胰源性糖尿病的发病机制与诊治进展
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240532
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王希望、王晨晓、张永华对研究思路或设计有关键贡献,参与研究数据的获取、分析、解释工作;金晶晶、王莹参与撰写及修改文章;王晓、顾亚娇对文章关键内容进行指导与修改。
-
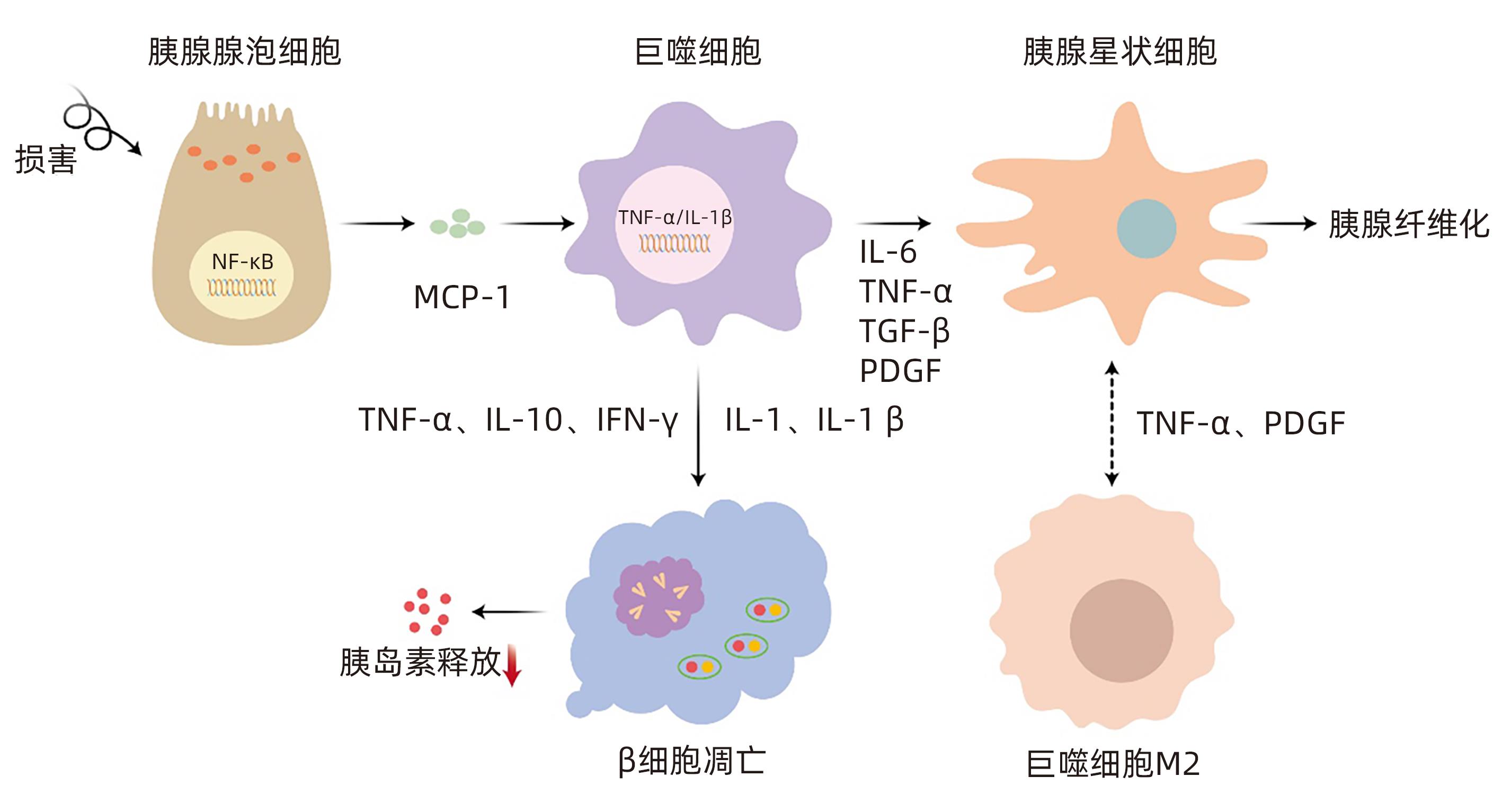
摘要: 胰源性糖尿病是一种继发于胰腺外分泌疾病的糖尿病,2014年被美国糖尿病学会正式提出,其最常见的病因是慢性胰腺炎,其次是胰腺癌。目前该病的临床误诊率极高,且胰源性糖尿病患者相较于2型糖尿病患者有更高的死亡和再入院风险。因此,充分了解、并早期正确识别及诊断胰源型糖尿病,对降低该病的致残率与病死率具有重要意义。本文全面总结了继发于胰腺炎及胰腺癌的胰源性糖尿病的可能发病机制、诊治与管理等方面的研究进展。Abstract: Pancreatogenic diabetes is a type of diabetes mellitus secondary to exocrine pancreatic disease, and it was officially proposed by the American Diabetes Association in 2014, with chronic pancreatitis as the most common etiology, followed by pancreatic cancer. At present, the misdiagnosis rate of this disease is extremely high, and patients with pancreatogenic diabetes have a higher risk of death and readmission than patients with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, it is of great significance to fully understand, correctly identify, and diagnose pancreatogenic diabetes in the early state, so as to reduce the disability rate and mortality rate of this disease. This article reviews the advances in the possible pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and management of pancreatic diabetes secondary to pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.
-
Key words:
- Pancreatic Diseases /
- Diabetes Mellitus /
- Insulin /
- Diagnosis /
- Therapeutics
-
[1] XIAO AY, TAN MLY, WU LM, et al. Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 1( 1): 45- 55. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30004-8. [2] PETROV MS, BASINA M. DIAGNOSIS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Diagnosing and classifying diabetes in diseases of the exocrine pancreas[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2021, 184( 4): R151- R163. DOI: 10.1530/EJE-20-0974. [3] HART PA, BELLIN MD, ANDERSEN DK, et al. Type 3c(pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 1( 3): 226- 237. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(16)30106-6. [4] CHO J, SCRAGG R, PETROV MS. Risk of mortality and hospitalization after post-pancreatitis diabetes mellitus vs type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based matched cohort study[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2019, 114( 5): 804- 812. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000225. [5] WOODMANSEY C, MCGOVERN AP, MCCULLOUGH KA, et al. Incidence, demographics, and clinical characteristics of diabetes of the exocrine pancreas(type 3c): A retrospective cohort study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2017, 40( 11): 1486- 1493. DOI: 10.2337/dc17-0542. [6] SANTOS R, COLEMAN HG, CAIRNDUFF V, et al. Clinical prediction models for pancreatic cancer in general and at-risk populations: A systematic review[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2023, 118( 1): 26- 40. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002022. [7] LIAO WC, CHEN PR, HUANG CC, et al. Relationship between pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes and cachexia[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2020, 11( 4): 899- 908. DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.12553. [8] DONATH MY. Targeting inflammation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Time to start[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2014, 13( 6): 465- 476. DOI: 10.1038/nrd4275. [9] LI GQ, SUN JF, ZHANG J, et al. Identification of inflammation-related biomarkers in diabetes of the exocrine pancreas with the use of weighted gene co-expression network analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13: 839865. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.839865. [10] ZHANG Y, ZHANG WQ, LIU XY, et al. Immune cells and immune cell-targeted therapy in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1151103. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1151103. [11] CASU AN, GRIPPO PJ, WASSERFALL C, et al. Evaluating the immunopathogenesis of diabetes after acute pancreatitis in the diabetes RElated to acute pancreatitis and its mechanisms study: From the type 1 diabetes in acute pancreatitis consortium[J]. Pancreas, 2022, 51( 6): 580- 585. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000002076. [12] PONDUGALA PK, SASIKALA M, GUDURU VR, et al. Interferon-γ decreases nuclear localization of pdx-1 and triggers β-cell dysfunction in chronic pancreatitis[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2015, 35( 7): 523- 529. DOI: 10.1089/jir.2014.0082. [13] ELSHARKAWI I, PARAMBATH D, SABER-AYAD M, et al. Exploring the effect of epigenetic modifiers on developing insulin-secreting cells[J]. Hum Cell, 2020, 33( 1): 1- 9. DOI: 10.1007/s13577-019-00292-y. [14] QIN WJ, KANG MX, LI C, et al. VNN1 overexpression in pancreatic cancer cells inhibits paraneoplastic islet function by increasing oxidative stress and inducing β-cell dedifferentiation[J]. Oncol Rep, 2023, 49( 6): 120. DOI: 10.3892/or.2023.8557. [15] HU FL, LOU N, JIAO JY, et al. Macrophages in pancreatitis: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 131: 110693. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110693. [16] ANDERSEN DK, KORC M, PETERSEN GM, et al. Diabetes, pancreatogenic diabetes, and pancreatic cancer[J]. Diabetes, 2017, 66( 5): 1103- 1110. DOI: 10.2337/db16-1477. [17] LIAO WC, HUANG BS, YU YH, et al. Galectin-3 and S100A9: Novel diabetogenic factors mediating pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2019, 42( 9): 1752- 1759. DOI: 10.2337/dc19-0217. [18] HU YF, ZENG N, GE YQ, et al. Identification of the shared gene signatures and biological mechanism in type 2 diabetes and pancreatic cancer[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2022, 13: 847760. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.847760. [19] XU TT, XU XX, LIU PC, et al. Transcriptomic analyses and potential therapeutic targets of pancreatic cancer with concomitant diabetes[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 563527. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.563527. [20] OLDFIELD L, EVANS A, RAO RG, et al. Blood levels of adiponectin and IL-1Ra distinguish type 3c from type 2 diabetes: Implications for earlier pancreatic cancer detection in new-onset diabetes[J]. EBioMedicine, 2022, 75: 103802. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103802. [21] LEE SH, PARK SY, CHOI CS. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2022, 46( 1): 15- 37. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0280. [22] GILLIES N, PENDHARKAR SA, ASRANI VM, et al. Interleukin-6 is associated with chronic hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in patients after acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2016, 16( 5): 748- 755. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2016.06.661. [23] OLESEN SS, SVANE HML, NICOLAISEN SK, et al. Clinical and biochemical characteristics of postpancreatitis diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study from the Danish nationwide DD2 cohort[J]. J Diabetes, 2021, 13( 12): 960- 974. DOI: 10.1111/1753-0407.13210. [24] ASLAM M, VIJAYASARATHY K, TALUKDAR R, et al. Reduced pancreatic polypeptide response is associated with early alteration of glycemic control in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2020, 160: 107993. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107993. [25] HENNIG R, KEKIS PB, FRIESS H, et al. Pancreatic polypeptide in pancreatitis[J]. Peptides, 2002, 23( 2): 331- 338. DOI: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00605-2. [26] CAI DS, YUAN MS, FRANTZ DF, et al. Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB[J]. Nat Med, 2005, 11( 2): 183- 190. DOI: 10.1038/nm1166. [27] HEO YJ, CHOI SE, JEON JY, et al. Visfatin induces inflammation and insulin resistance via the NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways in hepatocytes[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019, 2019: 4021623. DOI: 10.1155/2019/4021623. [28] CHEANG JY, MOYLE PM. Glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1)-based therapeutics: Current status and future opportunities beyond type 2 diabetes[J]. ChemMedChem, 2018, 13( 7): 662- 671. DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201700781. [29] TUDURÍ E, LÓPEZ M, DIÉGUEZ C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 analogs and their effects on pancreatic islets[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 27( 5): 304- 318. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.004. [30] DRUCKER DJ. Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of glucagon-like peptide-1[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27( 4): 740- 756. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.03.001. [31] SALGAÇO MK, OLIVEIRA LGS, COSTA GN, et al. Relationship between gut microbiota, probiotics, and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2019, 103( 23-24): 9229- 9238. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-019-10156-y. [32] TILG H, ZMORA N, ADOLPH TE, et al. The intestinal microbiota fuelling metabolic inflammation[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2020, 20( 1): 40- 54. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-019-0198-4. [33] TAO J, CHEEMA H, KESH K, et al. Chronic pancreatitis in a caerulein-induced mouse model is associated with an altered gut microbiome[J]. Pancreatology, 2022, 22( 1): 30- 42. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2021.12.003. [34] TALUKDAR R, SARKAR P, JAKKAMPUDI A, et al. The gut microbiome in pancreatogenic diabetes differs from that of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11( 1): 10978. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90024-w. [35] JANDHYALA SM, MADHULIKA A, DEEPIKA G, et al. Altered intestinal microbiota in patients with chronic pancreatitis: Implications in diabetes and metabolic abnormalities[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 43640. DOI: 10.1038/srep43640. [36] ZOU WB, TANG XY, ZHOU DZ, et al. SPINK1, PRSS1, CTRC, and CFTR genotypes influence disease onset and clinical outcomes in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2018, 9( 11): 204. DOI: 10.1038/s41424-018-0069-5. [37] LIU QC, ZHUANG ZH, ZENG K, et al. Prevalence of pancreatic diabetes in patients carrying mutations or polymorphisms of the PRSS1 gene in the Han population[J]. Diabetes Technol Ther, 2009, 11( 12): 799- 804. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2009.0051. [38] KIMURA H, KLEIN AP, HRUBAN RH, et al. The role of inherited pathogenic CDKN2A variants in susceptibility to pancreatic cancer[J]. Pancreas, 2021, 50( 8): 1123- 1130. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001888. [39] YIN LD, WEI JS, LU ZP, et al. Prevalence of germline sequence variations among patients with pancreatic cancer in China[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5( 2): e2148721. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48721. [40] MCWILLIAMS R, HIGHSMITH WE, RABE KG, et al. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator gene carrier status is a risk factor for young onset pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Gut, 2005, 54( 11): 1661- 1662. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.074534. [41] ABE K, KITAGO M, KITAGAWA Y, et al. Hereditary pancreatic cancer[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2021, 26( 10): 1784- 1792. DOI: 10.1007/s10147-021-02015-6. [42] ASSOCIATION AD. 2. classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2021[J]. Diabetes Care, 2021, 44( Suppl 1): S15- S33. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-S002. [43] LÖHR JM, DOMINGUEZ-MUNOZ E, ROSENDAHL J, et al. United European Gastroenterology evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and therapy of chronic pancreatitis(HaPanEU)[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2017, 5( 2): 153- 199. DOI: 10.1177/2050640616684695. [44] UC A, ANDERSEN DK, BELLIN MD, et al. Chronic pancreatitis in the 21st century-research challenges and opportunities: Summary of a national institute of diabetes and digestive and kidney diseases workshop[J]. Pancreas, 2016, 45( 10): 1365- 1375. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000713. [45] CUI YF, ANDERSEN DK. Pancreatogenic diabetes: Special considerations for management[J]. Pancreatology, 2011, 11( 3): 279- 294. DOI: 10.1159/000329188. [46] BELLIN MD. Pancreatogenic diabetes in children with recurrent acute and chronic pancreatitis: Risks, screening, and treatment(mini-review)[J]. Front Pediatr, 2022, 10: 884668. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.884668. [47] WU K, WANG WL, CHEN H, et al. Insulin promotes proliferation of pancreatic ductal epithelial cells by increasing expression of PLK1 through PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 509( 4): 925- 930. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.182. [48] YANG X, XU ZP, ZHANG CL, et al. Metformin, beyond an insulin sensitizer, targeting heart and pancreatic β cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2017, 1863( 8): 1984- 1990. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.09.019. [49] WANG CC, ZHANG TP, LIAO Q, et al. Metformin inhibits pancreatic cancer metastasis caused by SMAD4 deficiency and consequent HNF4G upregulation[J]. Protein Cell, 2021, 12( 2): 128- 144. DOI: 10.1007/s13238-020-00760-4. [50] CHEN K, QIAN WK, JIANG ZD, et al. Metformin suppresses cancer initiation and progression in genetic mouse models of pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16( 1): 131. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0701-0. [51] MAIDA A, LAMONT BJ, CAO X, et al. Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α in mice[J]. Diabetologia, 2011, 54( 2): 339- 349. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-010-1937-z. [52] GOODARZI MO, PETROV MS. Diabetes of the exocrine pancreas: Implications for pharmacological management[J]. Drugs, 2023, 83( 12): 1077- 1090. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-023-01913-5. [53] CAMPAGNOLA P, de PRETIS N, ZORZI A, et al. Chronic pancreatitis and nutritional support[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2023, 62-63: 101823. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2023.101823. [54] DUGGAN SN, SMYTH ND, MURPHY A, et al. High prevalence of osteoporosis in patients with chronic pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 12( 2): 219- 228. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.016. [55] DYTZ MG, MARCELINO PAH, de CASTRO SANTOS O, et al. Clinical aspects of pancreatogenic diabetes secondary to hereditary pancreatitis[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2017, 9: 4. DOI: 10.1186/s13098-017-0203-7. [56] DUGGAN SN, EWALD N, KELLEHER L, et al. The nutritional management of type 3c(pancreatogenic) diabetes in chronic pancreatitis[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2017, 71( 1): 3- 8. DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2016.127. -



 PDF下载 ( 749 KB)
PDF下载 ( 749 KB)

 下载:
下载:


