HBV相关慢加急性肝衰竭患者血清HMGB1、sCD163、PGE2的表达水平及其对预后的预测价值
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240610
Expression levels of serum high-mobility group box 1, soluble CD163, and prostaglandin E2 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related chronic-on-acute liver failure and their value in predicting prognosis
-
摘要:
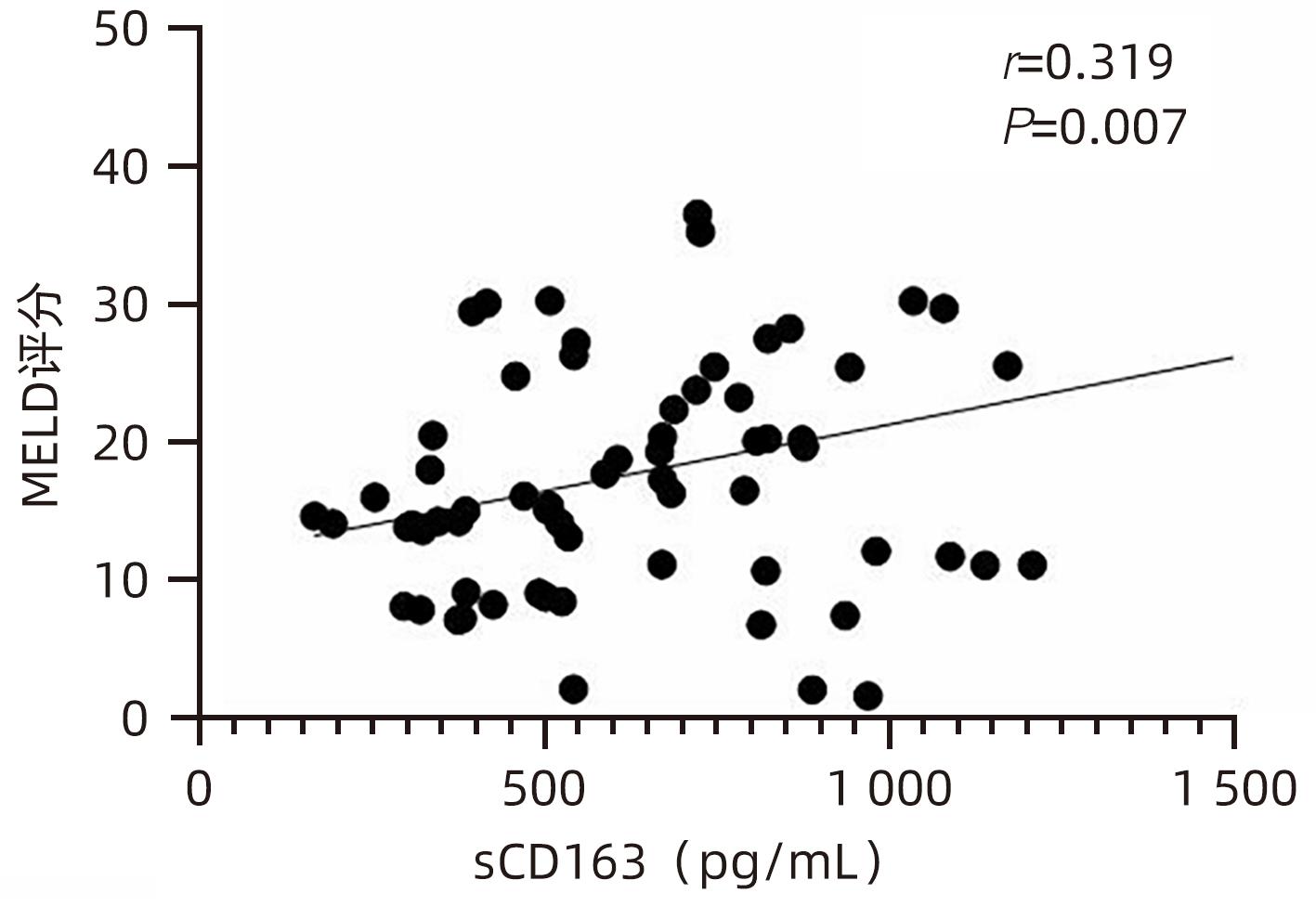
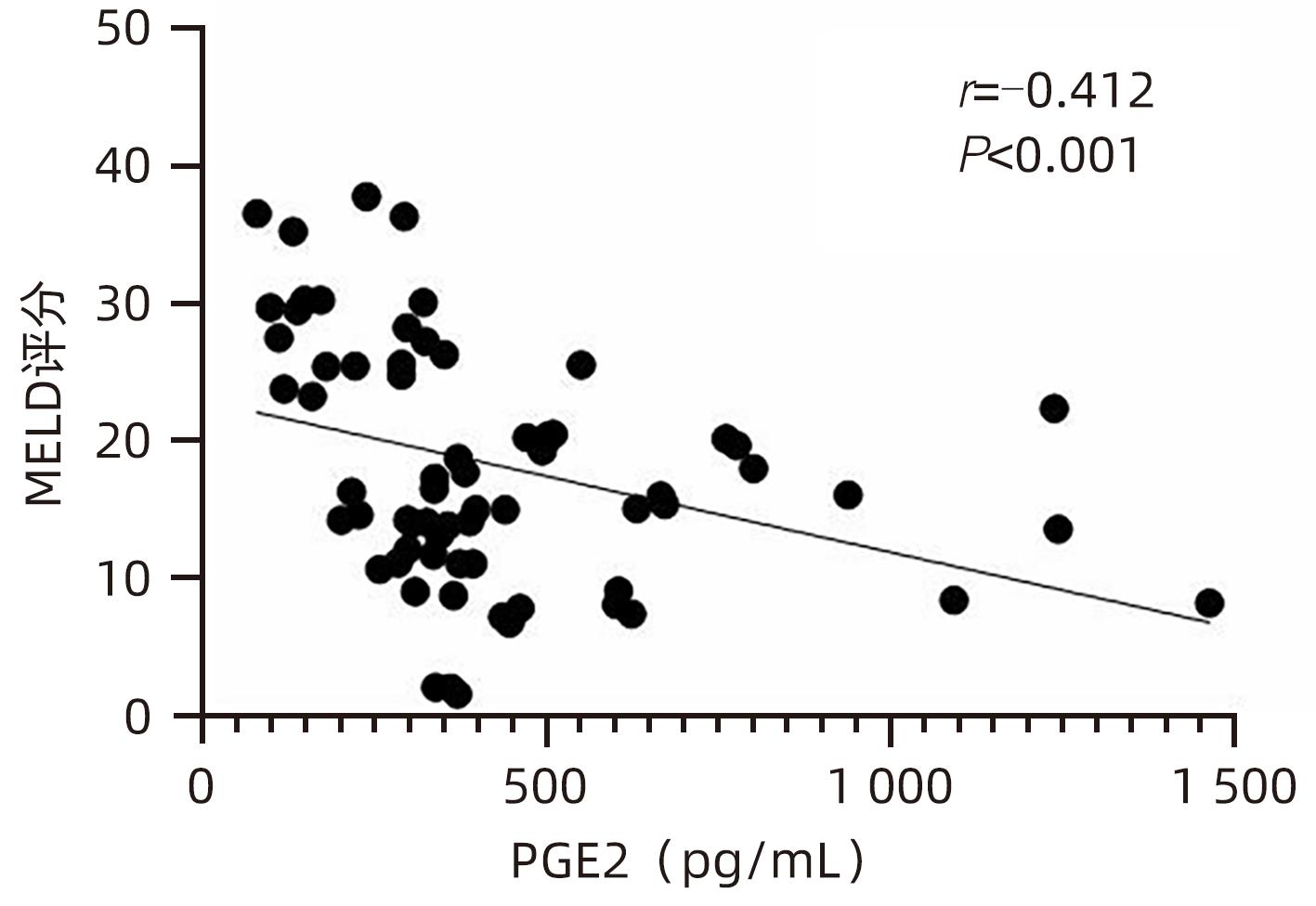
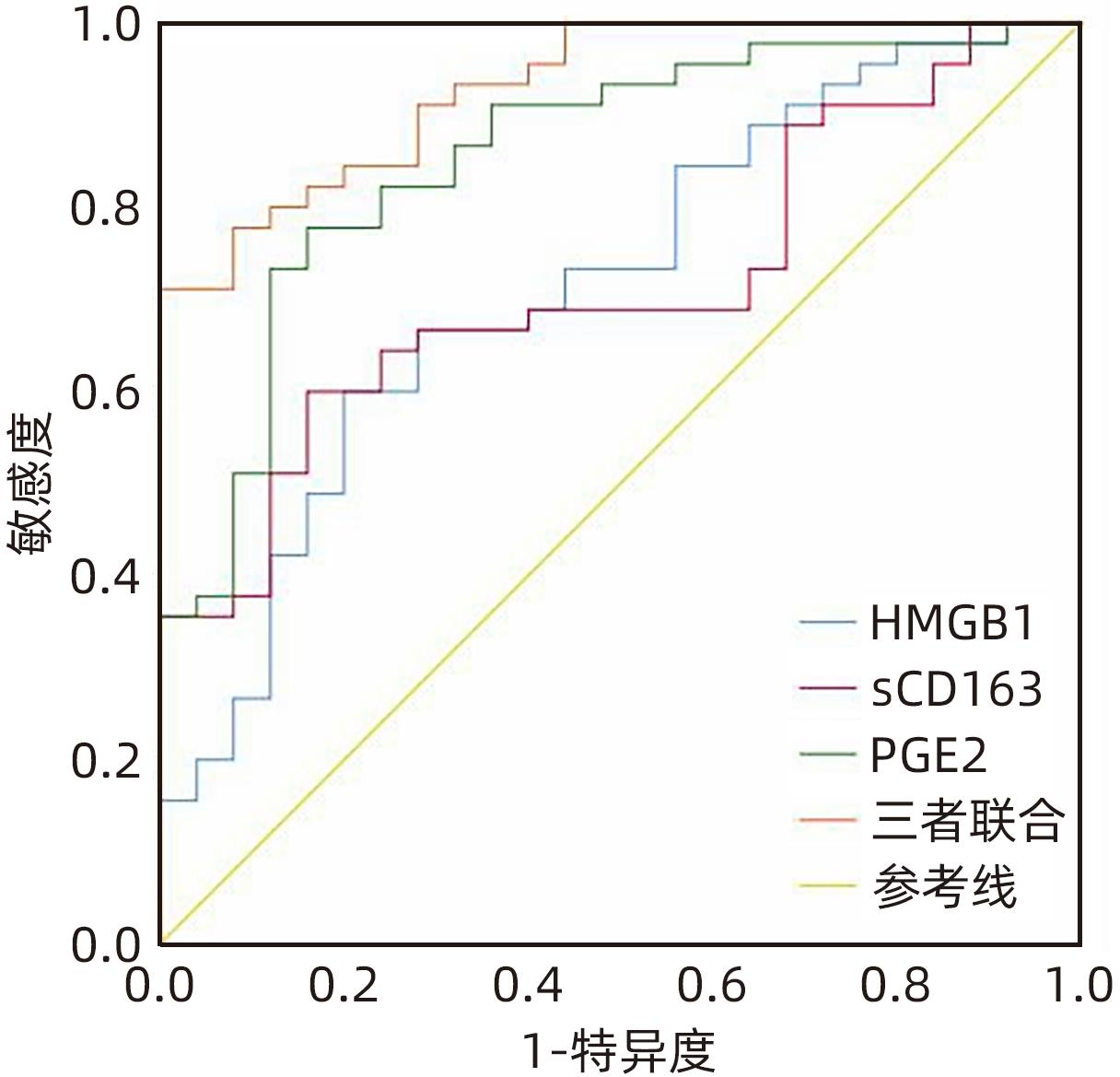
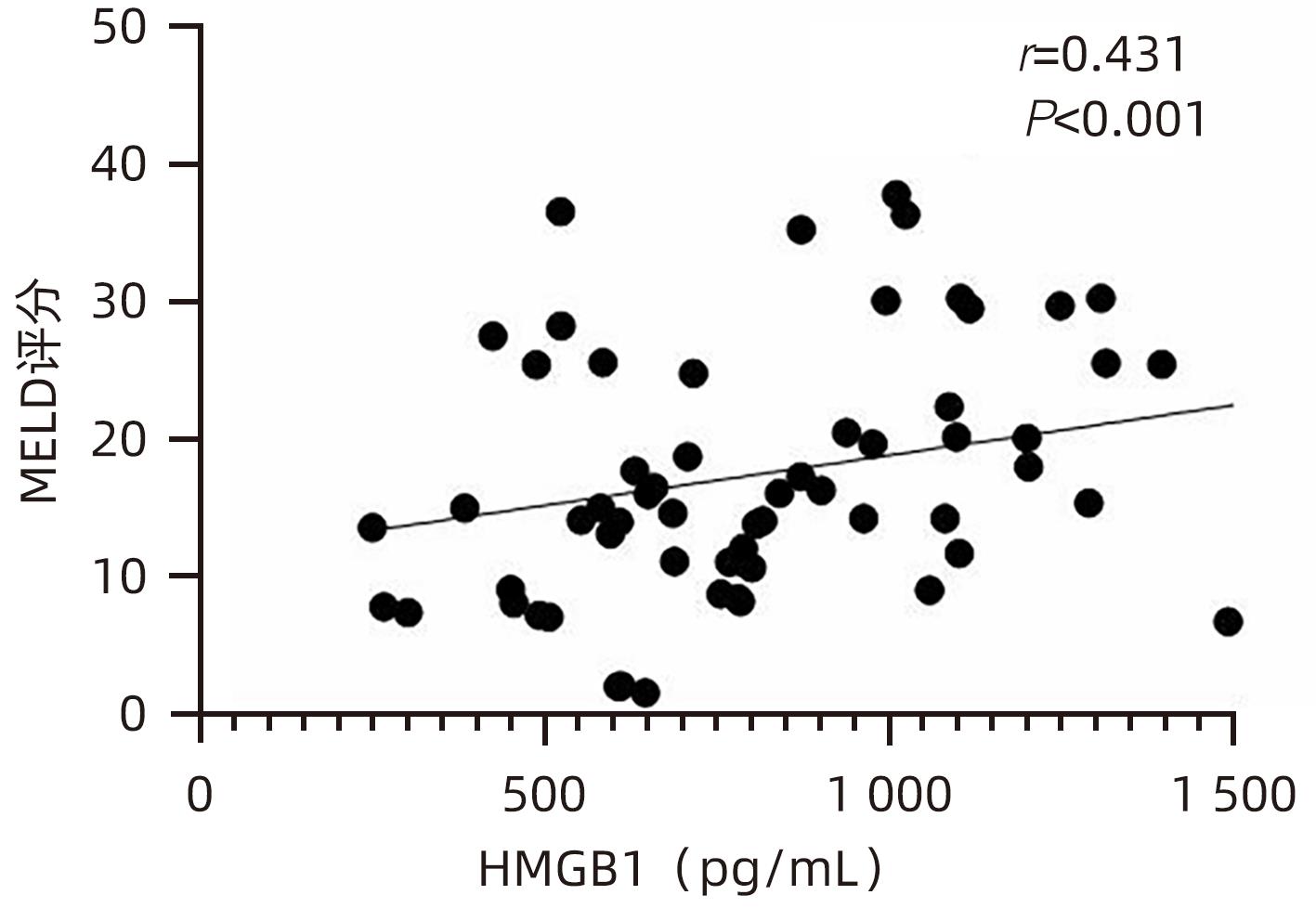
目的 观察HBV相关慢加急性肝衰竭(HBV-ACLF)患者血清高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)、可溶性CD163(sCD163)、前列腺素E2(PGE2)的表达水平,并评估三者单独及联合检测对预后的预测价值。 方法 收集2022年7月1日—2023年9月30日在新乡医学院第一附属医院感染内科住院的HBV-ACLF患者76例,根据28天预后情况,将其分为生存组(n=48)和死亡组(n=28)。收集患者一般资料,计算MELD评分,并采用ELISA法检测血清HMGB1、sCD163和PGE2水平。正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验,非正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验;计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。采用Spearman秩相关性分析HMGB1、sCD163和PGE2与MELD评分的相关性;采用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)分析HMGB1、sCD163和PGE2单独及联合检测对HBV-ACLF患者预后的预测价值。 结果 生存组和死亡组间TBil、WBC、中性粒细胞百分数、降钙素原、血清淀粉样蛋白A、IL-6、血清钠(Na+)、血清肌酐(SCr)差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。死亡组血清HMGB1(Z=-2.997,P=0.003)、sCD163(Z=-2.972,P=0.003)和MELD评分(t=-6.997,P<0.001)显著高于生存组,差异均有统计学意义;死亡组血清PGE2水平显著低于生存组,差异有统计学意义(Z=-4.909,P<0.001)。Spearman秩相关性分析发现,HMGB1、sCD163与MELD评分呈正相关(r值分别为0.431、0.319,P值均<0.05),PGE2与MELD评分呈负相关(r=-0.412,P<0.001)。ROC曲线分析发现,HMGB1、sCD163和PGE2单独预测的曲线下面积(AUC)分别为0.717、0.716、0.856,三者联合预测价值最高,AUC为0.930,敏感度为0.778,特异度为0.920。 结论 血清HMGB1、sCD163、PGE2单独及联合检测在预测HBV-ACLF患者预后方面均具有良好参考价值,三者联合预测价值最高,值得进一步观察和研究。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression levels of serum high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), soluble CD163 (sCD163), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in patients with hepatitis B virus-related chronic-on-acute liver failure (HBV-ACLF), and to evaluate the value of the three indicators used alone or in combination in predicting prognosis. Methods A total of 76 patients with HBV-ACLF who were hospitalized in Department of Infectious Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, from July 1, 2022 to September 30, 2023 were enrolled, and according to the 28-day prognosis, they were divided into survival group with 48 patients and death group with 28 patients. General data were collected, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score was calculated, and ELISA was used to measure the serum levels of HMGB1, sCD163, and PGE2. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between two groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between two groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. The Spearman rank correlation test was used to analyze the correlation of HMGB1, sCD163, and PGE2 with MELD score; the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the value of HMGB1, sCD163, and PGE2 used alone or in combination in predicting the prognosis of HBV-ACLF patients. Results There were significant differences between the two groups in total bilirubin, white blood cell count, the percentage of neutrophils, procalcitonin, serum amyloid A, interleukin-6, serum sodium, and serum creatinine (all P<0.05). Compared with the survival group, the death group had significantly higher serum levels of HMGB1 (Z=-2.997, P=0.003) and sCD163 (Z=-2.972, P=0.003), a significantly higher MELD score (t=-6.997, P<0.001), and a significantly lower serum level of PGE2 (Z=-4.909, P<0.001). The Spearman rank correlation test showed that HMGB1 and sCD163 were positively correlated with MELD score (r=0.431 and 0.319, both P<0.05), while PGE2 was negatively correlated with MELD score (r=-0.412, P<0.05). The ROC curve analysis showed that HMGB1, sCD163, and PGE2 used alone had an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.717, 0.716, and 0.856, respectively, while the combination of the three indicators had the highest predictive value, with an AUC of 0.930, a sensitivity of 0.778, and a specificity of 0.920. Conclusion Serum HMGB1, sCD163, and PGE2 used alone or in combination have a good reference value in predicting the prognosis of HBV-ACLF patients, and the combination of the three indicators has the highest predictive value, which holds promise for further observation and research. -
Key words:
- Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure /
- Prognosis /
- HMGB1 Protein /
- Soluble CD163 /
- Prostaglandin E2
-
表 1 两组患者一般资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
指标 生存组(n=48) 死亡组(n=28) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 34/14 21/7 χ2=0.154 0.695 年龄(岁) 51.213±13.074 52.643±14.794 t=-0.087 0.931 Alb(g/L) 31.000(28.575~33.775) 30.750(28.725~33.150) Z=-0.525 0.600 TBil(µmol/L) 355.203±183.567 475.193±229.273 t=-2.370 0.022 ALT(U/L) 105.000(38.500~269.750) 91.000(38.750~271.750) Z=-0.044 0.965 AST(U/L) 134.500(68.000~191.750) 220.000(82.250~401.500) Z=-1.083 0.279 LDH(U/L) 245.000(218.000~349.250) 368.000(213.750~591.250) Z=-1.421 0.155 PT(s) 19.400(15.425~22.400) 23.400(16.650~43.158) Z=-1.662 0.096 PTA(%) 47.360(38.758~61.998) 36.750(21.503~56.285) Z=-1.815 0.075 INR 1.660(1.337~1.952) 2.145(1.355~3.845) Z=-1.783 0.075 WBC(×109/L) 6.690(4.965~9.250) 11.370(8.340~15.557) Z=-2.821 0.005 PLT(×109/L) 110.500(58.250~202.000) 137.500(65.000~196.500) Z=-0.087 0.930 中性粒细胞百分数(%) 71.250(61.175~81.050) 84.050(79.150~91.225) Z=-3.707 <0.001 SCr(µmol/L) 43.750(36.425~57.975) 61.900(56.975~97.925) Z=-3.161 0.002 Na+(mmol/L) 133.625±3.833 128.857±4.928 t=3.599 0.001 CRP(mg/L) 10.945(5.047~36.680) 32.085(19.615~43.933) Z=-1.689 0.091 PCT(ng/ml) 0.416(0.183~1.100) 1.250(0.388~1.950) Z=-2.305 0.021 IL-6(pg/ml) 15.315(6.522~29.265) 34.250(21.047~84.992) Z=-2.960 0.003 SAA(mg/L) 3.100(1.575~5.175) 9.350(4.575~31.125) Z=-2.877 0.004 表 2 两组患者血清HMGB1、sCD163、PGE2水平和MELD评分比较
Table 2. Comparison of serum HMGB1, sCD163, PGE2 levels and MELD scores between the two groups
指标 生存组(n=48) 死亡组(n=28) 统计值 P值 HMGB1(pg/mL) 756.492(566.918~1 070.678) 1 011.152(795.188~1 465.057) Z=-2.997 0.003 sCD163(pg/mL) 508.675(361.567~825.933) 728.298(607.953~1 010.074) Z=-2.972 0.003 PGE2(pg/mL) 441.120(345.941~632.430) 262.286(158.389~334.938) Z=-4.909 <0.001 MELD评分(分) 13.705±6.243 26.454±8.928 t=-6.997 <0.001 表 3 HMGB1、sCD163、PGE2单独及联合检测对HBV-ACLF患者预后的预测价值
Table 3. Prognostic value of HMGB1, sCD163 and PGE2 alone and in combination in HBV-ACLF patients
指标 最佳截断值 约登指数 敏感度 特异度 AUC 95%CI P值 HMGB1(pg/mL) 788.344 0.400 0.600 0.800 0.717 0.593~0.841 0.003 sCD163(pg/mL) 544.297 0.440 0.600 0.840 0.716 0.596~0.835 0.003 PGE2(pg/mL) 342.819 0.618 0.778 0.840 0.856 0.764~0.948 <0.001 三者联合 0.698 0.778 0.920 0.930 0.875~0.985 <0.001 -
[1] XU MM, KONG M, YU PF, et al. Clinical course and outcome patterns of acute-on-chronic liver failure: a multicenter retrospective cohort study[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2021, 9( 5): 626- 634. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00179. [2] ABUDEIF A, SAYED E, GALAL GM. Characteristics and predictors of short-term mortality in decompensated cirrhotic patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2022, 8( 4): 300- 308. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2022.122332. [3] ABBAS N, RAJORIYA N, ELSHARKAWY AM, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF) in 2022: have novel treatment paradigms already arrived?[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 16( 7): 639- 652. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2022.2097070. [4] CHEN MJ, LI X, TANG SH. Research progress on multidimensional evaluation of liver function in the prognosis of liver failure patients[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05.陈美娟, 李雪, 汤善宏. 多维度评估肝功能在肝衰竭患者预后中研究进展[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05. [5] LIU Y, YUAN W, FANG M, et al. Determination of HMGB1 in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure patients with acute kidney injury: Early prediction and prognostic implications[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1031790. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1031790. [6] GRØNBAEK H, MØLLER HJ, SALIBA F, et al. Improved prediction of mortality by combinations of inflammatory markers and standard clinical scores in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure and acute decompensation[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 36( 1): 240- 248. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15125. [7] HUANG XP, WANG Y, CHEN L, et al. Elevated serum prostaglandin E2 predicts the risk of infection in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure patients[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2017, 10( 9): 916- 920. DOI: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.08.008. [8] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Society of Hepatology. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. [9] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [10] HERNAEZ R, KRAMER JR, LIU Y, et al. Prevalence and short-term mortality of acute-on-chronic liver failure: A national cohort study from the USA[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70( 4): 639- 647. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.018. [11] CHEN KD. Serum levels of miR-122 and HMGB1 and their relationship with disease condition and prognosis in patients with HBV-ACLF[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2022, 35( 2): 135- 140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2022.01.007.陈科第. HBV-ACLF患者血清miR-122和HMGB1水平及其与病情、预后的关系[J]. 传染病信息, 2022, 35( 2): 135- 140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2022.01.007. [12] LAI M, WANG X, YAO QW, et al. Predictive value of the initial MELD score and its derivative scores for early survival rate after liver transplantation in patients with liver failure[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2022, 13( 4): 489- 494. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.04.012.赖曼, 王鑫, 姚勤伟, 等. 术后首次MELD评分及其衍生评分对肝衰竭患者肝移植术后早期生存率的预测价值[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13( 4): 489- 494. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.04.012. [13] CHEN R, KANG R, TANG D. The mechanism of HMGB1 secretion and release[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2022, 54( 2): 91- 102. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-022-00736-w. [14] FANG P, DOU B, LIANG J, et al. Quercetin reduces oxidative stress and apoptosis by inhibiting HMGB1 and its translocation, thereby alleviating liver injury in ACLF rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 2898995. DOI: 10.1155/2021/2898995. [15] HOU W, WEI X, LIANG J, et al. HMGB1-induced hepatocyte pyroptosis expanding inflammatory responses contributes to the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF)[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2021, 14: 7295- 7313. DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S336626. [16] NI YA, CHEN H, NIE H, et al. HMGB1: An overview of its roles in the pathogenesis of liver disease[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2021, 110( 5): 987- 998. DOI: 10.1002/JLB.3MR0121-277R. [17] RASZEJA-WYSZOMIRSKA J, NIEWIŃSKI G, GRACZYŃSKA A, et al. Clinical implication of plasma CD163 in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Transplant Proc, 2022, 54( 4): 1011- 1016. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2022.02.048. [18] NIELSEN MC, HVIDBJERG GANTZEL R, CLÀRIA J, et al. Macrophage activation markers, CD163 and CD206, in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 5). DOI: 10.3390/cells9051175. [19] TRIANTAFYLLOU E, WOOLLARD KJ, MCPHAIL M, et al. The role of monocytes and macrophages in acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2948. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02948. [20] ZHAO R, WU W, ZHOU Z, et al. Prognostic utility of novel biomarkers in acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF) associated with hepatitis B: A multicenter prospective study[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49( 1): 42- 50. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13251. [21] GRONBAK H, RODGAARD-HANSEN S, AAGAARD NK, et al. Macrophage activation markers predict mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis without or with acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF)[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64( 4): 813- 822. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.021. [22] WANG Y, CHEN C, QI J, et al. Altered PGE2-EP2 is associated with an excessive immune response in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Transl Med, 2019, 17( 1): 93. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1844-0. [23] HANGAI S, AO T, KIMURA Y, et al. PGE2 induced in and released by dying cells functions as an inhibitory DAMP[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, 113( 14): 3844- 3849. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1602023113. -



 PDF下载 ( 826 KB)
PDF下载 ( 826 KB)

 下载:
下载: