微波消融与手术切除治疗肝细胞癌合并肝硬化效果及安全性的Meta分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240915
Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation versus hepatic resection in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with liver cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
目的 通过Meta分析系统评价微波消融(MWA)和手术切除(HR)在肝细胞癌(HCC)合并肝硬化中的有效性及安全性。 方法 本研究根据PRISMA指南完成,PROSPERO注册号:CRD42024509185。检索PubMed、Cochrane Library、EMBASE、Web of Science、中国知网、维普、万方数据库,时间均为从建库至2023年11月,搜索MWA对比HR治疗HCC合并肝硬化的随机对照试验(RCT)和队列研究,采用Stata 12.0软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入3项RCT和5项回顾性队列研究,共953例患者。Meta分析显示:MWA的1/2/3/5年总生存率(OS)与HR相比无统计学差异(P值均>0.05)。MWA的1/2/5年复发率与HR相比无统计学差异(P值均>0.05)。MWA的3年复发率高于HR(RR=1.59,95%CI:1.08~2.33,P=0.017)。MWA的1/3/5年无复发生存率(DFS)低于HR(RR=0.94,95%CI:0.89~0.99,P=0.018,I2=0.0%;RR=0.84,95%CI:0.72~0.98,P=0.023,I2=25.4%;RR=0.75,95%CI:0.58~0.98,P=0.032,I2=34.6%)。但亚组分析表明,在RCT组,MWA的1/2/3年OS和1/3年DFS与HR相比无统计学差异(P值均>0.05)。MWA的术中出血量、手术时间、住院时间、不良反应及肝功能均优于HR(SMD=-2.31,95%CI:-2.64~-1.97,P<0.001,I2=3.1%;SMD=-3.38,95%CI:-4.05~-2.71,P<0.001,I2=73.8%;SMD=-2.54,95%CI:-3.27~-1.80,P<0.001,I2=92.8%;RR=0.42,95%CI:0.30~0.59,P<0.001,I2=0.0%;SMD=-1.43,95%CI:-1.89~-0.97,P<0.001)。 结论 MWA与HR在局部复发、DFS及OS方面无明显差异。MWA术中出血量更少,手术时间更短,不良反应更少,对肝功能影响更小,住院时间更短。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the efficacy and safety of microwave ablation (MWA) versus hepatic resection (HR) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with liver cirrhosis using a meta-analysis. Methods This study was conducted according to the PRISMA guideline, with a PROSPERO registration number of CRD42024509185. PubMed, the Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Web of Science, CNKI, VIP, and Wanfang Data were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and cohort studies on MWA versus HR in the treatment of HCC with liver cirrhosis published up to November 2023, and Stata 12.0 was used to perform the meta-analysis. Results A total of 3 RCTs and 5 retrospective cohort studies were included, with 953 patients in total. The meta-analysis showed that there were no differences between MWA and HR in 1-, 2-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival (OS) rates (all P>0.05) and 1-, 2-, and 5-year recurrence rates (all P>0.05). Compared with HR, MWA had a significantly higher 3-year recurrence rate (risk ratio [RR]=1.59, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.08 — 2.33, P=0.017) and significantly lower 1-, 3-, and 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) rates (1-year DFS rate: RR=0.94, 95%CI: 0.89 — 0.99, P=0.018, I2=0.0%; 3-year DFS rate: RR=0.84, 95%CI: 0.72 — 0.98, P=0.023, I2=25.4%; 5-year DFS rate: RR=0.75, 95%CI: 0.58 — 0.98, P=0.032, I2=34.6%). However, subgroup analysis showed that there were no significant differences between MWA and HR in 1-, 2-, and 3-year OS rates and 1- and 3-year DFS rates in the RCT subgroup (all P>0.05). Compared with HR, MWA had significantly better intraoperative blood loss (standardized mean difference [SMD]=-2.31, 95%CI: -2.64 to -1.97, P<0.001, I2=3.1%), time of operation (SMD=-3.38, 95%CI: -4.05 to -2.71, P<0.001, I2=73.8%), length of hospital stay (SMD=-2.54, 95%CI: -3.27 to -1.80, P<0.001, I2=92.8%), adverse reactions (RR=0.42, 95%CI: 0.30 — 0.59, P<0.001, I2=0.0%), and liver function (SMD=-1.43, 95%CI: -1.89 — -0.97, P<0.001). Conclusion There are no significant differences between MWA and HR in local recurrence, DFS, and OS, but MWA tends to have a less intraoperative blood loss, a shorter time of operation, fewer adverse reactions, a less impact on liver function, and a shorter length of hospital stay. -
Key words:
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular /
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Meta-Analysis
-
表 1 纳入文献的基本特征
Table 1. The characteristics of studies
纳入研究 国家 例数
(T/C)
研究类型 年龄(岁)
(T/C)
男女比例
(T/C)
MWA方式 HBsAg阳性率(T/C,%) Child-Pugh分级 肿瘤个数及大小(cm) 随访时间(月) 结局指标 NOS(分) Zhang等2017[24] 中国 31/42 RCS 51.2±6.93/
54.1±7.23
20∶11/
29∶13
PMWA 45.2/61.9 A或B 单发且直径≤5或3个且最大直径≤3 >60 ①④ 6 Zhang等2016[25] 中国 68/122 RCS 55.4±9.9/
49.5±8.6
57∶11/
111∶11
PMWA 92.6/91.8 A 单个且直径<3 9~104 ①②③④⑧ 7 杨藩等2016[26] 中国 98/152 RCS 55.4±7.9/
52.5±8.0
82∶16/
133∶19
PMWA 91.8/91.4 A或B 单发且直径≤3 9~96 ①③④⑧ 8 黄炎等2017[27] 中国 26/24 RCS 57.6±6.0/
58.1±5.5
15∶11/
15∶9
LMWA - A或B 2.36±0.41/2.46±0.36;个数≤2 13~63/16~65 ①②④⑤⑥⑦⑧ 8 廖凌峰等2018[28] 中国 40/68 RCT 52.36±8.62/
52.20±8.60
28∶12/
50∶18
PMWA 90.00/88.24 A或B 2.32±0.64/
2.12±0.60
12~36 ①③④ 陈红健等2018[29] 中国 46/46 RCT 29~78 68∶24 UNK 100 A或B 单发且直径≤3或2个且直径之和≤3 24 ①④⑤⑥⑦⑧ 王辉坡等2019[30] 中国 45/45 RCT 53.8±3.2/
54.3±2.9
23∶22/
18∶27
UNK - - - - ⑥⑦⑧ 黄志明等2016[31] 中国 47/53 RCS 60.0±12.4/
55.8±11.3
42∶5/
48∶5
UNK - A或B 单发且直径≤3或3个且最大直径≤3 3~44 ①②④⑥⑧ 9 注:T,MWA组;C,HR组;UNK,未分类或未确定。①OS;②LR;③DFS;④不良反应;⑤肝功能;⑥手术时间;⑦术中出血量;⑧住院时间。-,未提供数据。
表 2 消融方式的亚组分析
Table 2. Subgroup analysis-method of ablation
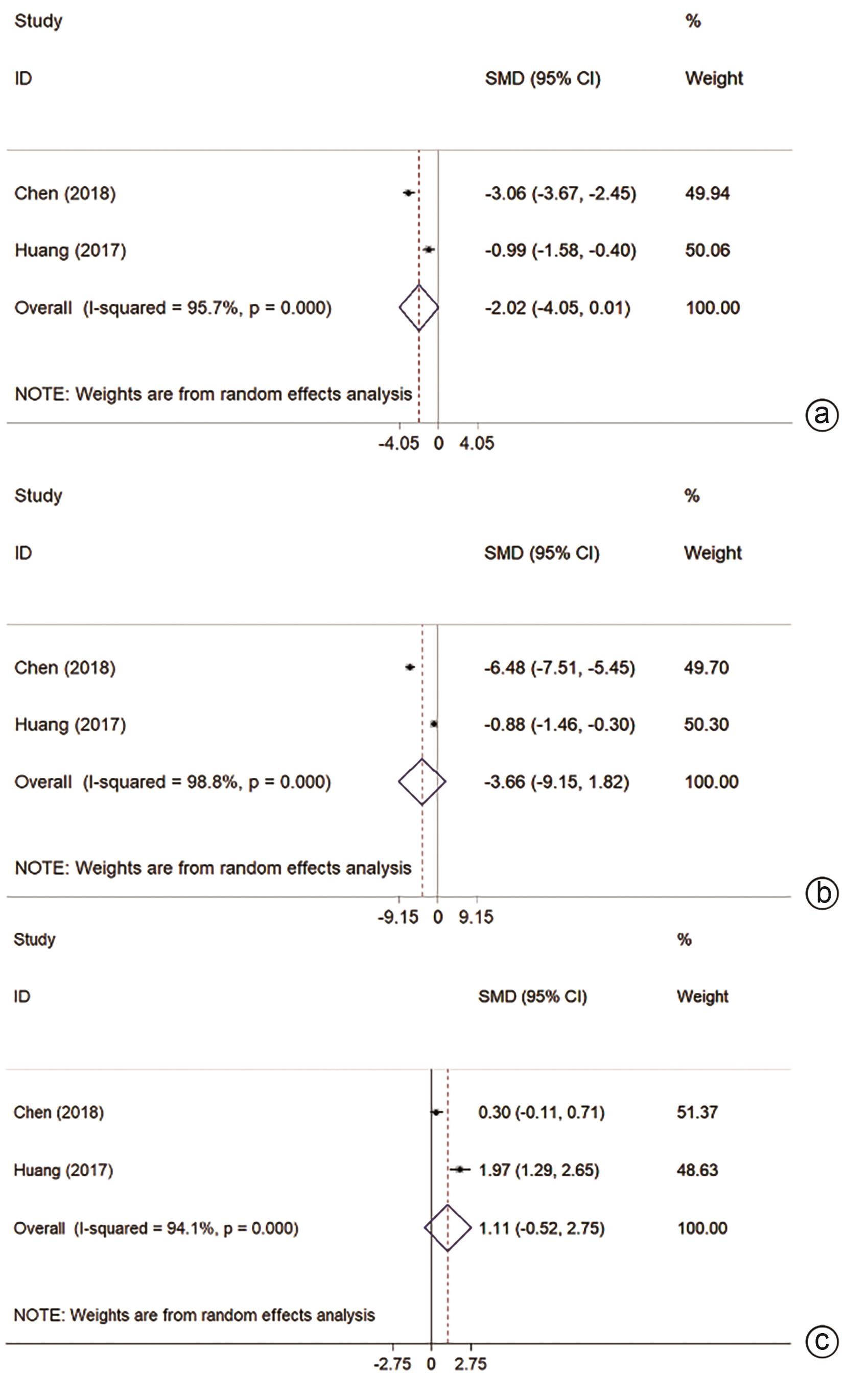
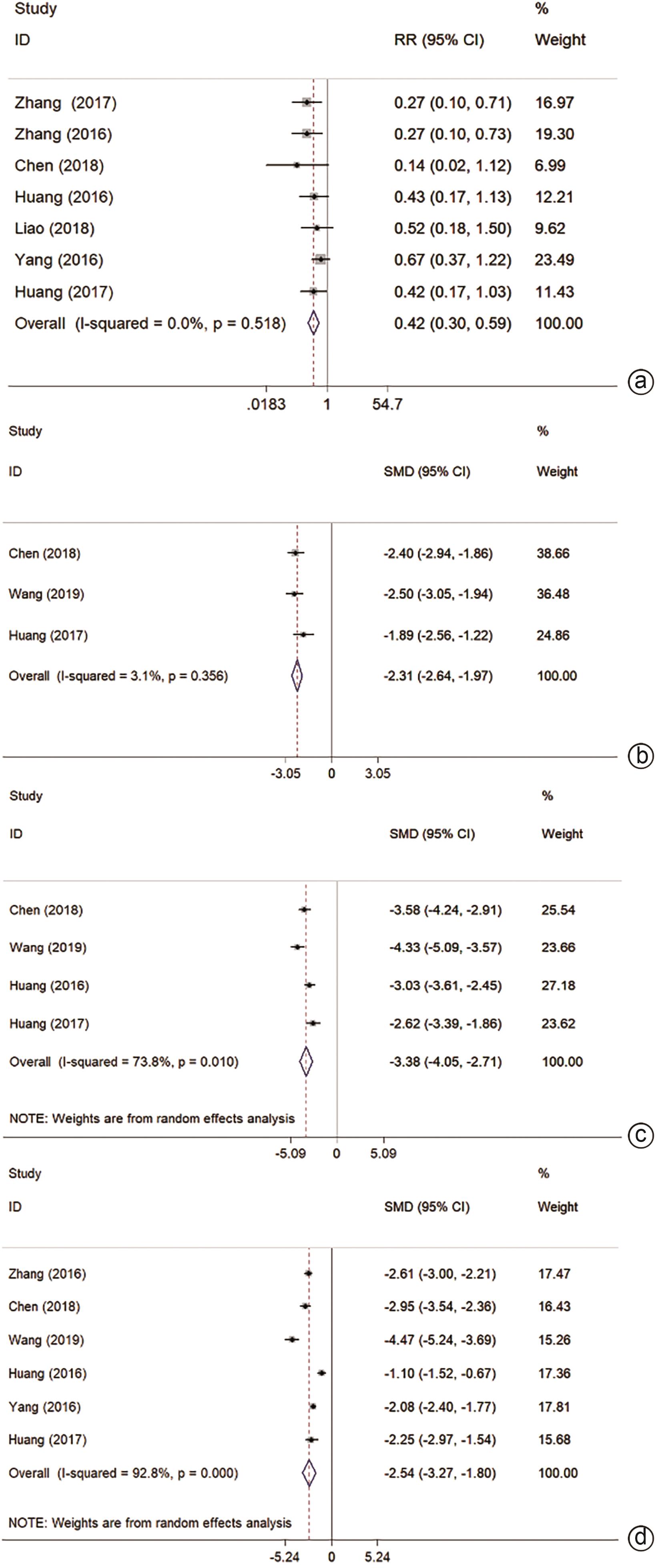
亚组 结局指标 纳入研究数量 效应值[RR或SMD (95%CI)] 异质性(I2) P值 优势组 PMWA 1年OS 4 0.99(0.96~1.01) 0.0% 0.326 2年OS 1 0.94(0.83~1.08) 0.406 3年OS 4 0.93(0.97~1.00) 0.0% 0.067 1年LR 1 1.79(0.46~6.95) 0.397 不良反应 4 0.44(0.29~0.66) 24.0% <0.001 MWA 住院时间 2 -2.33(-2.84~-1.82) 75.4% <0.001 MWA LMWA 1年OS 1 - - 2年OS 1 0.97(0.80~1.16) 0.704 3年OS 1 0.97(0.75~1.26) 0.813 ALT 1 -0.99(-1.58~-0.40) 0.001 MWA AST 1 -0.88(-1.46~-0.30) 0.003 MWA Alb 1 1.97(1.29~2.65) <0.001 MWA 不良反应 1 0.42(0.17~1.03) 0.059 手术时间 1 -2.62(-3.39~-1.86) <0.001 MWA 住院时间 1 -2.25(-2.97~-1.54) <0.001 MWA 术中出血量 1 -1.89(-2.56~-1.22) <0.001 MWA 未分类 1年OS 2 0.98(0.91~1.07) 0.0% 0.711 2年OS 2 0.95(0.83~1.10) 0.0% 0.529 1年LR 1 1.25(0.43~3.59) 0.683 ALT 1 -3.06(-3.67~-2.45) <0.001 MWA AST 1 -6.48(-7.51~-5.45) <0.001 MWA Alb 1 0.30(-0.11~0.71) 0.153 不良反应 2 0.33(0.14~0.77) 0.0% 0.011 MWA 手术时间 3 -3.61(-4.34~-2.89) 71.8% <0.001 MWA 住院时间 3 -2.82(-4.73~-0.90) 96.9% 0.004 MWA 术中出血量 2 -2.45(-2.83~-2.06) 0.0% <0.001 MWA 表 3 研究类型的亚组分析
Table 3. Subgroup analysis-type of research
亚组 结局指标 纳入研究数量 效应值[RR或SMD (95%CI)] 异质性(I2) P值 优势组 RCT 1年OS 2 0.97(0.91~1.04) 0.0% 0.437 2年OS 2 0.95(0.85~1.06) 0.0% 0.324 3年OS 1 1.02(0.74~1.41) 0.904 1年DFS 1 0.92(0.81~1.04) 0.175 3年DFS 1 1.05(0.64~1.70) 0.855 ALT 1 -3.06(-3.67~-2.45) <0.001 MWA AST 1 -6.48(-7.51~-5.45) <0.001 MWA Alb 1 0.30(-0.11~0.71) 0.153 不良反应 2 0.36(0.15~0.90) 20.4% 0.029 MWA 手术时间 2 -3.93(-4.67~-3.19) 53.2% <0.001 MWA 术中出血量 2 -2.45(-2.83~-2.06) 0.0% <0.001 MWA 住院时间 2 -3.69(-5.17~-2.20) 89.1% <0.001 MWA RCS 1年OS 5 0.99(0.96~1.02) 0.0% 0.495 2年OS 2 0.96(0.83~1.13) 0.0% 0.652 3年OS 4 0.93(0.87~0.99) 0.0% 0.026 HR 1年DFS 2 0.95(0.89~1.00) 0.0% 0.050 3年DFS 2 0.81(0.69~0.95) 45.4% 0.009 HR ALT 1 -0.99(-1.58~-0.40) 0.001 MWA AST 1 -0.88(-1.46~-0.30) 0.003 MWA Alb 1 1.97(1.29~2.65) <0.001 MWA 不良反应 5 0.43(0.29~0.62) 0.0% <0.001 MWA 手术时间 2 -2.88(-3.34~-2.42) 0.0% <0.001 MWA 术中出血量 1 -1.89(-2.56~-1.22) <0.001 MWA 住院时间 4 -2.00(-2.65~-1.35) 89.1% <0.001 MWA -
[1] MURAI H, KODAMA T, MAESAKA K, et al. Multiomics identifies the link between intratumor steatosis and the exhausted tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 1): 77- 91. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32573. [2] LI BH, LI YZ, ZHOU HJ, et al. Multiomics identifies metabolic subtypes based on fatty acid degradation allocating personalized treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2024, 79( 2): 289- 306. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000553. [3] SANKAR K, GONG J, OSIPOV A, et al. Recent advances in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2024, 30( 1): 1- 15. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0125. [4] HILL A, OLUMBA F, CHAPMAN W. Transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Surg Clin North Am, 2024, 104( 1): 103- 111. DOI: 10.1016/j.suc.2023.09.002. [5] YILMA M, MEHTA N. Optimal liver transplantation criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2024, 33( 1): 133- 142. DOI: 10.1016/j.soc.2023.06.011. [6] TRAN NH, MUÑOZ S, THOMPSON S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma downstaging for liver transplantation in the era of systemic combined therapy with anti-VEGF/TKI and immunotherapy[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76( 4): 1203- 1218. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32613. [7] KARDASHIAN A, FLORMAN SS, HAYDEL B, et al. Liver transplantation outcomes in a U.S. multicenter cohort of 789 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma presenting beyond Milan criteria[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 6): 2014- 2028. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31210. [8] IVANICS T, CLAASEN MPAW, SAMSTEIN B, et al. Living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma within and outside traditional selection criteria: A multicentric North American experience[J]. Ann Surg, 2024, 279( 1): 104- 111. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000006049. [9] CHOI J, JO C, LIM YS. Tenofovir versus entecavir on recurrence of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 2): 661- 673. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31289. [10] ZHU P, LIAO W, ZHANG WG, et al. A prospective study using propensity score matching to compare long-term survival outcomes after robotic-assisted, laparoscopic, or open liver resection for patients with BCLC stage 0-a hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2023, 277( 1): e103- e111. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005380. [11] RASIC G, de GEUS SWL, BEAULIEU-JONES B, et al. A nationwide propensity score analysis comparing ablation and resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2023, 127( 7): 1125- 1134. DOI: 10.1002/jso.27232. [12] XU JB, QI FZ, XU G, et al. Adjuvant interferon therapy after surgical treatment for hepatitis B/C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2014, 44( 2): 209- 217. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12109. [13] YANG S, LIN Q, LIN W, et al. Effect of adjuvant interferon therapy on hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2016, 14( 1): 159. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-016-0912-7. [14] ADWAN H, HAMMANN L, VOGL TJ. Microwave ablation of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgical resection[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12( 7): 2560. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12072560. [15] RYU T, TAKAMI Y, WADA Y, et al. Combined hepatectomy and microwave ablation for multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma: Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors[J]. Asian J Surg, 2021, 44( 1): 186- 191. DOI: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2020.05.008. [16] WANG Z, LIU M, ZHANG DZ, et al. Microwave ablation versus laparoscopic resection as first-line therapy for solitary 3-5-cm HCC[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76( 1): 66- 77. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32323. [17] WICKS JS, DALE BS, RUFFOLO L, et al. Comparable and complimentary modalities for treatment of small-sized HCC: Surgical resection, radiofrequency ablation, and microwave ablation[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12( 15): 5006. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12155006. [18] LIU KW, ZHENG H, SUI XZ, et al. Microwave ablation versus surgical resection for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score-matched study of long-term therapeutic outcomes[J]. Eur Radiol, 2023, 33( 3): 1938- 1948. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-022-09135-1. [19] DING WZ, YU J, LIU FY, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation versus robot-assisted hepatectomy for early hepatocellular carcinoma: A real-world single-center study[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2022, 54( 2): 243- 250. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.04.008. [20] TONG Y, CAI R, LI JX, et al. Liver resection versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in ideal candidates for ablation per Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging: A propensity score matching and inverse probability of treatment weighting analysis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 56( 11-12): 1602- 1614. DOI: 10.1111/apt.17263. [21] WANG WQ, LV X, LI J, et al. Repeat hepatectomy versus microwave ablation for solitary and small(≤3 cm) recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma with early or late recurrence: A propensity score matched study[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2023, 49( 5): 1001- 1008. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2022.12.016. [22] LIN YZ, SHI HY, MU XH. Diagnosis of small primary liver cancer under the background of liver cirrhosis by dual-source CT hepatic artery three-phase scanning and enhanced perfusion scanning[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2023, 26( 3): 412- 415. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2023.03.028.林永祝, 史红媛, 穆西虎. 双源CT肝动脉三期扫描和增强灌注扫描诊断肝硬化背景下小原发性肝癌价值研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2023, 26( 3): 412- 415. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2023.03.028. [23] HE J, CHEN WQ, SHEN HB, et al. China guideline for liver cancer screening(2022, Beijing)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 8): 1739- 1758. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.007.赫捷, 陈万青, 沈洪兵, 等. 中国人群肝癌筛查指南(2022, 北京)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 8): 1739- 1758. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.08.007. [24] ZHANG QB, ZHANG XG, JIANG RD, et al. Microwave ablation versus hepatic resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and oesophageal variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2017, 33( 3): 255- 262. DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2016.1257824. [25] ZHANG EL, YANG F, WU ZB, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of percutaneous microwave coagulation versus liver resection for single hepatocellular carcinoma ≤3 cm with Child-Pugh A cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2016, 42( 5): 690- 697. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.02.251. [26] YANG F, ZHANG EL, XIAO ZY, et al. Therapeutic outcomes of surgical resection versus percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for single small hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis(250 cases)[J]. Acta Med Univ Sci Technol Huazhong, 2016, 45( 2): 185- 189. DOI: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-0741.2016.02.014.杨藩, 张二雷, 肖震宇, 等. 经皮微波消融与手术切除治疗合并肝硬化的单发小肝癌的疗效比较(附250例)[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2016, 45( 2): 185- 189. DOI: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-0741.2016.02.014. [27] HUANG Y, CHEN J, LIU XS. Clinical efficacy of laparoscopic microwave ablation in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Minim Invasive Surg, 2017, 17( 6): 504- 508. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2017.06.008.黄炎, 陈坚, 刘绪舜. 腹腔镜微波消融治疗小肝癌合并肝硬化的临床疗效[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2017, 17( 6): 504- 508. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6604.2017.06.008. [28] LIAO LF, XUE JZ, LI SK. Survival analysis of percutan eous microwave ablation for patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma with underlying liver cirrhosis[J]. J Pract Hepatol, 2018, 21( 2): 257- 260. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2018.02.025.廖凌峰, 薛建章, 李士坤. 经皮微波消融术治疗合并肝硬化的原发性小肝癌患者生存分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2018, 21( 2): 257- 260. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2018.02.025. [29] CHEN HJ, CHEN Y, ZHANG SQ, et al. Comparison of microwave ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of 92 cases of small hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with cirrhosis[J]. Med J Commun, 2018, 32( 2): 163- 165.陈红健, 陈橼, 张素青, 等. 微波消融与手术切除治疗小肝癌合并肝硬化92例效果比较[J]. 交通医学, 2018, 32( 2): 163- 165. [30] WANG HP, JIA J. Comparative analysis of microwave ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of 90 cases of small hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with cirrhosis[J/CD]. Electron J Clin Med Lit, 2019, 6( 94): 52. DOI: 10.16281/j.cnki.jocml.2019.94.043.王辉坡, 贾静. 微波消融与手术切除治疗小肝癌合并肝硬化90例效果对比分析[J/CD]. 临床医药文献电子杂志, 2019, 6( 94): 52. DOI: 10.16281/j.cnki.jocml.2019.94.043. [31] HUANG ZM, ZHU CH, LI J. Clinical observation of microwave ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma with resectable cirrhosis[J]. Shenzhen J Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2016, 26( 23): 16- 18, 199. DOI: 10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2016.23.008.黄志明, 朱灿华, 李君. 微波消融与手术切除治疗可切除肝硬化型初治小肝癌的疗效观察[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 2016, 26( 23): 16- 18, 199. DOI: 10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2016.23.008. [32] WELLS G, SHEA B, O’CONNELL D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale(NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses[EB/OL]. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. http: //www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp [33] HIGGINS J, THOMAS J, CHANDLER J, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3, 2022[EB/OL]. http://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current. http: //training.cochrane.org/handbook/current [34] General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009.国家卫生健康委办公厅. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. [35] XIONG K, ZHU LP, LU Y, et al. Network Meta-analysis on the efficacy and safety of surgical resection and thermal ablations for hepatocellular carcinoma in China[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2019, 25( 11): 823- 827. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2019.11.007.熊琨, 朱莉萍, 陆勇, 等. 我国肝细胞癌手术切除与热消融疗效和安全性比较的网络荟萃分析[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2019, 25( 11): 823- 827. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.2019.11.007. [36] ZHANG T, HU H, JIA YS, et al. Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation and surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: A meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2022, 101( 52): e32470. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032470. [37] WANG WX, ZHANG FZ, XU XX, et al. Comparison on efficacy of TACE combined with radiofrequency ablation or microwave ablation for primary hepatocellular carcinoma: Meta-analysis[J]. Chin J Interv Imag Ther, 2023, 20( 8): 467- 472. DOI: 10.13929/j.issn.1672-8475.2023.08.005.王文轩, 张福洲, 徐晓雪, 等. 对比TACE联合射频消融与联合微波消融治疗原发性肝细胞癌效果:Meta分析[J]. 中国介入影像与治疗学, 2023, 20( 8): 467- 472. DOI: 10.13929/j.issn.1672-8475.2023.08.005. -



 PDF下载 ( 2928 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2928 KB)

 下载:
下载: