乙型肝炎肝硬化门静脉高压患者经颈静脉肝内门体分流术后显性肝性脑病风险预测模型的构建
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240613
Construction of a risk prediction model for overt hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis and portal hypertension
-
摘要:
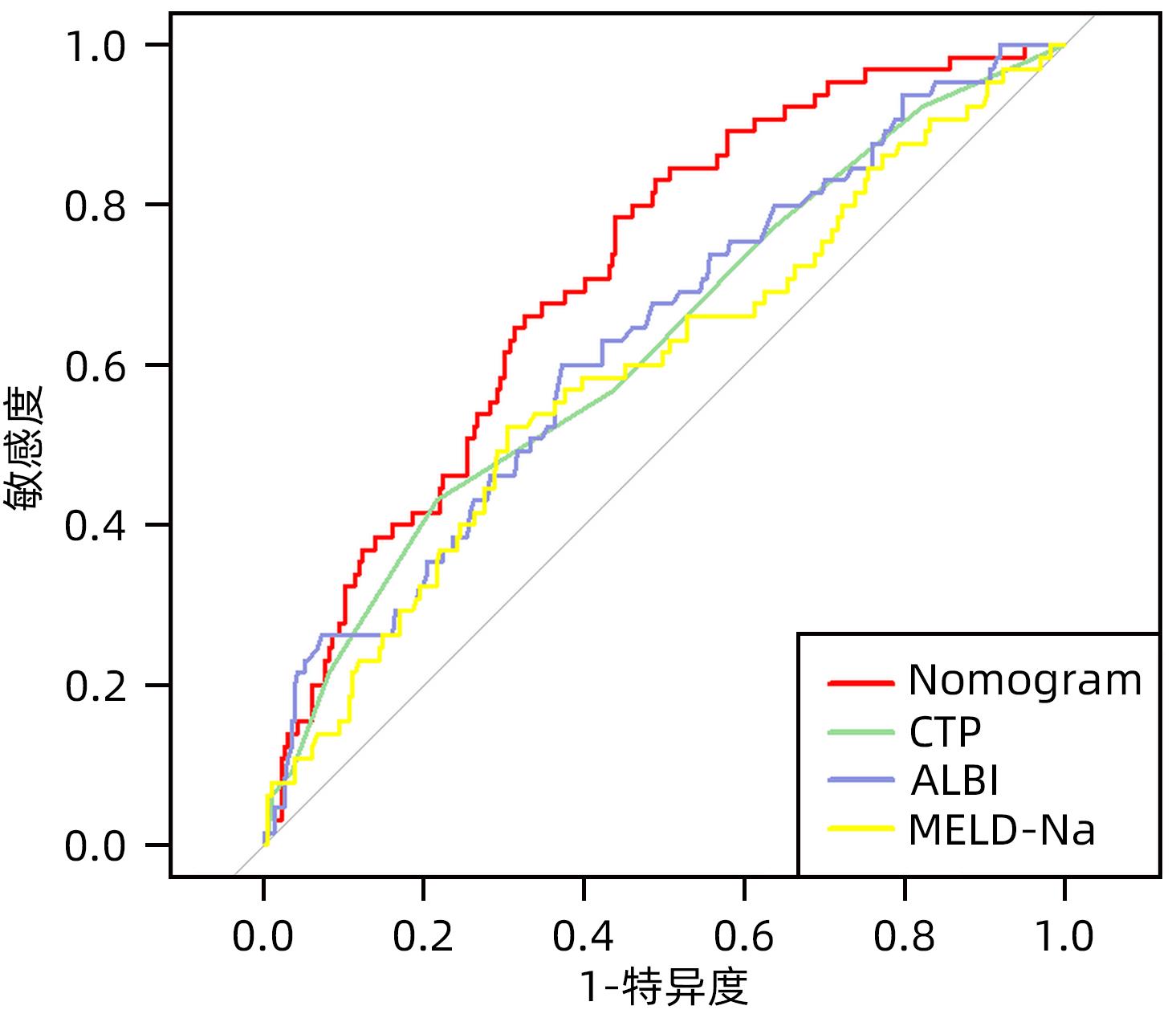
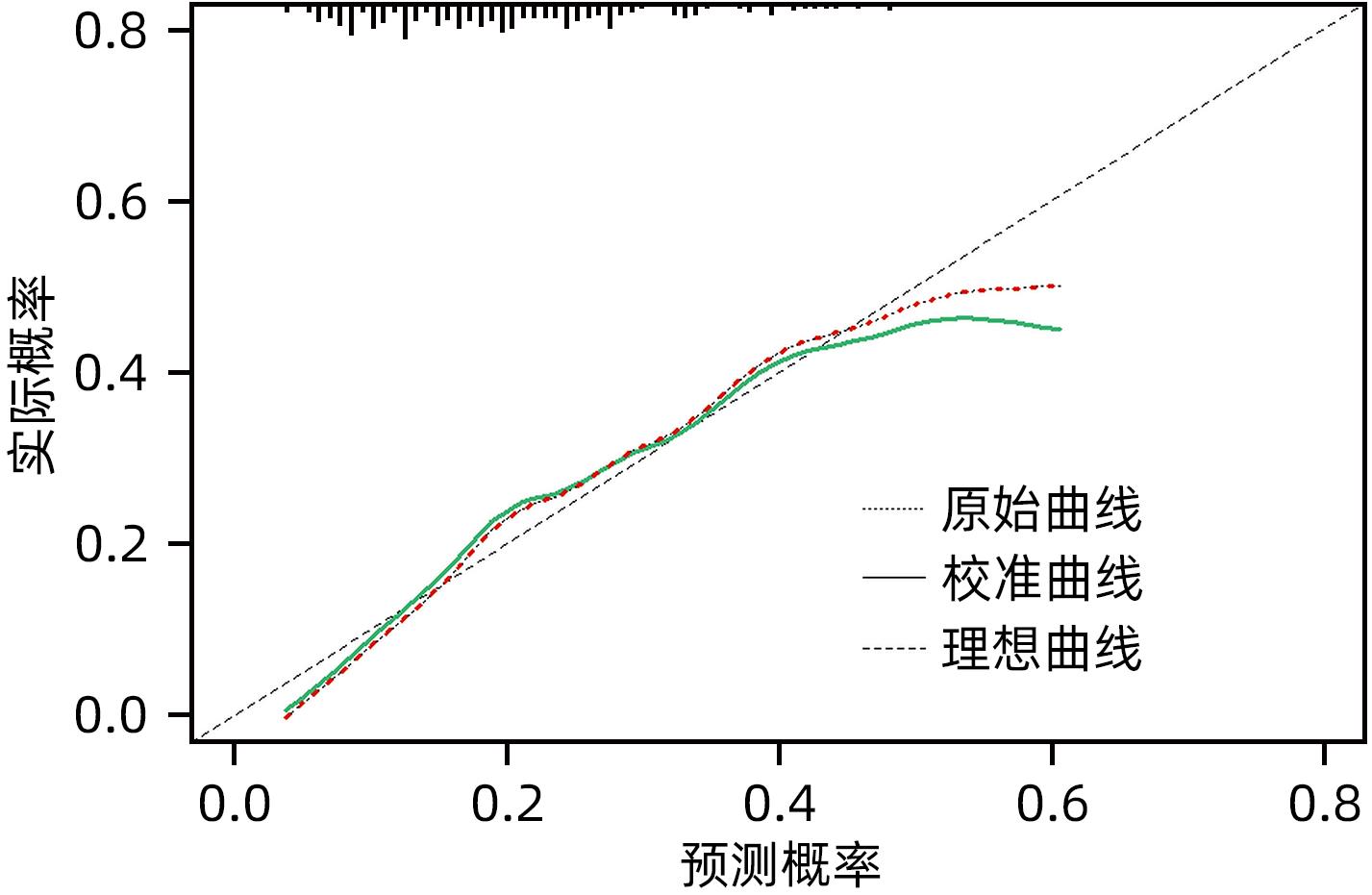
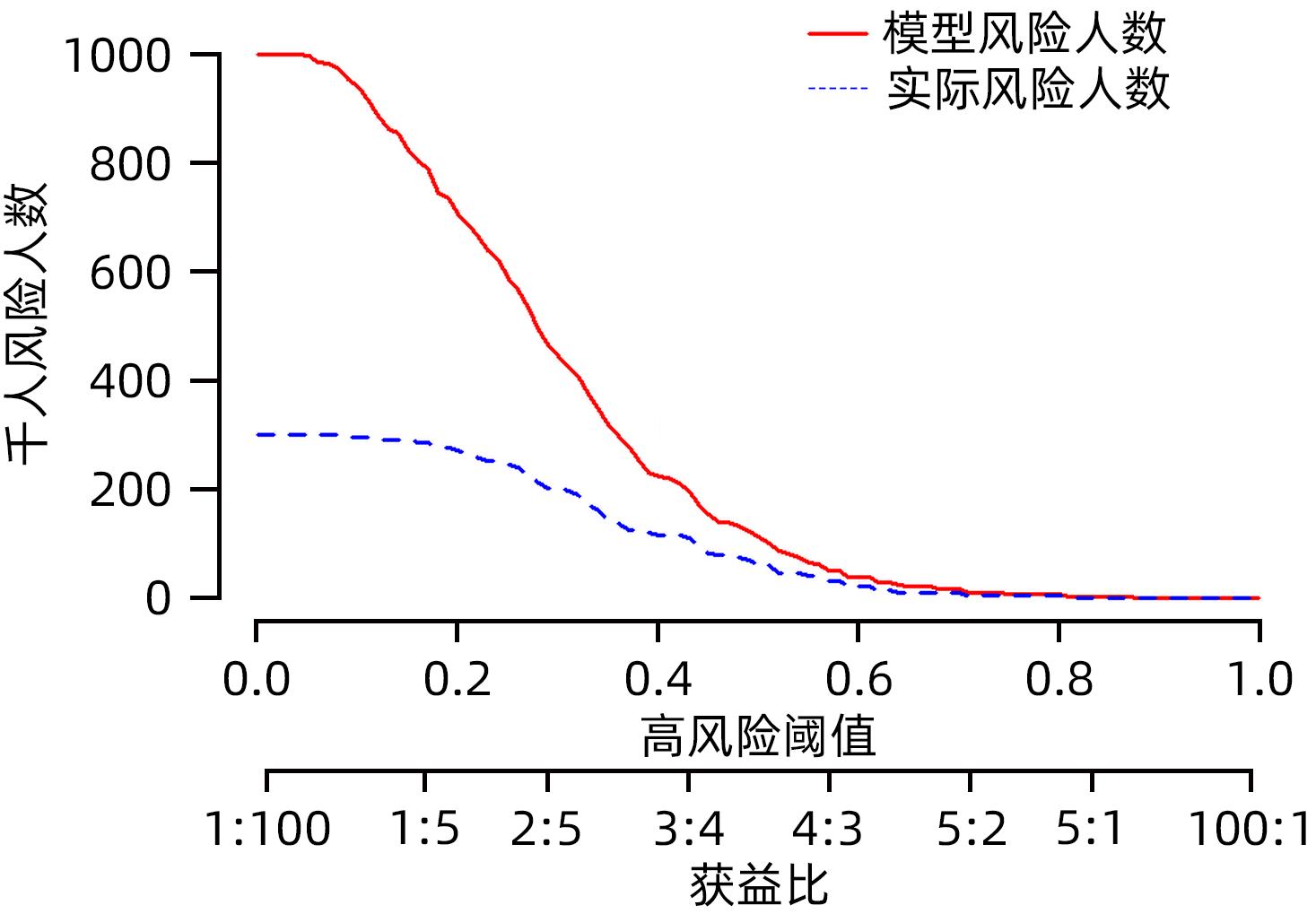
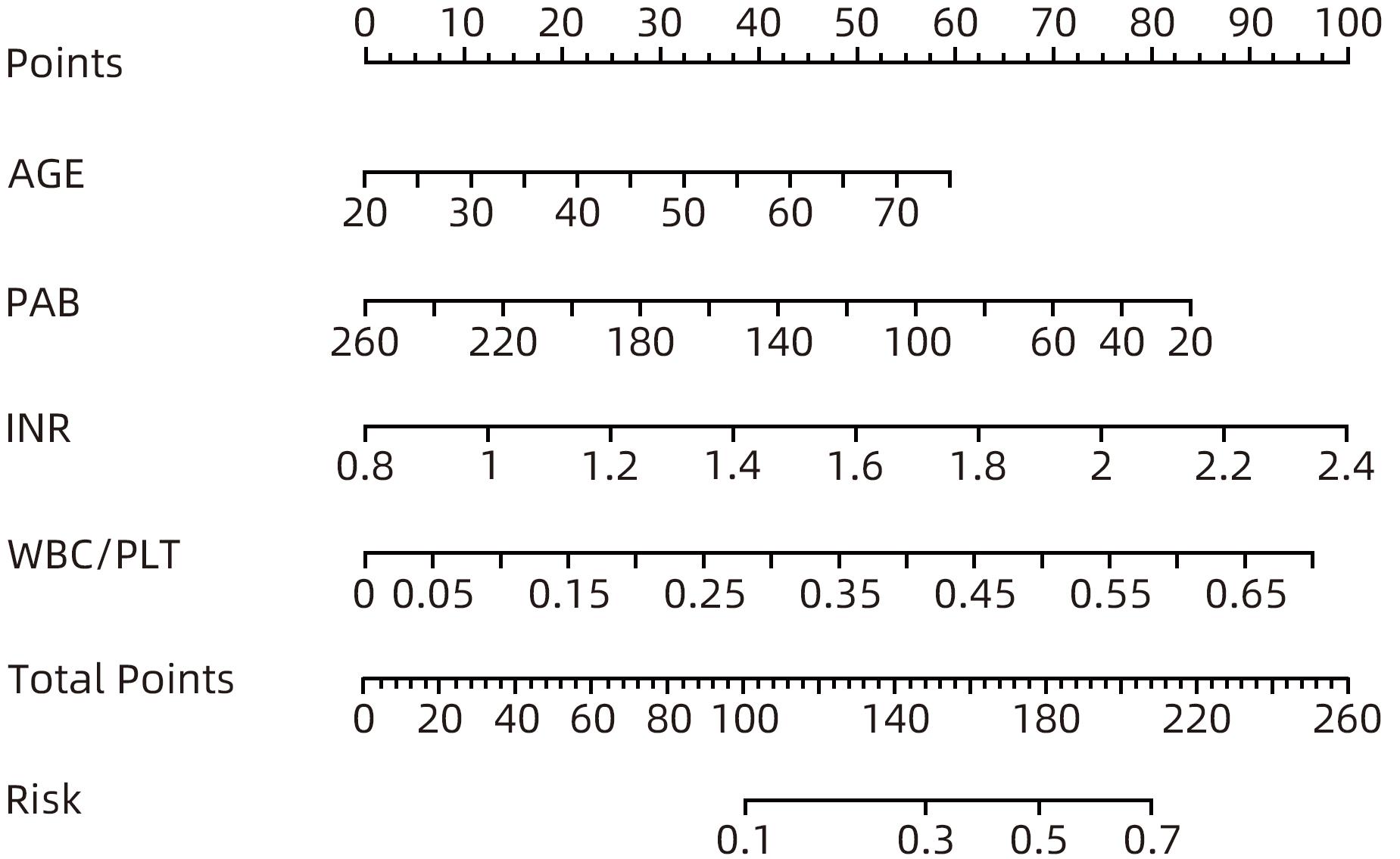
目的 探索乙型肝炎肝硬化患者经颈静脉肝内门体分流术(TIPS)术后显性肝性脑病(OHE)的影响因素,并构建个体化风险预测模型。 方法 选取2017年1月—2021年12月于西部战区总医院消化内科行TIPS治疗的乙型肝炎肝硬化患者302例,按术后是否发生OHE分为无OHE组(237例)和OHE组(65例)。比较两组患者术前的一般资料、实验室检查指标、CTP评分、MELD-Na评分及ALBI评分等。计量资料的两组间比较采用成组t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验,计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。采用单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析筛选乙型肝炎肝硬化患者TIPS术后OHE的影响因素,应用独立影响因素构建Nomogram模型,受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)及校准曲线评价模型的区分度及校准度,决策曲线及临床影响曲线评估模型的临床有效性。 结果 年龄(OR=1.035,95%CI:1.004~1.066)、WBC/PLT(OR=33.725,95%CI:1.220~932.377)、INR(OR=5.149,95%CI:1.052~25.207)、前白蛋白(OR=0.992,95%CI:0.983~1.000)是乙型肝炎肝硬化患者TIPS术后OHE发生的独立预测因素(P值均<0.05)。基于年龄、WBC/PLT、INR、前白蛋白构建的Nomogram模型ROC曲线下面积为0.716(95%CI:0.649~0.781),敏感度为78.5%,特异度为56.1%。 结论 基于年龄、WBC/PLT、INR、PAB建立Nomogram模型,有助于临床预测乙型肝炎肝硬化患者TIPS术后OHE发生风险。 -
关键词:
- 肝硬化 /
- 高血压, 门静脉 /
- 门体分流术, 经颈静脉肝内 /
- 肝性脑病 /
- 列线图
Abstract:Objective To investigate the influencing factors for overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE) in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), and to construct an individualized risk prediction model. Methods A total of 302 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis who underwent TIPS in Department of Gastroenterology, The General Hospital of Western Theater Command, from January 2017 to December 2021 were enrolled, and according to the presence or absence of OHE after surgery, they were divided into non-OHE group with 237 patients and OHE group with 65 patients. The two groups were compared in terms of general data, laboratory markers, Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score, MELD combined with serum sodium concentration (MELD-Na) score, and albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score before surgery. The independent-samples t test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. The univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify the influencing factors for OHE after TIPS in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis, and independent influencing factors were used to construct a nomogram model. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and the calibration curve analysis were used to evaluate the discriminatory ability and calibration of the model, and the decision curve analysis and the clinical impact curve (CIC) were used to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of the model. Results Age (odds ratio [OR]=1.035, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.004 — 1.066, P<0.05), white blood cell count (WBC)/platelet count (PLT) ratio (OR=33.725, 95%CI: 1.220 — 932.377, P<0.05), international normalized ratio (INR) (OR=5.149, 95%CI: 1.052 — 25.207, P<0.05), and pre-albumin (PAB) (OR=0.992, 95%CI: 0.983 — 1.000, P<0.05) were independent predictive factors for OHE after TIPS in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis. The nomogram model constructed based on age, WBC/PLT ratio, INR, and PAB had an area under the ROC curve of 0.716 (95%CI: 0.649 — 0.781), with a sensitivity of 78.5% and a specificity of 56.1%. Conclusion The nomogram model constructed based on age, WBC/PLT ratio, INR, and PAB can help to predict the risk of OHE after TIPS in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis. -
表 1 2组患者一般资料比较
Table 1. General data of patients
指标 非OHE组(n=237) OHE组(n=65) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 45.00(40.00~53.50) 48.00(45.00~55.50) Z=-2.348 0.019 性别[例(%)] χ2=1.706 0.220 男 187(78.90) 56(86.15) 女 50(21.10) 9(13.85) WBC/PLT 0.06(0.04~0.09) 0.07(0.05~0.11) Z=-2.614 0.009 血红蛋白(g/L) 80.00(69.50~97.50) 85.00(68.50~100.50) Z=-0.702 0.483 INR 1.24(1.13~1.39) 1.33(1.20~1.46) Z=-3.805 <0.001 前白蛋白(mg/L) 99.60(77.35~135.25) 81.90(57.10~109.75) Z=-3.562 <0.001 总胆红素(μmmol/L) 25.00(16.69~36.42) 28.90(17.10~37.35) Z=-0.973 0.330 直接胆红素(μmmol/L) 8.90(6.03~12.97) 9.80(6.00~13.75) Z=-0.662 0.508 间接胆红素(μmmol/L) 15.70(10.47~22.66) 16.70(10.70~23.50) Z=-0.808 0.419 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) 27.70(20.15~40.40) 38.60(25.45~55.75) Z=-3.606 <0.001 谷草转氨酶(U/L) 37.30(31.10~56.15) 49.10(35.60~66.95) Z=-2.927 0.003 尿素(mmol/L) 5.22(3.94~7.10) 5.40(4.20~7.09) Z=-0.773 0.440 血清肌酐(μmmol/L) 70.00(55.70~80.40) 65.10(55.35~83.70) Z=-0.649 0.517 血清钠(mmol/L) 138.30(136.00~140.10) 137.50(135.00~139.80) Z=-1.779 0.075 甲胎蛋白(ng/mL) 3.81(2.40~16.08) 5.58(2.60~16.08) Z=-1.501 0.133 MELD评分(分) 7.97(5.39~10.44) 8.89(5.76~11.11) Z=-1.445 0.149 CTP评分(分) 6(5~7) 7(6~8) Z=-3.150 0.002 MELD-Na评分(分) 9.50(5.76~12.60) 12.01(7.19~14.71) Z=-2.327 0.020 ALBI评分(分) -0.76±0.60 -0.46±0.62 t=-3.627 <0.001 腹水[例(%)] χ2=4.481 0.044 无或少量 151(63.71) 32(49.23) 中或大量 86(36.29) 33(50.77) 胸水[例(%)] χ2=0.123 0.847 无 200(84.39) 56(86.15) 有 37(15.61) 9(13.85) 急诊手术[例(%)] χ2=0.030 0.851 是 199(83.97) 54(83.08) 否 38(16.03) 11(16.92) 表 2 单因素Logistic 回归分析
Table 2. Univariate logistic regression analyses
指标 B值 SE Wald OR(95%CI) P值 年龄(岁) 0.028 0.014 4.087 1.029(1.001~1.057) 0.043 WBC/PLT 4.411 1.707 6.674 82.313(2.899~2 336.962) 0.010 INR 2.242 0.708 10.019 9.410(2.348~37.712) 0.002 前白蛋白(mg/L) -0.013 0.004 12.188 0.987(0.979~0.994) <0.001 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) 0.003 0.002 1.869 1.003(0.999~1.008) 0.172 谷草转氨酶(U/L) 0.004 0.003 2.129 1.004(0.999~1.010) 0.145 血清钠(mmol/L) -0.084 0.037 5.190 0.919(0.855~0.988) 0.023 腹水 0.594 0.282 4.417 1.811(1.041~3.150) 0.036 CTP评分(分) 0.273 0.082 11.140 1.314(1.119~1.542) <0.001 MELD-Na评分(分) 0.069 0.028 6.110 1.071(1.014~1.131) 0.013 ALBI评分(分) 0.852 0.245 12.075 2.343(1.450~3.788) <0.001 表 3 多因素Logistic 回归分析
Table 3. Multivariate logistic regression analyses
指标 B值 SE Wald OR(95%CI) P值 年龄(岁) 0.034 0.015 4.881 1.035(1.004~1.066) 0.027 WBC/PLT 3.518 1.694 4.315 33.725(1.220~932.377) 0.038 INR 1.639 0.810 4.090 5.149(1.052~25.207) 0.043 前白蛋白(mg/L) -0.008 0.004 3.893 0.992(0.983~1.000) 0.048 血清钠(mmol/L) -0.054 0.040 1.806 0.947(0.876~1.025) 0.179 腹水(中或大量) 0.160 0.319 0.251 1.173(0.628~2.194) 0.616 表 4 Nomogram模型、CTP评分、ALBI评分及MELD-Na评分对TIPS术后OHE的预测价值
Table 4. The predictive value of Nomogram model, CTP, ALBI and MELD-Na scores for OHE occurrence after TIPS
指标 AUC OR(95%CI) cut-off 特异度(%) 敏感度(%) 约登指数 P值 Nomogram模型 0.716 0.649~0.781 0.190 56.1 78.5 0.346 <0.001 CTP评分 0.626 0.548~0.703 7.500 78.5 43.1 0.216 0.002 ALBI评分 0.633 0.556~0.710 -0.575 62.9 60.0 0.229 0.001 MELD-Na评分 0.594 0.513~0.675 11.955 69.6 52.3 0.219 0.020 -
[1] SHAN S, ZHAO LH, MA H, et al. Definition, etiology, and epidemiology of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 1): 14- 16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.003.单姗, 赵连晖, 马红, 等. 肝硬化的定义、病因及流行病学[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 1): 14- 16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.003. [2] ZHANG K, LIU JL, LIU YL, et al. Clinical observation on the treatment of portal hypertension complicated with gastrointestinal bleeding due to cirrhosis by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt guided by 3D model constructed by computer based on CT thin-layer scanning data[J]. Clin J Med Off, 2023, 51( 6): 655- 656, 660. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.06.28.张凯, 刘晶磊, 刘燚隆, 等. 应用CT薄层扫描数据电脑构建3D模型指导经颈静脉肝内门体分流术治疗肝硬化门脉高压合并消化道出血临床效果观察[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2023, 51( 6): 655- 656, 660. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.06.28. [3] WANG LJ, YAO X, QI Q, et al. Prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy during the perioperative period of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2023, 15( 8): 1564- 1573. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i8.1564. [4] LIU SY, LI LH, LI SX, et al. Predictive value of controlled nutritional status score for overt hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt of Budd-Chiari syndrome[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 2): 260- 267. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221205-00733.刘胜炎, 李路豪, 李素新, 等. 控制营养状况评分对布-加综合征患者行经颈静脉肝内门腔内支架分流术后发生显性肝性脑病的预测价值[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22( 2): 260- 267. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20221205-00733. [5] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006.中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. [6] RUNYON BA, AASLD. Introduction to the revised American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Practice Guideline management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis 2012[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57( 4): 1651- 1653. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26359. [7] The Chinese College of Interventionalists. CCI clinical practice guidelines: Management of TIPS for portal hypertension(2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2694- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.010.中国医师协会介入医师分会. 中国门静脉高压经颈静脉肝内门体分流术临床实践指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 2694- 9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.010. [8] Group of Gastrointestinal Intervention, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for treatment of cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2014, 30( 3): 210- 213. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.03.003.中华医学会消化病学分会消化介入学组. 经颈静脉肝内门体静脉分流术治疗肝硬化门静脉高压共识意见[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2014, 30( 3): 210- 213. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.03.003. [9] QIN JP, TANG SH, JIANG MD, et al. Contrast enhanced computed tomography and reconstruction of hepatic vascular system for transjugular intrahepatic portal systemic shunt puncture path planning[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21( 32): 9623- 9629. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9623. [10] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 10): 2076- 2089. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.007.中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化肝性脑病诊疗指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 10): 2076- 2089. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.007. [11] VILSTRUP H, AMODIO P, BAJAJ J, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 2): 715- 735. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27210. [12] THABUT D, BOUZBIB C, MEUNIER L, et al. Diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy: The French recommendations[J]. Liver Int, 2023, 43( 4): 750- 762. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15510. [13] BOIKE JR, THORNBURG BG, ASRANI SK, et al. North American practice-based recommendations for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in portal hypertension[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20( 8): 1636- 1662. e 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.018. [14] LI YL, PANG HJ, HE XF. Establishment and validation of nomogram in patients with early hepatic encephalopathy after TIPS[J]. J Pract Med, 2020, 36( 7): 963- 968. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2020.07.026.李应龙, 庞桦进, 何晓峰. 经颈静脉肝内门腔静脉分流术后早期肝性脑病列线图的建立和验证[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2020, 36( 7): 963- 968. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2020.07.026. [15] LIU F, CAI LY, ZHONG L, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease combined with serum prealbumin to predict the prognosis of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis[J]. J Dig Dis, 2010, 11( 6): 352- 357. DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2010.00465.x. [16] NARDELLI S, LATTANZI B, TORRISI S, et al. Sarcopenia is risk factor for development of hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 15( 6): 934- 936. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.028. [17] AMODIO P, BEMEUR C, BUTTERWORTH R, et al. The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: International Society for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Nitrogen Metabolism Consensus[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58( 1): 325- 336. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26370. [18] LI JN, DU MH, LI H, et al. Low prealbumin levels were associated with increased frequency of hepatic encephalopathy in hepatitis B virus(HBV)-related decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2023, 29: e937772. DOI: 10.12659/MSM.937772. [19] CHATTERJEE M, GEISLER T. Inflammatory contribution of platelets revisited: New players in the arena of inflammation[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2016, 42( 3): 205- 214. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1570081. [20] AFDHAL N, MCHUTCHISON J, BROWN R, et al. Thrombocytopenia associated with chronic liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48( 6): 1000- 1007. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.03.009. [21] RAWI S, WU GY. Pathogenesis of thrombocytopenia in chronic HCV infection: A review[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2020, 8( 2): 184- 191. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00007. -



 PDF下载 ( 915 KB)
PDF下载 ( 915 KB)

 下载:
下载: