三维可视化技术辅助肝细胞癌消融治疗有效性及安全性的Meta分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240718
Efficacy and safety of three-dimensional visualization technology in assisting ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
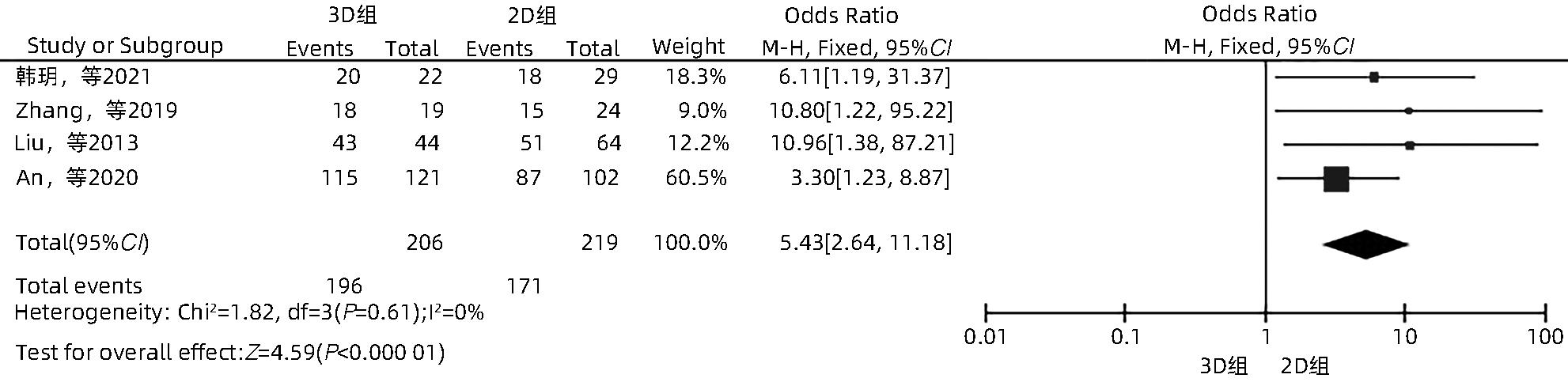
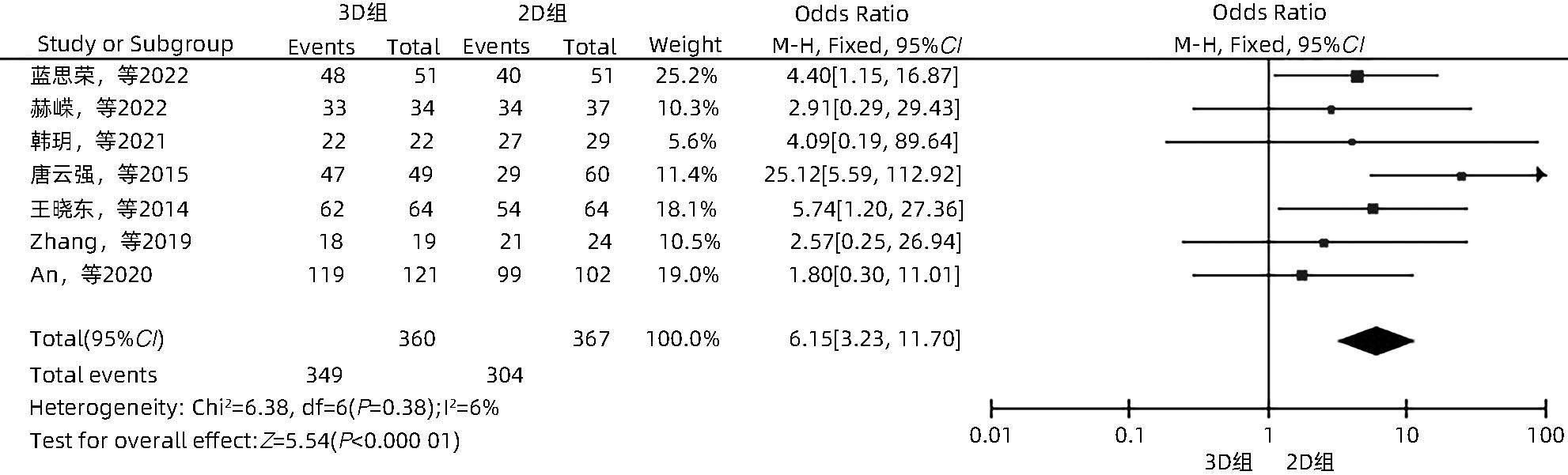
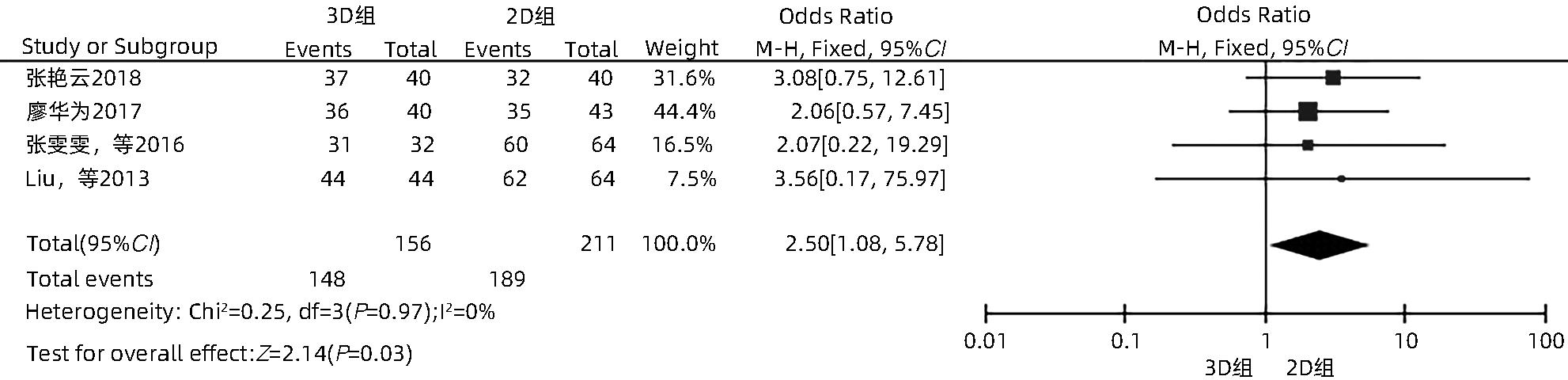
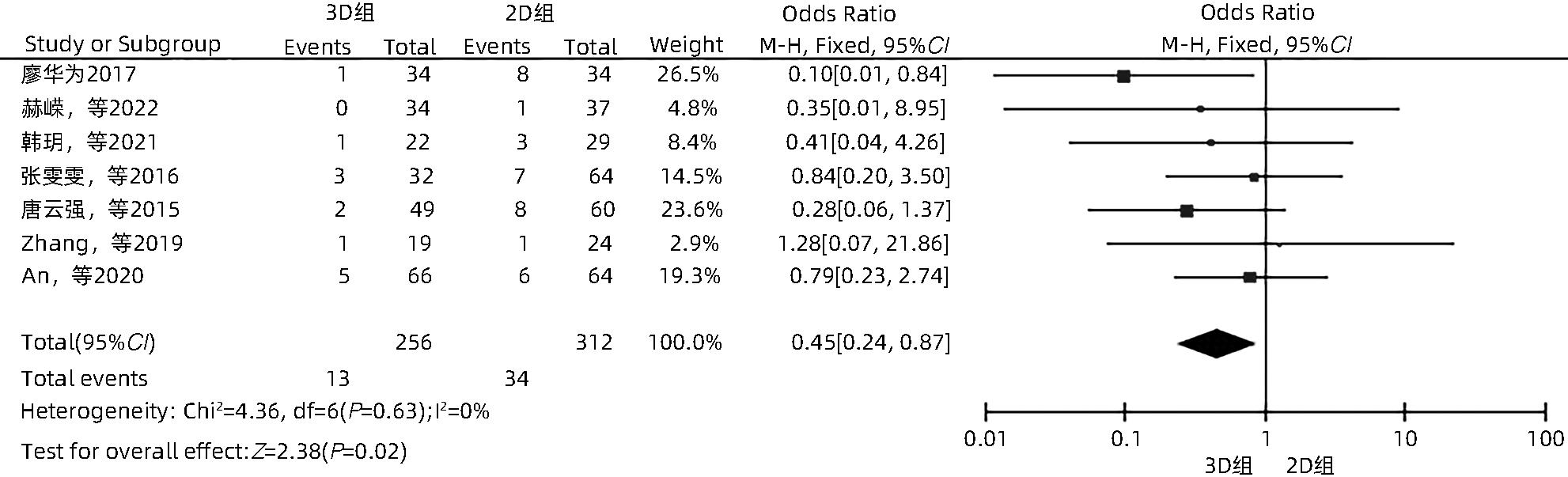
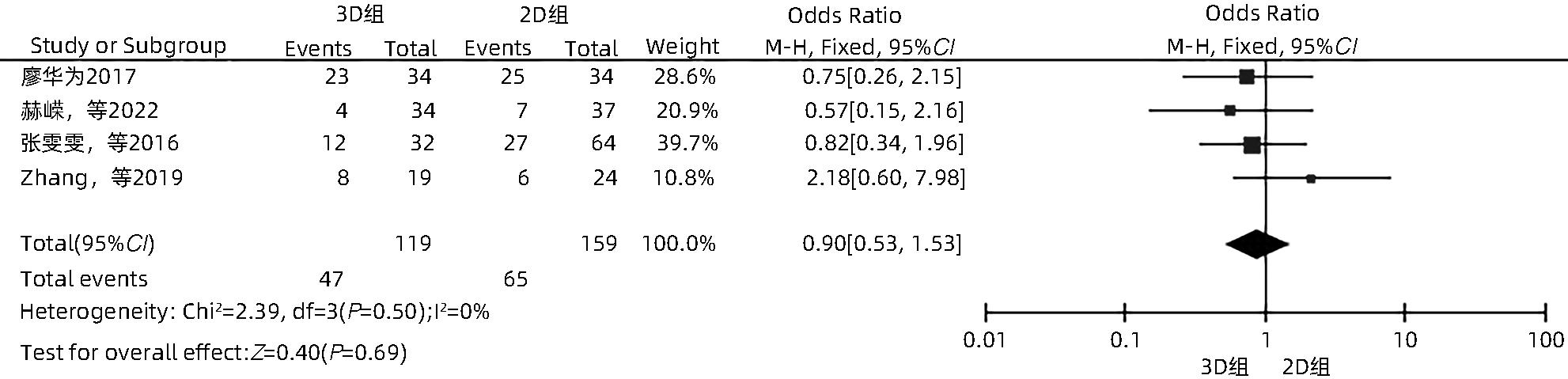
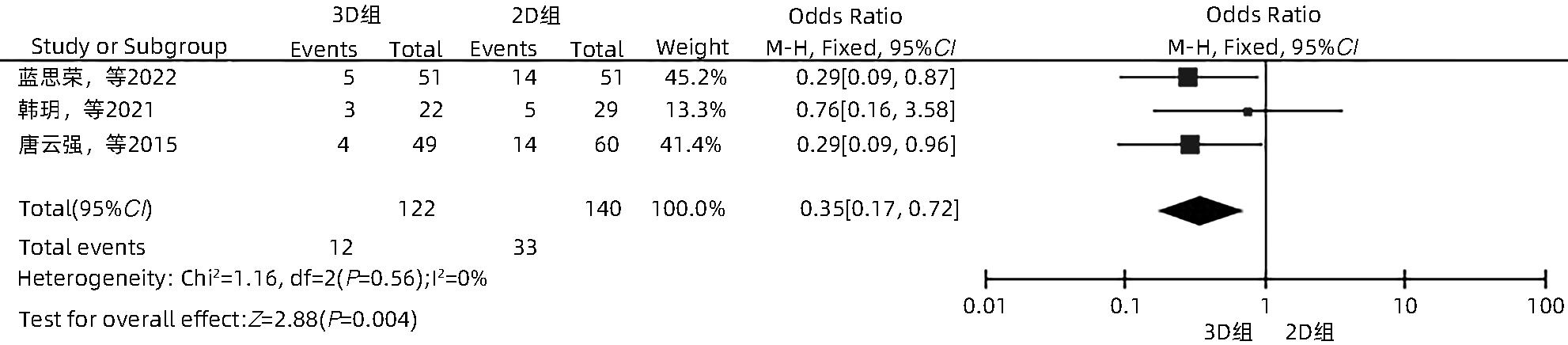
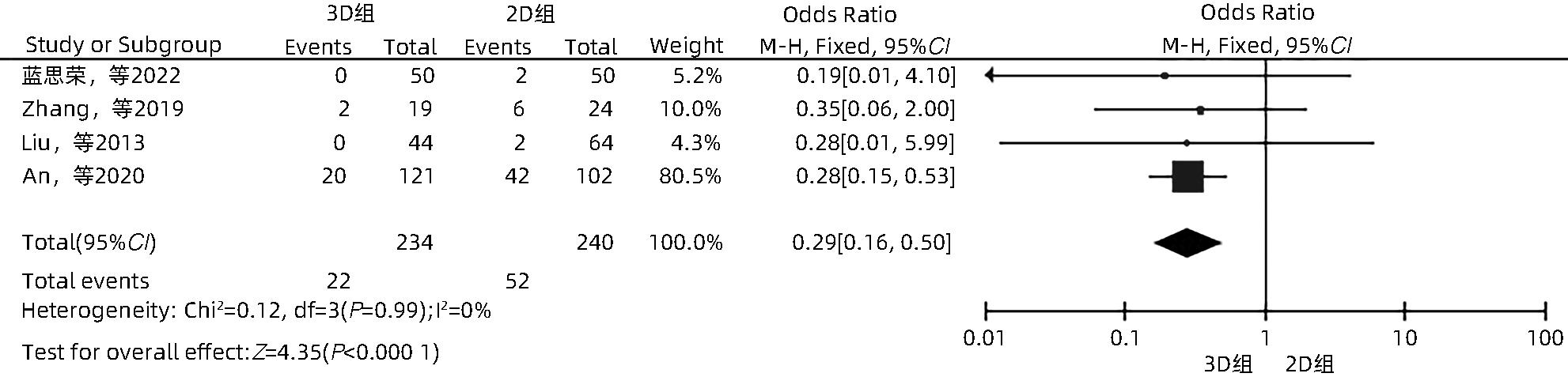
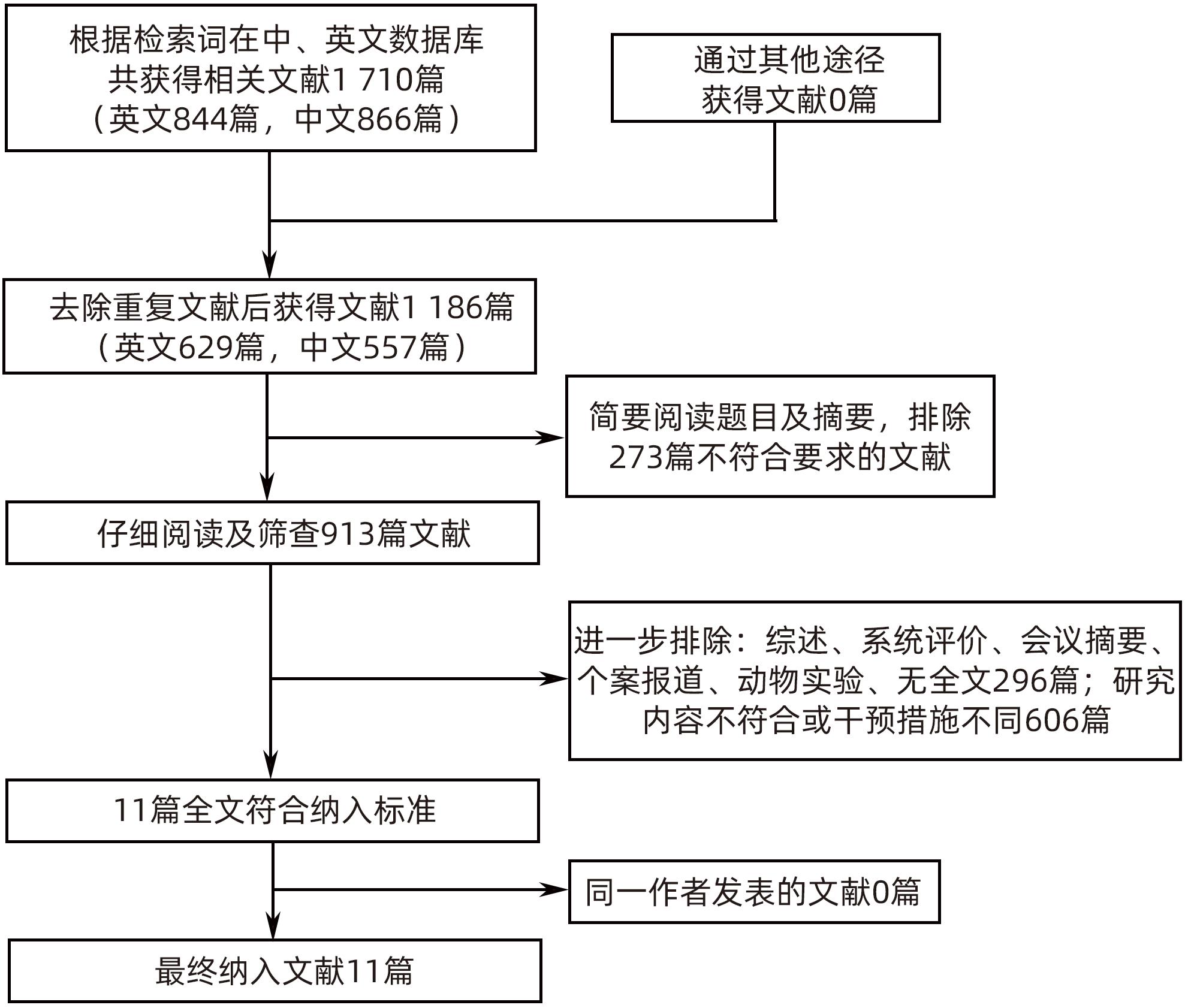
目的 系统性评价三维可视化技术辅助肝细胞癌消融治疗的有效性和安全性。 方法 本研究根据PRISMA指南完成,PROSPERO注册号:CRD42023488398。计算机检索PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网数据库、万方数据库、维普数据库和中国生物医学文献数据库中公开发表的有关三维可视化技术辅助肝细胞癌消融治疗的所有中、英文文献,检索时间为自建库至2023年3月。对纳入的研究进行质量评价和数据提取后,采用RevMan 5.4软件进行Meta分析。 结果 最终纳入11篇文献,共972例患者,其中447例采用三维可视化技术辅助消融(3D组),525例采用常规二维影像技术辅助消融(2D组)。Meta分析结果显示,3D组首次治疗成功率(OR=5.43,95%CI:2.64~11.18,P<0.001)、技术有效率(OR=6.15,95%CI:3.23~11.70,P<0.001)、完全消融率(OR=2.50,95%CI:1.08~5.78,P=0.03)均显著高于2D组;在安全性方面,严重并发症发生率(OR=0.45,95%CI:0.24~0.87,P=0.02)、局部复发率(OR=0.35,95%CI:0.17~0.72,P=0.004)和局部肿瘤进展率(OR=0.29,95%CI:0.16~0.50,P<0.001)均明显低于2D组;两组的轻度并发症发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 三维可视化技术辅助肝细胞癌消融治疗安全可行,可以提高消融率,并降低严重并发症发生率、局部复发率及局部肿瘤进展率,在临床中有重要应用价值。 Abstract:Objective To systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of three-dimensional visualization technology in assisting ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Methods This study was conducted according to PRISMA guidelines, with a PROSPERO registration number of CRD42023488398. PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, CNKI, Wanfang Data, VIP, and CBM were searched for Chinese and English articles on three-dimensional visualization technology in assisting ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma published up to March 2023. After quality assessment and data extraction of the studies included, RevMan 5.4 software was used to perform the meta-analysis. Results A total of 11 studies were included, with 972 patients in total, among whom 447 underwent ablation assisted by three-dimensional visualization technology (3D group) and 525 underwent ablation assisted by traditional two-dimensional imaging technology (2D group). The meta-analysis showed that compared with the 2D group, the 3D group had significantly higher success rate of first-time ablation treatment (odds ratio [OR]=5.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.64 — 11.18, P<0.001), technical efficiency (OR=6.15, 95%CI: 3.23 — 11.70, P<0.001), and complete ablation rate (OR=2.50, 95%CI: 1.08 — 5.78, P=0.03), as well as significantly lower incidence rate of major complications (OR=0.45, 95%CI: 0.24 — 0.87, P=0.02), local recurrence rate (OR=0.35, 95%CI: 0.17 — 0.72, P=0.004), and local tumor progression rate (OR=0.29, 95%CI: 0.16 — 0.50, P<0.001), while there was no significant difference in the incidence rate of mild complications between the two groups (P>0.05). Conclusion Three-dimensional visualization technology is safe and feasible in assisting ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma and can improve ablation rate and reduce the incidence rate of serious complications, local recurrence rate, and local tumor progression rate, thereby showing an important application value in clinical practice. -
表 1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1. Basic characteristics of the included studies
纳入文献 年份 国家 研究 类型 消融 方式 引导方式 样本量(例) 肿瘤大小(cm) 单发/多发 Child-Pugh分级 观察指标1) 3D组 2D组 3D组 2D组 3D组 2D组 蓝思荣等[16] 2022 中国 RCT 微波消融 CEUS联合 3D超声 CEUS 51 51 1.90±0.60 A/B ②⑥⑦ 张艳云[17] 2018 中国 RCT 微波消融 超声联合 3D技术 超声 40 40 大肝癌 ③ 廖华为[18] 2017 中国 RCT 微波消融 3D技术 超声 34 34 大肝癌 多发 A/B ③④⑤ 赫嵘等[19] 2022 中国 RCT 射频消融 超声 超声 34 37 1.40~2.50 1.50~2.40 多发 A/B ②④⑤ 韩玥等[20] 2021 中国 RCT 微波消融 超声 22 29 2.50±0.80 2.70±1.10 多发 A/B ①②④⑥ 张雯雯等[21] 2016 中国 非RCT 射频消融 腹腔镜 腹腔镜 32 64 <5.00 A/B ③④⑤ 唐云强等[13] 2015 中国 非RCT 射频消融 超声 超声 49 60 3.00~5.00 单发 A/B ②④⑥ 王晓东等[22] 2014 中国 RCT 射频消融 3D-CEUS联合2D-CEUS 2D-CEUS 64 64 3.46±0.88 3.45±1.05 单发 ② Zhang等[10] 2019 中国 非RCT 微波消融 超声联合 3D技术 超声 19 24 4.14±0.95 4.07±0.91 单发 A/B ①②④ ⑤⑦ Liu等[23] 2013 中国 非RCT 微波消融 超声 超声 36 58 3.11±1.30 3.05±1.04 多发 A/B/C ①③⑦ An等[24] 2020 中国 非RCT 微波消融 CEUS CEUS 66 64 5.00±1.50 5.00±1.60 多发 A/B ①②④⑦ 注:1)观察指标包括①首次治疗成功率;②技术有效率;③完全消融率;④严重并发症发生率;⑤轻度并发症发生率;⑥局部复发率;⑦局部肿瘤进展率。CEUS,超声造影;3D-CEUS,三维超声造影;2D-CEUS,二维超声造影;大肝癌,文献未具体描述大小。 表 2 RCT研究的质量评价
Table 2. Quality assessment of RCT studies
表 3 非RCT研究的质量评价
Table 3. Quality assessment of non-RCT studies
-
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [2] General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009.国家卫生健康委办公厅. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. [3] NGUYEN QT, TSIEN RY. Fluorescence-guided surgery with live molecular navigation: A new cutting edge[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2013, 13( 9): 653- 662. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3566. [4] POMPILI M, SAVIANO A, de MATTHAEIS N, et al. Long-term effectiveness of resection and radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3 cm. Results of a multicenter Italian survey[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59( 1): 89- 97. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.009. [5] LIVRAGHI T. Single HCC smaller than 2 cm: surgery or ablation: Interventional oncologist’s perspective[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2010, 17( 4): 425- 429. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-009-0244-x. [6] FENG K, YAN J, LI XW, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 57( 4): 794- 802. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.05.007. [7] SOLBIATI L, IERACE T, TONOLINI M, et al. Guidance and monitoring of radiofrequency liver tumor ablation with contrast-enhanced ultrasound[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2004, 51 Suppl: S19- S23. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2004.03.035. [8] Chinese Society of Digital Medicine, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Liver Cancer, Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Clinical Precision Medicine Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, et al. Three-dimensional visualization and accurate diagnosis and treatment guidelines for complex liver tumors(2019 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2019, 39( 8): 766- 774. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.08.02.中华医学会数字医学分会, 中国医师协会肝癌专业委员会, 中国医师协会临床精准医学专业委员会, 等. 复杂性肝脏肿瘤三维可视化精准诊治指南(2019版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2019, 39( 8): 766- 774. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.08.02. [9] WANG C, HUANG Q, YANG J. Meta-analysis of application value of three-dimensional visualization technique in liver cancer surgery[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2020, 29( 1): 19- 26. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.01.003.王程, 黄强, 杨骥. 三维可视化技术在肝脏恶性肿瘤手术中应用价值Meta分析[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2020, 29( 1): 19- 26. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.01.003. [10] ZHANG DZ, LIANG WZ, ZHANG M, et al. Multiple antenna placement in microwave ablation assisted by a three-dimensional fusion image navigation system for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2019, 35( 1): 122- 132. DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1484183. [11] AHMED M, SOLBIATI L, BRACE CL, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update[J]. Radiology, 2014, 273( 1): 241- 260. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14132958. [12] DINDO D, DEMARTINES N, CLAVIEN PA. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey[J]. Ann Surg, 2004, 240( 2): 205- 213. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. [13] TANG YQ, JIANG P, SHI BY, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction to improve the success rate in the first attempt of radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2015, 21( 10): 664- 667. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2015.10.005.唐云强, 江鹏, 石波云, 等. 三维重建在提高肝癌第一次射频消融治疗成功率的应用价值[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2015, 21( 10): 664- 667. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2015.10.005. [14] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary?[J]. Control Clin Trials, 1996, 17( 1): 1- 12. DOI: 10.1016/0197-2456(95)00134-4. [15] LUCHINI C, STUBBS B, SOLMI M, et al. Assessing the quality of studies in meta-analyses: Advantages and limitations of the Newcastle Ottawa Scale[J]. World J Meta Anal, 2017, 5( 4): 80. DOI: 10.13105/wjma.v5.i4.80. [16] LAN SR, XU JW, ZHANG YM, et al. Guidance of real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and 3D ultrasound fusion imaging for ablation area in patients with primary liver cancer during microwave ablation therapy[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2022, 25( 6): 889- 892. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2022.06.033.蓝思荣, 徐继威, 张耀明, 等. 实时超声造影与3D超声融合成像导航评估微波消融治疗原发性肝癌患者价值研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2022, 25( 6): 889- 892. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2022.06.033. [17] ZHANG YY. To explore the clinical effect of microwave ablation guided by ultrasound combined with three-dimensional imaging technology in the treatment of large liver cancer[J]. Cap Food Med, 2018, 25( 17): 69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8257.2018.17.052.张艳云. 探讨超声联合三维影像技术引导微波消融治疗大肝癌的临床疗效[J]. 首都食品与医药, 2018, 25( 17): 69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8257.2018.17.052. [18] LIAO HW. Study on three-dimensional visualization technology in microwave ablation of liver cancer[J]. World Latest Med Inf, 2017, 17( 61): 46. DOI: 10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2017.61.033.廖华为. 三维可视化技术在微波消融治疗肝癌中的研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2017, 17( 61): 46. DOI: 10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2017.61.033. [19] HE R, JIA Z, JIANG L, et al. Application of the three-dimensional visualization ablation planning system in radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 9): 2046- 2052. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.019.赫嵘, 贾哲, 蒋力, 等. 三维可视化消融辅助系统在肝细胞癌射频消融术中的应用价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 9): 2046- 2052. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.09.019. [20] HAN Y, LIU CB, LI J. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation assisted by three-dimensional visualization operative planning for liver cancer abutting diaphragmatic dome[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 30( 11): 1256- 1261. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2021.11.011.韩玥, 刘春波, 李津. 三维可视化术前规划辅助超声引导下经皮微波消融治疗临近膈顶肝癌[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2021, 30( 11): 1256- 1261. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2021.11.011. [21] ZHANG WW, WANG HG, SHI XJ, et al. Significance of three-dimensional reconstruction as a method of preoperative planning of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation[J]. Chin J Surg, 2016, 54( 9): 692- 699. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2016.09.009.张雯雯, 王宏光, 史宪杰, 等. 三维重建术前规划在腹腔镜超声引导的肝癌射频消融术中的应用探讨[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2016, 54( 9): 692- 699. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-5815.2016.09.009. [22] WANG XD, ZHAO P. Comparison between two-dimensional and three-dimensional contrast-enhanced ultrasound radiofrequency ablation in application of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Sun Yat Sen Univ Med Sci, 2014, 35( 4): 602- 606.王晓东, 赵萍. 二维与三维超声造影在原发性肝癌射频治疗中的应用比较[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2014, 35( 4): 602- 606. [23] LIU FY, LIANG P, YU XL, et al. A three-dimensional visualisation preoperative treatment planning system in microwave ablation for liver cancer: A preliminary clinical application[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2013, 29( 7): 671- 677. DOI: 10.3109/02656736.2013.834383. [24] AN C, LI X, ZHANG M, et al. 3D visualization ablation planning system assisted microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma(Diameter>3): A precise clinical application[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20( 1): 44. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-6519-y. [25] LIANG P, WANG Y. Microwave ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncology, 2007, 72( Suppl 1): 124- 131. DOI: 10.1159/000111718. [26] FENSTER A, SURRY K, SMITH W, et al. 3D ultrasound imaging: Applications in image-guided therapy and biopsy[J]. Comput Graph, 2002, 26( 4): 557- 568. DOI: 10.1016/s0097-8493(02)00101-2. [27] YUAN YC, YUAN XC, WANG Q, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation assisted by three-dimensional planning system combined with transhepatic arterial chemoembolization for treating single large hepatocellular carcinoma: A primary study of survival[J/CD]. Chin J Med Ultrasound(Electronic Edition), 2020, 17( 4): 315- 319. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2020.04.005.袁迎春, 袁晓春, 王琦, 等. 三维可视化术前规划系统辅助超声引导微波消融联合肝动脉化疗栓塞治疗大肝癌效果的初步研究[J/CD]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2020, 17( 4): 315- 319. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2020.04.005. [28] ROBERTS DW, STROHBEHN JW, HATCH JF, et al. A frameless stereotaxic integration of computerized tomographic imaging and the operating microscope[J]. J Neurosurg, 1986, 65( 4): 545- 549. DOI: 10.3171/jns.1986.65.4.0545. [29] JIANG JH, PEI L, JIANG RY. Clinical efficacy and safety of 3D vascular reconstruction combined with 3D navigation in laparoscopic hepatectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 13( 3): 1215- 1223. DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-198. [30] ZHAO QX, YU J, DONG LN, et al. Analysis of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma treated by microwave ablation assisted by three-dimensional visualization[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2019, 39( 10): 1068- 1070, 1076. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.10.18.赵勤显, 于杰, 董立男, 等. 三维可视化辅助经皮微波消融治疗复发性肝癌价值分析[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2019, 39( 10): 1068- 1070, 1076. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.10.18. [31] BALE R, SCHULLIAN P, EBERLE G, et al. Stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: A histopathological study in explanted livers[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 3): 840- 850. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30406. [32] LAIMER G, SCHULLIAN P, JASCHKE N, et al. Minimal ablative margin(MAM) assessment with image fusion: An independent predictor for local tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30( 5): 2463- 2472. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06609-7. [33] HOCQUELET A, TRILLAUD H, FRULIO N, et al. Three-dimensional measurement of hepatocellular carcinoma ablation zones and margins for predicting local tumor progression[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2016, 27( 7): 1038- 1045. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.02.031. [34] PERRODIN S, LACHENMAYER A, MAURER M, et al. Percutaneous stereotactic image-guided microwave ablation for malignant liver lesions[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 13836. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-50159-3. [35] LIANG P, DONG BW, YU XL, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous microwave ablation[J]. Radiology, 2005, 235( 1): 299- 307. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2351031944. -



 PDF下载 ( 1241 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1241 KB)

 下载:
下载: