间充质干细胞联合免疫抑制剂对肝移植大鼠模型免疫排斥的影响
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240622
伦理学声明: 本研究方案于2023年5月25日经由福建医科大学孟超肝胆医院实验动物伦理委员会审批,批号:MCHH-AEC-2023-04,符合实验室动物管理与使用准则。
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:李海涛负责设计论文框架,起草论文;俞赛花、刘海岩负责实验操作,研究过程的实施;陈丽红、赖子森、刘红枝、沈聪龙负责数据收集,统计学分析。
Effect of mesenchymal stem cells combined with immunosuppressants on immune rejection in a rat model of liver transplantation
-
摘要:
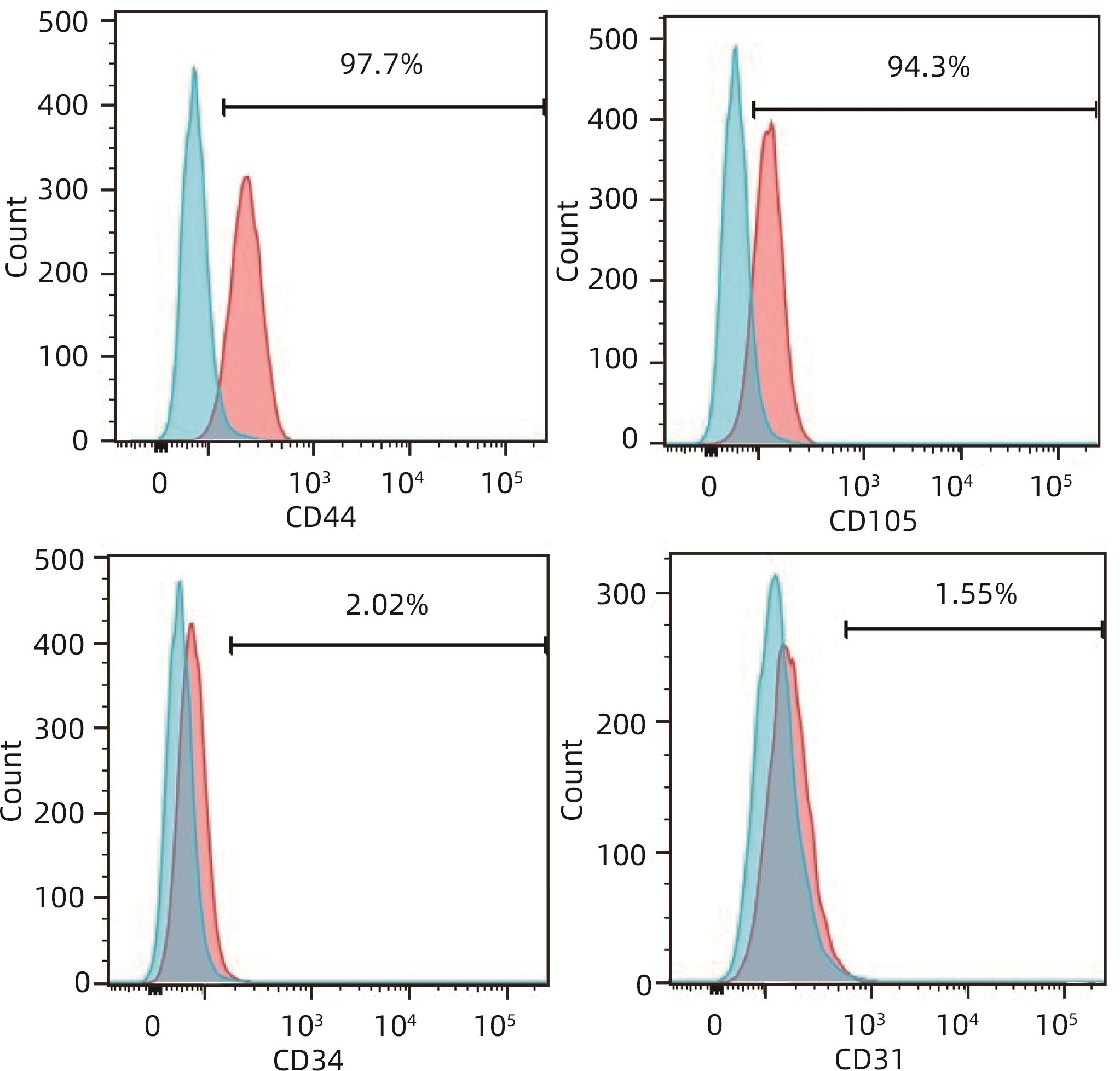
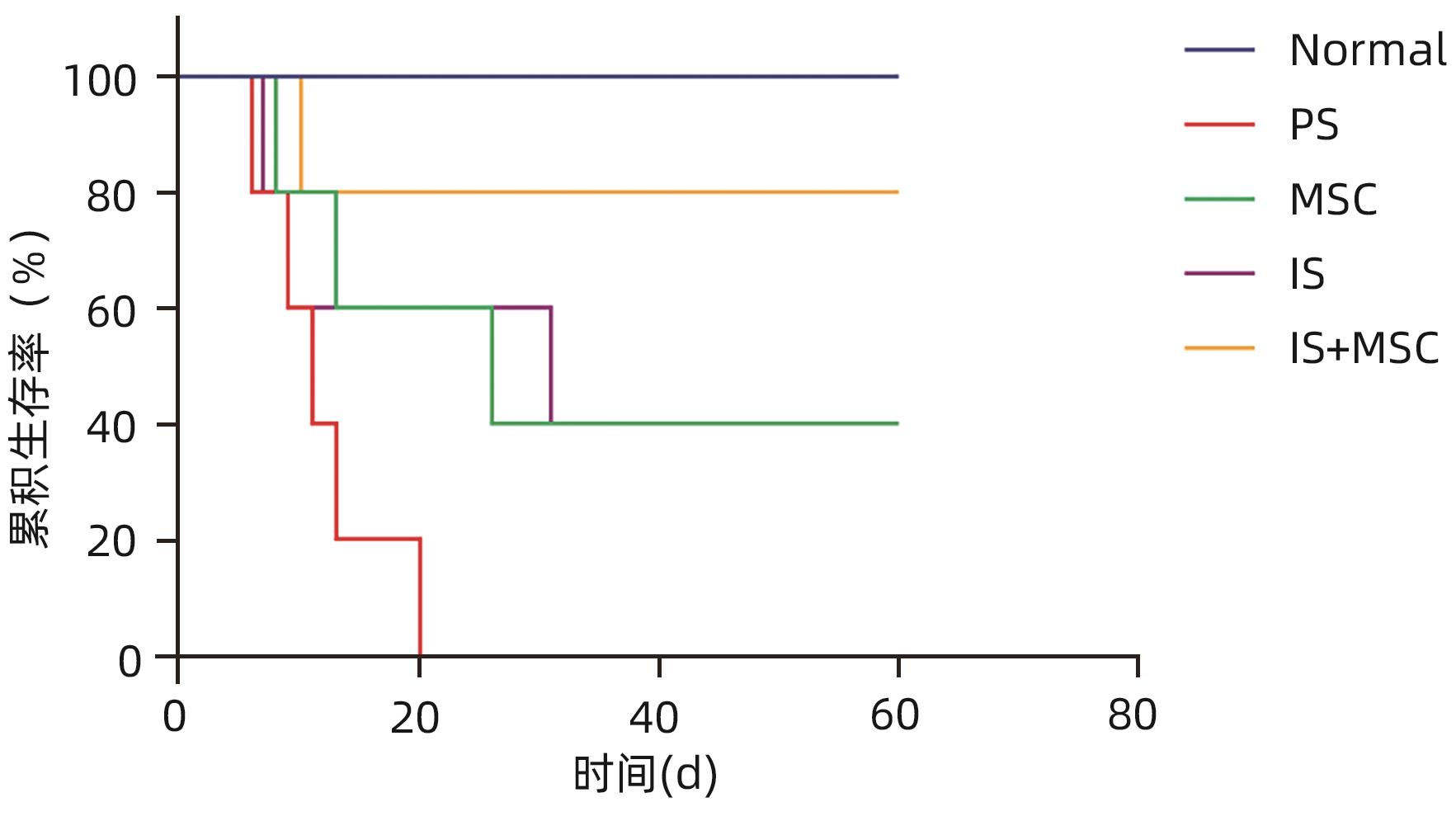
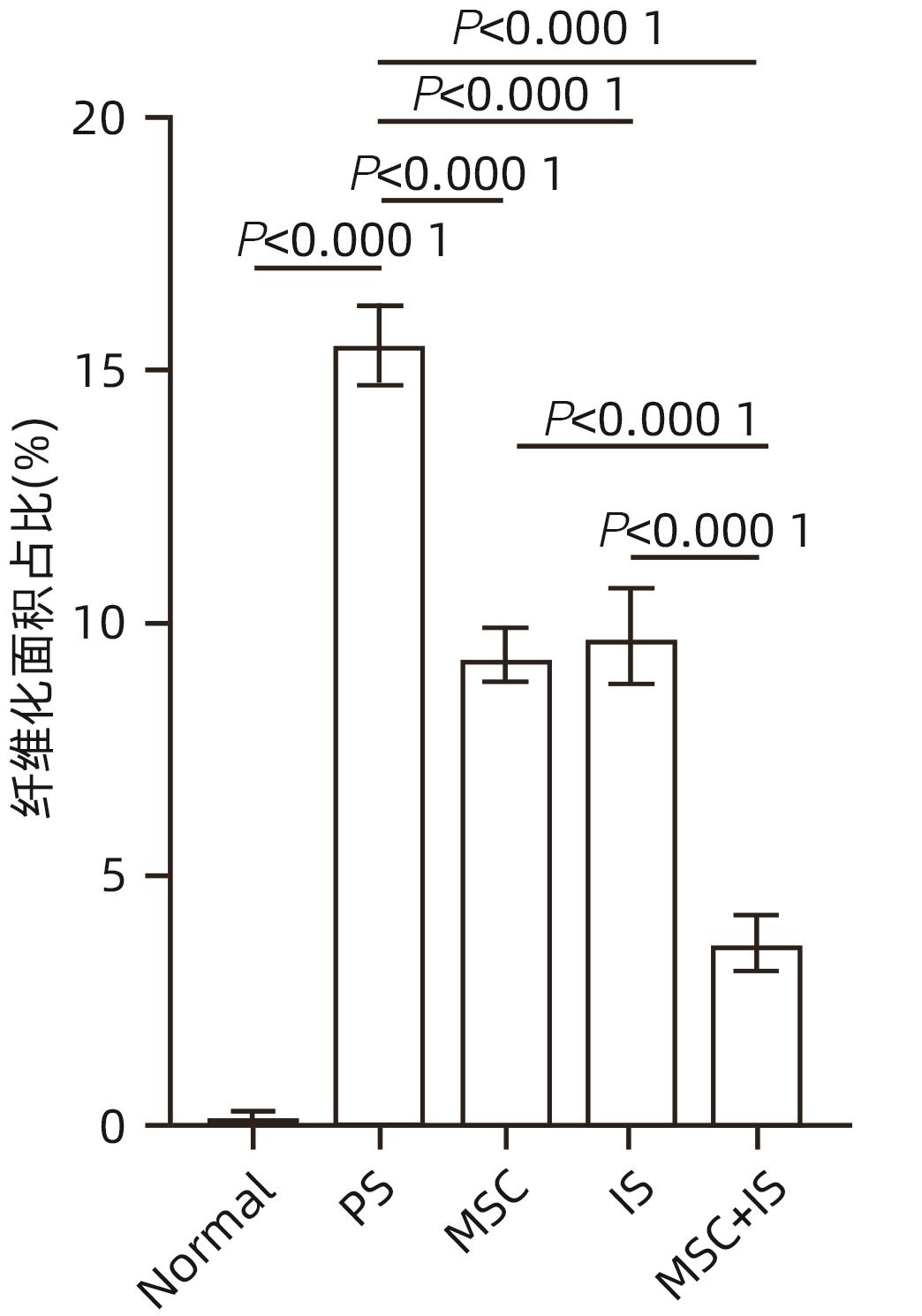
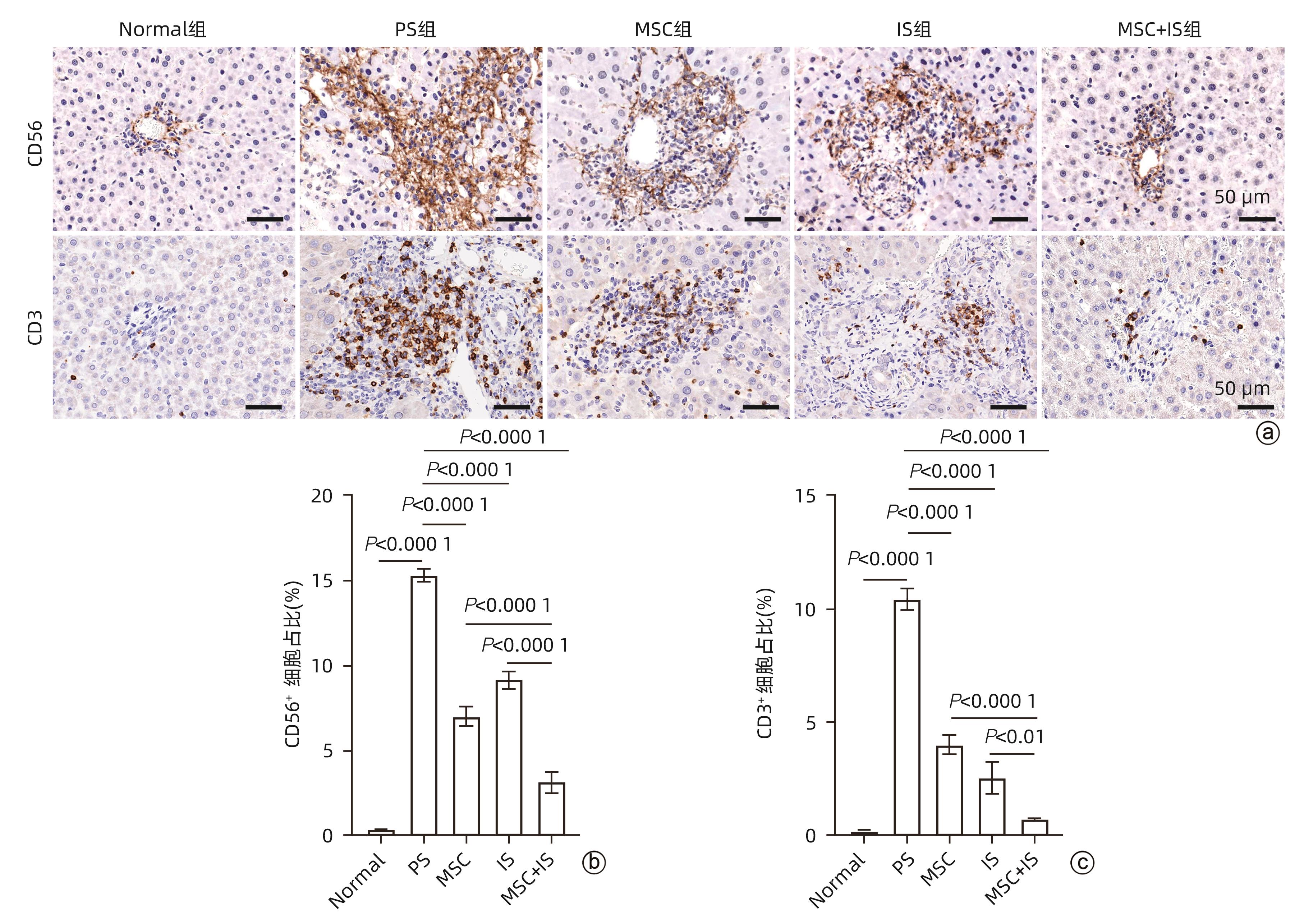
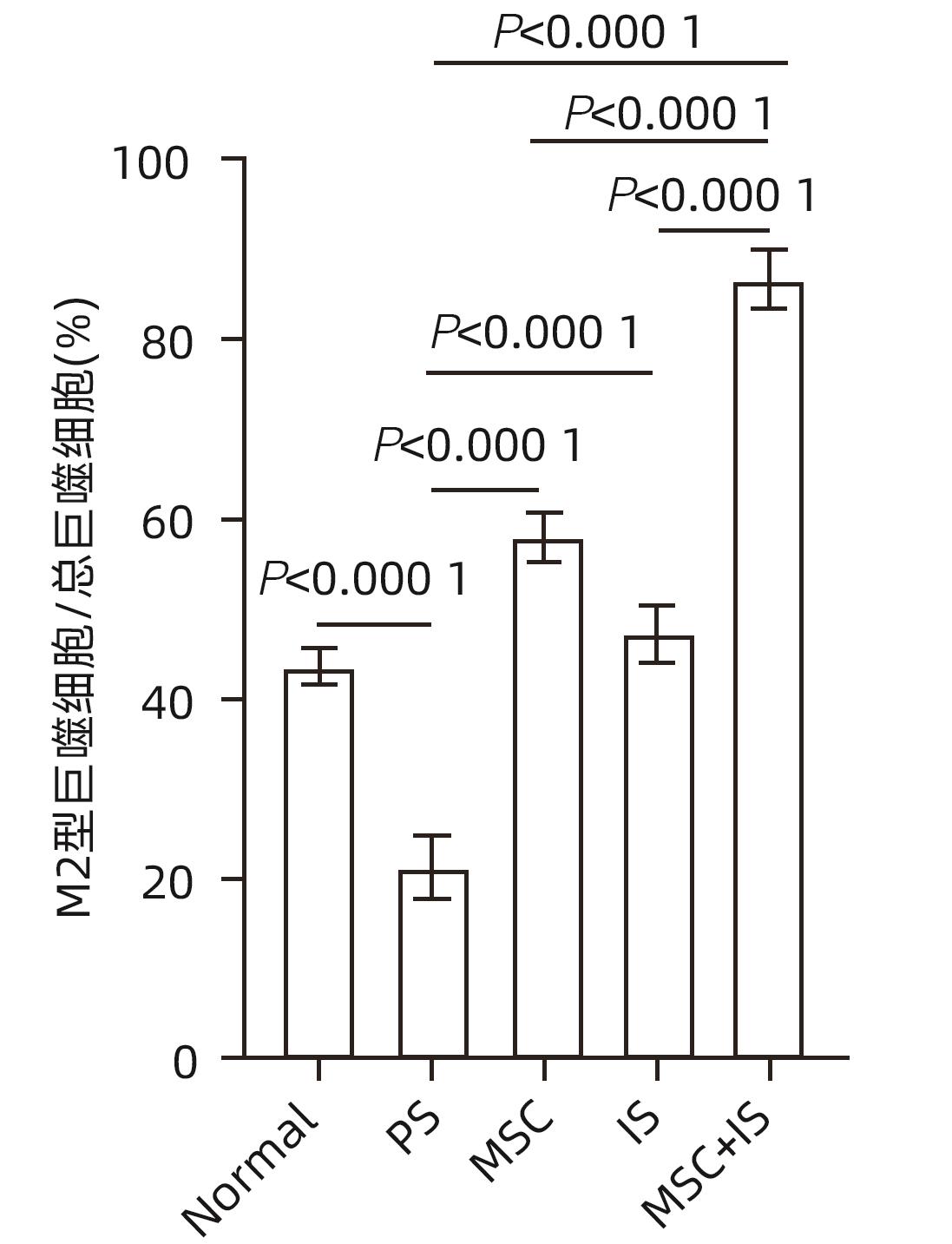
目的 探讨间充质干细胞(MSC)联合免疫抑制剂(IS)对肝移植大鼠模型免疫排斥反应的影响。 方法 将F344大鼠分成5组:Normal组(不进行任何干预)、PS组(注射等量生理盐水)、MSC组(注射MSC)、IS组(注射IS)、MSC+IS组(注射MSC和IS),每组8只。除Normal组以外,各组均采用Kamada双袖套法不重建肝动脉建立原位肝移植模型。大鼠肝组织进行HE染色、Masson染色并进行纤维化程度统计,免疫组化实验检测T淋巴细胞和NK细胞浸润情况,免疫荧光实验分析巨噬细胞M2极化情况。计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,生存分析采用Log-rank检验。 结果 与PS组相比,MSC+IS组生存期显著延长(P<0.01),MSC组、IS组和MSC+IS组的肝组织结构明显改善,纤维化程度显著降低(P值均<0.000 1),NK细胞和T淋巴细胞浸润数量显著减少(P值均<0.000 1),巨噬细胞M2极化程度显著增加(P值均<0.000 1),提示MSC+IS组的疗效显著优于MSC组和IS组。 结论 MSC联合IS可以改善大鼠肝移植术后肝组织病理,降低炎性细胞浸润,促进巨噬细胞M2极化,起免疫抑制作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) combined with immunosuppressants (IS) on immune rejection in a rat model of liver transplantation. Methods F344 rats were divided into Normal group (without any intervention), PS group (injected with an equal volume of normal saline), MSC group (injected with MSC), IS group (injected with IS), and MSC+IS group (injected with MSC and IS), with 8 rats in each group. For all rats except those in the Normal group, the Kamada’s double-cuff method was used to establish a model of orthotopic liver transplantation, without reconstruction of the hepatic artery. HE staining and Masson staining were performed for rat liver tissue, and the degree of liver fibrosis was analyzed; immunohistochemical experiments were used to measure the infiltration of T cells and NK cells, and immunofluorescence assay was used to analyze macrophage M2 polarization. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to plot survival curves, and the log-rank test was used for survival analysis. Results Compared with the PS group, the MSC+IS group had a significantly prolonged survival time (P<0.01), and the MSC group, the IS group, and the MSC+IS group had a significant improvement in the histological structure of the liver and a significant reduction in the degree of liver fibrosis (all P<0.000 1), as well as a significant reduction in the infiltration of NK and T cells (all P<0.000 1) and a significant increase in the degree of macrophage M2 polarization (all P<0.000 1). The MSC+IS group had a significantly better effect than the MSC group and the IS group. Conclusion MSCs combined with IS can improve liver histopathology, reduce inflammatory cell infiltration, promote macrophage M2 polarization, and exert an immunosuppressive effect in rats after liver transplantation. -
Key words:
- Liver Transplantation /
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells /
- Graft Rejection
-
-
[1] NEUBERGER J. Developments in liver transplantation[J]. Gut, 2004, 53( 5): 759- 768. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2003.024927. [2] HONG SK, HAN D, LEE SK, et al. Short-term therapy with anti-ICAM-1 monoclonal antibody induced long-term liver allograft survival in nonhuman Primates[J]. Am J Transplant, 2021, 21( 9): 2978- 2991. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16486. [3] Branch of Organ Tansplantation of Chinese Medical Association. Diagnosis and treatment specification for immunosuppressive therapy and rejection of liver transplantation in China(2019 edition)[J]. Organ Transplant, 2021, 12( 1): 8- 14, 28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2021.01.002.中华医学会器官移植学分会. 中国肝移植免疫抑制治疗与排斥反应诊疗规范(2019版)[J]. 器官移植, 2021, 12( 1): 8- 14, 28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2021.01.002. [4] TAN PS, MUTHIAH MD, KOH T, et al. Asian liver transplant network clinical guidelines on immunosuppression in liver transplantation[J]. Transplantation, 2019, 103( 3): 470- 480. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002532. [5] DI MAIRA T, LITTLE EC, BERENGUER M. Immunosuppression in liver transplant[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2020, 46-47: 101681. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2020.101681. [6] ZHAO L, CHEN SQ, SHI XW, et al. A pooled analysis of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for liver disease[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2018, 9( 1): 72. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-018-0816-2. [7] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement[J]. Cytotherapy, 2006, 8( 4): 315- 317. DOI: 10.1080/14653240600855905. [8] LU XF, GUO HJ, WEI XY, et al. Current status and prospect of delivery vehicle based on mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in liver diseases[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2023, 18: 2873- 2890. DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S404925. [9] LI HT, YU SH, CHEN LH, et al. Immunomodulatory role of mesenchymal stem cells in liver transplantation: Status and prospects[J]. Dig Dis Basel Switz, 2024, 42( 1): 41- 52. DOI: 10.1159/000534003. [10] KAMADA N, CALNE RY. Orthotopic liver transplantation in the rat[J]. Transplantation, 1979, 28( 1): 47- 50. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-197907000-00011. [11] CEN YL, LOU GH, QI JJ, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit JNK-mediated mitochondrial retrograde pathway to alleviate acetaminophen-induced liver injury[J]. Antioxidants, 2023, 12( 1): 158. DOI: 10.3390/antiox12010158. [12] ZHOU Q, RONG C, GU TF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve liver fibrosis and protect hepatocytes by promoting microRNA-148a-5p-mediated inhibition of Notch signaling pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13( 1): 354. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-03030-8. [13] TIAN SY, ZHOU X, ZHANG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect against liver fibrosis via delivering miR-148a to target KLF6/STAT3 pathway in macrophages[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13( 1): 330. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-03010-y. [14] MONTANO-LOZA AJ, RODRÍGUEZ-PERÁLVAREZ ML, PAGEAUX GP, et al. Liver transplantation immunology: Immunosuppression, rejection, and immunomodulation[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 78( 6): 1199- 1215. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.01.030. [15] D'ELIA JA, WEINRAUCH LA. Hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia with kidney or liver transplantation: A review[J]. Biology, 2023, 12( 9): 1185. DOI: 10.3390/biology12091185. [16] NORÉN Å, OLTEAN M, FRIMAN S, et al. Liver graft proteomics reveals potential incipient mechanisms behind early renal dysfunction after liver transplantation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 19): 11929. DOI: 10.3390/ijms231911929. -



 PDF下载 ( 7108 KB)
PDF下载 ( 7108 KB)

 下载:
下载: