基质金属蛋白酶7在肝癌细胞迁移及免疫细胞浸润中的作用与预后价值
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240721
Role and prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase-7 in the migration and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要:
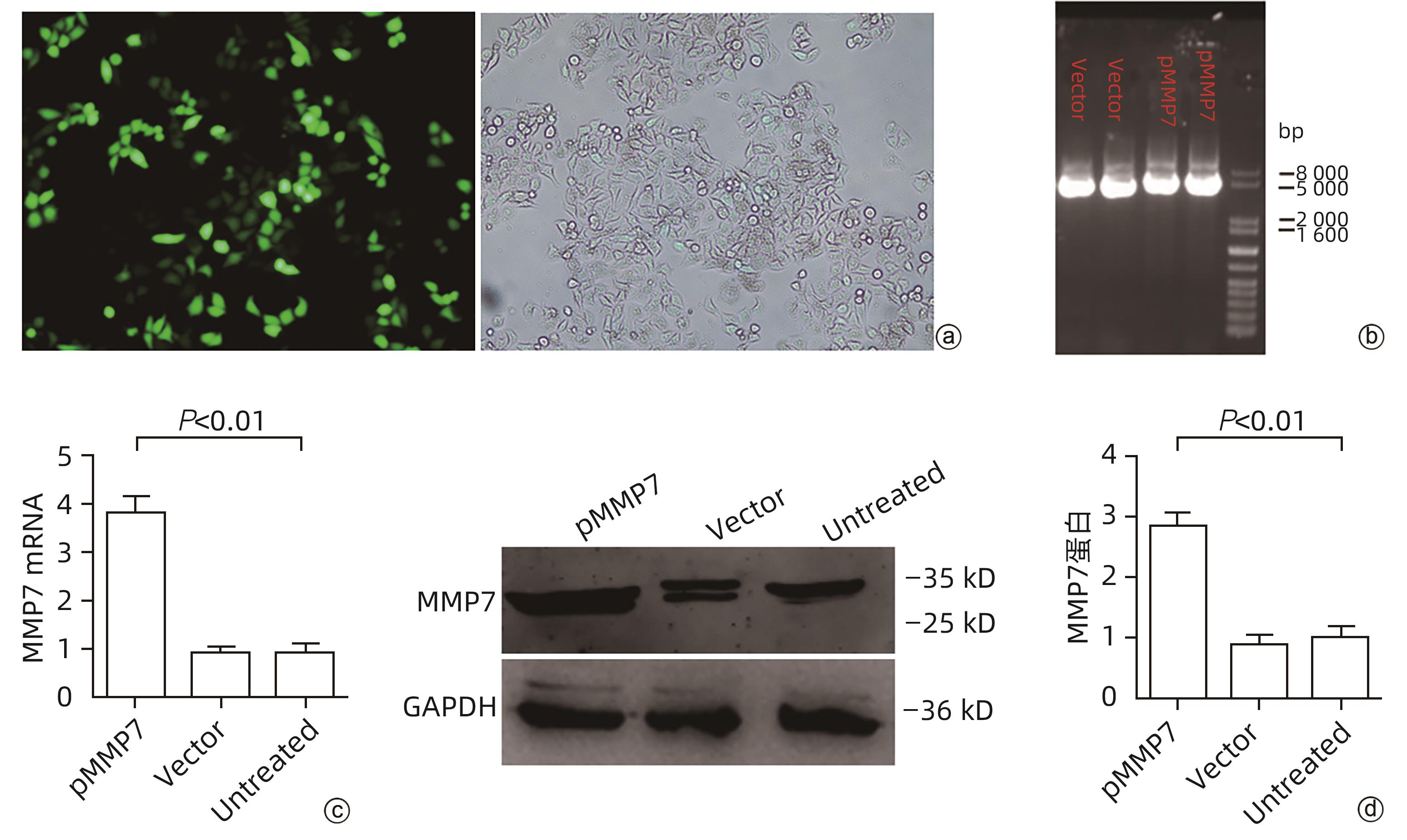
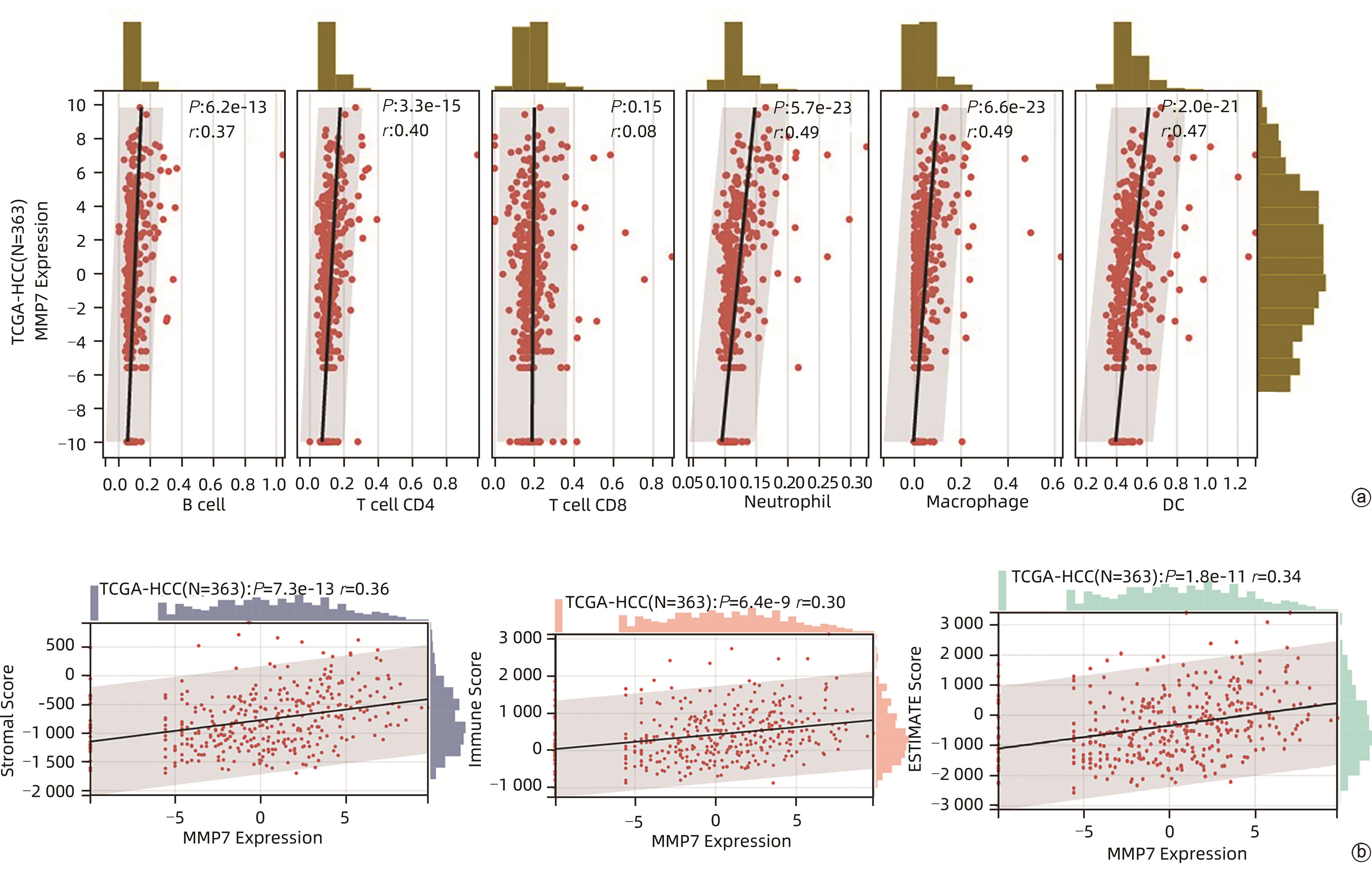
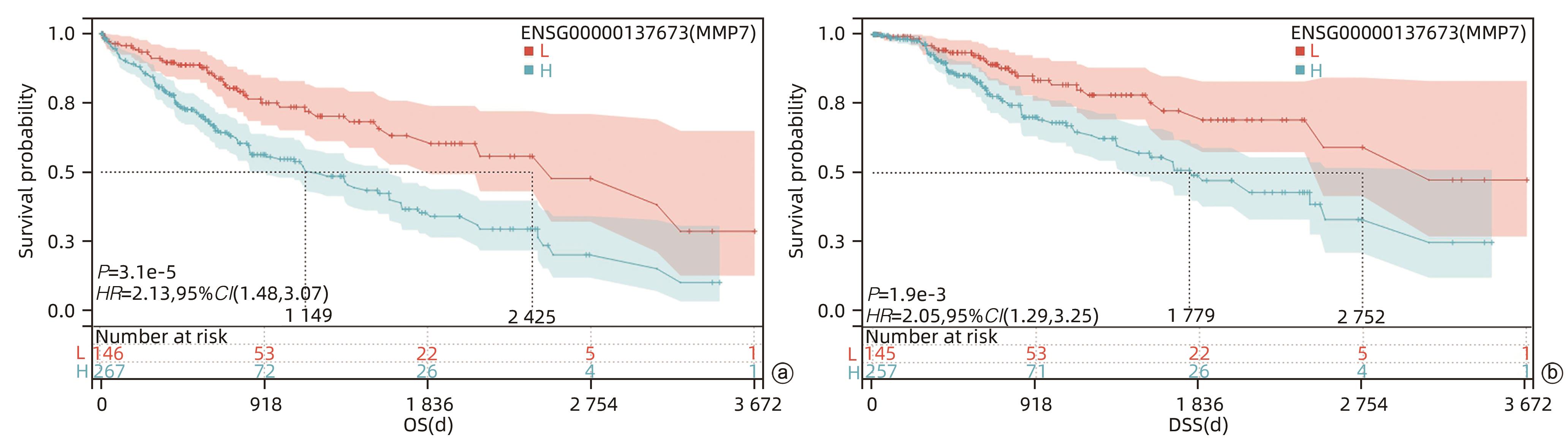
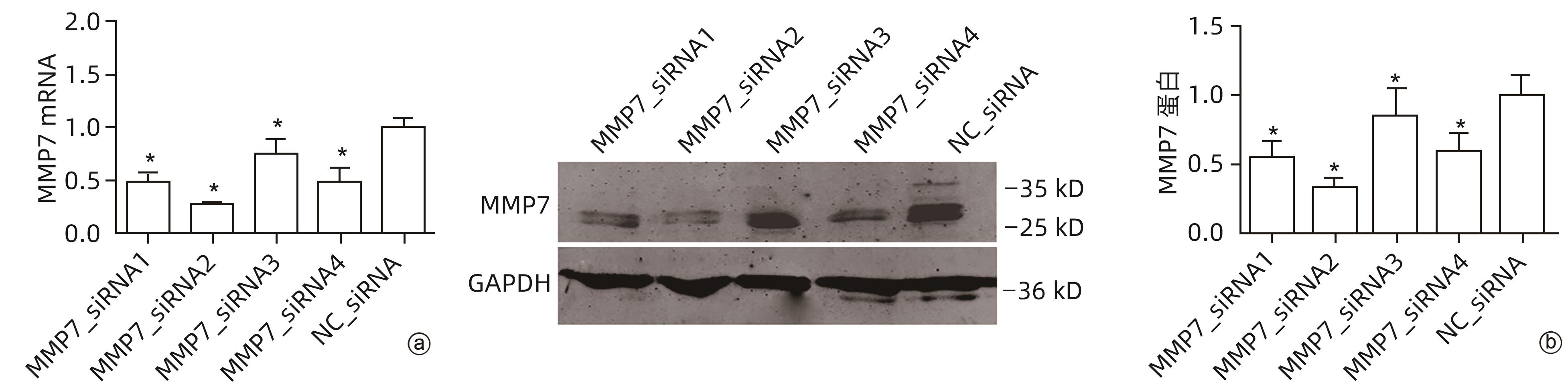
目的 评估基质金属蛋白酶7(MMP7)在肝癌细胞迁移及免疫细胞浸润中的作用及预后价值。 方法 分别构建下调或上调靶基因MMP7的MMP7_siRNA、pMMP7转染肝癌细胞株(MHCC97H)。采用RT-qPCR、Western Blot分别检测细胞中靶基因mRNA及蛋白的表达水平。扫描电镜和Transwell小室实验分别观察细胞伪足和迁移能力的变化,并采用生物信息学的方法,在TCGA、TIMER数据库分析MMP7与免疫细胞及肝癌患者免疫浸润评分之间的相关性,并进一步研究MMP7与肝癌患者预后的相关性。相关性分析采用Spearman方法。Sanger Box在线工具评估MMP7在肝癌总体生存期、疾病特异性生存期方面的意义。Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,Log-rank检验评估不同组样本之间的预后差异。 结果 构建的MMP7_siRNA、pMMP7转染MHCC97H细胞后均能有效下调或上调靶基因MMP7的表达,在MHCC97H细胞中MMP7被干扰后细胞伪足明显减少,并且变短,但是过表达MMP7之后细胞表面丝状伪足数量明显增多,并且伪足长度变长,放射状排列。Transwell小室结果发现,MMP7_siRNA2能够显著降低细胞迁移能力(P<0.05),而转染pMMP7后,细胞迁移能力显著增加(P<0.05)。MMP7的表达与B淋巴细胞(r=0.37)、CD4+T淋巴细胞(r=0.40)、中性粒细胞(r=0.49)、巨噬细胞(r=0.49)、树突状细胞(r=0.47)显著相关(P值均<0.05)。在TCGA数据库中,基于总体生存期最佳截断值将肝癌患者分成MMP7高表达组(n=267)和MMP7低表达组(n=146),结果发现,MMP7高表达组的总体生存期明显低于MMP7低表达组(P<0.05);基于疾病特异性生存期最佳截断值将肝癌患者分成MMP7高表达组(n=257)和MMP7低表达组(n=145),结果发现,MMP7高表达组的疾病特异性生存期也低于MMP7低表达组(P<0.05)。 结论 MMP7促进了肝癌细胞的迁移,并在免疫细胞浸润中发挥主要作用,MMP7的表达也与肝癌的预后具有明显相关性。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the role and prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7) in the migration and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma. Methods MMP7_siRNA for downregulating the target gene MMP7 and pMMP7 for upregulating MMP7 were constructed and were used to transfect hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (MHCC97H). RT-qPCR and Western Blot were used to measure the mRNA and protein expression levels of the target gene in cells. Scanning electron microscopy and Transwell assay were used to observe the changes in cell pseudopodia and migration ability, and bioinformatics methods were used to investigate the correlation of MMP7 with immune cells and immune infiltration score in TCGA and TIMER databases in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as the association between MMP7 and the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. The Spearman method was used for correlation analysis. Sanger Box online tool was used to assess the value of MMP7 in the overall survival curve and disease-specific survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to plot survival curves, and the Log-rank test was used for comparison of prognosis between different samples. Results After MHCC97H cells were transfected with MMP7_siRNA or pMMP7, there was a significant reduction or increase in the expression of the target gene MMP7; after downregulation of MMP7, there were significant reductions in the number and length of the pseudopodia, while after MMP7 overexpression, there were significant increases in the number and length of filopodia with radial arrangement. The Transwell chamber assay showed that MMP7_siRNA2 significantly reduced the migration ability of cells (P<0.05), and there was a significant increase in migration ability after pMMP7 transfection. The expression of MMP7 was significantly correlated with B lymphocytes (r=0.37, P<0.05), CD4+ T lymphocytes (r=0.40, P<0.05), neutrophils (r=0.49, P<0.05), macrophages (r=0.49, P<0.05), and dendritic cells (r=0.47, P<0.05). In the TCGA database, the patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were divided into MMP7 high expression group with 267 patients and MMP7 low expression group with 146 patients based on overall survival, and the results showed that the MMP7 high expression group had a significantly shorter overall survival time than the MMP7 low expression group (P<0.05); based on the disease-specific survival time, the patients were divided into MMP7 high expression group with 257 patients and MMP7 low expression group with 145 patients, and the analysis showed that the MMP7 high expression group also had a significantly shorter disease-specific survival time than the MMP7 low expression group (P<0.05). Conclusion MMP7 promotes the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and plays a major role in immune cell infiltration, and the expression of MMP7 is also significantly associated with the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. -
Key words:
- Liver Neoplasms /
- Matrix Metalloproteinase 7 /
- Cell Movement
-
表 1 siRNA 序列
Table 1. Sequences of siRNA
基因名称 序列(5′-3′) MMP7_siRNA1 正义链 GGAAAGAGAAGUAAUUCAAdTdT 反义链 UUGAAUUACUUCUCUUUCCdTdT MMP7_siRNA2 正义链 GACGGAUGGUAGCAGUCUAdTdT 反义链 UAGACUGCUACCAUCCGUCdTdT MMP7_siRNA3 正义链 CGAUUAGUGUCAAAGGCUUdTdT 反义链 AAGCCUUUGACACUAAUCGdTdT MMP7_siRNA4 正义链 GCAUUUCAGGAAAGUUGUAdTdT 反义链 UACAACUUUCCUGAAAUGCdTdT NC_siRNA 正义链 UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUdTdT 反义链 ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAAdTdT 表 2 RT-qPCR 引物序列
Table 2. Sequences of RT-qPCR primers
基因名称 序列(5′-3′) 长度(bp) MMP7 F:ACAGGCTCAGGACTATCTCAAG 179 R:CAACATCTGGCACTCCACATC GAPDH F:GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC 226 R:GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [2] CRISTESCU R, MOGG R, AYERS M, et al. Pan-tumor genomic biomarkers for PD-1 checkpoint blockade-based immunotherapy[J]. Science, 2018, 362( 6411): eaar3593. DOI: 10.1126/science.aar3593. [3] THOMPSON SM, CALLSTROM MR, JONDAL DE, et al. Heat stress-induced PI3K/mTORC2-dependent AKT signaling is a central mediator of hepatocellular carcinoma survival to thermal ablation induced heat stress[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11( 9): e0162634. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162634. [4] MASUZAKI R, YOSHIDA H, TATEISHI R, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in viral hepatitis: Improving standard therapy[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 22( 6): 1137- 1151. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2008.11.005. [5] HERNANDEZ-GEA V, TOFFANIN S, FRIEDMAN SL, et al. Role of the microenvironment in the pathogenesis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144( 3): 512- 527. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.002. [6] CHEN JF, LU XL, ZHANG XY, et al. Expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 9): 2169- 2174. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.020.陈金凤, 陆小柳, 张晓韵, 等. 基质金属蛋白酶7(MMP7)和硫酸乙酰肝素糖蛋白2(HSPG2)在胰腺癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 9): 2169- 2174. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.09.020. [7] CHEN L, KE XY. MMP7 as a potential biomarker of colon cancer and its prognostic value by bioinformatics analysis[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100( 9): e24953. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024953. [8] LI XF, AIERKEN ALD, SHEN L. IPO5 promotes malignant progression of esophageal cancer through activating MMP7[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24( 8): 4246- 4254. DOI: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_21004. [9] GOBIN E, BAGWELL K, WAGNER J, et al. A pan-cancer perspective of matrix metalloproteases(MMP) gene expression profile and their diagnostic/prognostic potential[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19( 1): 581. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-5768-0. [10] DING XX, ZHU QG, ZHANG SM, et al. Precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma: Driver mutations and targeted therapy[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8( 33): 55715- 55730. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18382. [11] LI TW, FAN JY, WANG BB, et al. TIMER: A web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77( 21): e108- e110. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0307. [12] XU WX, ZHANG J, HUA YT, et al. An integrative pan-cancer analysis revealing LCN2 as an oncogenic immune protein in tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 605097. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.605097. [13] GTEX CONSORTIUM. The genotype-tissue expression(GTEx) project[J]. Nat Genet, 2013, 45( 6): 580- 585. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2653. [14] SHEN W, SONG Z, ZHONG X, et al. Sangerbox: A comprehensive, interaction-friendly clinical bioinformatics analysis platform[J]. Imeta, 2022, 1( 3): e36. https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.36 DOI: 10.1002/imt2.36 [15] AJUCARMELPRECILLA A, PANDI J, DHANDAPANI R, et al. In silico identification of hub genes as observing biomarkers for gastric cancer metastasis[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 6316158. DOI: 10.1155/2022/6316158. [16] RAJENDRAN L, IVANICS T, CLAASEN MP, et al. The management of post-transplantation recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2022, 28( 1): 1- 16. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0217. [17] YANG JD, HAINAUT P, GORES GJ, et al. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16( 10): 589- 604. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y. [18] LEOWATTANA W, LEOWATTANA T, LEOWATTANA P. Systemic treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29( 10): 1551- 1568. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i10.1551. [19] ZAVADIL J, ROHAN T, JURÁČEK J, et al. Biomarkers as prognostic and predictive factors in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing radiological oncological interventions[J]. Klin Onkol, 2023, 36( 2): 104- 111. DOI: 10.48095/ccko2023104. [20] ZHANG JF, ZHANG J. Research progress on diagnosis and treatments for microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma[J/CD]. Chin J Hepat Surg(Electronic Edition), 2022, 11( 1): 104- 108. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2022.01.022.张剑锋, 张剑. 肝细胞癌微血管浸润诊治研究进展[J/CD]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2022, 11( 1): 104- 108. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2022.01.022. [21] SZARVAS T, CSIZMARIK A, VÁRADI M, et al. The prognostic value of serum MMP-7 levels in prostate cancer patients who received docetaxel, abiraterone, or enzalutamide therapy[J]. Urol Oncol, 2021, 39( 5): 296. DOI: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.09.005. [22] TREGUNNA R. Serum MMP7 levels could guide metastatic therapy for prostate cancer[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2020, 17( 12): 658. DOI: 10.1038/s41585-020-00396-3. [23] DU F, FENG WB, CHEN S, et al. Sex determining region Y-box 12(SOX12) promotes gastric cancer metastasis by upregulating MMP7 and IGF1[J]. Cancer Lett, 2019, 452: 103- 118. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.03.035. [24] JAFFAR J, WONG M, FISHBEIN GA, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is increased in lung bases but not apices in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. ERJ Open Res, 2022, 8( 4): 00191- 02022. DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00191-2022. [25] SANG HY, WU S, CHEN XF, et al. FAM46B suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer via β-catenin/MMP7 signaling[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2019, 8( 4): 1497- 1505. DOI: 10.21037/tcr.2019.07.27. [26] RONG WQ, ZHANG Y, YANG L, et al. Post-surgical resection prognostic value of combined OPN, MMP7, and PSG9 plasma biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Med, 2019, 13( 2): 250- 258. DOI: 10.1007/s11684-018-0632-1. [27] YE LT, KRIEGL L, REITER FP, et al. Prognostic significance and functional relevance of olfactomedin 4 in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2020, 11( 1): e00124. DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000124. [28] HE XX, SHI LL, QIU MJ, et al. Molecularly targeted anti-cancer drugs inhibit the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the expression of MMP and TIMP gene families[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 504( 4): 878- 884. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.203. [29] LIAO LJ, DUAN DY, LIU YF, et al. LHPP inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and metastasis[J]. Cell Cycle, 2020, 19( 14): 1846- 1854. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1783472. [30] JEGGO PA, PEARL LH, CARR AM. DNA repair, genome stability and cancer: A historical perspective[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2016, 16( 1): 35- 42. DOI: 10.1038/nrc.2015.4. [31] CHATTERJEE A, RODGER EJ, ECCLES MR. Epigenetic drivers of tumourigenesis and cancer metastasis[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018, 51: 149- 159. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.08.004. [32] CHEN F, FAN YM, CAO PX, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of the prognostic and immunological role of HSF1: A potential target for survival and immunotherapy[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 5551036. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5551036. [33] XU ZH, HE CY, FANG XD. Research progress in relationship between mitochondrial inner membrane mitochondrial protein and tumor[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2023, 49( 1): 231- 236. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230131.徐仲航, 何成彦, 房学东. 线粒体内膜蛋白与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49( 1): 231- 236. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230131. [34] LI TW, FU JX, ZENG ZX, et al. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48( W1): W509- W514. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa407. [35] ANGELOVA M, CHAROENTONG P, HACKL H, et al. Characterization of the immunophenotypes and antigenomes of colorectal cancers reveals distinct tumor escape mechanisms and novel targets for immunotherapy[J]. Genome Biol, 2015, 16( 1): 64. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-015-0620-6. [36] LEE N, ZAKKA LR, MIHM MC Jr, et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in melanoma prognosis andcancerimmunotherapy[J]. Pathology, 2016, 48( 2): 177- 187. DOI: 10.1016/j.pathol.2015.12.006. [37] DENKERT C, VON MINCKWITZ G, DARB-ESFAHANI S, et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2018, 19( 1): 40- 50. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30904-X. [38] GALON J, BRUNI D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019, 18( 3): 197- 218. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-018-0007-y. [39] ZHAO YD, SCHAAFSMA E, GORLOV IP, et al. A leukocyte infiltration score defined by a gene signature predicts melanoma patient prognosis[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2019, 17( 1): 109- 119. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0173. [40] MCGRANAHAN N, SWANTON C. Clonal heterogeneity and tumor evolution: Past, present, and the future[J]. Cell, 2017, 168( 4): 613- 628. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.018. [41] WEI GG, ZHANG HL, ZHAO HP, et al. Emerging immune checkpoints in the tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 511: 68- 76. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.021. [42] ZHANG YY, ZHANG ZM. The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17( 8): 807- 821. DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6. [43] MURCIANO-GOROFF YR, WARNER AB, WOLCHOK JD. The future of cancer immunotherapy: Microenvironment-targeting combinations[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30( 6): 507- 519. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-020-0337-2. -



 PDF下载 ( 4637 KB)
PDF下载 ( 4637 KB)

 下载:
下载: