhosis: CDNA array analysis of intrahepatic differential gene expression[J]. Gut, 2001, 49( 4): 565- 576. DOI: 10.1136/gut.49.4.565. [42] TANAKA A, LEUNG PS, KENNY TP, et al. Genomic analysis of differentially expressed genes in liver and biliary epithelial cells of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. J Autoimmun, 2001, 17( 1): 89- 98. DOI: 10.1006/jaut.2001.0522. [43] THOMPSON MD, AWUAH P, SINGH S, et al. Disparate cellular basis of improved liver repair in beta-catenin-overexpressing mice after long-term exposure to 3, 5-diethoxycarbonyl-1, 4-dihydrocollidine[J]. Am J Pathol, 2010, 177( 4): 1812- 1822. DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100173. [44] OKABE H, YANG J, SYLAKOWSKI K, et al. Wnt signaling regulates hepatobiliary repair following cholestatic liver injury in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64( 5): 1652- 1666. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28774. [45] SACKETT SD, GAO Y, SHIN S, et al. Foxl1 promotes liver repair following cholestatic injury in mice[J]. Lab Invest, 2009, 89( 12): 1387- 1396. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2009.103. [46] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68( 6): 394- 424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. [47] GILES RH, van ES JH, CLEVERS H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2003, 1653( 1): 1- 24. DOI: 10.1016/s0304-419x(03)00005-2. [48] WANG Z, SHENG YY, GAO XM, et al. β-catenin mutation is correlated with a favorable prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Clin Oncol, 2015, 3( 4): 936- 940. DOI: 10.3892/mco.2015.569. [49] DING X, YANG Y, HAN BD, et al. Transcriptomic characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma with CTNNB1 mutation[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9( 5): e95307. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095307. [50] LIAO X, SONG G, XU ZH, et al. Oxaliplatin resistance is enhanced by saracatinib via upregulation Wnt-ABCG1 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20( 1): 31. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-6480-9. [51] LEUNG HW, LEUNG CON, LAU EY, et al. EPHB2 activates β-catenin to enhance cancer stem cell properties and drive sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81( 12): 3229- 3240. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0184. [52] KARABICICI M, AZBAZDAR Y, OZHAN G, et al. Changes in Wnt and TGF-β signaling mediate the development of regorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HuH7[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 639779. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.639779. [53] CADORET A, OVEJERO C, SAADI-KHEDDOUCI S, et al. Hepatomegaly in transgenic mice expressing an oncogenic form of beta-catenin[J]. Cancer Res, 2001, 61( 8): 3245- 3249. [54] ZHAN N, MICHAEL AA, WU KY, et al. The effect of selective c-MET inhibitor on hepatocellular carcinoma in the MET-active, β-catenin-mutated mouse model[J]. Gene Expr, 2018, 18( 2): 135- 147. DOI: 10.3727/105221618X15174108894682. [55] PATIL MA, LEE SA, MACIAS E, et al. Role of cyclin D1 as a mediator of c-met- and beta-catenin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69( 1): 253- 261. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2514. [56] BANALES JM, CARDINALE V, CARPINO G, et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma(ENS-CCA)[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 13( 5): 261- 280. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.51. [57] TOKUMOTO N, IKEDA S, ISHIZAKI Y, et al. Immunohistochemical and mutational analyses of Wnt signaling components and target genes in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas[J]. Int J Oncol, 2005, 27( 4): 973- 980. [58] ZHANG KS, ZHOU Q, WANG YF, et al. Inhibition of Wnt signaling induces cell apoptosis and suppresses cell proliferation in cholangiocarcinoma cells[J]. Oncol Rep, 2013, 30( 3): 1430- 1438. DOI: 10.3892/or.2013.2560. [59] SUGIMACHI K, TAGUCHI K, AISHIMA S, et al. Altered expression of beta-catenin without genetic mutation in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2001, 14( 9): 900- 905. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.3880409. [60] LOILOME W, BUNGKANJANA P, TECHASEN A, et al. Activated macrophages promote Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cholangiocarcinoma cells[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35( 6): 5357- 5367. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-1698-2. [61] BOULTER L, GUEST RV, KENDALL TJ, et al. WNT signaling drives cholangiocarcinoma growth and can be pharmacologically inhibited[J]. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125( 3): 1269- 1285. DOI: 10.1172/JCI76452. [62] SHEN DY, ZHANG W, ZENG X, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling downregulates P-glycoprotein and reverses multi-drug resistance of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Sci, 2013, 104( 10): 1303- 1308. DOI: 10.1111/cas.12223. [63] HUANG GL, LUO Q, RUI G, et al. Oncogenic activity of retinoic acid receptor γ is exhibited through activation of the Akt/NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2013, 33( 17): 3416- 3425. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00384-13. [64] KOCH A, DENKHAUS D, ALBRECHT S, et al. Childhood hepatoblastomas frequently carry a mutated degradation targeting box of the beta-catenin gene[J]. Cancer Res, 1999, 59( 2): 269- 273. [65] FORBES SA, BEARE D, BOUTSELAKIS H, et al. COSMIC: Somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45( D1): D777- D783. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw1121. [66] ARMENGOL C, CAIRO S, FABRE M, et al. Wnt signaling and hepatocarcinogenesis: The hepatoblastoma model[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2011, 43( 2): 265- 270. DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.012. [67] CAIRO S, ARMENGOL C, DE REYNIÈS A, et al. Hepatic stem-like phenotype and interplay of Wnt/beta-catenin and Myc signaling in aggressive childhood liver cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2008, 14( 6): 471- 484. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.11.002. [68] TAO JY, CALVISI DF, RANGANATHAN S, et al. Activation of β-catenin and Yap1 in human hepatoblastoma and induction of hepatocarcinogenesis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 147( 3): 690- 701. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.05.004. -



 PDF下载 ( 936 KB)
PDF下载 ( 936 KB)

 下载:
下载:


