中草药相关肝损伤的物质基础及其毒性机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240802
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:刘雪莹负责检索文献与论文撰写;师荟荟、王浩文参与文献收集与协助撰写;杨涛负责拟定文章思路,修改与定稿。
-
摘要: 中草药相关肝损伤的毒性物质基础及其毒性机制复杂,影响中药的安全应用。本文对中草药引起肝损伤的主要毒性成分及其作用机制进行了归纳分析,中草药肝损伤毒性成分可以分为药源性与非药源性两大类,药源性毒性成分主要有生物碱类、萜类、蒽醌类以及苯丙素类化合物,作用机制涉及氧化应激、细胞凋亡与坏死、CYP450酶、基因毒性等。非药源性物质主要有农药残留、二氧化硫残留、重金属、真菌、植物生长调节剂,机制涉及氧化应激、凋亡、代谢紊乱、CYP450酶等。在此基础上进一步提出了目前待解决的问题与研究难点,以期促进中草药肝毒性的基础研究。
-
关键词:
- 中草药 /
- 化学性与药物性肝损伤 /
- 物质基础
Abstract: Herb-induced liver injury (HILI) tends to have complex toxic material basis and toxic mechanism, which greatly affects the safety of traditional Chinese medicine. This article summarizes the main toxic components of Chinese herbal medicine causing liver injury and their mechanism of action. The toxic components of Chinese herbal medicine causing liver injury can be classified into two categories of drug-derived and non-drug-derived toxic components. Drug-derived toxic components mainly include alkaloids, terpenoids, anthraquinones, and phenylpropanoids, and their mechanism of action involves oxidative stress, apoptosis and necrosis, CYP450 enzymes, and genotoxicity. Non-drug-derived toxic components mainly include pesticide residues, sulfur dioxide residues, heavy metals, fungi, and plant growth regulators, and their mechanisms involve oxidative stress, apoptosis, metabolic disorders, and CYP450 enzymes. On this basis, this article further proposes the unsolved problems and research difficulties, in order to promote the basic research on the hepatotoxicity of traditional Chinese medicine. -
[1] MA YX, FENG YL, WU YY, et al. Toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids in Chinese herbal medicine: Control status and advances in analytical method[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2021, 52( 24): 7645- 7657. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.24.028.马跃新, 冯有龙, 吴嫣艳, 等. 中草药中毒性吡咯里西啶类生物碱分析方法研究进展及控制现状[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52( 24): 7645- 7657. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.24.028. [2] SMITH LW, CULVENOR CC. Plant sources of hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids[J]. J Nat Prod, 1981, 44( 2): 129- 152. DOI: 10.1021/np50014a001. [3] ZHUGE YZ, LIU YL, XIE WF, et al. Expert consensus on the clinical management of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34( 4): 634- 642. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14612. [4] XIONG F, GU LH, YANG L, et al. Risk evaluation of Chinese patent medicine containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2021, 52( 17): 5389- 5400. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.17.031.熊芬, 谷丽华, 杨莉, 等. 含吡咯里西啶生物碱中成药潜在风险评估[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52( 17): 5389- 5400. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.17.031. [5] MA J, XIA QS, FU PP, et al. Pyrrole-protein adducts- A biomarker of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. J Food Drug Anal, 2018, 26( 3): 965- 972. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.05.005. [6] GONG BW, ZHANG SY, WANG X, et al. Inflammation intensifies monocrotaline-induced liver injury[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2023. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07939.[ Online ahead of print] [7] CHEN Y, YE XL, WANG XJ, et al. The protective effect of ritonavir against Gynura japonica-induced liver injury in rats[J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 2022, 57( 2): 392- 398. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2021-0902.陈岩, 叶铉玲, 王汛江, 等. 利托那韦对菊三七致大鼠肝毒性的保护作用[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57( 2): 392- 398. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2021-0902. [8] JI LL, CHEN Y, LIU TY, et al. Involvement of Bcl-xL degradation and mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic pathway in pyrrolizidine alkaloids-induced apoptosis in hepatocytes[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2008, 231( 3): 393- 400. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.05.015. [9] ZUCKERMAN M, STEENKAMP V, STEWART MJ. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease as a result of a traditional remedy: Confirmation of toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids as the cause, using an in vitro technique[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2002, 55( 9): 676- 679. DOI: 10.1136/jcp.55.9.676. [10] XIONG AZ, YANG F, FANG LX, et al. Metabolomic and genomic evidence for compromised bile acid homeostasis by senecionine, a hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloid[J]. Chem Res Toxicol, 2014, 27( 5): 775- 786. DOI: 10.1021/tx400451q. [11] LIU KL, LIANG JW, WANG S, et al. Study on the quantitative structure-genetic toxicity relationships of pyrrolizidine alkaloids[J]. Chin J Pharmacovigil, 2019, 16( 6): 321- 324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8629.2019.06.001.刘凯利, 梁经纬, 王珊, 等. 吡咯里西啶类生物碱基因毒性的构效关系研究[J]. 中国药物警戒, 2019, 16( 6): 321- 324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8629.2019.06.001. [12] HUANG GY, JIANG QY, LIANG XL, et al. Pharmacokinetics study of brucine and strychnine in rat liver microsomes under different chemical environments[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2018, 49( 12): 2919- 2924. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.12.028.黄国勇, 蒋且英, 梁新丽, 等. 不同化学环境下的马钱子碱和士的宁在大鼠肝微粒体内代谢动力学研究[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49( 12): 2919- 2924. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.12.028. [13] CHEN X, LAI Y, CAI Z. Simultaneous analysis of strychnine and brucine and their major metabolites by liquid chromatography-electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry[J]. J Anal Toxicol, 2012, 36( 3): 171- 176. DOI: 10.1093/jat/bks004. [14] ZHAO CJ, LI EW, WANG ZY, et al. Nux vomica exposure triggered liver injury and metabolic disturbance in zebrafish larvae[J]. Zebrafish, 2018, 15( 6): 610- 628. DOI: 10.1089/zeb.2018.1632. [15] ZHOU ZY, LIN YK, GAO L, et al. Cyp3a11 metabolism-based chronotoxicity of brucine in mice[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2019, 313: 188- 195. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.07.007. [16] ZHANG FL, HE X, ZHAI YR, et al. Mechanism-based inhibition of CYPs and RMs-induced hepatoxicity by rutaecarpine[J]. Xenobiotica, 2015, 45( 11): 978- 989. DOI: 10.3109/00498254.2015.1038742. [17] YUAN ZQ, HASNAT M, LIANG PS, et al. The role of inflammasome activation in Triptolide-induced acute liver toxicity[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 75: 105754. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105754. [18] FU Q, HUANG X, SHU B, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain is involved in triptolide-induced liver injury[J]. Fitoterapia, 2011, 82( 8): 1241- 1248. DOI: 10.1016/j.fitote.2011.08.019. [19] HASNAT M, YUAN ZQ, NAVEED M, et al. Drp1-associated mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial autophagy: A novel mechanism in triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2019, 35( 3): 267- 280. DOI: 10.1007/s10565-018-9447-8. [20] HASNAT M, YUAN ZQ, ULLAH A, et al. Mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity is associated with the Drp1 activation[J]. Toxicol Mech Methods, 2020, 30( 2): 124- 133. DOI: 10.1080/15376516.2019.1669247. [21] PENG R, MA SR, FU J, et al. Transforming of triptolide into characteristic metabolites by the gut microbiota[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25( 3): 606. DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030606. [22] LIU YT, HU YQ, WANG YL, et al. Antibiotic pretreatment promotes orally-administered triptolide absorption and aggravates hepatotoxicity and intestinal injury in mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 292: 115224. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115224. [23] CHEN P, CHEN Y, WANG YR, et al. Comparative evaluation of hepatoprotective activities of geniposide, crocins and crocetin by CCl4-Induced liver injury in mice[J]. Biomol Ther, 2016, 24( 2): 156- 162. DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2015.094. [24] YANG HJ, FU MH, WU ZL, et al. Experimental studies on hepatotoxicity of rats induced by Fructus Gardeniae[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2006, 31( 13): 1091- 1093. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-5302.2006.13.017.杨洪军, 付梅红, 吴子伦, 等. 栀子对大鼠肝毒性的实验研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2006, 31( 13): 1091- 1093. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-5302.2006.13.017. [25] REN YQ, TIAN YR, LI C, et al. Cytotoxic effect of geniposide and its metabolite genipin on HepG2 cells and mechanism[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2016, 32( 12): 1755- 1760, 1761. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.12.023.任艳青, 田宇柔, 李琛, 等. 京尼平苷及其体内代谢产物京尼平对HepG2细胞毒性的比较及机制研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2016, 32( 12): 1755- 1760, 1761. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.12.023. [26] KAWASAKI T, KOMORI T, SETOGUCHI S. Furanoid norditerpenes from Dioscoreaceae plants. I. diosbulbins A, B and C from Dioscorea bulbifera L. forma spontanea MAKINO et NEMOTO[J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1968, 16( 12): 2430- 2435. DOI: 10.1248/cpb.16.2430. [27] MA M, JIANG ZZ, RUAN JL, et al. Toxicity of a diterpene lactone isolated from Dioscorea bulbifera on hepatocytes[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2011, 9( 4): 280- 285. DOI: 10.1016/s1875-5364(11)60065-4. [28] WANG HJ, YANG DZ, LI L, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of Rhein, an anthraquinone compound, and its applications in treating arthritis: A review[J]. Nat Prod Bioprospect, 2020, 10( 6): 445- 452. DOI: 10.1007/s13659-020-00272-y. [29] SHAKIB Z, SHAHRAKI N, RAZAVI BM, et al. Aloe vera as an herbal medicine in the treatment of metabolic syndrome: A review[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33( 10): 2649- 2660. DOI: 10.1002/ptr.6465. [30] STOMPOR-GORĄCY M. The health benefits of emodin, a natural anthraquinone derived from rhubarb-a summary update[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 17): 9522. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179522. [31] LV GP, MENG LZ, HAN DQ, et al. Effect of sample preparation on components and liver toxicity of Polygonum multiflorum[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2015, 109: 105- 111. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.02.029. [32] YAO S, LI Y, KONG LY. Preparative isolation and purification of chemical constituents from the root of Polygonum multiflorum by high-speed counter-current chromatography[J]. J Chromatogr A, 2006, 1115( 1-2): 64- 71. DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.02.071. [33] WANG Q, ZHANG XH, WEN HR, et al. Study on potential hepatotoxicity of main monomers of Polygonum multiflorum based on liver micro-tissue[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2020, 45( 12): 2954- 2959. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200322.401.汪祺, 张茜蕙, 文海若, 等. 基于肝微组织考察何首乌主要单体潜在肝毒性[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45( 12): 2954- 2959. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200322.401. [34] WANG CY, LI DK, QUAN ZY, et al. Hepatotoxicity and related components of polygoni multiflori Radix based on cytochrome oxidase CYP2D6[J]. Chin J Pharmacovigil, 2021, 18( 3): 220- 227, 239. DOI: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.2021.03.04.王呈谕, 李登科, 全正扬, 等. 基于细胞色素氧化酶CYP2D6的何首乌肝细胞毒性及相关成分研究[J]. 中国药物警戒, 2021, 18( 3): 220- 227, 239. DOI: 10.19803/j.1672-8629.2021.03.04. [35] LIU Y, WANG RX, YOU LT, et al. Study on hepatotoxicity and mechanism of aloe-emodin based on zebrafish[J]. Glob Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 13( 1): 18- 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2020.01.004.刘艺, 王瑞昕, 游龙泰, 等. 芦荟大黄素诱导斑马鱼肝毒性及作用机制研究[J]. 环球中医药, 2020, 13( 1): 18- 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2020.01.004. [36] LI CP, RAO T, CHEN XP, et al. HLA-B*35:01 allele is a potential biomarker for predicting Polygonum multiflorum-induced liver injury in humans[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 1): 346- 357. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30660. [37] CHUNG YT, CHEN CL, WU CC, et al. Safrole-DNA adduct in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with betel quid chewing[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2008, 183( 1-3): 21- 27. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.09.013. [38] NIE AZ, ZHAO XR, ZHU CS, et al. Historical evolution and rational use of Asari Radix et Rhizoma[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2018, 49( 23): 5719- 5723. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.23.034.聂安政, 赵雪睿, 朱春胜, 等. 细辛用药沿革与合理用药思考[J]. 中草药, 2018, 49( 23): 5719- 5723. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.23.034. [39] LIU TY, CHEN CC, CHEN CL, et al. Safrole-induced oxidative damage in the liver of Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 1999, 37( 7): 697- 702. DOI: 10.1016/s0278-6915(99)00055-1. [40] BENEDETTI MS, MALNOË A, BROILLET AL. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of safrole in the rat and man[J]. Toxicology, 1977, 7( 1): 69- 83. DOI: 10.1016/0300-483x(77)90039-7. [41] BORCHERT P, MILLER JA, MILLER EC, et al. 1’-Hydroxysafrole, a proximate carcinogenic metabolite of safrole in the rat and mouse[J]. Cancer Res, 1973, 33( 3): 590- 600. [42] LUO G, GUENTHNER TM. Covalent binding to DNA in vitro of 2’, 3’- oxides derived from allylbenzene analogs[J]. Drug Metab Dispos, 1996, 24( 9): 1020- 1027. [43] DONG X, LU S, TIAN Y, et al. Bavachinin protects the liver in NAFLD by promoting regeneration via targeting PCNA[J]. J Adv Res, 2024, 55: 131- 144. DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.02.007. [44] ZHOU W, CHEN X, ZHAO GL, et al. Psoralen induced liver injury by attenuating liver regenerative capability[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 1179. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01179. [45] GAO SY, ZHAO JC, XIA Q, et al. Evaluation of the hepatotoxicity of Psoralea corylifolia L. based on a zebrafish model[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15: 1308655. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1308655. [46] YU YL, WANG PL, YU RL, et al. Long-term exposure of psoralen and isopsoralen induced hepatotoxicity and serum metabolites profiles changes in female rats[J]. Metabolites, 2019, 9( 11): 263. DOI: 10.3390/metabo9110263. [47] ZHANG C, ZHAO JQ, SUN JX, et al. Psoralen and isopsoralen from Psoraleae Fructus aroused hepatotoxicity via induction of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated CYP1A2 expression[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 297: 115577. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115577. [48] ZHANG Y, WANG Q, WANG ZX, et al. A study of NMR-based hepatic and serum metabolomics in a liver injury sprague-dawley rat model induced by psoralen[J]. Chem Res Toxicol, 2018, 31( 9): 852- 860. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.8b00082. [49] ZHAO CH, SU DD, LI C, et al. Synthetic biology risks and biosafety strategies in the view of overall national security concept[J]. China Biotechnol, 2022, 42( 12): 120- 128. DOI: 10.13523/j.cb.2206014.赵赤鸿, 苏丹丹, 厉春, 等. 总体国家安全观下合成生物学风险和应对策略研究[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2022, 42( 12): 120- 128. DOI: 10.13523/j.cb.2206014. [50] LIANG AH, WANG JH, XUE BY, et al. Study on hepatoxicity and nephrotoxicity of cinnabar in rats[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2009, 34( 3): 312- 318. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-5302.2009.03.018.梁爱华, 王金华, 薛宝云, 等. 朱砂对大鼠的肝肾毒性研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2009, 34( 3): 312- 318. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn: 1001-5302.2009.03.018. [51] DOU YJ, LIU H, LI XM, et al. Research progress on residual status and risk assessment of exogenous hazardous substances in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs, 2023, 54( 2): 396- 407. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.02.006.窦亚洁, 刘慧, 李晓萌, 等. 中药中外源性有害物的残留现状及风险评估的研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54( 2): 396- 407. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.02.006. [52] FU QZ, LU JX, WANG M, et al. Research progress of pesticide residue in Chinese herbal medicine causes and prevention measures[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2014, 25( 4): 925- 927. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2014.04.071.傅巧真, 路俊仙, 王萌, 等. 中药材农药残留原因及防治措施的研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2014, 25( 4): 925- 927. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2014.04.071. [53] FUKUYAMA T, TAJIMA Y, UEDA H, et al. Allergic reaction induced by dermal and/or respiratory exposure to low-dose phenoxyacetic acid, organophosphorus, and carbamate pesticides[J]. Toxicology, 2009, 261( 3): 152- 161. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.05.014. [54] QIU LZ. Correlation evaluation of sulfur fumigation on the quality of Achyranthes bidentata pieces[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2012.仇立志. 硫磺熏蒸对怀牛膝饮片质量的相关性评价[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2012. [55] DING T, LUO JY, YANG SH, et al. Recent research progress on natural medicines in treatment of cadmium toxicity[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2018, 43( 10): 2006- 2013.丁通, 骆骄阳, 杨世海, 等. 天然药物防治镉中毒的现代研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2018, 43( 10): 2006- 2013. [56] ZHU CX. Pharmacodynamic evaluation and mechanism of Polygonatum polysaccharide against liver injury caused by lead-cadmium complex heavy metals[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2021.朱成香. 黄精多糖抗铅-镉复合重金属致肝损伤药效学评价及作用机制研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2021. [57] ZHU HY, CHU Y, ZHOU YQ, et al. Anti-epilepsy traditional Chinese medicine caused heavy metal poisoning characterized by abdominal cramps and liver damage: One case report[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 20( 1): 46, 50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2011.01.014.朱洪怡, 楚毅, 周雨迁, 等. 以腹绞痛、肝损害为主要表现的抗癫痫中药致重金属中毒1例[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2011, 20( 1): 46, 50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2011.01.014. [58] WU RS, YE C, HU QP, et al. Research progress on mycotoxin contamination of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Guangdong Chem Ind, 2024, 51( 4): 76- 79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2024.04.022.吴润松, 叶聪, 胡绮萍, 等. 中药材真菌毒素污染检测研究进展[J]. 广东化工, 2024, 51( 4): 76- 79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2024.04.022. [59] JIANG JY. Preparation of monoclonal antibody against aflatoxin B1 and its application in rapid detection of Chinese herbal medicine pollution[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2020.蒋佳伊. 黄曲霉毒素B1单克隆抗体的制备及其在中药材污染快速检测中的应用[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2020. [60] TAN J, ZHENG RS, WANG WL, et al. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxins and Zearalenone in Chinese crude drugs by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2012, 23( 10): 2469- 2472. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2012.10.036.谭婧, 郑润生, 王文丽, 等. 中药饮片中黄曲霉毒素和玉米赤霉烯酮的液质联用检测分析[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2012, 23( 10): 2469- 2472. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2012.10.036. [61] ZHAO L. General situation of research on plant growth regulators[J]. Mod Agric, 2022, 1: 44- 46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2022.01.010.赵蕾. 植物生长调节剂的研究概况[J]. 现代农业, 2022, 1: 44- 46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0708.2022.01.010. [62] YUE KX, LIU ZQ, PI ZF, et al. Network pharmacology combined with metabolomics approach to investigate the toxicity mechanism of paclobutrazol[J]. Chem Res Toxicol, 2022, 35( 4): 626- 635. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00404. -



 PDF下载 ( 1503 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1503 KB)

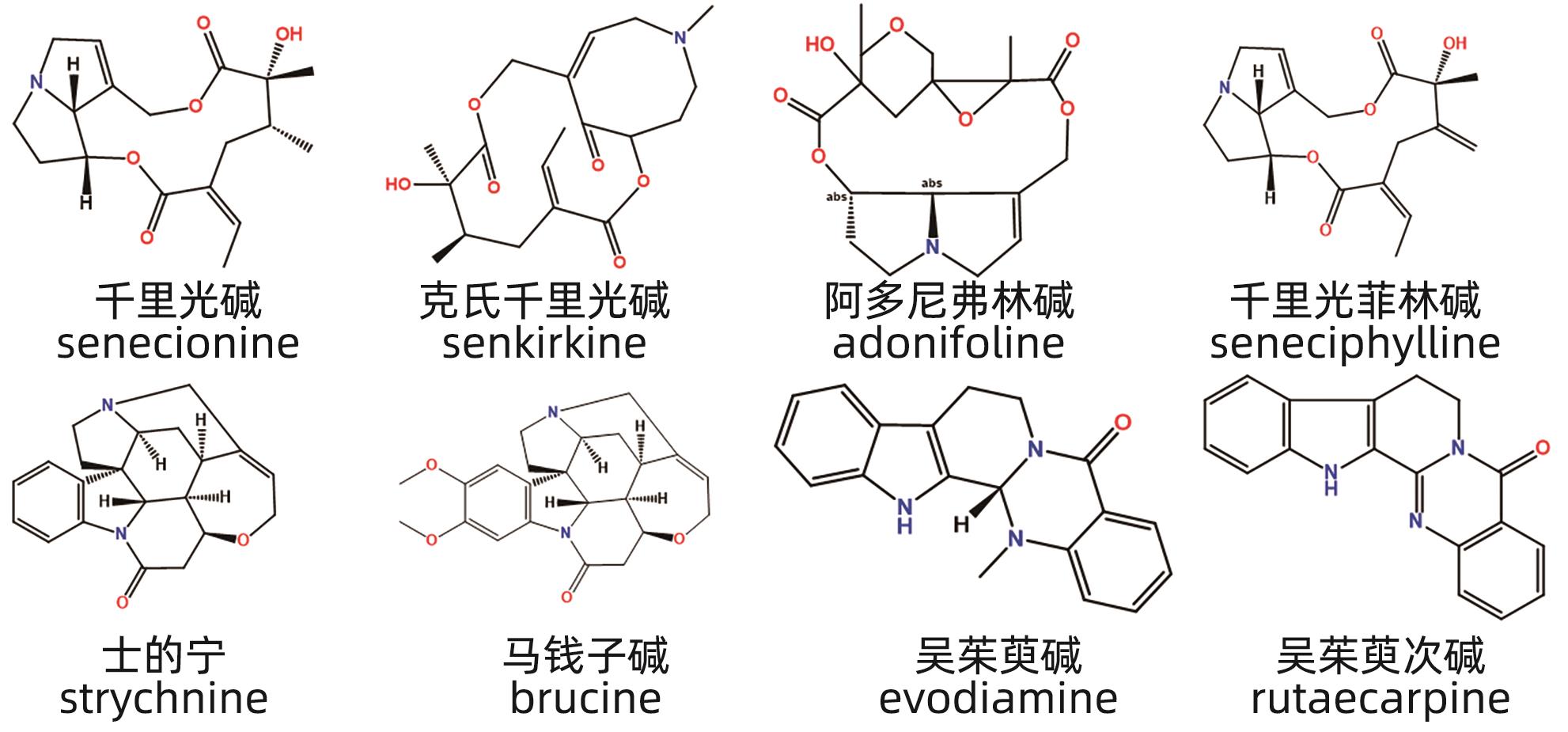
 下载:
下载: