生物钟调控的线粒体动力学在非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240826
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:张策负责撰写论文;苗嘉芮负责设计并讨论文章构架;樊旭负责指导撰写文章、修改论文。
The role of circadian clock-controlled mitochondrial dynamics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
-
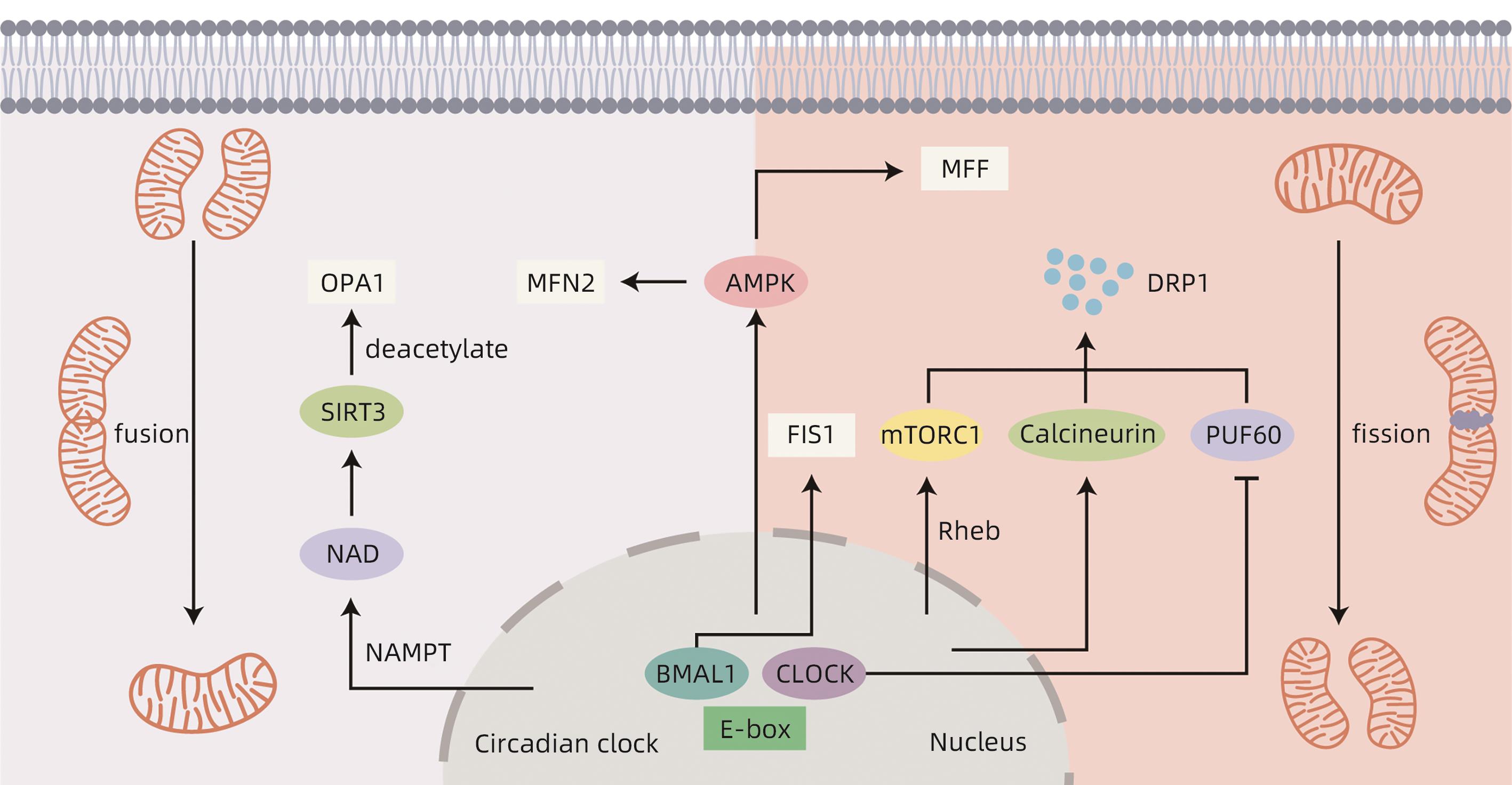
摘要: 非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)是一种与代谢异常密切相关的疾病,是目前最常见的慢性肝病之一。线粒体是高度动态的细胞器,参与肝脏中的多种代谢和生物能量通路,通过线粒体动力学对环境变化做出高度动态反应。生物钟能够调控线粒体动力学,使其表现出节律性变化。当昼夜节律紊乱时,线粒体动力学失去节律性,使得线粒体不能对不同环境中不断变化的能量需求做出反应,导致NAFLD的发生发展。本文总结了生物钟调控的线粒体动力学在NAFLD病因学中的重要作用。Abstract: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a disease closely associated with metabolic abnormalities and is currently one of the most common chronic liver diseases. Mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles involved in a variety of metabolic and bioenergetic pathways in the liver, and they respond to environmental changes in a highly dynamic manner through mitochondrial dynamics. The circadian clock is able to modulate mitochondrial dynamics, making it exhibit rhythmic changes. In case of circadian rhythm disorders, mitochondrial dynamics loses rhythmicity, and mitochondria are unable to respond to changing energy demands in different environments, leading to the development and progression of NAFLD. This article summarizes the important role of circadian clock-controlled mitochondrial dynamics in the etiology of NAFLD.
-
-
[1] SANYAL AJ. Past, present and future perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 16( 6): 377- 386. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0144-8. [2] CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67( 1): 328- 357. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29367. [3] THANAPIROM K, TSOCHATZIS EA. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and the quest for effective treatments[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2019, 8( 1): 77- 79. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.11.06. [4] ZHU XX, DUAN XH, LI RX, et al. Advances in the relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Shandong Med J, 2018, 58( 29): 108- 111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2018.29.033.朱潇旭, 段小花, 李瑞霞, 等. 线粒体功能障碍与非酒精性脂肪肝发病关系的研究进展[J]. 山东医药, 2018, 58( 29): 108- 111. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2018.29.033 [5] SCHMITT K, GRIMM A, DALLMANN R, et al. Circadian control of DRP1 activity regulates mitochondrial dynamics and bioenergetics[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27( 3): 657- 666. e 5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.01.011. [6] JACOBI D, LIU SH, BURKEWITZ K, et al. Hepatic Bmal1 regulates rhythmic mitochondrial dynamics and promotes metabolic fitness[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 22( 4): 709- 720. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.08.006. [7] TIAN SW, LIU QP, MA JX, et al. Research progress on the correlation between circadian rhythm and clock genes and the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Int Eye Sci, 2023, 23( 8): 1290- 1294. DOI: 10.3980/J.issn.1672-5123.2023.8.10.田思雯, 刘秋平, 马继贤, 等. 昼夜节律和生物钟基因与糖尿病视网膜病变发病的相关性研究进展[J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2023, 23( 8): 1290- 1294. DOI: 10.3980/J.issn.1672-5123.2023.8.10. [8] de GOEDE P, WEFERS J, BROMBACHER EC, et al. Circadian rhythms in mitochondrial respiration[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2018, 60( 3): R115- R130. DOI: 10.1530/jme-17-0196. [9] UCHIYAMA Y. Circadian alterations in tubular structures on the outer mitochondrial membrane of rat hepatocytes[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 1981, 214( 3): 519- 527. DOI: 10.1007/BF00233492. [10] HUANG CCY, KO ML, VERNIKOVSKAYA DI, et al. Calcineurin serves in the circadian output pathway to regulate the daily rhythm of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels in the retina[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2012, 113( 3): 911- 922. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.23419. [11] XU LR, LIN JX, LIU YT, et al. CLOCK regulates Drp1 mRNA stability and mitochondrial homeostasis by interacting with PUF60[J]. Cell Rep, 2022, 39( 2): 110635. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110635. [12] KOYANO F, OKATSU K, KOSAKO H, et al. Ubiquitin is phosphorylated by PINK1 to activate parkin[J]. Nature, 2014, 510( 7503): 162- 166. DOI: 10.1038/nature13392. [13] ZOU J, ZHOU L, DU XX, et al. Rheb1 is required for mTORC1 and myelination in postnatal brain development[J]. Dev Cell, 2011, 20( 1): 97- 108. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.11.020. [14] YUAN QY, CHEN MN, YANG WC, et al. Circadian Rheb oscillation alters the dynamics of hepatic mTORC1 activity and mitochondrial morphology[J]. FEBS Lett, 2021, 595( 3): 360- 369. DOI: 10.1002/1873-3468.14009. [15] SARDON PUIG L, VALERA-ALBERNI M, CANTÓ C, et al. Circadian rhythms and mitochondria: Connecting the dots[J]. Front Genet, 2018, 9: 452. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00452. [16] KETTNER NM, VOICU H, FINEGOLD MJ, et al. Circadian homeostasis of liver metabolism suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2016, 30( 6): 909- 924. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.10.007. [17] SIDARALA V, ZHU J, LEVI-D’ANCONA E, et al. Mitofusin 1 and 2 regulation of mitochondrial DNA content is a critical determinant of glucose homeostasis[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13( 1): 2340. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29945-7. [18] SCHULTZ J, WATERSTRADT R, KANTOWSKI T, et al. Precise expression of Fis1 is important for glucose responsiveness of beta cells[J]. J Endocrinol, 2016, 230( 1): 81- 91. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-16-0111. [19] KABRA UD, JASTROCH M. Mitochondrial dynamics and insulin secretion[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 18): 13782. DOI: 10.3390/ijms241813782. [20] VEZZA T, DÍAZ-POZO P, CANET F, et al. The role of mitochondrial dynamic dysfunction in age-associated type 2 diabetes[J]. World J Men’s Health, 2022, 40: 399- 411. DOI: 10.5534/wjmh.210146. [21] LIN HY, WENG SW, CHANG YH, et al. The causal role of mitochondrial dynamics in regulating insulin resistance in diabetes: Link through mitochondrial reactive oxygen species[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 7514383. DOI: 10.1155/2018/7514383. [22] BODEN G, RUIZ J, URBAIN JL, et al. Evidence for a circadian rhythm of insulinsecretion[J]. Am J Physiol, 1996, 271( 2 Pt 1): E246- E252. DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.1996.271.2.E246 [23] LUO QY, XIAO YC, ALEX A, et al. The diurnal rhythm of insulin receptor substrate-1(IRS-1) and Kir4.1 in diabetes: Implications for a clock gene Bmal1[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2019, 60( 6): 1928- 1936. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.18-26045. [24] NAGAYA T, YOSHIDA H, TAKAHASHI H, et al. Markers of insulin resistance in day and shift workers aged 30-59 years[J]. Int Arch Occup Environ Health, 2002, 75( 8): 562- 568. DOI: 10.1007/s00420-002-0370-0. [25] MARCHEVA B, RAMSEY KM, BUHR ED, et al. Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes[J]. Nature, 2010, 466( 7306): 627- 631. DOI: 10.1038/nature09253. [26] SHIMBA S, OGAWA T, HITOSUGI S, et al. Deficient of a clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1(BMAL1), induces dyslipidemia and ectopic fat formation[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6( 9): e25231. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025231. [27] LIU J, ZHOU B, YAN MH, et al. CLOCK and BMAL1 regulate muscle insulin sensitivity via SIRT1 in male mice[J]. Endocrinology, 2016, 157( 6): 2259- 2269. DOI: 10.1210/en.2015-2027. [28] GABRIEL BM, ALTıNTAŞ A, SMITH JAB, et al. Disrupted circadian oscillations in type 2 diabetes are linked to altered rhythmic mitochondrial metabolism in skeletal muscle[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7( 43): eabi9654. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abi9654. [29] YE L, WU HX, XU WH. Deletion of Bmal1 impairs pancreaticβ-cell function via mitochondrial signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 9803024. DOI: 10.1155/2020/9803024. [30] RECTOR RS, THYFAULT JP, UPTERGROVE GM, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction precedes insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis and contributes to the natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an obese rodent model[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 52( 5): 727- 736. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.11.030. [31] WILLEMS PH, ROSSIGNOL R, DIETEREN CE, et al. Redox Homeostasis and mitochond-rial dynamics[J]. Cell Metab, 2015, 22( 2): 207- 18. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.06.006. [32] GENG YF, WANG Y, SUN RM, et al. Carnosol alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis through targeting of PRDX3[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2021, 432: 115758. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2021.115758. [33] BOUREBABA L, ŁYCZKO J, ALICKA M, et al. Inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B and LMPTP promotes palmitate/oleate-challenged HepG2 cell survival by reducing lipoapoptosis, improving mitochondrial dynamics and mitigating oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9( 5): 1294. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9051294. [34] GALLOWAY CA, LEE H, BROOKES PS, et al. Decreasing mitochondrial fission alleviates hepatic steatosis in a murine model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2014, 307( 6): G632- G641. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00182.2014. [35] SHI LX, JI YH, ZHAO SF, et al. Crosstalk between reactive oxygen species and dynamin-related protein 1 in periodontitis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2021, 172: 19- 32. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.05.031. [36] MOLINA AJ, WIKSTROM JD, STILES L, et al. Mitochondrial networking protects beta-cells from nutrient-induced apoptosis[J]. Diabetes, 2009, 58( 10): 2303- 2315. DOI: 10.2337/db07-1781. [37] YU TZ, SHEU SS, ROBOTHAM JL, et al. Mitochondrial fission mediates high glucose-induced cell death through elevated production of reactive oxygen species[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2008, 79( 2): 341- 351. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvn104. [38] ROVIRA-LLOPIS S, BAÑULS C, DIAZ-MORALES N, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics in type 2 diabetes: Pathophysiological implications[J]. Redox Biol, 2017, 11: 637- 645. DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.013. [39] WU SN, ZHOU FF, ZHANG ZZ, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress causes mitochondrial fragmentation via differential modulation of mitochondrial fission-fusion proteins[J]. FEBS J, 2011, 278( 6): 941- 954. DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08010.x. [40] de JESUS DS, BARGI-SOUZA P, CRUZAT V, et al. BMAL1 modulates ROS generation and insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells: An effect possibly mediated via NOX2[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2022, 555: 111725. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111725. [41] HUANG C, CHEN HL, SONG B, et al. Research progress on mutual regulation of redox homeostasis and clock genes and its application prospect in space medicine[J]. Space Med Med Eng, 2021, 34( 1): 80- 88. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2021.01.013.黄超, 陈海龙, 宋波, 等. 氧化还原内稳态与节律基因相互调控的研究进展及在航天医学应用展望[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2021, 34( 1): 80- 88. DOI: 10.16289/j.cnki.1002-0837.2021.01.013. [42] MUSIEK ES, LIM MM, YANG GR, et al. Circadian clock proteins regulate neuronal redox homeostasis and neurodegeneration[J]. J Clin Invest, 2013, 123( 12): 5389- 5400. DOI: 10.1172/JCI70317. [43] GONG CX, LI CW, QI XQ, et al. The daily rhythms of mitochondrial gene expression and oxidative stress regulation are altered by aging in the mouse liver[J]. Chronobiol Int, 2015, 32( 9): 1254- 1263. DOI: 10.3109/07420528.2015.1085388. [44] YANG Z, KIM H, ALI A, et al. Interaction between stress responses and circadian metabolism in metabolic disease[J]. Liver Res, 2017, 1( 3): 156- 162. DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.11.002. [45] ZENG WL, WANG Y. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and liver injury in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2023, 28( 6): 633- 636. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.06.002.曾伟兰, 汪艳. 内质网应激与非酒精性脂肪性肝病肝损伤[J]. 肝脏, 2023, 28( 6): 633- 636. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.06.002. [46] MUÑOZ JP, IVANOVA S, SÁNCHEZ-WANDELMER J, et al. Mfn2 modulates the UPR and mitochondrial function via repression of PERK[J]. EMBO J, 2013, 32( 17): 2348- 2361. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.168. [47] ZHUAN B, WANG X, WANG MD, et al. Hypoxia induces pulmonary artery smooth muscle dysfunction through mitochondrial fragmentation-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Aging(Albany NY), 2020, 12( 23): 23684- 23697. DOI: 10.18632/aging.103892. [48] IGARASHI T, IZUMI H, UCHIUMI T, et al. Clock and ATF4 transcription system regulates drug resistance in human cancer cell lines[J]. Oncogene, 2007, 26( 33): 4749- 4760. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210289. [49] PLUQUET O, DEJEANS N, CHEVET E. Watching the clock: Endoplasmic reticulum-mediated control of circadian rhythms in cancer[J]. Ann Med, 2014, 46( 4): 233- 243. DOI: 10.3109/07853890.2013.874664. [50] FERRAZ-BANNITZ R, BERALDO RA, COELHO PO, et al. Circadian misalignment induced by chronic night shift work promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress activation impacting directly on human metabolism[J]. Biology(Basel), 2021, 10( 3): 197. DOI: 10.3390/biology10030197. [51] ZHU BK, ZHANG Q, PAN YH, et al. A cell-autonomous mammalian 12hr clock coordinates metabolic and stress rhythms[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 25( 6): 1305- 1319.e9. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.05.004. [52] PANG LJ, LIU K, LIU DJ, et al. Differential effects of reticulophagy and mitophagy on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9( 2): 90. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-017-0136-y. [53] LIU PY, LIN HK, XU YY, et al. Frataxin-mediated PINK1-parkin-dependent mitophagy in hepatic steatosis: The protective effects of quercetin[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2018, 62( 16): e1800164. DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201800164. [54] ZIVIANI E, TAO RN, WHITWORTH AJ. Drosophila parkin requires PINK1 for mitochondrial translocation and ubiquitinates mitofusin[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107( 11): 5018- 5023. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0913485107. [55] TANAKA A, CLELAND MM, XU S, et al. Proteasome and p97 mediate mitophagy and degradation of mitofusins induced by Parkin[J]. J Cell Biol, 2010, 191( 7): 1367- 1380. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201007013. [56] XUE R, YANG J, JIA L, et al. Mitofusin2, as a protective target in the liver, controls the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 601. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00601. [57] ZHEN YQ, YUAN ZX, ZHANG JH, et al. Flubendazole induces mitochondrial dysfunction and DRP1-mediated mitophagy by targeting EVA1A in breast cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13( 4): 375. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04823-8. [58] GOMES LC, SCORRANO L. High levels of Fis1, a pro-fission mitochondrial protein, trigger autophagy[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2008, 1777( 7-8): 860- 866. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.05.442. [59] MA D, PANDA S, LIN JD. Temporal orchestration of circadian autophagy rhythm by C/EBPβ[J]. EMBO J, 2011, 30( 22): 4642- 4651. DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.322. [60] CHEN YD, LI JR, LI S, et al. Uncovering the novel role of NR1D1 in regulating BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in ulcerative colitis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 18): 14222. DOI: 10.3390/ijms241814222. [61] JIN R, WANG XX, LIU F, et al. Research advances in pharmacotherapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 7): 1634- 1640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.033.靳睿, 王晓晓, 刘峰, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的药物治疗进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 7): 1634- 1640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.07.033. -



 PDF下载 ( 1259 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1259 KB)

 下载:
下载:



