HBV急性感染相关肝衰竭临床治愈伴HBsAg血清学转换1例报告
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240724
Clinical cure of acute hepatitis B virus infection-related liver failure with HBsAg seroconversion: A case report
-
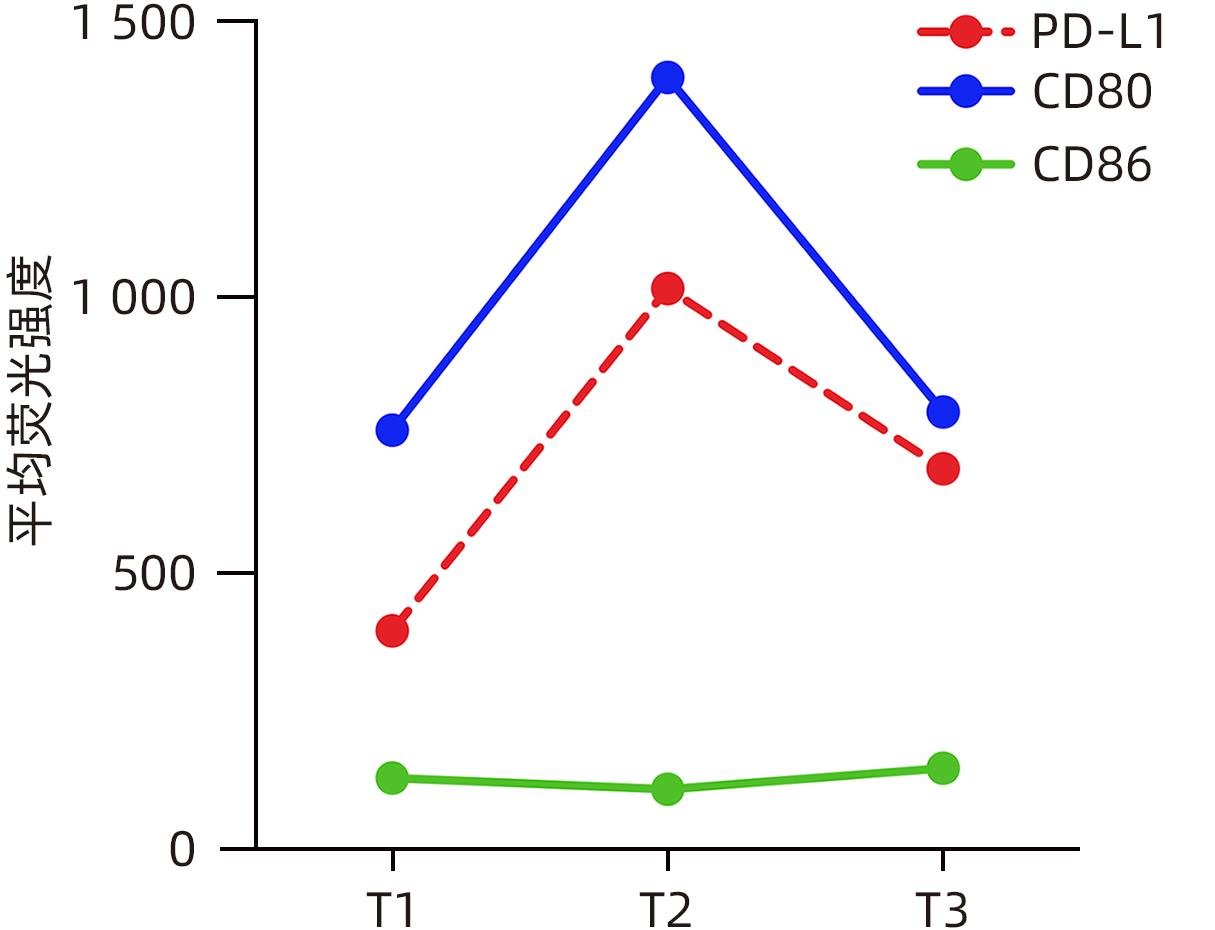
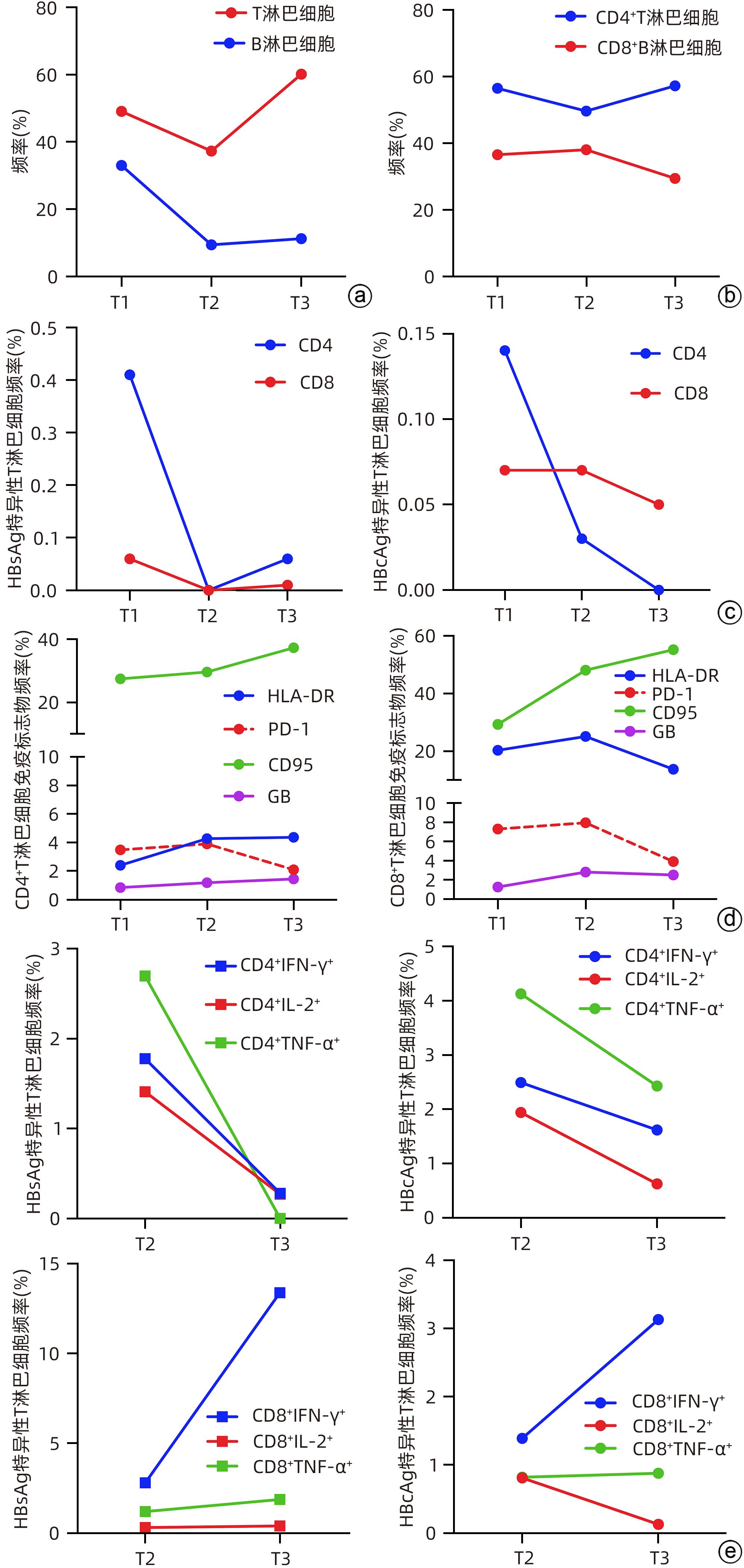
摘要: 急性乙型肝炎患者中约1%可进展至急性肝衰竭,75%的HBV相关急性肝衰竭患者需要接受肝移植或死亡。本研究报道1例HBV急性感染相关肝衰竭患者经过抗病毒及对症支持治疗后达到临床治愈和HBsAg血清学转换,并动态监测其外周血免疫学变化特征。Abstract: About 1% of the patients with acute hepatitis B can progress to acute liver failure, and 75% of the patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related acute liver failure need to undergo liver transplantation or face death. This article reports a patient with HBV infection-related acute liver failure who achieved clinical cure and HBsAg seroconversion after antiviral therapy and symptomatic/supportive treatment, and dynamic monitoring was performed for immunological markers in peripheral blood.
-
Key words:
- Liver Failure, Acute /
- Hepatitis B virus /
- Immunity
-
表 1 实验室指标动态变化
Table 1. Dynamic changes of laboratory indexes
指标 2022年5月26日(外院) 2022年5月27日(外院) 2022年5月28日(外院) 2022年5月28日(本院) 2022年5月31日(本院) 2022年6月8日(本院) 2022年6月14日(本院) 2023年7月10日(本院) ALT(U/L) 2 035 1 821 1 221 1 023 423 80 32 9 AST(U/L) 2 039 1 528 484 369 92 46.4 37 19 TBil(μmol/L) 129.5 132 138 182.7 118.8 46.4 28.2 9 PT(s) 45.7 30.3 29.9 29.2 18 12 11.8 12.7 PTA(%) 12.6 23.2 22.3 未检测 未检测 未检测 未检测 106 INR 3.61 2.43 2.46 2.64 1.62 0.98 0.96 0.97 APTT(s) 63.8 90.2 69 48.9 51 46.3 46 42.6 血氨(μmol/L) 未检测 未检测 未检测 109 69 未检测 未检测 未检测 AFP(μg/L) 3.4 未检测 未检测 未检测 485.8 未检测 未检测 1.8 注:APTT,活化部分凝血活酶时间。 表 2 HBV血清学及病毒学指标动态变化
Table 2. Dynamic changes of HBV serological and virological indexes
指标 2022年5月26日 (外院) 2022年5月28日 (本院) 2022年5月31日 (本院) 2022年6月8日 (本院) 2023年7月10日 (本院) HBsAg(IU/mL) 27.64 0.26 阴性 阴性 阴性 抗-HBs(mIU/mL) 6.01 1.66 275.5 196.5 159.1 HBeAg(IU/mL) 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 阴性 抗-HBe 阳性 阳性 阳性 阳性 阳性 抗-HBc(IU/mL) 阴性 6.16 33.6 32.5 38.5 抗-HBc-IgM 阴性 阴性 阳性 未检测 未检测 HBV DNA(IU/mL) 2.82×104 未检测 2.2×102 73.5 <20 HBV RNA(拷贝/mL) 未检测 未检测 393 239 <50 -
[1] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [2] LIANG TJ. Hepatitis B: The virus and disease[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 49( 5 Suppl): S13- S21. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22881. [3] JIA JD, WEI L, HOU JL, et al. Chinese standards for diagnosis and treatment of liver disease-White paper excerpt[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2014, 30( 3): 197- 209. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.03.002.贾继东, 魏来, 侯金林, 等.《中国肝病诊疗管理规范》白皮书(节选)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2014, 30( 3): 197- 209. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.03.002. [4] GUIDOTTI LG, ISOGAWA M, CHISARI FV. Host-virus interactions in hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2015, 36: 61- 66. DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.06.016. [5] KONDO Y, KOBAYASHI K, ASABE S, et al. Vigorous response of cytotoxic T lymphocytes associated with systemic activation of CD8 T lymphocytes in fulminant hepatitis B[J]. Liver Int, 2004, 24( 6): 561- 567. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.0982.x. [6] CHEN ZC, DIAZ G, POLLICINO T, et al. Role of humoral immunity against hepatitis B virus core antigen in the pathogenesis of acute liver failure[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115( 48): E11369- E11378. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1809028115. [7] SHINGINA A, MUKHTAR N, WAKIM-FLEMING J, et al. Acute liver failure guidelines[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2023, 118( 7): 1128- 1153. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002340. [8] ZHANG Z, ZHANG JY, WHERRY EJ, et al. Dynamic programmed death 1 expression by virus-specific CD8 T cells correlates with the outcome of acute hepatitis B[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134( 7): 1938- 1949. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.037. [9] KHAN AR, HAMS E, FLOUDAS A, et al. PD-L1hi B cells are critical regulators of humoral immunity[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 5997. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6997. [10] XIONG SE, ZHU D, LIANG BY, et al. Longitudinal characterization of phenotypic profile of T cells in chronic hepatitis B identifies immune markers associated with HBsAg loss[J]. EBioMedicine, 2021, 69: 103464. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103464. [11] SPRENGERS D, van der MOLEN RG, KUSTERS JG, et al. Analysis of intrahepatic HBV-specific cytotoxic T-cells during and after acute HBV infection in humans[J]. J Hepatol, 2006, 45( 2): 182- 189. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.12.022. -



 PDF下载 ( 851 KB)
PDF下载 ( 851 KB)

 下载:
下载: