草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷(IGBR)对TGF-β1诱导的HepG2细胞上皮间质转化模型的影响
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240617
Effect of iridoid glycosides from Boschniakia rossica on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HepG2 cells induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1
-
摘要:
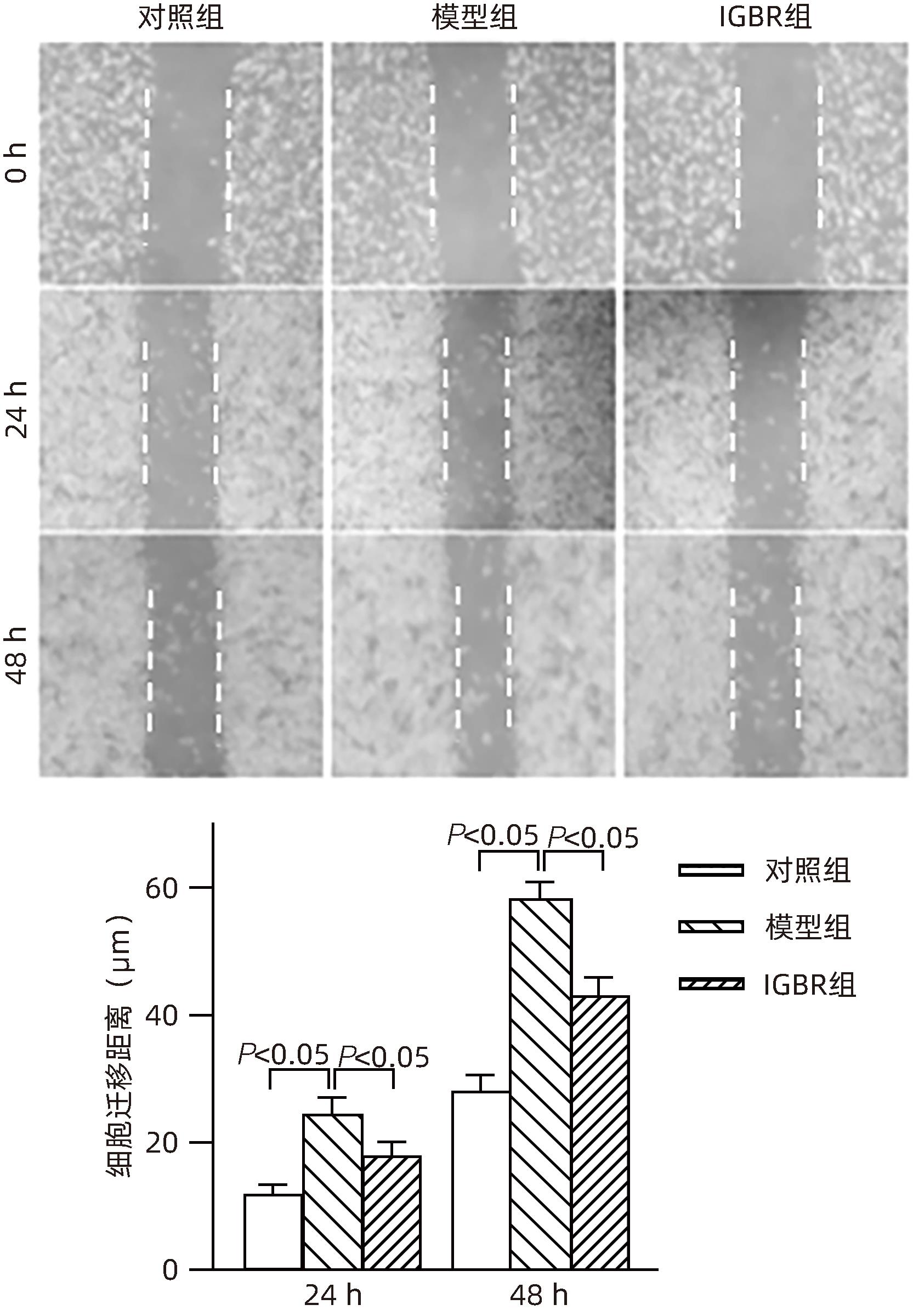
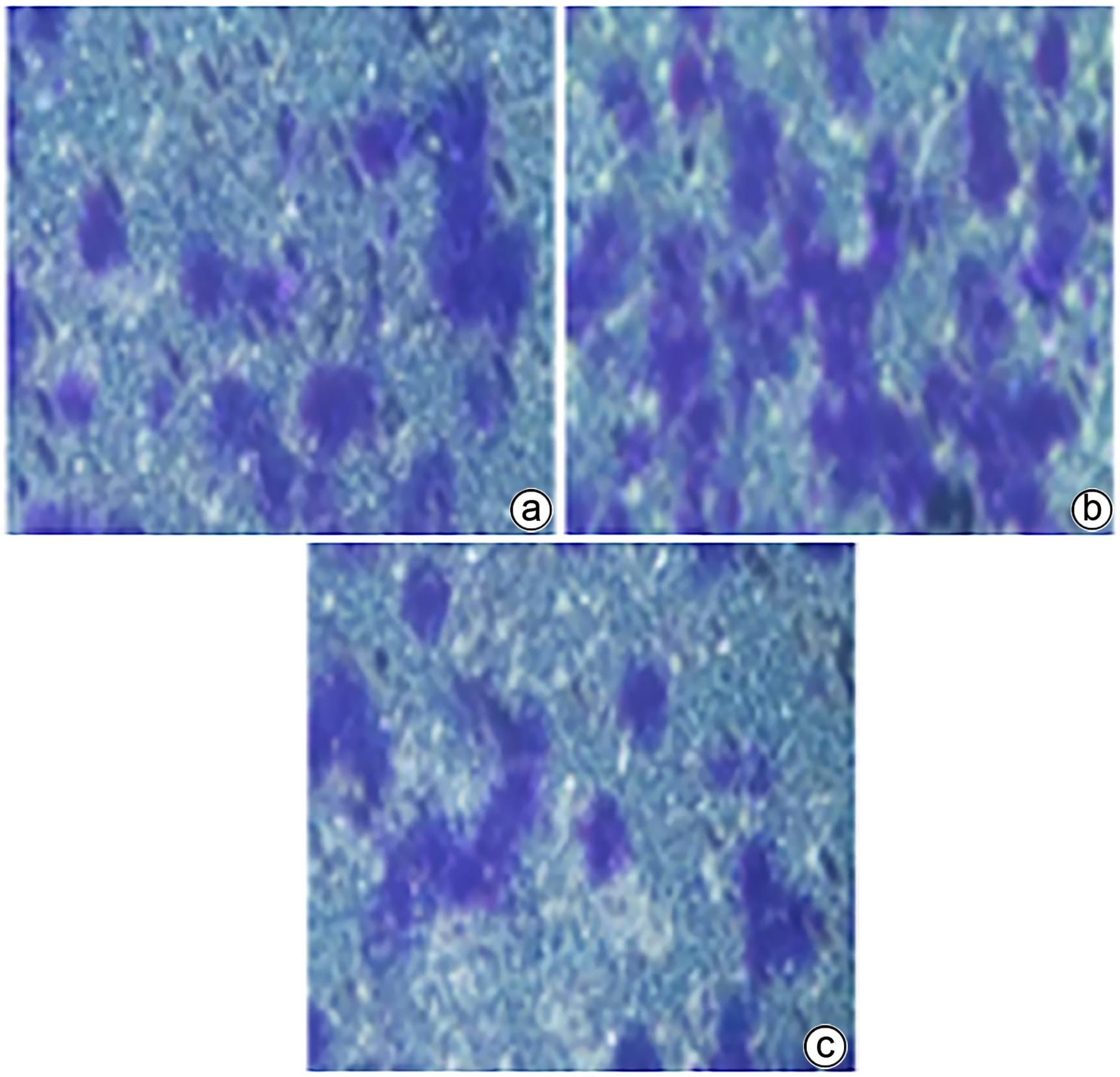
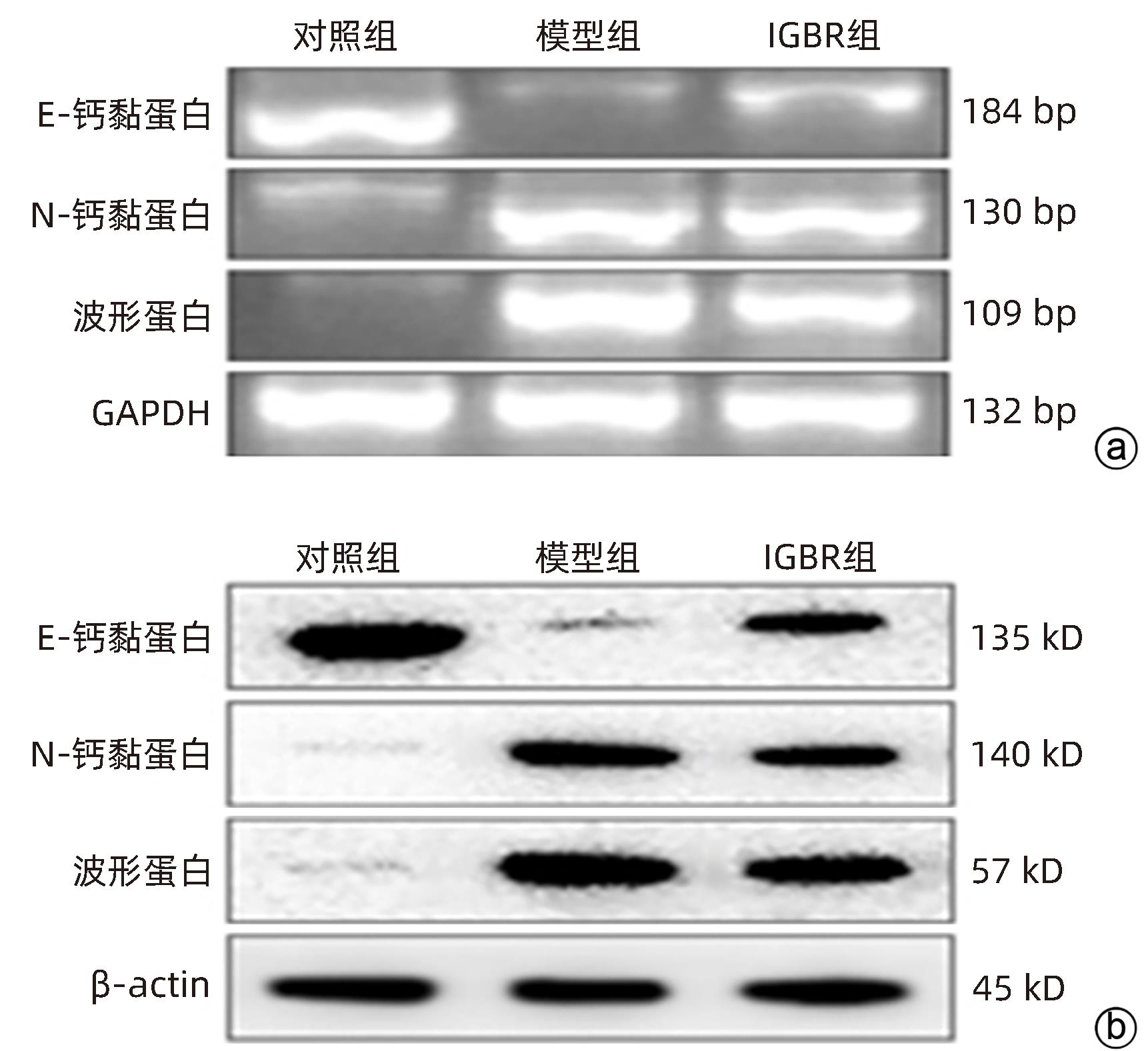
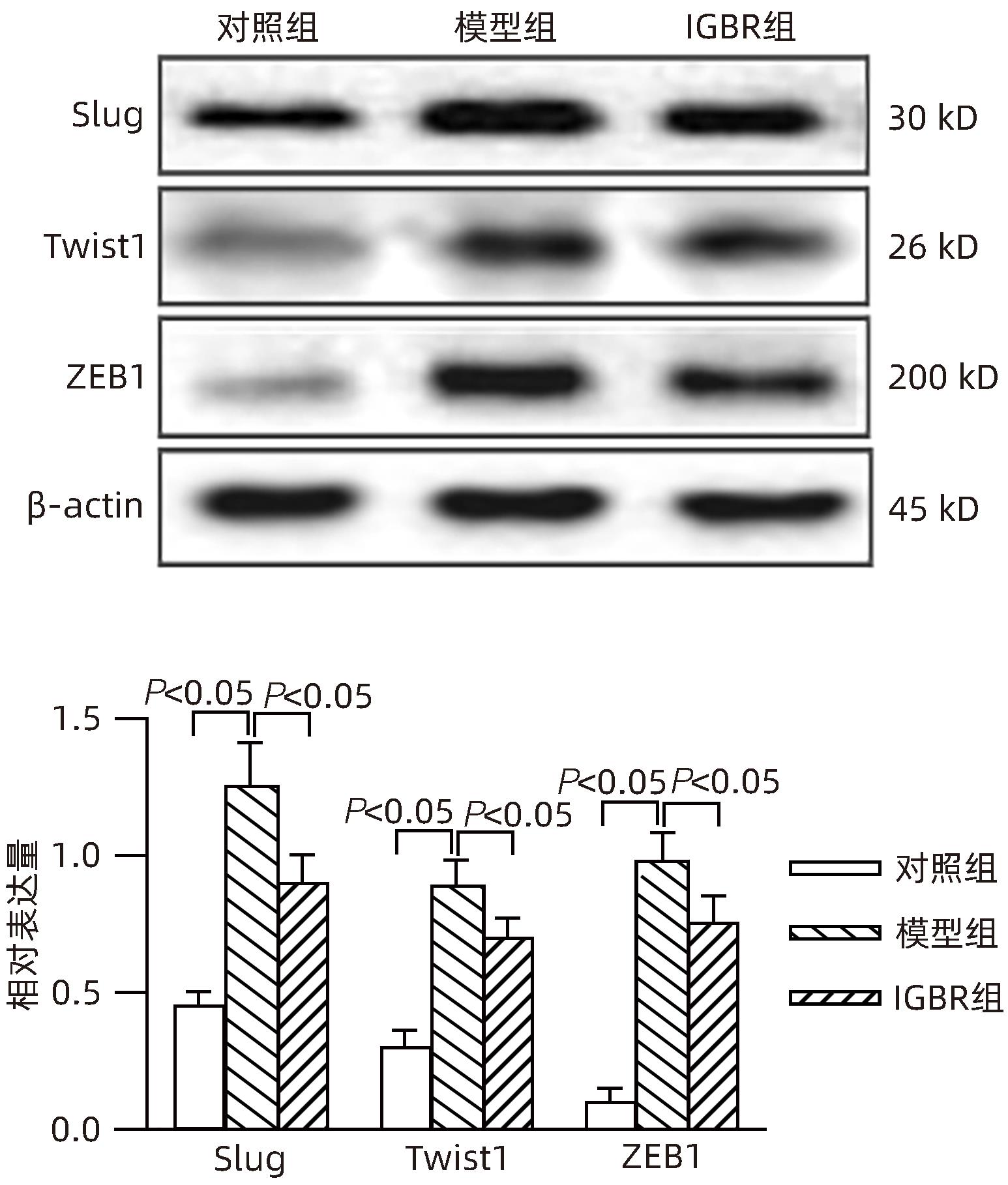
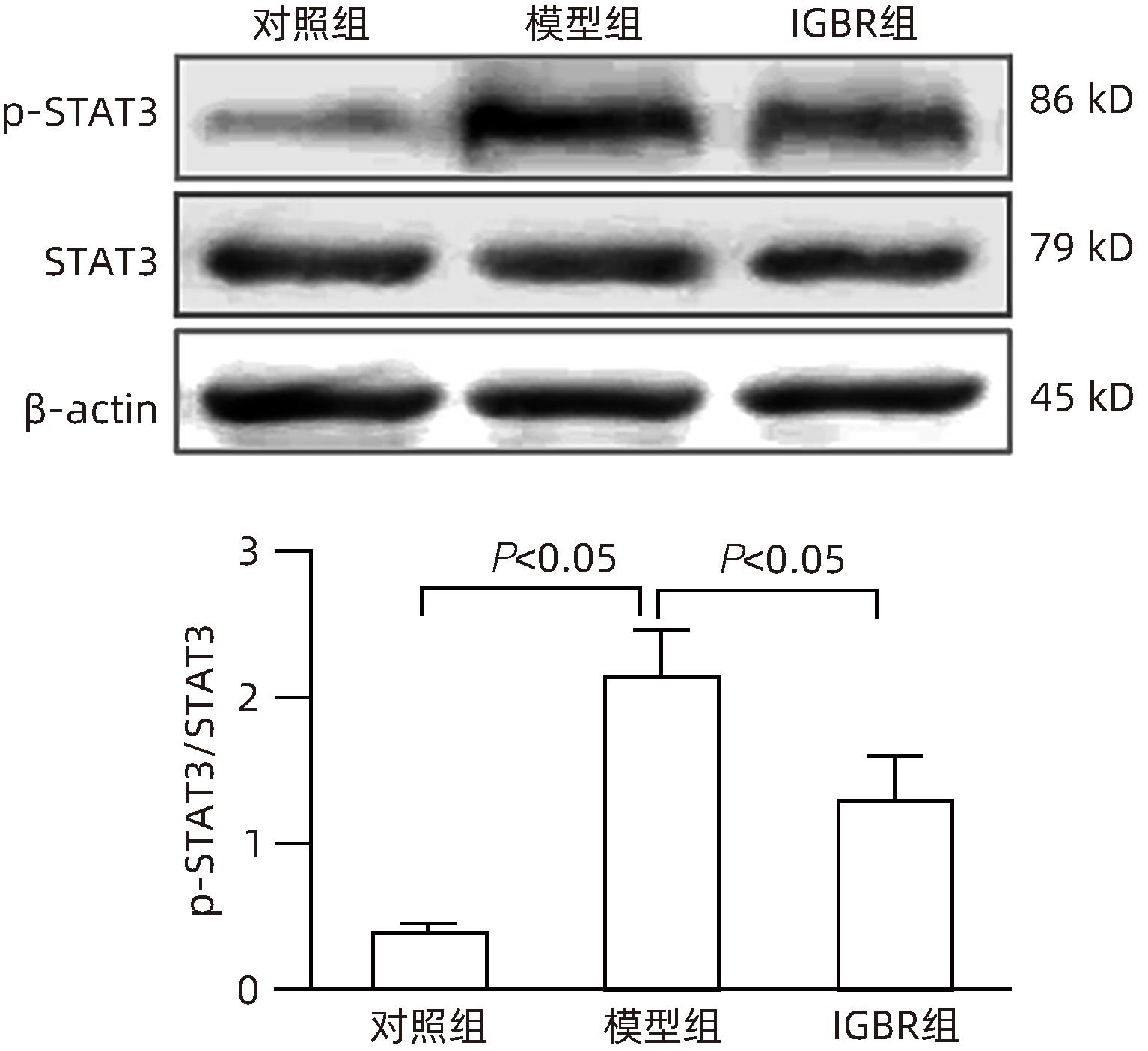
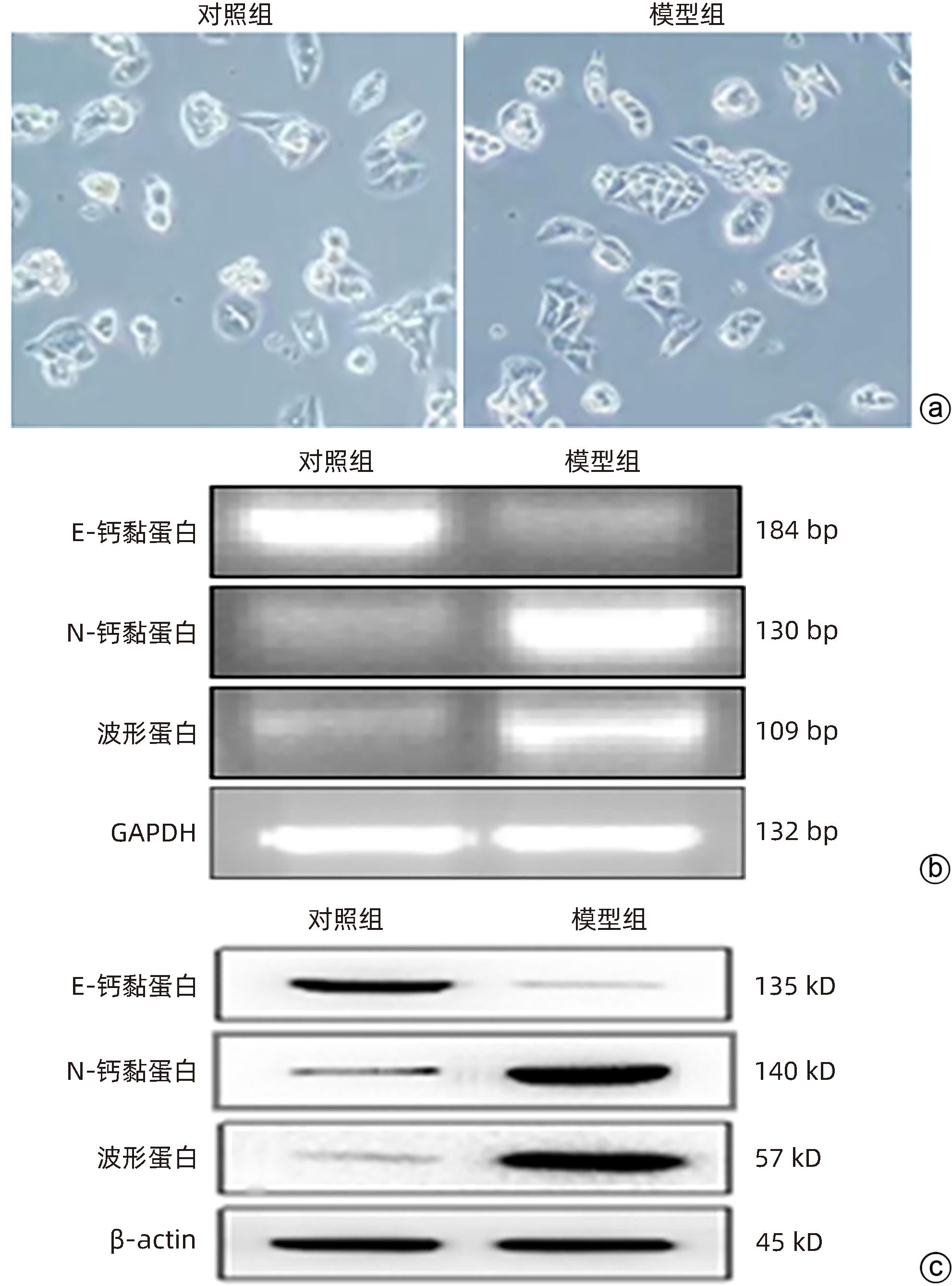
目的 研究草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷(IGBR)对TGF-β1诱导肝癌HepG2细胞上皮间质转化(EMT)的影响作用。 方法 用10 μg/L TGF-β1诱导HepG2肝癌细胞株构建肝癌细胞EMT模型。实验分为对照组、模型组与IGBR组3组,对照组用无血清DMEM处理,模型组用10 μg/L TGF-β1处理,IGBR组用10 μg/L TGF-β1和500 mg/L IGBR联合处理,培养48 h。利用细胞黏附实验、划痕愈合实验和Transwell小室实验观察细胞迁移和侵袭能力。RT-PCR法和Western Blot法检测细胞中E-钙黏蛋白、N-钙黏蛋白、波形蛋白的mRNA和蛋白表达,Western Blot法检测Slug、Twist1、ZEB1、p-STAT3、STAT3的蛋白表达。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验;两组间比较采用成组t检验。 结果 TGF-β1诱导后,模型组HepG2细胞呈现长梭形改变;与模型组比较,IGBR组细胞黏附率降低,抑制细胞迁移、侵袭能力(P值均<0.05),E-钙黏蛋白的mRNA表达和蛋白表达均增高(P值均<0.05),N-钙黏蛋白和波形蛋白的mRNA表达和蛋白表达均降低(P值均<0.05),Slug、Twist1、ZEB1蛋白表达和p-STAT3蛋白表达均降低(P值均<0.05)。 结论 IGBR可抑制TGF-β1诱导的HepG2细胞EMT过程,从而减弱HepG2细胞黏附力和细胞迁移、侵袭能力,上调E-钙黏蛋白,下调N-钙黏蛋白和波形蛋白,上调Slug、Twist1、ZEB1、STAT3的蛋白表达,其作用可能通过抑制STAT3通路下调Slug、Twist1、ZEB1等EMT转录因子来实现。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of iridoid glycosides from Boschniakia rossica (IGBR) on epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of HepG2 hepatoma cells induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1). Methods HepG2 hepatoma cells were induced by 10 μg/L TGF-β1 to construct an EMT model of hepatoma cells. The cells were divided into control group (treated with serum-free DMEM), model group (treated with 10 μg/L TGF-β1), and IGBR group (treated with 10 μg/L TGF-β1 and 500 mg/L IGBR), and all cells were cultured for 48 hours. Cell adhesion assay, wound healing assay, and Transwell chamber assay were used to observe the migration and invasion abilities of cells. RT-PCR and Western blot were used to measure the mRNA and protein expression levels of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in cells, and Western blot was used to measure the protein expression levels of Slug, Twist1, ZEB1, p-STAT3, and STAT3. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups; the independent-samples t test was used for comparison between two groups. Results After TGF-β1 induction, HepG2 cells in the model group showed long spindle-shape changes, while those in the control group showed polygonal epithelia-like changes. Compared with the model group, the IGBR group had a significant reduction in cell adhesion rate and significant inhibition of cell migration and invasion abilities (all P<0.05), as well as significant increases in the mRNA and protein expression levels of E-cadherin (P<0.05), significant reductions in the mRNA and protein expression levels of N-cadherin and vimentin (all P<0.05), and significant reductions in the protein expression levels of Slug, Twist1, ZEB1, and p-STAT3 (all P<0.05). Conclusion IGBR can inhibit TGF-β1-induced EMT process in HepG2 cells, thereby attenuating cell adhesion, migration, and invasion abilities, and it can also upregulate E-cadherin, downregulate N-cadherin and vimentin, and upregulate the protein expression of Slug, Twist1, ZEB1, and STAT3, possibly by inhibiting the STAT3 pathway to downregulate the EMT transcription factors such as Slug, Twist1, and ZEB1. -
Key words:
- Liver Neoplasms /
- Orobanche Coerulescens /
- Iridoids /
- Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
-
表 1 HepG2细胞EMT模型中E-钙黏蛋白、N-钙黏蛋白和波形蛋白表达的比较
Table 1. Comparison of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin expression in the EMT model of HepG2 cells
组别 mRNA 蛋白 E-钙黏蛋白 N-钙黏蛋白 波形蛋白 E-钙黏蛋白 N-钙黏蛋白 波形蛋白 对照组 1.41±0.11 0.25±0.06 0.36±0.08 1.40±0.13 0.42±0.06 0.36±0.12 模型组 0.26±0.09 1.45±0.14 0.89±0.10 0.31±0.09 1.63±0.14 2.10±0.10 t值 14.015 13.646 7.168 11.940 13.759 19.294 P值 0.000 2 0.000 2 0.002 0 0.000 3 0.000 2 <0.000 1 表 2 IGBR对HepG2细胞E-钙黏蛋白、N-钙黏蛋白和波形蛋白表达的比较
Table 2. Comparison of IGBR on E-cadherin, N-cadheractin, and vimentin expression in HepG 2 cells
组别 mRNA 蛋白 E-钙黏蛋白 N-钙黏蛋白 波形蛋白 E-钙黏蛋白 N-钙黏蛋白 波形蛋白 对照组 0.80±0.05 0.17±0.06 0.14±0.04 1.45±0.05 0.12±0.06 0.14±0.05 模型组 0.20±0.091) 0.78±0.061) 1.20±0.101) 0.25±0.031) 1.08±0.091) 1.37±0.101) IGBR组 0.42±0.072) 0.58±0.032) 0.65±0.092) 0.08±0.102) 0.70±0.122) 1.10±0.142) F值 53.50 107.40 128.40 242.40 69.01 127.90 P值 0.000 1 <0.000 1 <0.000 1 <0.000 1 <0.000 1 <0.000 1 注:与对照组相比,1) P<0.05;与模型组相比,2) P<0.05。 -
[1] ZHU JB, DONG XH, CUI XD, et al. Inhibitory effect of iridoid glucosides from Boschniakia rossica on SK-Hep1 cell EMT and its mechanism[J]. Guangdong Med J, 2019, 40( 22): 3103- 3107. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.20191100.朱洁波, 董学花, 崔香丹, 等. 草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷对SK-Hep1细胞EMT的抑制作用及其机制[J]. 广东医学, 2019, 40( 22): 3103- 3107. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.20191100. [2] LIN P, CAI MQ, FANG JW, et al. Research status and progress on surgical treatment of postoperative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2022, 13( 1): 111- 119. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.01.017.林鹏, 蔡敏清, 房俊伟, 等. 肝癌术后复发的外科治疗研究现状及进展[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13( 1): 111- 119. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.01.017. [3] CHEN CM, ZHANG GZ, LIU PP, et al. Berberine inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human liver cancer HepG2 cells via TGF-β/Smad pathway[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2020, 36( 2): 261- 267. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.02.021.陈春苗, 张国哲, 刘平平, 等. 小檗碱通过TGF-β/Smad通路抑制TGF-β1诱导的人肝癌HepG2细胞上皮间质转化的研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2020, 36( 2): 261- 267. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.02.021. [4] HU ZY, ZHANG H, GU L, et al. The role of DEPDC1B in the proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma and clinical relevance[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2023, 33( 8): 692- 697. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2023.008.004.胡志勇, 张海, 顾磊, 等. DEPDC1B在肝癌增殖、迁移和上皮间质转化中的作用及其临床相关性研究[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2023, 33( 8): 692- 697. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2023.008.004. [5] DING R, GE RR, WANG EY, et al. Extract from modified Xiao Xianxiongtang inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion and migration mediated by TGF-β1 of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells via Wnt5a/Ca2+/NFAT signaling pathway[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2021, 27( 4): 37- 46. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20202326.丁芮, 葛瑞瑞, 王恩宇, 等. 加味小陷胸汤水提物通过Wnt5a/Ca2+/NFAT信号通路抑制TGF-β1介导的人胃癌MGC-803细胞上皮-间质转化及侵袭迁移[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2021, 27( 4): 37- 46. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20202326. [6] CUI XD, ZHENG F, ZHU JB, et al. Inhibitive effect of iridoid glycosides from Boschniakia rossica on apoptosis of liver cancer cells[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2018, 34( 4): 521- 524. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1117089.崔香丹, 郑峰, 朱洁波, 等. 草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷对肝癌抑制作用[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2018, 34( 4): 521- 524. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1117089. [7] QUAN JS, PIAO L, XU HX, et al. Protective effect of iridoid glucosides from Boschniakia rossica on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 2009, 73( 4): 849- 854. DOI: 10.1271/bbb.80757. [8] LIN LC, LEE LC, HUANG C, et al. Effects of boschnaloside from Boschniakia rossica on dysglycemia and islet dysfunction in severely diabetic mice through modulating the action of glucagon-like peptide-1[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 62: 152946. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152946. [9] YIN ZZ, KIM HS, KIM YH, et al. Iridoid compounds from Boschniakia rossica[J]. Arch Pharm Res, 1999, 22( 1): 78- 80. DOI: 10.1007/BF02976441. [10] DONG XH, ZHU JB, YAN GH, et al. Inhibitory effect of Iridoid glycosides from Boschniakia rossica combined with 5-fluorouracil on EMT in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2020, 31( 5): 1038- 1042. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.05.004.董学花, 朱洁波, 延光海, 等. 草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷联合5-氟尿嘧啶对人肝癌SMMC-7721细胞EMT的抑制作用[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2020, 31( 5): 1038- 1042. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.05.004. [11] LEE H, PYO MJ, BAE SK, et al. Nemopilema nomurai jellyfish venom exerts an anti-metastatic effect by inhibiting Smad- and NF-κB-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HepG2 cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8( 1): 2808. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20724-3. [12] ZHANG L, ZHAO YS, WANG ZA, et al. The genus Boschniakia in China: An ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2016, 194: 987- 1004. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.051. [13] LI CF, WANG XQ, LIU Y, et al. Advances in studies on chemical constituents of Boschniakia rossica and their pharmacological activities[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2014, 45( 7): 1016- 1023. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2014.7.023.李彩峰, 王晓琴, 刘勇, 等. 草苁蓉化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2014, 45( 7): 1016- 1023. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2014.7.023. [14] YIN XZ, XU HX, JIN AH, et al. Anti-tumor effect of iridoid glucosides from Boschniakia rossica in VX2-bearing rabbits[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae, 2010, 16( 6): 134- 136, 140. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2010.06.075.尹学哲, 许惠仙, 金爱花, 等. 草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷对移植鳞癌VX2荷瘤兔的抑瘤作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2010, 16( 6): 134- 136, 140. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2010.06.075. [15] CUI XD, ZHENG F, ZHU JB, et al. Effect of Iridoid Glucosides from Boschniakia Rossica on rat models of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinomat[J]. China J Mod Med, 2017, 27( 27): 7- 11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.27.002.崔香丹, 郑峰, 朱洁波, 等. 草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷对二乙基亚硝胺诱发肝癌大鼠细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2017, 27( 27): 7- 11. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.27.002. [16] ZHU DM, KONG LB, JIA WB, et al. ANKRD1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating epithelial mesenchymal transition pathway[J]. J Nanjing Med Univ Nat Sci, 2023, 43( 4): 484- 491. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20230406.朱德明, 孔连宝, 贾文博, 等. ANKRD1通过介导上皮细胞间充质转化促进肝细胞肝癌增殖与转移[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43( 4): 484- 491. DOI: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20230406. [17] SHI YJ, CHEN YM, HUANG SC, et al. Serine arginine protein kinase 1 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transformation in hepatoma cells through Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation[J]. Med J West China, 2023, 35( 7): 951- 958. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2023.07.003.石永杰, 陈旖鹛, 黄思聪, 等. SRPK1激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进肝癌细胞上皮间充质转化[J]. 西部医学, 2023, 35( 7): 951- 958. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2023.07.003. [18] WARE KE, THOMAS BC, OLAWUNI PD, et al. A synthetic lethal screen for Snail-induced enzalutamide resistance identifies JAK/STAT signaling as a therapeutic vulnerability in prostate cancer[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2023, 10: 1104505. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1104505. [19] CHAI FY, ZHANG JF, FU T, et al. Identification of SLC2A3 as a prognostic indicator correlated with the NF-κB/EMT axis and immune response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Channels, 2023, 17( 1): 2208928. DOI: 10.1080/19336950.2023.2208928. [20] FAN CN, WANG Q, KUIPERS TB, et al. LncRNA LITATS1 suppresses TGF-β-induced EMT and cancer cell plasticity by potentiating TβRI degradation[J]. EMBO J, 2023, 42( 10): e112806. DOI: 10.15252/embj.2022112806. [21] LUO BF, YUAN Y, ZHU YF, et al. MicroRNA-145-5p inhibits prostate cancer bone metastatic by modulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 988794. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.988794. [22] PADUA D, MASSAGUÉ J. Roles of TGFβ in metastasis[J]. Cell Res, 2009, 19( 1): 89- 102. DOI: 10.1038/cr.2008.316. [23] VINCENT T, NEVE EPA, JOHNSON JR, et al. A SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2009, 11( 8): 943- 950. DOI: 10.1038/ncb1905. [24] PEINADO H, QUINTANILLA M, CANO A. Transforming growth factor beta-1 induces snail transcription factor in epithelial cell lines: Mechanisms for epithelial mesenchymal transitions[J]. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278( 23): 21113- 21123. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M211304200. [25] CHEN ZH, ZHU WJ, SHEN BB, et al. Inhibitory effect of 6-paradol on the proliferation, migration, and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells and its mechanism[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 4): 857- 864. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.04.022.陈泽昊, 朱文杰, 申兵兵, 等. 6-姜酮酚抑制肝内胆管癌细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭作用及其机制探讨[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 4): 857- 864. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.04.022. [26] ZHANG H, LIU LX, ZHAO ZX, et al. Role of transforming growth factor-β in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 12): 2892- 2896. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.12.041.张浩, 刘林勋, 赵占学, 等. 转化生长因子β在胰腺癌发生发展中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 12): 2892- 2896. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.12.041. [27] LI YL, ZHANG MM, WU LW, et al. DYRK1A reinforces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via cooperatively activating STAT3 and SMAD[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2022, 29( 1): 34. DOI: 10.1186/s12929-022-00817-y. [28] HORIGUCHI K, SHIRAKIHARA T, NAKANO A, et al. Role of Ras signaling in the induction of snail by transforming growth factor-beta[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284( 1): 245- 253. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M804777200. -



 PDF下载 ( 1510 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1510 KB)

 下载:
下载: