间充质干细胞对慢加急性肝衰竭治疗效果的Meta分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240822
Therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells on acute-on-chronic liver failure: A Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
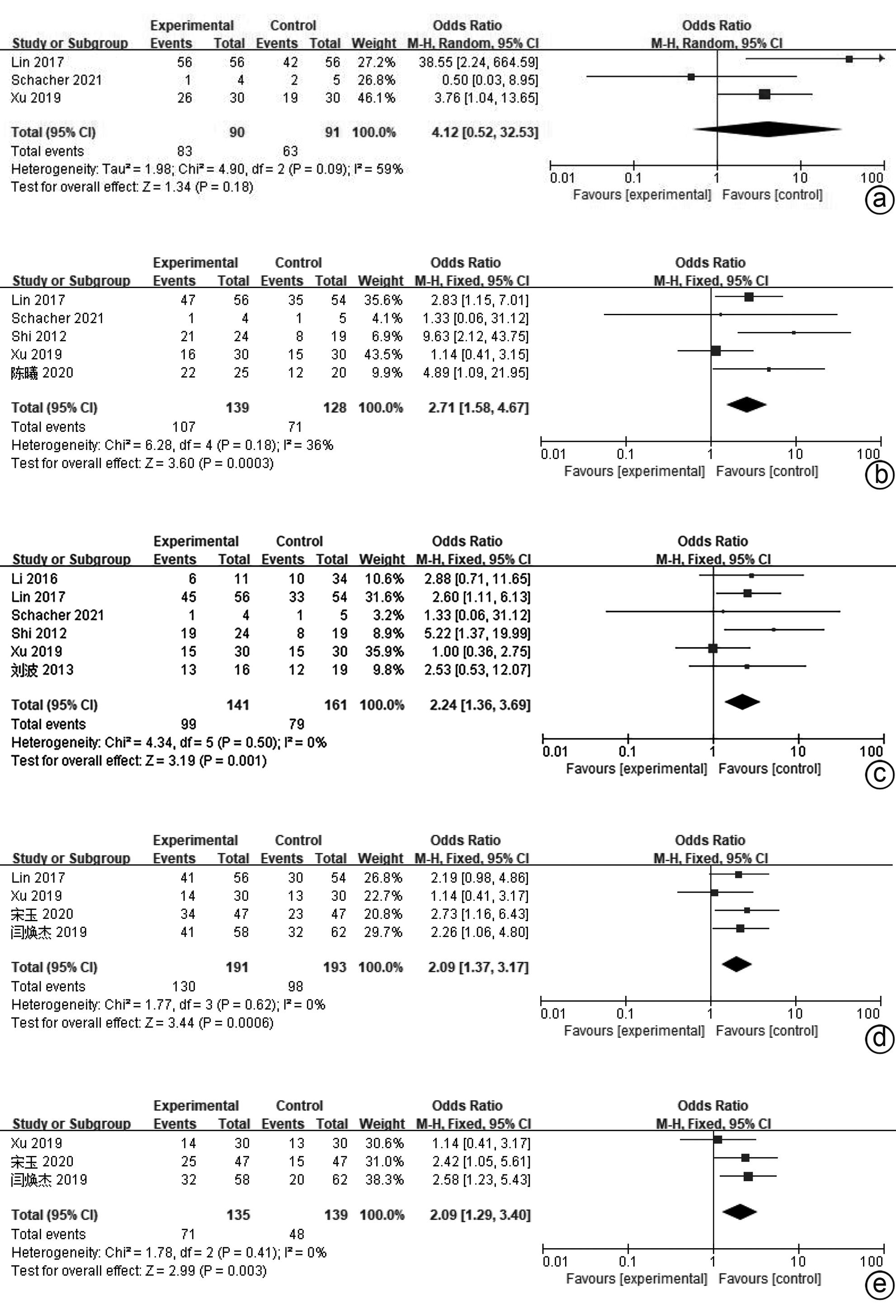
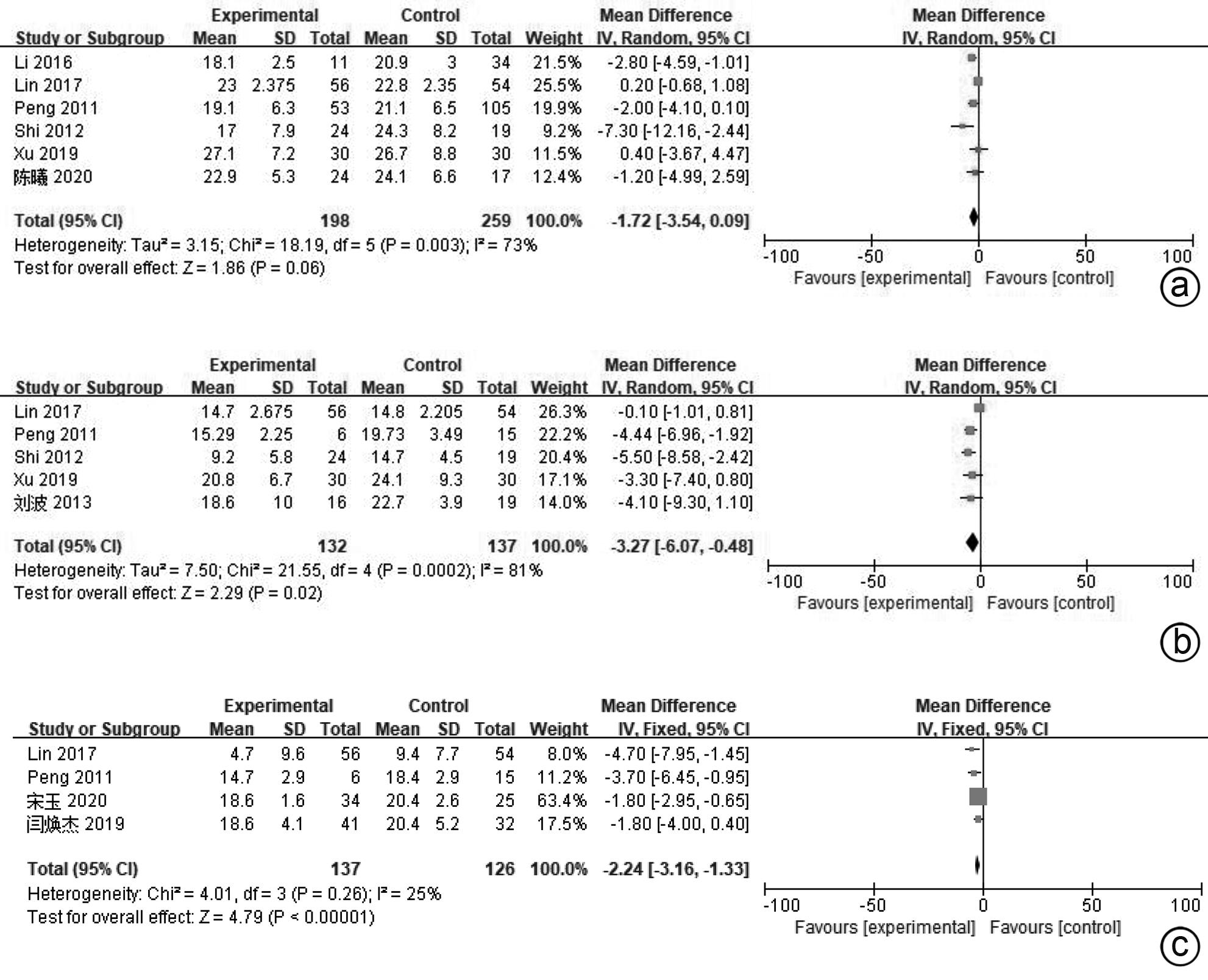
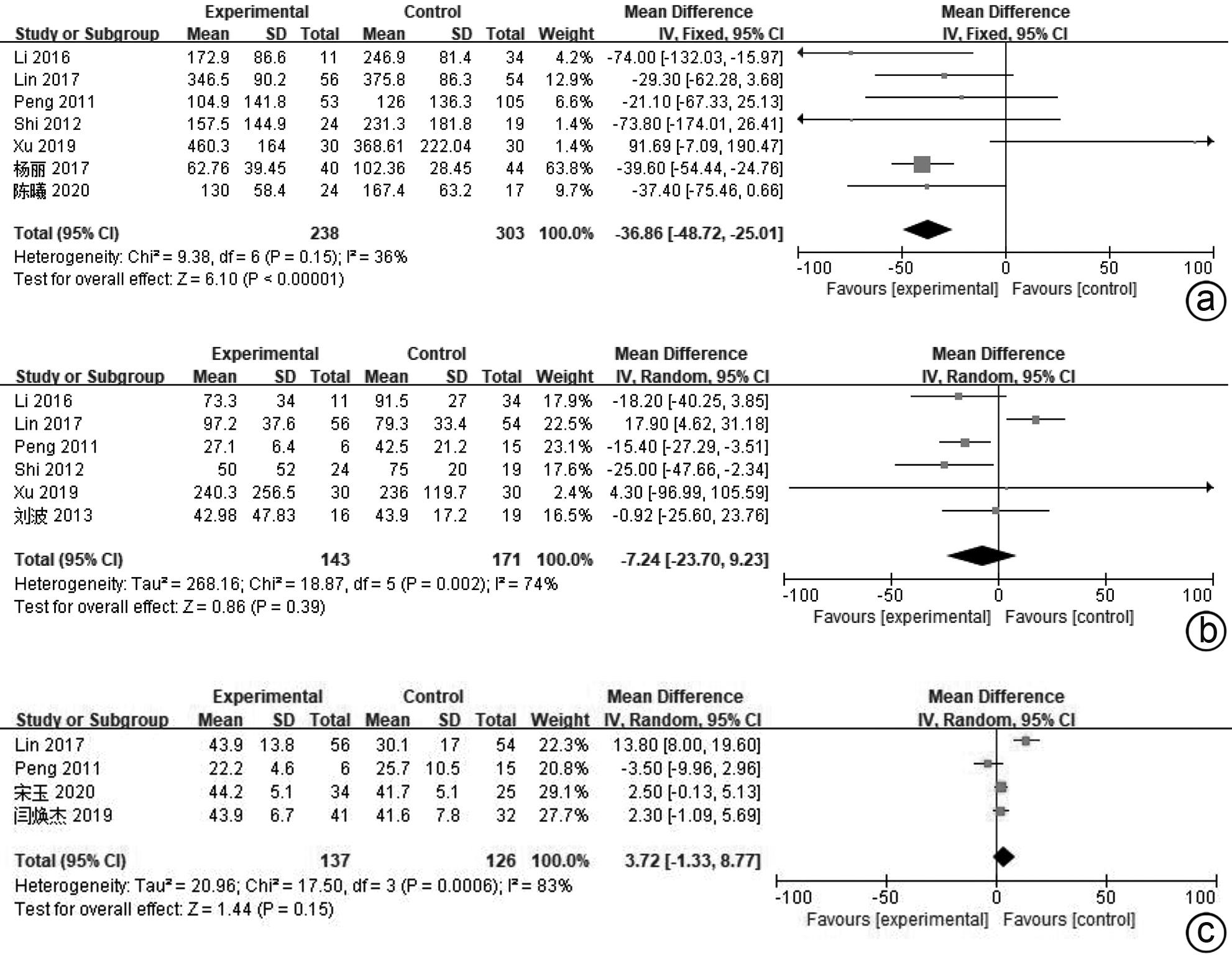
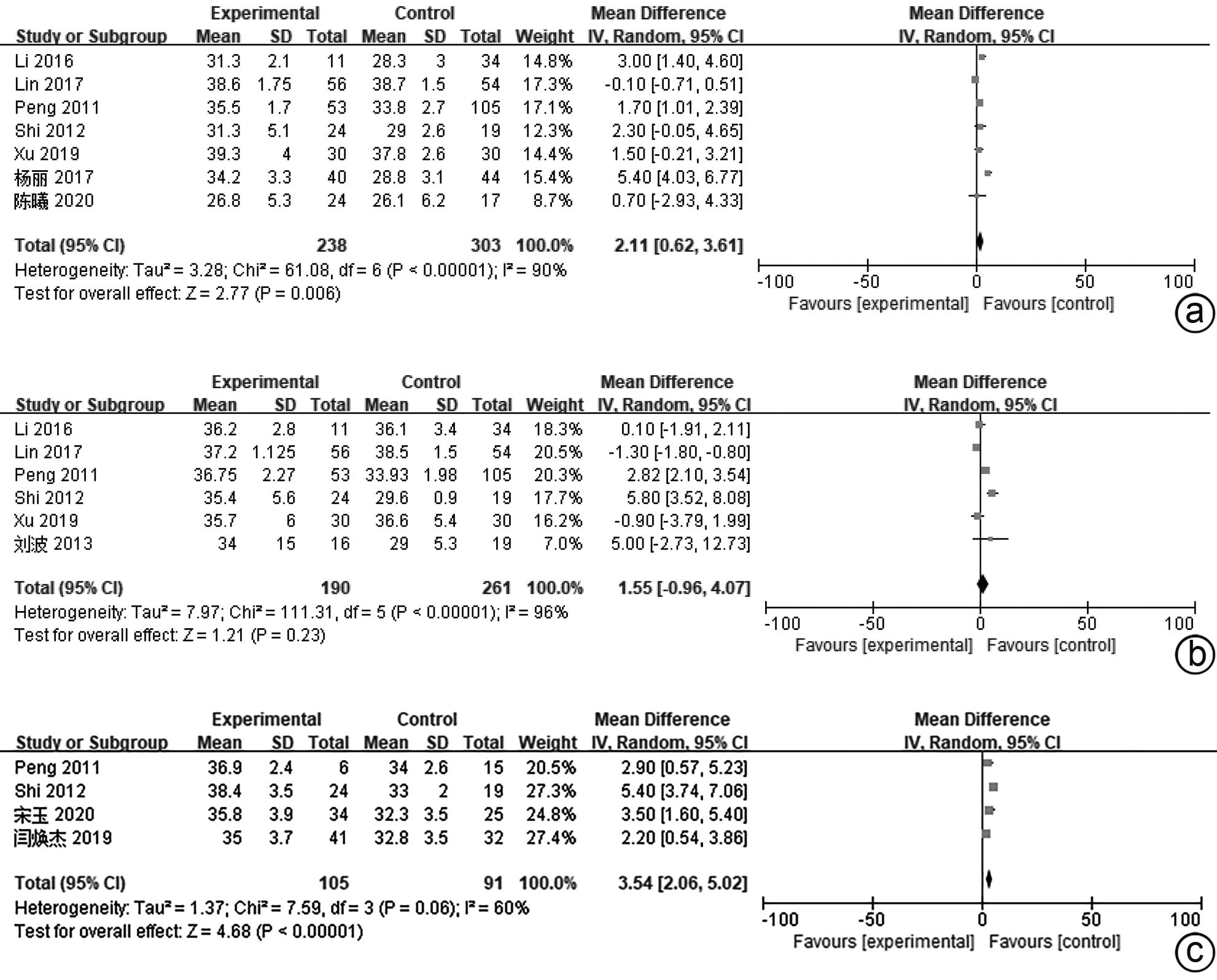
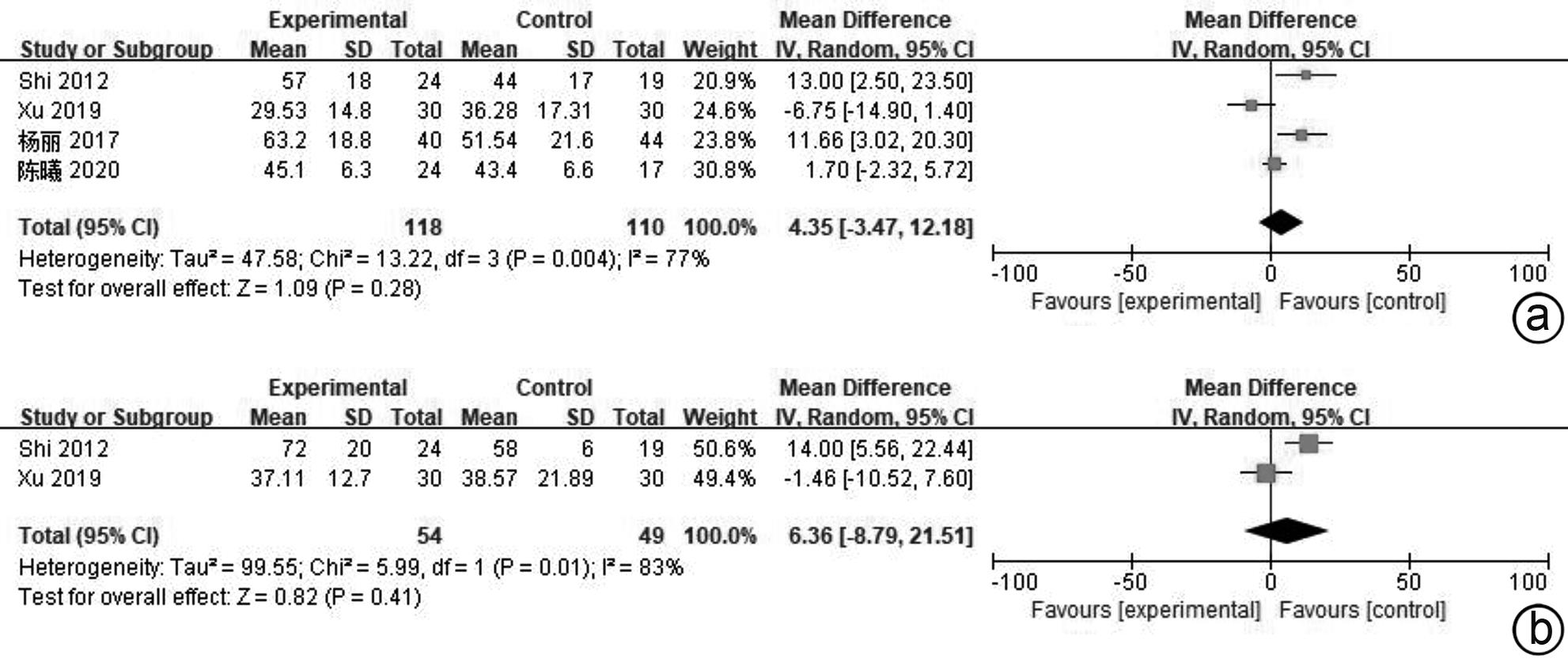
目的 系统评价间充质干细胞(MSC)治疗慢加急性肝衰竭的有效性和安全性。 方法 本研究根据PRISMA指南完成,PROSPERO注册号:CRD42024517851。计算机检索PubMed、Embase、万方数据库、维普数据库和中国知网、中国生物医学数据库、Cochrane图书馆,搜集建库至2023年11月1日发表的有关于MSC治疗慢加急性肝衰竭的随机对照研究(RCT)、队列研究,根据纳入和排除标准对文献进行筛选,并对文献进行数据提取和质量评估,采用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入11篇文献,803名研究对象进行本次Meta分析。结果表明,MSC治疗可提高ACLF患者8周生存率(OR=2.71,95%CI:1.58~4.67,P=0.000 3)、12周生存率(OR=2.24,95%CI:1.36~3.69,P=0.001)、24周生存率(OR=2.09,95%CI:1.37~3.17,P=0.000 6)、48周生存率(OR=2.09,95%CI:1.29~3.40,P=0.003);可降低12周MELD评分(MD=-3.27,95%CI:-6.07~-0.48,P=0.02)、24周MELD评分(MD=-2.24,95%CI:-3.16~-1.33,P<0.000 01);可降低治疗后4周的TBil水平(MD=-36.86,95%CI:-48.72~-25.01,P<0.000 01);提高治疗后4周、24周的Alb水平(MD=2.11,95%CI:0.62~3.61,P=0.006;MD=3.54,95%CI:2.06~5.02,P<0.000 01)。共6篇文献对不良事件进行了评价,无严重不良事件发生。 结论 MSC治疗安全性良好,可提高患者生存率,一定程度上改善肝功能,具有临床应用价值。 Abstract:Objective To systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in the treatment of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). Methods This study was conducted according to PRISMA guidelines, with the PROSPERO registration number of CRD42024517851. PubMed, Embase, Wanfang Data, VIP, CNKI, CBM, and the Cochrane Library were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCT) and cohort studies on MSC in the treatment of ACLF published up to November 1, 2023, and the articles were screened according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. After data extraction and quality assessment, RevMan 5.3 software was used to perform the Meta-analysis. Results A total of 11 articles involving 803 subjects were included in this meta-analysis. The results showed that for the patients with ACLF, MSC could improve 8-week survival rate (odds ratio [OR]=2.71, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.58 — 4.67, P=0.000 3), 12-week survival rate (OR=2.24, 95%CI: 1.36 — 3.69, P=0.001), 24-week survival rate (OR=2.09, 95%CI: 1.37 — 3.17, P=0.000 6), and 48-week survival rate (OR=2.09, 95%CI: 1.29 — 3.40, P=0.003) and reduce 12-week Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (mean difference [MD]=-3.27, 95%CI: -6.07 to -0.48, P=0.02) and 24-week MELD score (MD=-2.24, 95%CI: -3.16 to -1.33, P<0.000 01); it could also reduce the level of total bilirubin after 4 weeks of treatment (MD=-36.86, 95%CI: -48.72 to -25.01, P<0.000 01) and increase 4-week albumin level (MD=2.11, 95%CI: 0.62 — 3.61, P=0.006) and 24-week albumin level (MD=3.54, 95%CI: 2.06 — 5.02, P<0.000 01). Adverse events were evaluated in 6 studies, with no serious adverse events. Conclusion MSC have a good safety in treatment and can improve the survival rate of patients and enhance liver function to some extent, and therefore, it holds promise for clinical application. -
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征及质量评价
Table 1. Basic characteristics and quality evaluation of 11 included literature
纳入文献 国家 研究
类型
病因 干预措施 对照
措施
频率 路径 实验/对照(例) 细胞剂量 随访
时间
质量
评分
Peng[14](2011) 中国 队列研究 HBV 自体BM-MSC SMT 单次 HA 53/105 (3.4±3.8) ×108/kg 192周 8 Shi[7](2012) 中国 RCT HBV 异体UC-MSC SMT 多次 PV 24/19 0.5×106/kg 72周 5 刘波[10](2013) 中国 队列研究 HBV、HBV合并 酒精、HEV或HAV 异体UC-MSC SMT 单次 PV、HA 16/19 >0.5×107/kg 12周 6 Li[4](2016) 中国 队列研究 HBV 异体UC-MSC+PE SMT+PE 单次 HA 11/34 1.0×108/kg 96周 8 Lin[5](2017) 中国 RCT HBV 异体BM-MSC SMT 多次 PV 56/54 (1~10)×105/kg 24周 6 杨丽[13](2017) 中国 队列研究 HBV 异体UC-MSC ALSS+SMT 单次 PV 40/44 1.0×107/kg 4周 5 Xu[8](2019) 中国 RCT HBV 异体UC-MSC SMT 多次 PV 30/30 1.0×105/kg 48周 5 闫焕杰[12](2019) 中国 队列研究 HBV 自体BM-MSC+PDF SMT+PDF 单次 HA 58/62 (1.2~96) ×107/kg 48周 6 陈曦[9](2020) 中国 队列研究 HBV、HBV合并HCV、HAV、药物或酒精 异体UC-MSC+DPMAS SMT+DPMAS 单次 PV、HA、
门静脉
25/20 4.0×108/kg 8周 7 宋玉[11](2020) 中国 RCT HBV 自体BM-MSC+PDF SMT+PDF 单次 HA 47/47 (5~50)×107/kg 24周 5 Schacher[6](2021) 德国 RCT 酒精、HBV、 HCV、NASH 异体BM-MSC SMT 多次 PV 4/5 1.0×106/kg 12周 6 注:HAV,甲型肝炎病毒;HBV,乙型肝炎病毒;HCV,丙型肝炎病毒;HEV,戊型肝炎病毒;NASH,非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;SMT,标准医学治疗;DPMAS,双重血浆分子吸附系统;PE,单纯血浆置换;PDF,血浆透析滤过;ALSS,人工肝支持系统;UC-MSC,脐带间充质干细胞;BM-MSC,骨髓间充质干细胞;PV,外周静脉;HA,肝动脉。
-
[1] SARIN SK, CHOUDHURY A, SHARMA MK, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver(APASL): An update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13( 4): 353- 390. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09946-3. [2] Group of Stem Cell Engineering, Medical Engineering Society of Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on standardized treatment of decompensated liver cirrhosis with stem cell transplantation(2021)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 7): 1540- 1544. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.07.012.中华医学会医学工程学分会干细胞工程专业学组. 干细胞移植规范化治疗肝硬化失代偿的专家共识(2021)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 7): 1540- 1544. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.07.012. [3] LIU JX, GAO JF, LIANG ZX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and their microenvironment[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13( 1): 429. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02985-y. [4] LI YH, XU Y, WU HM, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in hepatitis B virus related acute-on-chronic liver failure treated with plasma exchange and entecavir: A 24-month prospective study[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2016, 12( 6): 645- 653. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-016-9683-3. [5] LIN BL, CHEN JF, QIU WH, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66( 1): 209- 219. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29189. [6] SCHACHER FC, MARTINS PEZZI DA SILVA A, SILLA LMDR, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in acute-on-chronic liver failure grades 2 and 3: A phase I-II randomized clinical trial[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 2021: 3662776. DOI: 10.1155/2021/3662776. [7] SHI M, ZHANG Z, XU RN, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transfusion is safe and improves liver function in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients[J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2012, 1( 10): 725- 731. DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0034. [8] XU WX, HE HL, PAN SW, et al. Combination treatments of plasma exchange and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: A clinical trial in China[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2019, 2019: 4130757. DOI: 10.1155/2019/4130757. [9] CHEN X, CHEN ZL, DONG J, et al. Efficacy of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation at base of double plasma molecular absorption system in treamtment of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2020, 23( 4): 544- 547. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.04.023.陈曦, 陈照林, 董静, 等. 脐带间充质干细胞联合双重血浆分子吸附治疗慢加急性肝衰竭患者临床效果初步观察[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2020, 23( 4): 544- 547. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.04.023. [10] LIU B, DONG J, ZHANG JF, et al. Efficacy of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of patients with subacute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2013, 16( 1): 29- 31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2013.01.010.刘波, 董静, 张骏飞, 等. 人脐带间充质干细胞治疗慢加急性肝衰竭患者近期疗效与安全性分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2013, 16( 1): 29- 31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2013.01.010. [11] SONG Y, WANG F. Efficacy of transhepatic artery autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation in the treatment of patients with hepatitis B-induced acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2020, 23( 3): 388- 391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.03.022.宋玉, 王芳. 自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗慢加急性乙型肝炎肝衰竭患者疗效初步研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2020, 23( 3): 388- 391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2020.03.022. [12] YAN HJ, ZHANG SQ, ZHAO WJ. Therapeutic efficacy of autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation for treatment of patients with hepatitis B-induced acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2019, 22( 1): 81- 84. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2019.01.022.闫焕杰, 张淑芹, 赵文静. 自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗慢加急性乙型肝炎肝衰竭患者疗效初步研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2019, 22( 1): 81- 84. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2019.01.022. [13] YANG L, MA YJ, LIU GJ, et al. Study of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Med Res, 2017, 46( 6): 151- 153. DOI: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.06.039.杨丽, 马英杰, 刘桂举, 等. 脐血间充质干细胞治疗慢性乙型肝炎加急性肝衰竭的疗效分析[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2017, 46( 6): 151- 153. DOI: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.06.039. [14] PENG L, XIE DY, LIN BL, et al. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in liver failure patients caused by hepatitis B: short-term and long-term outcomes[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54( 3): 820- 828. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24434. [15] FAN Q, LI Z. Liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2022, 13( 3): 333- 337. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.03.008.范祺, 李照. 慢加急性肝衰竭的肝移植治疗[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13( 3): 333- 337. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.03.008. [16] FORBES SJ, GUPTA S, DHAWAN A. Cell therapy for liver disease: From liver transplantation to cell factory[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62( 1 Suppl): S157- S169. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.040. [17] ZHANG B, DILIHUMAER ZYE, ZHANG SY, et al. Progress on pathogenesis and medical treatment of hepatitis B virus-related chronic and acute liver failure[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis(Electronic Version), 2023, 15( 1): 28- 33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2023.01.005.张斌, 迪丽胡玛尔·扎依尔, 张诗雨, 等. 乙型肝炎相关慢加急性肝衰竭发病机制及治疗进展[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2023, 15( 1): 28- 33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2023.01.005. [18] DONG JL, CHEN Y. Prognostic grade of acute-on-chronic liver failure: Different outcomes of the same disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 9): 2030- 2032. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.09.006.董金玲, 陈煜. 慢加急性肝衰竭长期预后转归的等级分析: 同病不同结局[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 9): 2030- 2032. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.09.006. [19] WONG F, PIANO S, SINGH V, et al. Clinical features and evolution of bacterial infection-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74( 2): 330- 339. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.046. [20] SHI M, LI YY, XU RN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in decompensated liver cirrhosis: A long-term follow-up analysis of the randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Hepatol Int, 2021, 15( 6): 1431- 1441. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-021-10199-2. [21] WENG WZ, CHEN JF, MEI YY, et al. Treatment effect of allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation to patients in different phase of HBV acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Sun Yat-Sen Univ(Med Sci), 2013, 34( 3): 422- 428. DOI: 10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).2013.0067.翁伟镇, 陈俊峰, 梅咏予, 等. 异体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗不同时相慢加急性乙肝肝衰竭患者的疗效[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2013, 34( 3): 422- 428. DOI: 10.13471/j.cnki.j.sun.yat-sen.univ(med.sci).2013.0067. [22] ZHOU GP, JIANG YZ, SUN LY, et al. Therapeutic effect and safety of stem cell therapy for chronic liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020, 11( 1): 419. DOI: 10.1186/s13287-020-01935-w. [23] LALU MM, MCINTYRE L, PUGLIESE C, et al. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells(SafeCell): A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7( 10): e47559. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047559. [24] CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells: Time to change the name![J]. Stem Cells Transl Med, 2017, 6( 6): 1445- 1451. DOI: 10.1002/sctm.17-0051. [25] LI JJ, XUN YH. Research advances on the immunomodulatory role of mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in acute liver failure[J]. Zhejiang Med J, 2023, 45( 21): 2338- 2343. DOI: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2023.45.21.2023-731.李佳静, 荀运浩. 间充质干细胞及其外泌体在急性肝衰竭中免疫调节作用的研究进展[J]. 浙江医学, 2023, 45( 21): 2338- 2343. DOI: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2023.45.21.2023-731. [26] WANG ZR, ZHU B, YU LM, et al. Role of stem cell-derived exosomes in treatment of liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 3): 699- 706. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.03.034.王卓然, 朱冰, 余丽梅, 等. 干细胞衍生的外泌体在肝脏疾病治疗中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 3): 699- 706. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.03.034. -



 PDF下载 ( 1767 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1767 KB)

 下载:
下载: