年龄≤30岁慢性HBV感染者启动抗病毒治疗无创预测模型的构建及分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240708
Establishment of a noninvasive predictive model for antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and an age of ≤30 years
-
摘要:
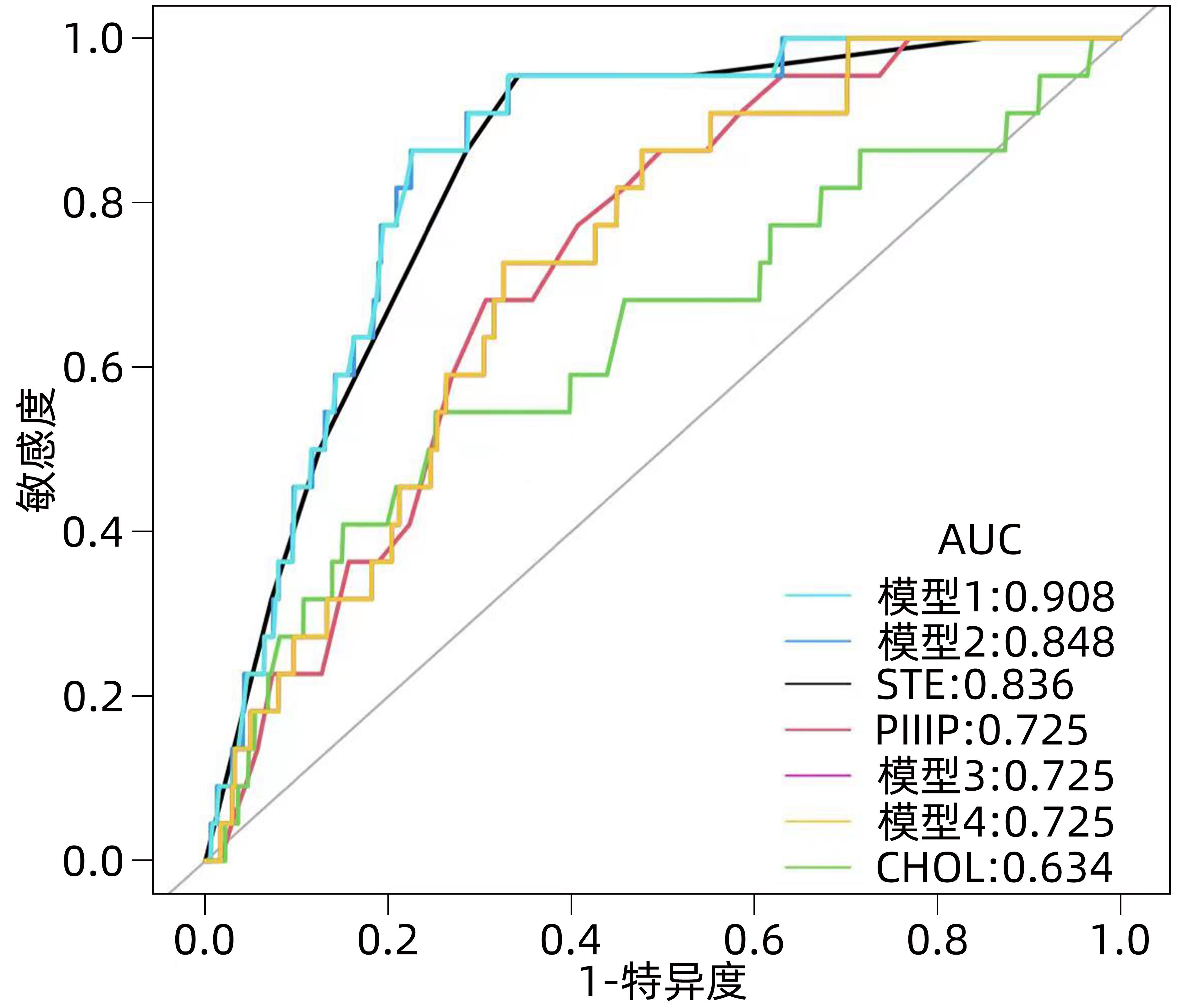
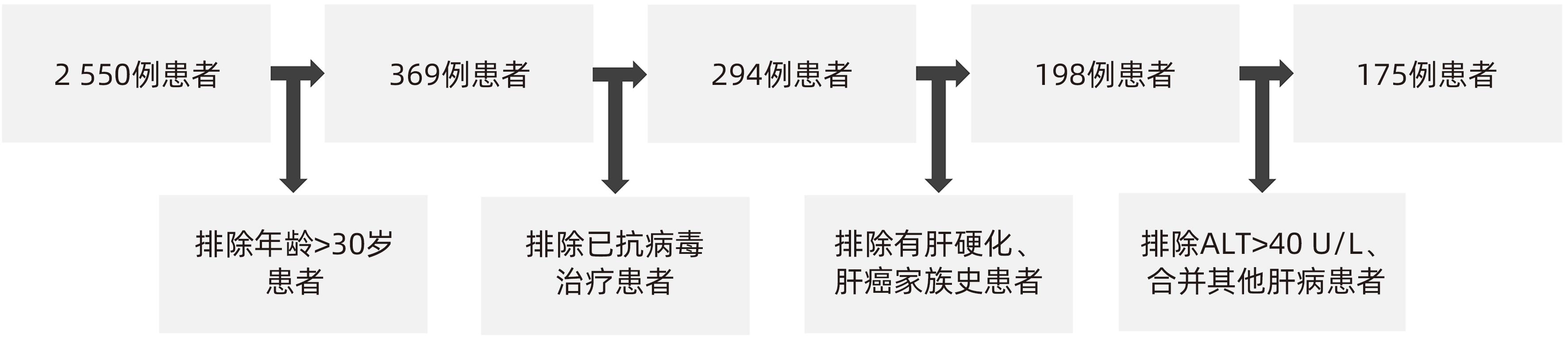
目的 通过构建无创模型预测年龄≤30岁的慢性HBV感染者是否需要抗病毒治疗,并验证其诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析2017年1月—2023年1月深圳市第三人民医院收治的175例符合纳入标准的慢性HBV感染者的临床资料,根据肝穿刺病理结果,将患者分为治疗组(有抗病毒治疗指征,n=41)和观察组(无抗病毒治疗指征,n=134)。分析两组患者的临床资料、影像学检查、血清生化学等指标,通过单因素及多因素Logistic回归分析影响患者具有抗病毒治疗指征的参数,通过相关参数构建不同的预测需要抗病毒治疗的模型,采用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)比较不同模型的诊断价值。符合正态分布的计量资料组间比较采用成组t检验;不符合正态分布的计量资料组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U秩和检验。计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher检验。 结果 治疗组和观察组两组间ALT、铁蛋白、总胆固醇(CHOL)、TG、PLT、肝硬度(STE)、Ⅲ型前胶原N末端肽(PⅢP)比较,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,CHOL(OR=0.4,95%CI:0.2~1.0)、STE(OR=1.5,95%CI:1.0~2.1)、PⅢP(OR=1.1,95%CI:1.0~1.1)是具有抗病毒治疗指征的独立预测因子。模型1(STE+PⅢP+CHOL)、模型2(STE+PⅢP)、模型3(STE+CHOL)、模型4(PⅢP+CHOL)及STE、PⅢP、CHOL的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.908、0.848、0.725、0.725、0.836、0.725、0.634,模型1 ROC曲线下面积最大,特异度为77.34%,敏感度为96.36%,与STE、PⅢP、CHOL及模型2、模型3、模型4比较,差异均有统计学意义(Z值分别为0.21、3.08、3.06、3.23、0.89、0.88,P值均<0.05)。 结论 通过由CHOL、STE、PⅢP指标构建的无创模型对年龄≤30岁的慢性HBV感染者是否需要抗病毒治疗有较好的预测价值。 Abstract:Objective To predict whether antiviral therapy is required in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and an age of ≤30 years by establishing a noninvasive model, and to investigate the diagnostic value of this model. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 175 patients with chronic HBV infection who were admitted to Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital from January 2017 to January 2023 and met the inclusion criteria, and according to the results of liver biopsy, they were divided into treatment group with 41 patients (with indications for antiviral therapy) and observation group with 134 patients (without indications for antiviral therapy). The two groups were analyzed in terms of the indicators including clinical data, imaging examinations, and serum biochemical parameters. The univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analyses were used to investigate the parameters affecting the indication for antiviral therapy, and different models for predicting the need for antiviral therapy were constructed based on related parameters. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to compare the diagnostic value of different models. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous variables between groups, and the Mann-Whitney U rank sum test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous variables between groups; the chi-square test or the Fisher’s exact test was used for comparison of categorical data between groups. Results There were significant differences between the treatment group and the observation group in alanine aminotransferase, ferritin, total cholesterol (CHOL), triglyceride, platelet count, liver stiffness measured by sound touch elastography (STE), and procollagen III N-terminal propeptide (PIIIP) (all P<0.05). The multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that CHOL (odds ratio [OR]=0.4, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.2 — 1.0), STE (OR=1.5, 95%CI: 1.0 — 2.1), and PIIIP (OR=1.1, 95%CI: 1.0 — 1.1) were independent predictive factors for the indications for antiviral therapy. Model 1 (STE+PIIIP+CHOL), model 2 (STE+PIIIP), model 3 (STE+CHOL), model 4 (PIIIP+CHOL) had an area under the ROC curve of 0.908, 0.848, 0.725, and 0.725, respectively, while STE, PIIIP, and CHOL used alone had an AUC of 0.836, 0.725, and 0.634, respectively, suggesting that model 1 had the largest AUC, with a specificity of 77.34% and a sensitivity of 96.36%, and had a significant difference compared with STE, PIIIP, CHOL, and the models 2, 3, and 4 (Z=0.21, 3.08, 3.06, 3.23, 0.89, and 0.88, all P<0.05). Conclusion The noninvasive model established based on CHOL, STE, and PIIIP has a good value in predicting the need for antiviral therapy in patients with chronic HBV infection and an age of ≤30 years. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B virus /
- Forecasting /
- Age Distribution
-
表 1 两组患者一般临床特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of the general clinical characteristics between the two patient groups
项目 观察组(n=134) 治疗组(n=41) 统计值 P值 ALT(U/L) 20.1±7.9 23.4±8.4 t=-2.288 0.023 AST(U/L) 29.3±8.2 30.9±8.3 t=0.893 0.051 Alb(g/L) 44.9±6.2 44.3±3.7 t=0.519 0.604 Ferr(ng/mL) 196.5(68.3~391.5) 268.5(98.2~429.2) Z=-1.173 0.032 CHOL(mmol/L) 4.3±0.7 3.8±1.1 t=3.303 0.001 GLU(mmol/L) 4.6±0.5 4.5±0.6 t=0.510 0.611 TG(mmol/L) 1.1±0.8 0.8±0.3 t=2.270 0.024 Cr(μmol/L) 70.2±17.3 71.7±15.6 t=-0.489 0.625 WBC(×109/L) 6.2±1.7 5.6±1.3 t=1.955 0.052 PLT(×109/L) 233.4±47.2 206.4±59.7 t=3.001 0.003 AFP(ng/mL) 2.3(1.7~3.1) 3.2(2.1~6.4) Z=-1.012 0.064 HA(ng/mL) 46.1±24.1 44.1±18.3 t=0.475 0.635 STE(kPa) 6.8±1.4 7.7±2.0 t=-2.479 0.015 脾厚度(mm) 32.0±5.2 32.0±5.6 t=0.015 0.988 合并脂肪肝[例(%)] 21(15.7) 4(9.8) χ2=0.897 0.344 门静脉内径(mm) 10.1±1.8 10.4±2.0 t=-1.038 0.301 PⅢP(ng/mL) 21.0±10.5 25.9±12.9 t=-2.423 0.016 CⅣ(ng/mL) 15.5±6.5 17.9±8.4 t=-1.865 0.064 LN(ng/mL) 15.5±8.3 16.9±9.1 t=-0.917 0.361 HBsAg(IU/mL) 7 987.4(1 890.7~55 986.7) 6 102.5(2 386.9~26 459.1) Z=-1.402 0.255 HBV DNA[例(%)] χ2=5.809 0.056 <103 IU/mL 69(51.5) 21(51.2) 103~105 IU/mL 12(8.9) 9(22.0) >105 IU/mL 53(39.6) 11(26.8) 性别[例(%)] χ2=0.005 0.944 女 58(43.3) 18(43.9) 男 76(56.7) 23(56.1) 年龄(岁) 27.3±3.1 27.1±3.2 t=0.292 0.771 乙型肝炎家族史[例(%)] 48(35.8) 18(43.9) χ2=0.873 0.350 BMI(kg/m2) 21.4±2.8 21.2±3.2 t=0.286 0.775 表 2 单因素及多因素Logistic 回归分析结果
Table 2. Results of the univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analysis
变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 ALT 1.1(1.0~1.1) 0.025 1.0(0.9~1.1) 0.749 AST 1.2(1.1~1.3) <0.001 1.1(0.9~1.4) 0.252 Ferr 1.0(1.0~1.0) 0.038 1.0(1.0~1.0) 0.195 CHOL 0.5(0.3~0.8) 0.003 0.4(0.2~1.0) 0.046 TG 0.3(0.1~0.8) 0.020 0.2(0.0~1.5) 0.115 PLT 1.0(1.0~1.0) 0.004 1.0(1.0~1.0) 0.416 STE 1.4(1.0~1.9) 0.025 1.5(1.0~2.1) 0.029 PⅢP 1.0(1.0~1.1) 0.021 1.1(1.0~1.1) 0.049 表 3 需要抗病毒治疗的预测模型构建及比较
Table 3. Predictive model construction and comparison requiring antiviral therapy
参数 AUC 95%CI P值 特异度 敏感度 STE 0.836 0.773~0.899 <0.001 0.657 7 0.954 5 PⅢP 0.725 0.641~0.810 <0.001 0.693 3 0.681 8 CHOL 0.634 0.502~0.766 <0.001 0.748 0 0.545 5 模型1 0.908 0.790~0.937 <0.001 0.773 4 0.963 6 模型2 0.848 0.790~0.907 <0.001 0.775 3 0.863 6 模型3 0.725 0.638~0.812 <0.001 0.674 0 0.727 3 模型4 0.725 0.638~0.812 <0.001 0.674 0 0.727 3 注:模型1,STE+PⅢP+CHOL;模型2,STE+PⅢP,模型3,STE+CHOL,模型4,PⅢP+CHOL。 -
[1] World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report, 2017[EB/OL].( 2019-04-04)[ 2022-07-05]. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global hepatitis report2017/en/. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global hepatitis report2017/en/ [2] LIU J, LIANG WN, JING WZ, et al. Countdown to 2030: Eliminating hepatitis B disease, China[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2019, 97( 3): 230- 238. DOI: 10.2471/BLT.18.219469. [3] FATTOVICH G, BORTOLOTTI F, DONATO F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48( 2): 335- 352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.11.011. [4] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2022)[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 传染病信息, 2023, 36( 1): 1- 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2023.01.01. [5] XIAO GQ, YANG JY, YAN LN. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis-4 index for detecting liver fibrosis in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systemic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61( 1): 292- 302. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27382. [6] EKIN N, UCMAK F, EBIK B, et al. GPR, King’s Score and S-Index are superior to other non-invasive fibrosis markers in predicting the liver fibrosis in chronic Hepatitis B patients[J]. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2022, 85( 1): 62- 68. DOI: 10.51821/85.1.9156. [7] LIANG XE, DAI L, YANG SL, et al. Combining routine markers improves the accuracy of transient elastography for hepatitis B cirrhosis detection[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2016, 48( 5): 512- 518. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.02.002. [8] ZHOU XL, MA X, WANG YB, et al. Value of aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index, fibrosis-4, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio in diagnosis of liver inflammation grade in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 9): 2066- 2070. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.09.013.周新兰, 马鑫, 王雁冰, 等. APRI、FIB-4和GPR对慢性乙型肝炎肝脏炎症程度的诊断价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 9): 2066- 2070. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.09.013. [9] GUHA IN, ROSENBERG WM. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis: Serum markers, imaging, and other modalities[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2008, 12( 4): 883- 900, x. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2008.07.010. [10] ZACCHERINI G, BERNARDI M. The role and indications of albumin in advanced liver disease[J]. Acta Gastroenterol Belg, 2019, 82( 2): 301- 308. [11] LIN WQ, SUN XC, FENG T, et al. Application of serum cholinesterase albumin total cholesterol level in liver function evaluation of patients with hepatitis cirrhosis[J]. J Pract Med Tech, 2020, 27( 4): 459- 461. DOI: 10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2020.04.021.林伟强, 孙小纯, 冯涛, 等. 血清胆碱酯酶白蛋白总胆固醇水平检测在肝炎肝硬化患者肝功能评估中的应用[J]. 实用医技杂志, 2020, 27( 4): 459- 461. DOI: 10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2020.04.021. [12] ZHANG LJ, SHU XC, XIAO YH. Clinical significance of serum total cholesterol, albumin, prealbum and total bile acid determination in paitients with liver cirrhosis[J]. China Pract Med, 2010, 5( 15): 15- 16. DOI: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2010.15.095.张丽娟, 舒晓春, 肖艳辉. 血清TC、ALB、PA和TBA测定在肝硬化中的临床意义[J]. 中国实用医药, 2010, 5( 15): 15- 16. DOI: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2010.15.095. [13] MA LJ, JI D, WANG CY, et al. A noninvasive diagnosis model for chronic hepatitis B patient based on conventional parameters[J]. Med J Chin People’s Liberation Army, 2019, 44( 10): 857- 861. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2019.10.08.马丽君, 纪冬, 王春艳, 等. 基于常规指标建立肝脏炎症及纤维化无创诊断模型[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2019, 44( 10): 857- 861. DOI: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2019.10.08. [14] YANG K, PAN Y, JIN L. Clinical value on serum sCD14 level in predicting liver inflammation and fibrosis grade in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Jiujiang Univ Nat Sci Ed, 2021, 36( 3): 85- 89. DOI: 10.19717/j.cnki.jjun.2021.03.022.杨凯, 潘颖, 金蕾. 慢性乙型肝炎患者血清sCD14分子预测肝脏炎症和纤维化等级的临床价值[J]. 九江学院学报(自然科学版), 2021, 36( 3): 85- 89. DOI: 10.19717/j.cnki.jjun.2021.03.022. [15] ZHU L, YANG JR, HE LL, et al. Advances on the application of transient elastography in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2023, 15( 3): 16- 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2023.03.003.朱璐, 杨君茹, 何玲玲, 等. 瞬时弹性成像在肝纤维化诊断中的应用研究进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2023, 15( 3): 16- 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2023.03.003. [16] ZHENG M, CAI WM, WENG HL, et al. ROC curve in evaluation of serum fibrosis index for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2002, 20( 4): 225- 228. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn: 1000-6680.2002.04.009.郑敏, 蔡卫民, 翁红雷, 等. ROC曲线评价血清纤维化指标对诊断肝纤维化的价值[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2002, 20( 4): 225- 228. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn:1000-6680.2002.04.009. -



 PDF下载 ( 905 KB)
PDF下载 ( 905 KB)

 下载:
下载: