肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血患者经颈静脉肝内门体分流术后非计划再入院的危险因素分析及列线图模型构建
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240913
Risk factors for unplanned readmission after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhotic patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding and construction of a nomogram model
-
摘要:
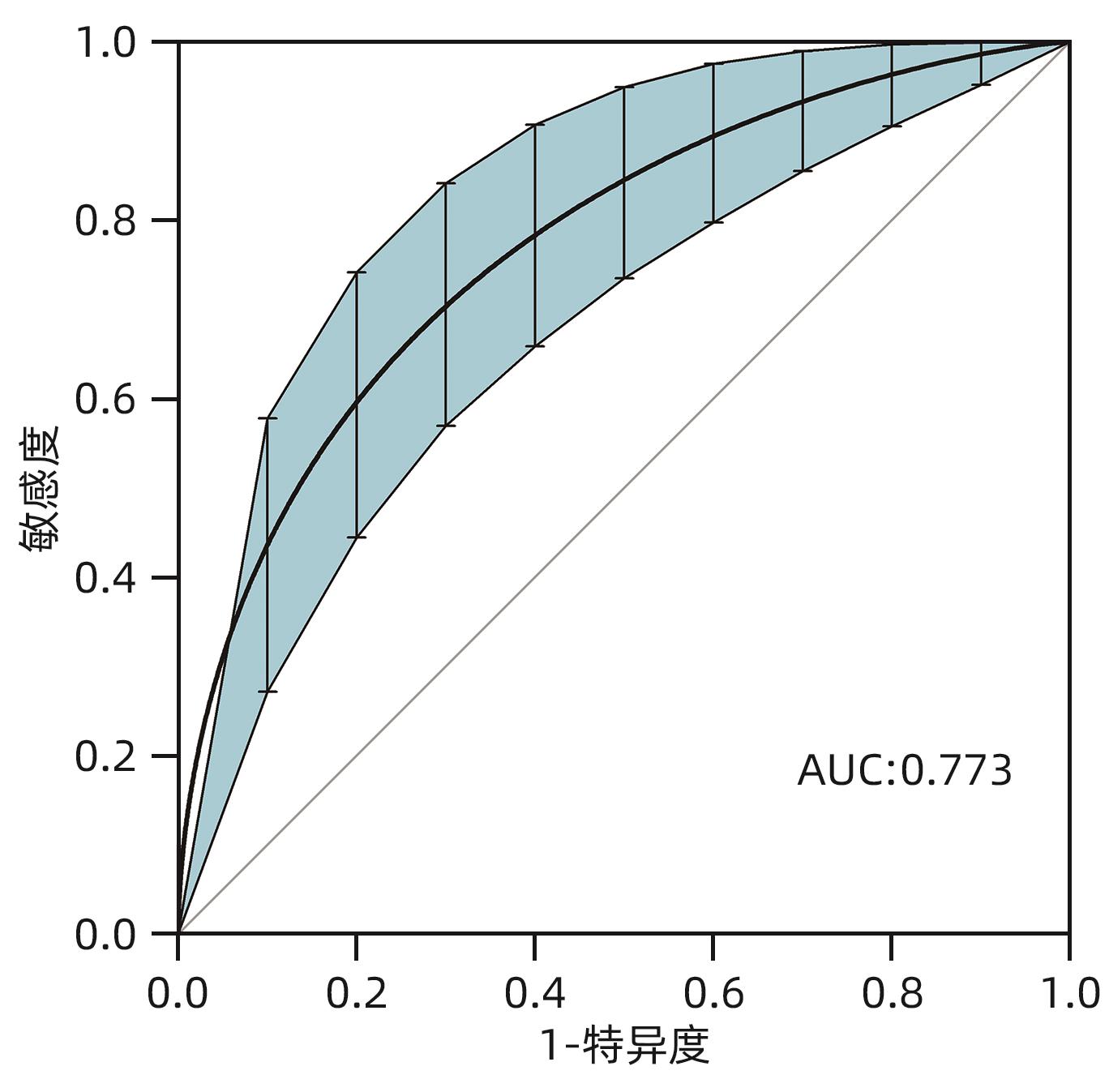
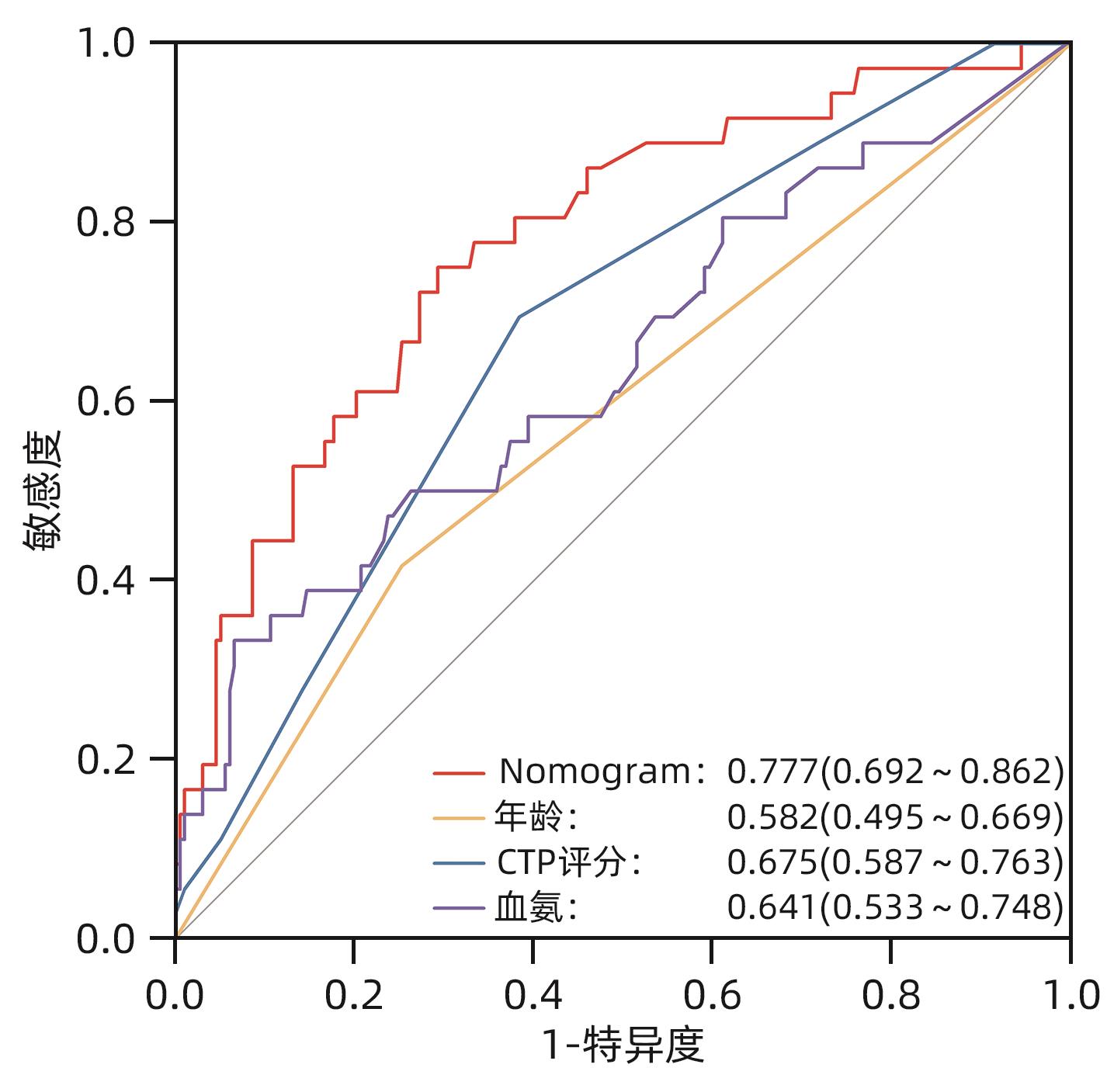
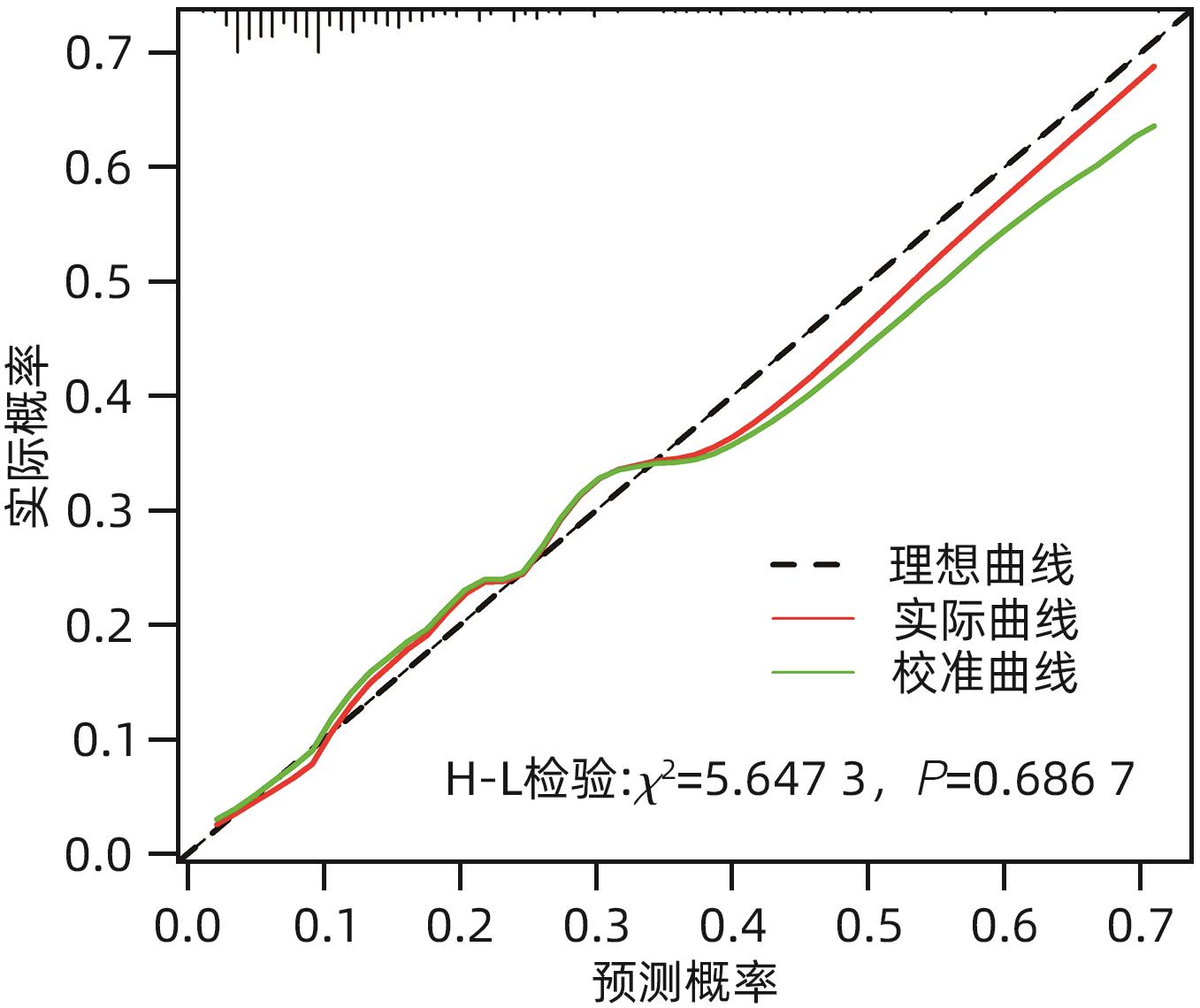
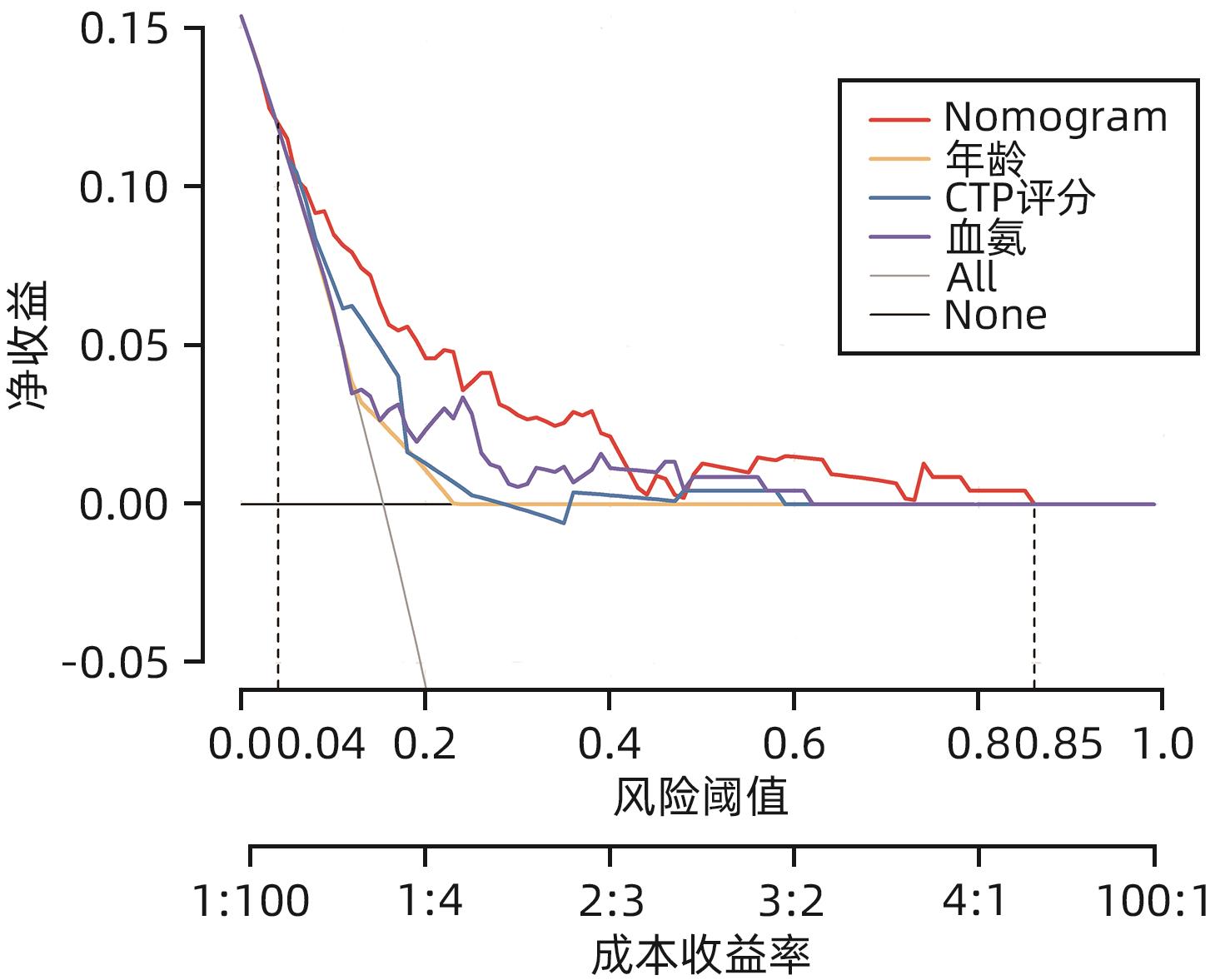
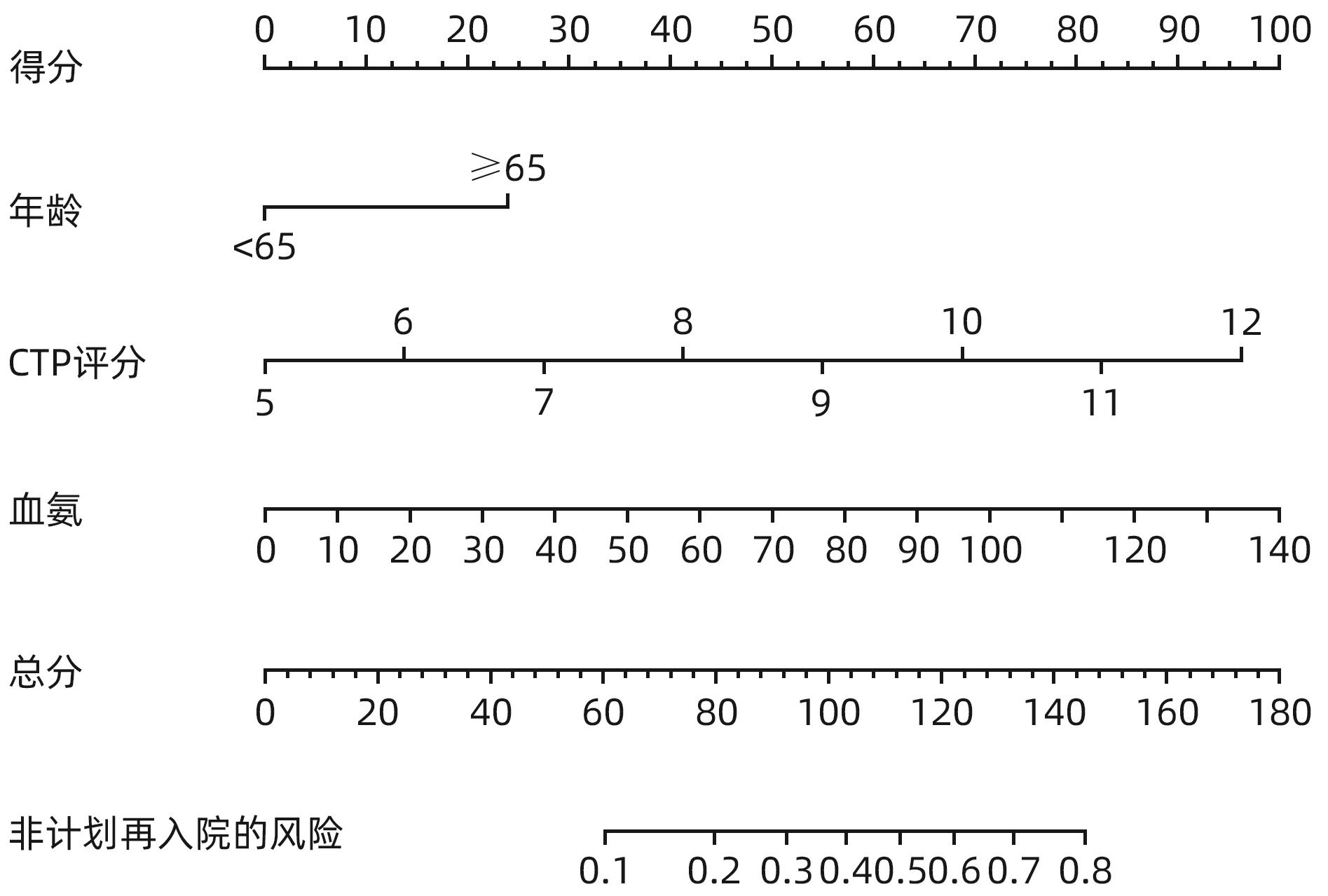
目的 探讨经颈静脉肝内门体分流术(TIPS)的肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血患者出院30 d内发生非计划再入院危险因素,并构建风险预测列线图模型。 方法 选取2020年1月—2023年6月在南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院因肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血行TIPS的241例患者作为研究对象。分析患者30 d内非计划再入院情况,并依据是否发生非计划再入院分为再入院组(n=36)和未再入院组(n=198)。收集患者临床资料,符合正态分布的计量资料2组间比较采用成组t检验,偏态分布的计量资料2组间比较采Mann-Whitney U检验;计数资料2组间比较采用χ2检验。Logistic回归分析筛选出与非计划再入院相关的独立危险因素。建立列线图预测模型,绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)评估列线图模型预测非计划再入院发生的区分度;绘制校准曲线评估列线图模型预测非计划再入院发生的一致性,采用R语言ResourceSelection包进行Hosmer-Lemeshow评估模型的拟合度,决策曲线分析评估模型的实用性。 结果 年龄(OR=2.664,95%CI:1.139~6.233)、CTP评分(OR=1.655,95%CI:1.098~2.495)、血氨(OR=1.032,95%CI:1.016~1.048)是行TIPS患者出院30 d内非计划再入院的独立危险因素(P值均<0.05)。依据多因素分析结果,构建风险预测列线图模型,通过Bootstrap法重复抽样1 000次展开内部验证,ROC曲线下面积为0.773,高于年龄(0.582)、CTP评分(0.675)、血氨(0.641),校准曲线显示列线图模型预测非计划再入院的概率与实际概率具有较好一致性,Hosmer-Lemeshow显示拟合优度良好(χ2=5.647 3,P=0.686 7)。 结论 年龄、CTP评分和血氨是TIPS术后30 d非计划再入院的独立危险因素,以此建立的列线图预测模型有助于预测行TIPS患者非计划再入院发生风险,为早期预防提供较为准确的决策依据。 -
关键词:
- 肝硬化 /
- 门体分流术, 经颈静脉肝内 /
- 危险因素
Abstract:Objective To investigate the risk factors for unplanned readmission within 30 days after discharge in cirrhotic patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), and to construct a nomogram predictive model. Methods A total of 241 cirrhotic patients who underwent TIPS due to esophagogastric variceal bleeding in Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School from January 2020 to June 2023 were enrolled as subjects, and unplanned readmission within 30 days was analyzed. According to the presence or absence of unplanned readmission, they were divided into readmission group with 36 patients and non-readmission group with 198 patients, and related clinical data were collected from all patients. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between two groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between two groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. A logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent risk factors for unplanned readmission. A nomogram prediction model was constructed, and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to assess its discriminatory ability for unplanned readmission; the calibration curve was plotted to evaluate the consistency of the nomogram model in predicting unplanned readmission; the ResourceSelection package of R language was used for the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test to evaluate the degree of fitting of the mode; the decision curve analysis was used to investigate the practicality of the model. Results Age (odds ratio [OR]=2.664, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.139 — 6.233, P<0.05), CTP score (OR=1.655, 95%CI: 1.098 — 2.495, P<0.05), and blood ammonia (OR=1.032, 95%CI: 1.016 — 1.048, P<0.05) were independent risk factors for unplanned readmission within 30 days after discharge in the patients undergoing TIPS. The multivariate analysis showed that for the nomogram predictive model constructed in this study, repeated sampling for 1 000 times using the Bootstrap method was performed for internal validation, and the area under the ROC curve was 0.773, which was significantly higher than that of age (0.582), CTP score (0.675), and blood ammonia (0.641). The calibration curve showed good consistency between the probability of unplanned readmission predicted by the nomogram model and the actual probability, and the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test showed good degree of fitting (c2 =5.647 3, P=0.686 7). Conclusion Age, CTP score, and blood ammonia are independent risk factors for unplanned readmission within 30 days after TIPS, and the nomogram prediction model constructed based on these factors can help to predict the risk of unplanned readmission in TIPS patients and provide an accurate decision-making basis for early prevention. -
表 1 TIPS患者出院30 d内非计划再入院单因素分析
Table 1. Univariate analysis of unplanned readmission within 30 days of discharge for TIPS patients
项目 再入院组(n=36) 非再入院组(n=198) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 21/15 114/84 χ2=0.007 0.933 年龄(<65岁/≥65岁,例)1) 21/15 148/50 χ2=4.091 0.043 入院途径(急诊/门诊,例) 17/19 89/109 χ2=0.063 0.801 住院时间(d) 11.0(9.0~14.5) 12.0(9.0~14.0) Z=-0.844 0.399 术后住院时间(d) 7.00(5.00~8.75) 7.00(5.75~9.00) Z=-0.961 0.337 支付类型(医保/非医保,例) 28/8 53/145 χ2=0.327 0.568 高血压(有/无,例) 8/28 47/151 χ2=0.039 0.844 糖尿病(有/无,例) 7/29 47/151 χ2=0.316 0.574 合并门静脉血栓(有/否,例) 15/21 64/134 χ2=1.189 0.276 既往出血次数(1次/≥2次,例) 15/21 70/128 χ2=0.525 0.469 腹水(无-轻度/中重度,例) 9/27 97/101 χ2=7.075 0.008 CTP评分(分) 8(7~9) 7(6~8) Z=-3.427 0.001 MELD评分(分) 11.36±2.94 10.94±2.83 t=1.108 0.274 静脉曲张分型
(EV+GOV1/GOV2+IGV1,例)
19/17 97/101 χ2=0.175 0.676 TIPS术中联合侧支血管栓塞
(未栓塞/栓塞,例)
8/28 27/171 χ2=1.765 0.184 术前实验室检查项目 WBC(×109/L) 3.85(2.23~5.85) 2.80(1.80~5.03) Z=-1.554 0.120 Hb(g/L) 73.00(61.25~85.75) 75.00(65.75~87.00) Z=-0.622 0.534 PLT(×109/L) 59.50(40.00~136.75) 60.50(39.75~85.25) Z=-0.470 0.639 ALT(U/L) 72.00(54.75~85.25) 19.45(14.55~29.73) Z=-0.626 0.531 AST(U/L) 27.30(21.00~40.85) 27.00(20.50~36.65) Z=-0.319 0.750 TBil(μmol/L) 22.30(12.68~36.68) 19.90(13.85~31.03) Z=-0.637 0.524 Alb(g/L) 32.25(30.30~34.73) 33.60(31.20~36.70) Z=-2.100 0.036 肌酐(μmol/L) 56.60(49.25~78.00) 62.00(51.75~73.00) Z=-0.493 0.622 PT(s) 14.75(13.73~16.35) 14.50(13.28~15.60) Z=-1.266 0.205 INR 1.30(1.21~1.45) 1.28(1.17~1.38) Z=-1.157 0.247 术后实验室检查项目 WBC(×109/L) 4.75(3.15~6.58) 4.60(3.00~6.60) Z=-0.794 0.427 Hb(g/L) 81.00(71.00~86.75) 80.00(72.00~93.00) Z=-0.928 0.354 PLT(×109/L) 60.00(39.00~108.50) 61.50(42.00~92.25) Z=-0.256 0.798 ALT(U/L) 30.20(19.73~50.53) 36.15(22.80~69.60) Z=-1.413 0.158 AST(U/L) 45.10(25.83~69.73) 45.55(33.70~70.25) Z=-0.395 0.693 TBil(μmol/L) 34.90(21.53~47.85) 33.25(21.55~47.68) Z=-0.096 0.923 Alb(g/L) 32.15(28.85~35.55) 33.40(30.98~36.35) Z=-1.775 0.076 肌酐(μmol/L) 51.50(43.00~66.50) 54.35(46.95~68.00) Z=-1.108 0.268 血氨(μmol/L) 41.50(22.18~68.75) 26.00(14.75~46.00) Z=-2.685 0.007 注:1)按照世界卫生组织定义,一个国家的老龄化是以65岁以上人口占全国人口比率划分。
表 2 TIPS患者出院30 d内非计划再入院的多因素回归分析
Table 2. Multivariate regression analysis of unplanned readmission within 30 days of discharge for TIPS patients
项目 β值 SE Wald值 OR 95%CI P值 常数 -6.346 2.978 4.542 0.020 0.033 年龄 0.980 0.434 5.104 2.664 1.139~6.233 0.024 CTP评分 0.504 0.209 5.788 1.655 1.098~2.495 0.016 腹水 0.494 0.546 0.817 1.638 0.561~4.781 0.366 术前Alb 0.033 0.068 0.234 1.034 0.904~1.182 0.628 术后Alb -0.068 0.063 1.151 0.934 0.825~1.058 0.283 术后血氨 0.031 0.008 15.341 1.032 1.016~1.048 <0.001 -
[1] BOIKE JR, THORNBURG BG, ASRANI SK, et al. North American practice-based recommendations for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in portal hypertension[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20( 8): 1636- 1662. e 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.018. [2] de FRANCHIS R, BAVENO VI FACULTY. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63( 3): 743- 752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. [3] LYU Y, FAN DM, HAN GH. Application status and future prospect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in gastroesophageal variceal bleeding in liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 6): 1229- 1233. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.004.吕勇, 樊代明, 韩国宏. 经颈静脉肝内门体分流术在肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血中的应用现状与未来展望[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 6): 1229- 1233. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.004. [4] ZHANG K, LIU JL, LIU YL, et al. To observe the clinical effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt guided by 3D model constructed by CT thin-layer scanning data computer in the treatment of cirrhotic portal hypertension complicated with gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 6): 655- 656, 660. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.06.28.张凯, 刘晶磊, 刘燚隆, 等. 应用CT薄层扫描数据电脑构建3D模型指导经颈静脉肝内门体分流术治疗肝硬化门脉高压合并消化道出血临床效果观察[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2023, 51( 6): 655- 656, 660. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.06.28. [5] CHEN GH, WANG GC, ZHANG CQ. Current status of research on hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 5): 1201- 1204. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.047.陈功海, 王广川, 张春清. 经颈静脉肝内门体分流术后肝性脑病的研究现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37( 5): 1201- 1204. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.047. [6] FENG LJ, WANG Y, JIA JD. Clinical management of common complications of liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2023, 28( 1): 13- 16. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.01.033.冯丽娟, 王宇, 贾继东. 肝硬化常见并发症的临床管理[J]. 肝脏, 2023, 28( 1): 13- 16. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.01.033. [7] The Chinese College of Interventionalists. CCI clinical practice guidelines: Management of TIPS for portal hypertension(2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2694- 2699. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.010.中国医师协会介入医师分会. 中国门静脉高压经颈静脉肝内门体分流术临床实践指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 2694- 2699. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.010. [8] ZHOU NS, ZHANG J, MA XM, et al. The study of unplanned readmission within 31 days after being discharged in one general third-level grade A hospital in Beijing[J]. Chin Hosp Manag, 2010, 30( 4): 18- 20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5329.2010.04.008.周念松, 张俊, 马谢民, 等. 北京市某三甲医院31天内非计划性再入院研究[J]. 中国医院管理, 2010, 30( 4): 18- 20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5329.2010.04.008. [9] General Office of the Ministry of Health. Notice on printing and distributing the indicators of medical quality management and control in tertiary general hospitals(2011 edition)[EB/OL].( 2011-01-27)[ 2023-11-10]. http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2011-01/27/content_1793358.htm. http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2011-01/27/content_1793358.htm卫生部办公厅. 关于印发《三级综合医院医疗质量管理与控制指标(2011年版)》的通知[EB/OL].( 2011-01-27)[ 2023-11-10]. http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2011-01/27/content_1793358.htm. http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2011-01/27/content_1793358.htm [10] HAN Q. Analysis of types of diseases, days of interval and influencing factors of unplanned re-admission patients within 31 days after discharge[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34( 16): 2862- 2867. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2020.16.010.韩祺. 出院31 d内非计划再入院病人疾病种类、间隔天数与影响因素分析[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34( 16): 2862- 2867. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2020.16.010. [11] SARWAR A, WEINSTEIN JL, NOVACK V, et al. Causes and rates of 30-day readmissions after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2020, 215( 1): 235- 241. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.19.21732. [12] SHENG S, HUANG Y. Establishment and validation of the interactive nomogram model for all-cause readmission within 90-days in patients with heart failure[J]. Chin J Integr Med Cardio Cerebrovasc Dis, 2023, 21( 16): 2909- 2915. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.16.002.盛松, 黄烨. 心力衰竭病人90 d内再入院的交互式列线图模型建立与验证[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 21( 16): 2909- 2915. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.16.002. [13] CHEN XY, LI K, WANG X, et al. Establishment of prediction model of unplanned readmission within 30 days after discharge in elderly patients receiving total knee arthroplasty[J]. Pract Geriatr, 2023, 37( 8): 772- 776. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9198.2023.08.005.陈翔宇, 李凯, 王旭, 等. 老年病人行全膝关节置换术出院后30天内非计划再入院预测模型的建立[J]. 实用老年医学, 2023, 37( 8): 772- 776. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9198.2023.08.005. [14] MA L, WANG ZX, LUO B. Predictive value of HALP index for unplanned readmission within 30 days after discharge in elderly patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Pract J Card Cereb Pneumal Vasc Dis, 2024, 32( 2): 20- 23. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1008-5971.2024.00.028.马玲, 王志贤, 罗兵. HALP指数对老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者出院后30 d内非计划再入院的预测价值[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2024, 32( 2): 20- 23. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1008-5971.2024.00.028. [15] ZHANG JQ, WANG ZC, YANG JY, et al. Construction and validation of the risk prediction model for secondary hepatic encephalopathy in patients with chronic hepatitis B and cirrhosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2023, 28( 8): 916- 920, 931. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.08.011.张家齐, 王再超, 杨家耀, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎肝硬化患者继发肝性脑病风险预测模型的构建与验证[J]. 肝脏, 2023, 28( 8): 916- 920, 931. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.08.011. [16] PUGH RN, MURRAY-LYON IM, DAWSON JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices[J]. Br J Surg, 1973, 60( 8): 646- 649. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [17] LI H, XIA ZB, XIAO NJ, et al. Current research status of prognostic models for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 5): 1191- 1196. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.030.李慧, 夏志波, 肖年军, 等. 经颈静脉肝内门体分流术预后模型的研究现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 5): 1191- 1196. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.030. [18] LIU ZL, FAN ZP, LIU YL, et al. Value of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease and Child-Turcotte-Pugh score in predicting the prognosis of patients with hepatic sinus obstruction syndrome associated with Gynura segetum(Lour.) Merr[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 11): 2462- 2466. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.013.刘贞利, 范作鹏, 柳雅立, 等. 终末期肝病模型及CTP评分系统对土三七相关肝窦阻塞综合征患者预后的预测价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36( 11): 2462- 2466. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.013. [19] ZHANG F, LIU B, SHI YQ, et al. Analysis of risk factors for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig, 2018, 26( 11): 934- 937. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.11.10.张飞, 刘斌, 施彦卿, 等. 肝硬化上消化道出血患者并发肝性脑病的危险因素分析[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2018, 26( 11): 934- 937. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.11.10. [20] LOCKWOOD AH. Blood ammonia levels and hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2004, 19( 3-4): 345- 349. DOI: 10.1023/b: mebr.0000043980.74574.eb. [21] VILSTRUP H, AMODIO P, BAJAJ J, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 2): 715- 735. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27210. [22] BROWN JR, ALONSO A, MAZIMBA S, et al. Improved 30 day heart failure rehospitalization prediction through the addition of device-measured parameters[J]. ESC Heart Failure, 2020, 7( 6): 3762- 3771. DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12956. [23] GLANCE LG, KELLERMANN AL, OSLER TM, et al. Hospital readmission after noncardiac surgery: the role of major complications[J]. JAMA Surg, 2014, 149( 5): 439- 445. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.4. -



 PDF下载 ( 1108 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1108 KB)

 下载:
下载: