小窝蛋白1在肝脏疾病中的调控作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240631
-
摘要: 小窝蛋白(CAV)1是质膜上小窝的结构蛋白,是肝脏功能的重要调节因子。CAV1可通过多种分子通路调节肝脏脂质沉积、脂质和葡萄糖代谢、线粒体功能和肝细胞增殖等。因此,CAV1在肝脂肪变性和肝细胞增殖等代谢调节过程中维持肝脏生理方面起着至关重要的作用。此外,CAV1还参与调节不同类型肝损伤、肝炎、肝硬化等疾病的发生发展过程。本文就CAV1在肝脏及相关疾病中的作用及调控肝巨噬细胞的机制进行综述,为靶向CAV1治疗肝脏相关疾病提供理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 小窝蛋白1 /
- 化学性与药物性肝损伤 /
- 肝纤维化 /
- 巨噬细胞
Abstract: Caveolin-1 (CAV1) is a structural protein of caveolae on the plasma membrane and is an important regulatory factor for liver function. CAV1 regulates hepatic lipid deposition, lipid and glucose metabolism, mitochondrial function, and hepatocyte proliferation through various molecular pathways. Therefore, CAV1 plays a crucial role in maintaining liver physiology during the metabolic regulatory processes such as hepatic steatosis and hepatocyte proliferation. Furthermore, CAV1 is also involved in the development and progression of different types of liver injury, hepatitis, and liver cirrhosis. This article reviews the role of CAV1 in liver-related diseases and its mechanism in the regulation of liver macrophages, so as to provide a theoretical basis for targeting CAV1 in the treatment of liver-related diseases.-
Key words:
- Caveolin-1 /
- Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury /
- Hepatic Fibrosis /
- Macrophages
-
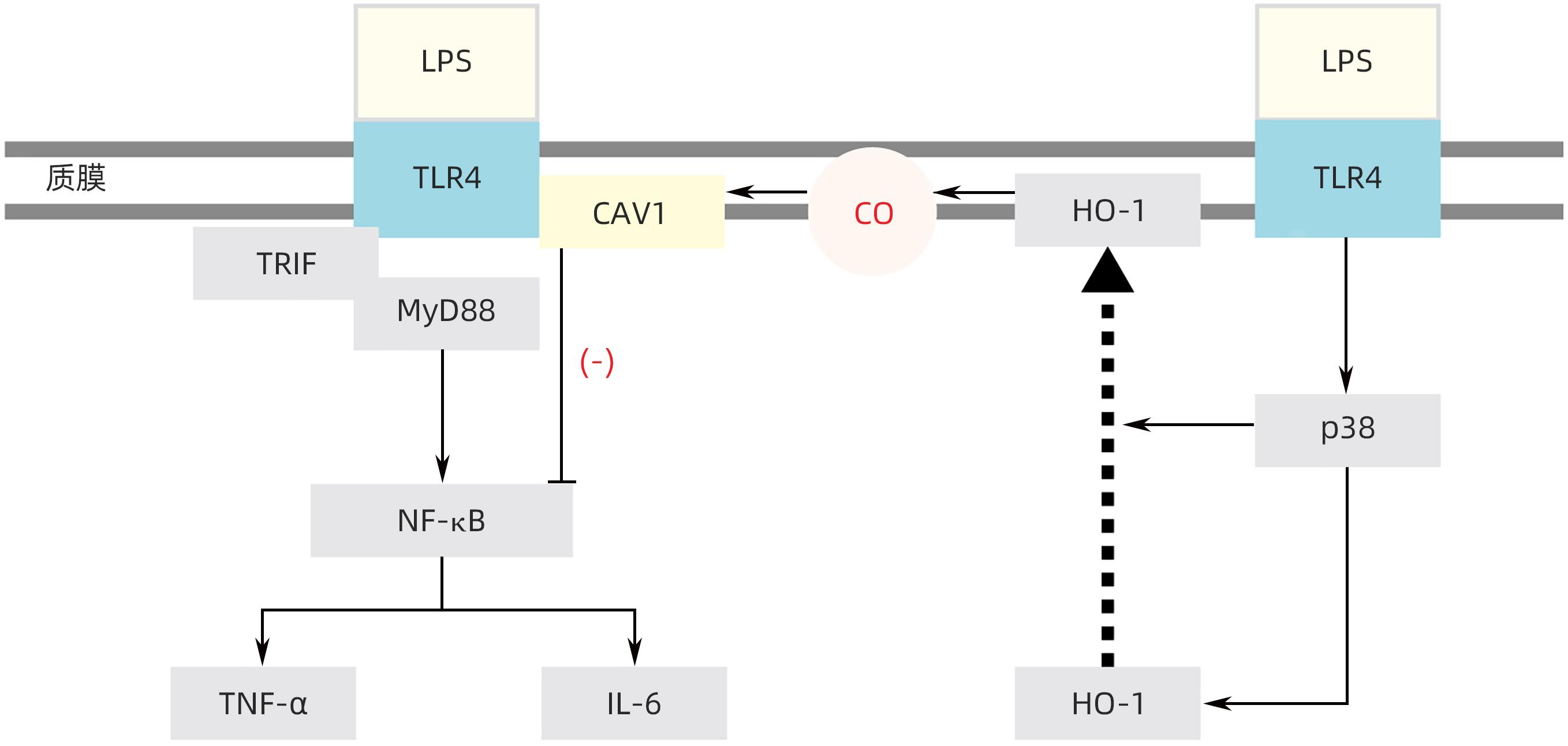
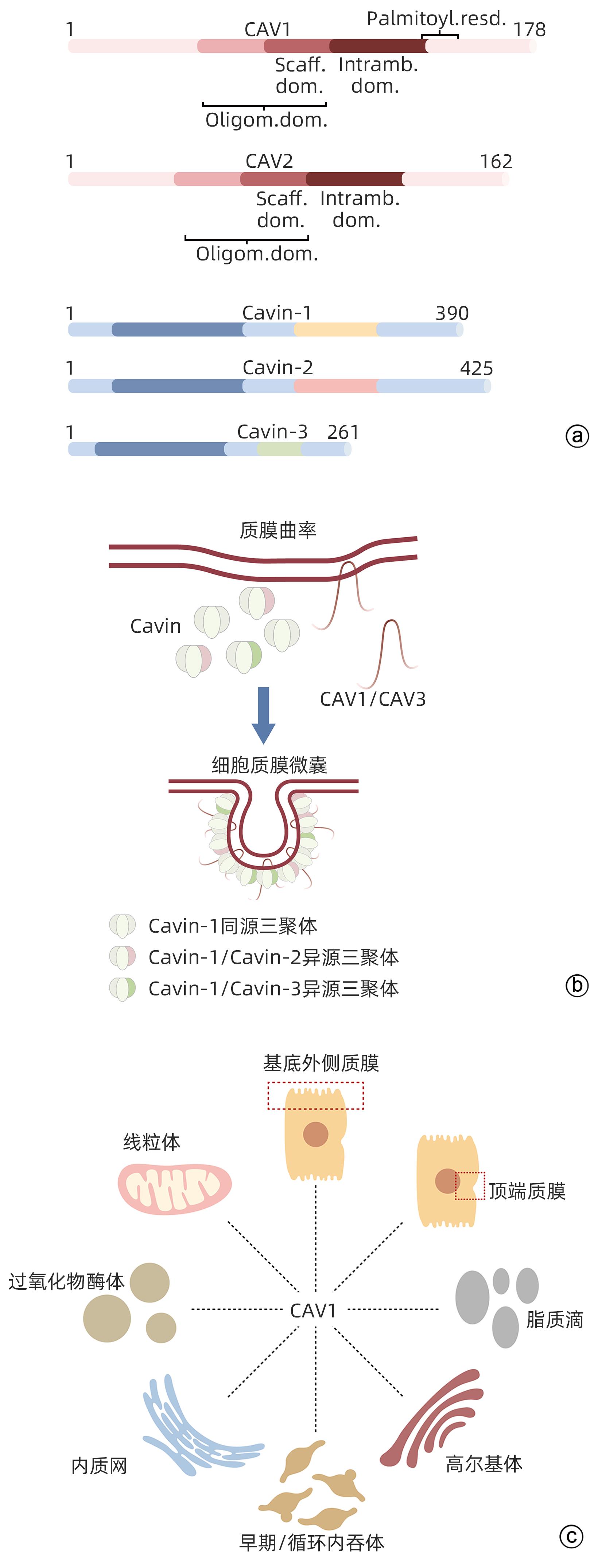
注: a,CAV1和CAV2蛋白中不同氨基酸结构域及Cavin-1,-2,-3蛋白示意图。CAV1和Cavin-1,-2,-3负责小窝的形成、完整性、动力学、内化和信号传导。b,小窝的形成:CAV1被招募到质膜上,与脂质形成低聚物和簇。这吸引了Cavin接近细胞表面的CAV1阳性区域,形成初始膜曲率。CAV1和Cavin募集到质膜刺激其初始曲率,逐步发展到小窝完全形成。c,CAV1在肝细胞的分布:CAV1在肝细胞基底外侧质膜形成小窝,顶端质膜CAV1调节胆汁分泌到微管,以及位于再生肝细胞的脂滴表面。在其他胞内小室如高尔基体、内质网、早期和再循环内体、过氧化物酶体和线粒体也观察到了CAV1的分布。
图 1 CAV和CAV腔隙形成的模型示意图[1]
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the cavity formation model of Caveolins and Caveolins[1]
-
[1] VOLONTE D, GALBIATI F. Caveolin-1, a master regulator of cellular senescence[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2020, 39( 2): 397- 414. DOI: 10.1007/s10555-020-09875-w. [2] SMART EJ, GRAF GA, MCNIVEN MA, et al. Caveolins, liquid-ordered domains, and signal transduction[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 1999, 19( 11): 7289- 7304. DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7289. [3] LI WP, LIU P, PILCHER BK, et al. Cell-specific targeting of caveolin-1 to caveolae, secretory vesicles, cytoplasm or mitochondria[J]. J Cell Sci, 2001, 114( Pt 7): 1397- 1408. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.114.7.1397. [4] FERNANDES IPG, OLIVEIRA-BRETT AM. Caveolin proteins electrochemical oxidation and interaction with cholesterol[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, 133: 107451. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2019.107451. [5] GAO L, ZHOU YC, ZHONG WC, et al. Caveolin-1 is essential for protecting against binge drinking-induced liver damage through inhibiting reactive nitrogen species[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 2): 687- 699. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27162. [6] FERNANDEZ-ROJO MA, RAMM GA. Caveolin-1 function in liver physiology and disease[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2016, 22( 10): 889- 904. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2016.08.007. [7] PIKE LJ. Growth factor receptors, lipid rafts and caveolae: An evolving story[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2005, 1746( 3): 260- 273. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.05.005. [8] WANG XM, KIM HP, NAKAHIRA K, et al. The heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide pathway suppresses TLR4 signaling by regulating the interaction of TLR4 with caveolin-1[J]. J Immunol, 2009, 182( 6): 3809- 3818. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0712437. [9] BAKER N, TUAN RS. The less-often-traveled surface of stem cells: Caveolin-1 and caveolae in stem cells, tissue repair and regeneration[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2013, 4( 4): 90. DOI: 10.1186/scrt276. [10] YIN YL, WEI LY, CASELEY EA, et al. Leveraging the ATP-P2X7 receptor signalling axis to alleviate traumatic CNS damage and related complications[J]. Med Res Rev, 2023, 43( 5): 1346- 1373. DOI: 10.1002/med.21952. [11] SAVIO LEB, de ANDRADE MELLO P, SANTOS SACS, et al. P2X7 receptor activation increases expression of caveolin-1 and formation of macrophage lipid rafts, thereby boosting CD39 activity[J]. J Cell Sci, 2020, 133( 5): jcs237560. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.237560. [12] PARAT MO, RIGGINS GJ. Caveolin-1, caveolae, and glioblastoma[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2012, 14( 6): 679- 688. DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nos079. [13] JIANG W, WANG JR, XUE WJ, et al. Caveolin-1 attenuates acetaminophen aggravated lipid accumulation in alcoholic fatty liver by activating mitophagy via the Pink-1/Parkin pathway[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 908: 174324. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174324. [14] FU DD, WU S, JIANG XF, et al. Caveolin-1 alleviates acetaminophen-induced vascular oxidative stress and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2023, 195: 245- 257. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.12.095. [15] MARCHESE S, POLO A, ARIANO A, et al. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological properties and their involvement in cancer development[J]. Toxins(Basel), 2018, 10( 6): 214. DOI: 10.3390/toxins10060214. [16] XU QQ, SHI WW, LV P, et al. Critical role of caveolin-1 in aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity via the regulation of oxidation and autophagy[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11( 1): 6. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-2197-6. [17] SILVERSTEIN R. D-galactosamine lethality model: Scope and limitations[J]. J Endotoxin Res, 2004, 10( 3): 147- 162. DOI: 10.1179/096805104225004879. [18] JIRILLO E, CACCAVO D, MAGRONE T, et al. The role of the liver in the response to LPS: Experimental and clinical findings[J]. J Endotoxin Res, 2002, 8( 5): 319- 327. DOI: 10.1179/096805102125000641. [19] TSAI TH, TAM K, CHEN SF, et al. Deletion of caveolin-1 attenuates LPS/GalN-induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22( 11): 5573- 5582. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13831. [20] ANTONIADES CG, BERRY PA, WENDON JA, et al. The importance of immune dysfunction in determining outcome in acute liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 49( 5): 845- 861. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.08.009. [21] MEDINA FA, COHEN AW, de ALMEIDA CJ, et al. Immune dysfunction in caveolin-1 null mice following infection with Trypanosoma cruzi(Tulahuen strain)[J]. Microbes Infect, 2007, 9( 3): 325- 333. DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2006.12.011. [22] SELZNER N, RUDIGER H, GRAF R, et al. Protective strategies against ischemic injury of the liver[J]. Gastroenterology, 2003, 125( 3): 917- 936. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(03)01048-5. [23] GAO L, CHEN XM, PENG T, et al. Caveolin-1 protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury through ameliorating peroxynitrite-mediated cell death[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2016, 95: 209- 215. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.03.023. [24] GARCÍA-CARDEÑA G, MARTASEK P, MASTERS BS, et al. Dissecting the interaction between nitric oxide synthase(NOS) and caveolin. Functional significance of the nos caveolin binding domain in vivo[J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272( 41): 25437- 25440. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.272.41.25437. [25] RUEGER SY, MCNAMARA PJ, KING AC. Expanding the utility of the Biphasic Alcohol Effects Scale(BAES) and initial psychometric support for the Brief-BAES(B-BAES)[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 2009, 33( 5): 916- 924. DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.00914.x. [26] NWOSU ZC, EBERT MP, DOOLEY S, et al. Caveolin-1 in the regulation of cell metabolism: A cancer perspective[J]. Mol Cancer, 2016, 15( 1): 71. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-016-0558-7. [27] LI L, LI LJ, LI W, et al. TAp73-induced phosphofructokinase-1 transcription promotes the Warburg effect and enhances cell proliferation[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9( 1): 4683. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07127-8. [28] SRIVASTAVA M, NAMBIAR M, SHARMA S, et al. An inhibitor of nonhomologous end-joining abrogates double-strand break repair and impedes cancer progression[J]. Cell, 2012, 151( 7): 1474- 1487. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.054. [29] ZHANG Y, ZHANG YJ, CHEN TT, et al. Caveolin-1 depletion attenuates hepatic fibrosis via promoting SQSTM1-mediated PFKL degradation in HSCs[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2023, 204: 95- 107. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.04.009. [30] LE SAUX CJ, TEETERS K, MIYASATO SK, et al. Down-regulation of caveolin-1, an inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling, in acute allergen-induced airway remodeling[J]. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283( 9): 5760- 5768. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M701572200. [31] RAZANI B, ZHANG XL, BITZER M, et al. Caveolin-1 regulates transforming growth factor(TGF)-beta/SMAD signaling through an interaction with the TGF-beta type I receptor[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276( 9): 6727- 6738. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M008340200. [32] LU J, ZHANG J, WANG Y, et al. Caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptides alleviate liver fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1/smad signaling in mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19( 6): 1729. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19061729. [33] FANG JT, de BRUIN A, VILLUNGER A, et al. Cellular polyploidy in organ homeostasis and regeneration[J]. Protein Cell, 2023, 14( 8): 560- 578. DOI: 10.1093/procel/pwac064. [34] FERNÁNDEZ MA, ALBOR C, INGELMO-TORRES M, et al. Caveolin-1 is essential for liver regeneration[J]. Science, 2006, 313( 5793): 1628- 1632. DOI: 10.1126/science.1130773. [35] WEN YK, LAMBRECHT J, JU C, et al. Hepatic macrophages in liver homeostasis and diseases-diversity, plasticity and therapeutic opportunities[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2021, 18( 1): 45- 56. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-00558-8. [36] KRENKEL O, HUNDERTMARK J, ABDALLAH AT, et al. Myeloid cells in liver and bone marrow acquire a functionally distinct inflammatory phenotype during obesity-related steatohepatitis[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 3): 551- 563. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318382. [37] TACKE F, ZIMMERMANN HW. Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60( 5): 1090- 1096. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.025. [38] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233( 9): 6425- 6440. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.26429. [39] WANG B, TONTONOZ P. Liver X receptors in lipid signalling and membrane homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14( 8): 452- 463. DOI: 10.1038/s41574-018-0037-x. [40] NAIK SU, WANG X, da SILVA JS, et al. Pharmacological activation of liver X receptors promotes reverse cholesterol transport in vivo[J]. Circulation, 2006, 113( 1): 90- 97. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.560177. [41] WU QH, JIN RR, FENG T, et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles and induced autophagy in human monocytes[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2017, 12: 3993- 4005. DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S135189. [42] GU HM, WANG FQ, ZHANG DW. Caveolin-1 interacts with ATP binding cassette transporter G1(ABCG1) and regulates ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1841( 6): 847- 858. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.02.002. [43] RAMĺREZ CM, TORRECILLA-PARRA M, PARDO-MARQUÉS V, et al. Crosstalk between LXR and caveolin-1 signaling supports cholesterol efflux and anti-inflammatory pathways in macrophages[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2021, 12: 635923. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.635923. [44] YANG ZH, ZHANG J, WANG Y, et al. Caveolin-1 deficiency protects mice against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury through regulating polarization of hepatic macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 713808. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713808. -



 PDF下载 ( 979 KB)
PDF下载 ( 979 KB)

 下载:
下载: