AU富集元件结合因子1(AUF1)在肝细胞癌中的表达及预后评估价值
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240918
Expression of AU-rich element RNA-binding factor 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its value in prognostic evaluation
-
摘要:
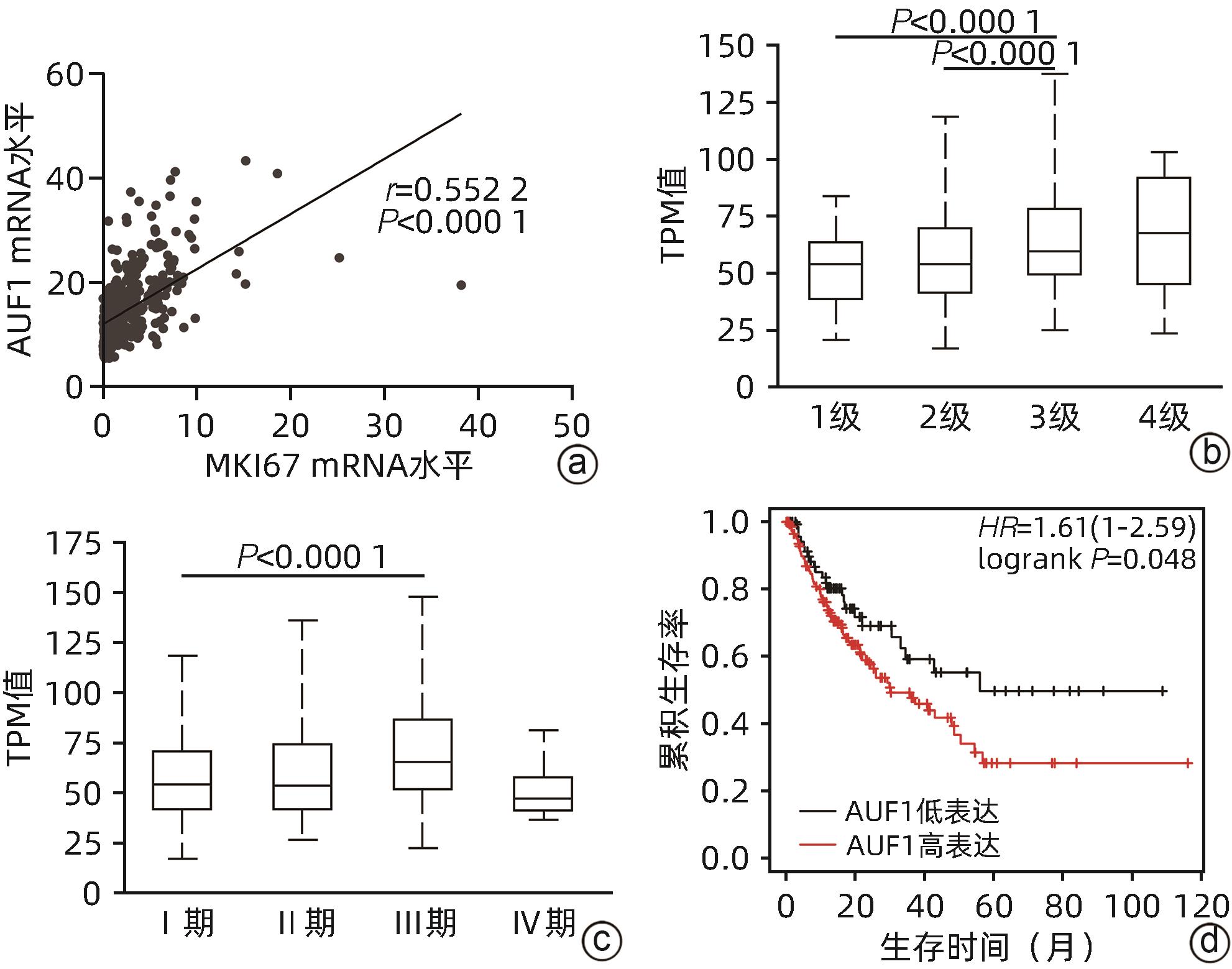
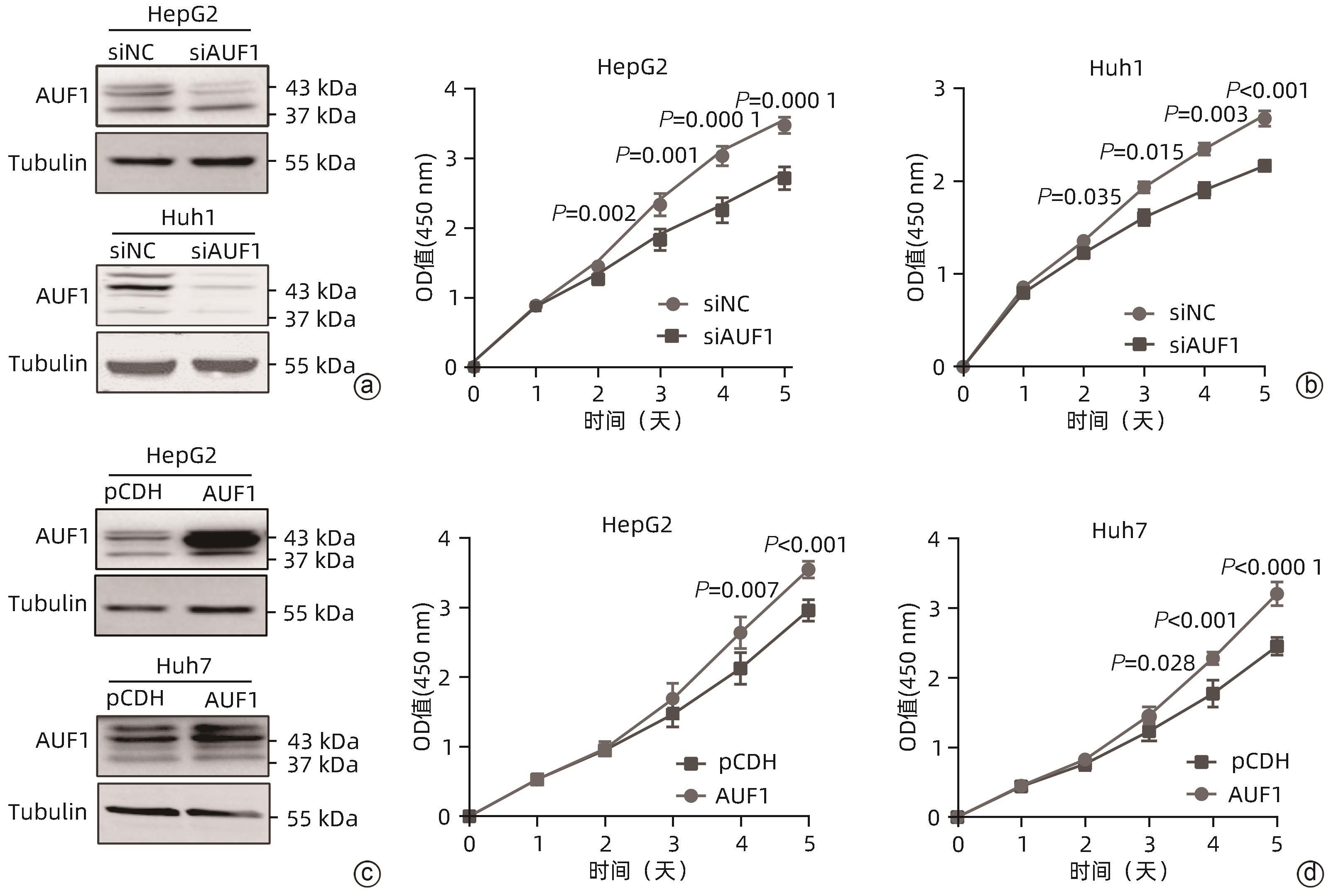
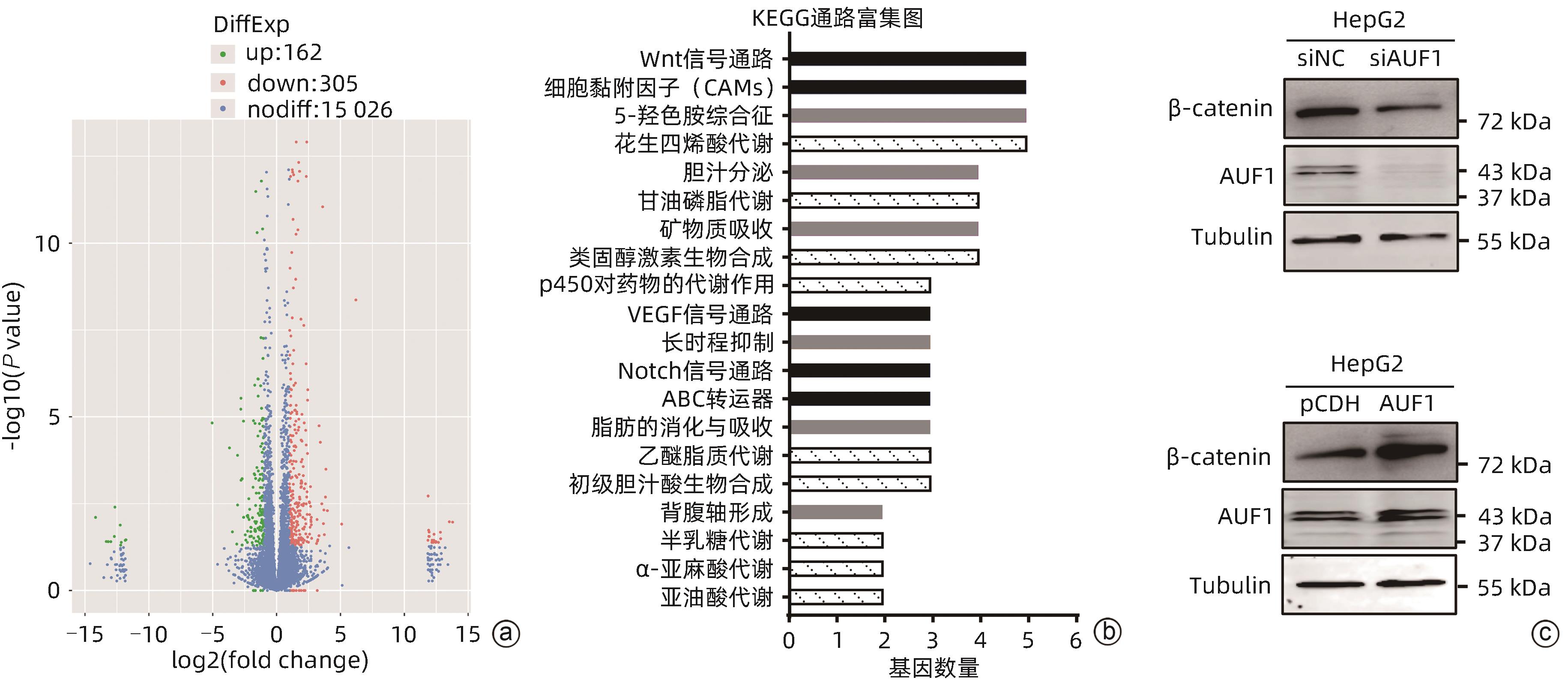
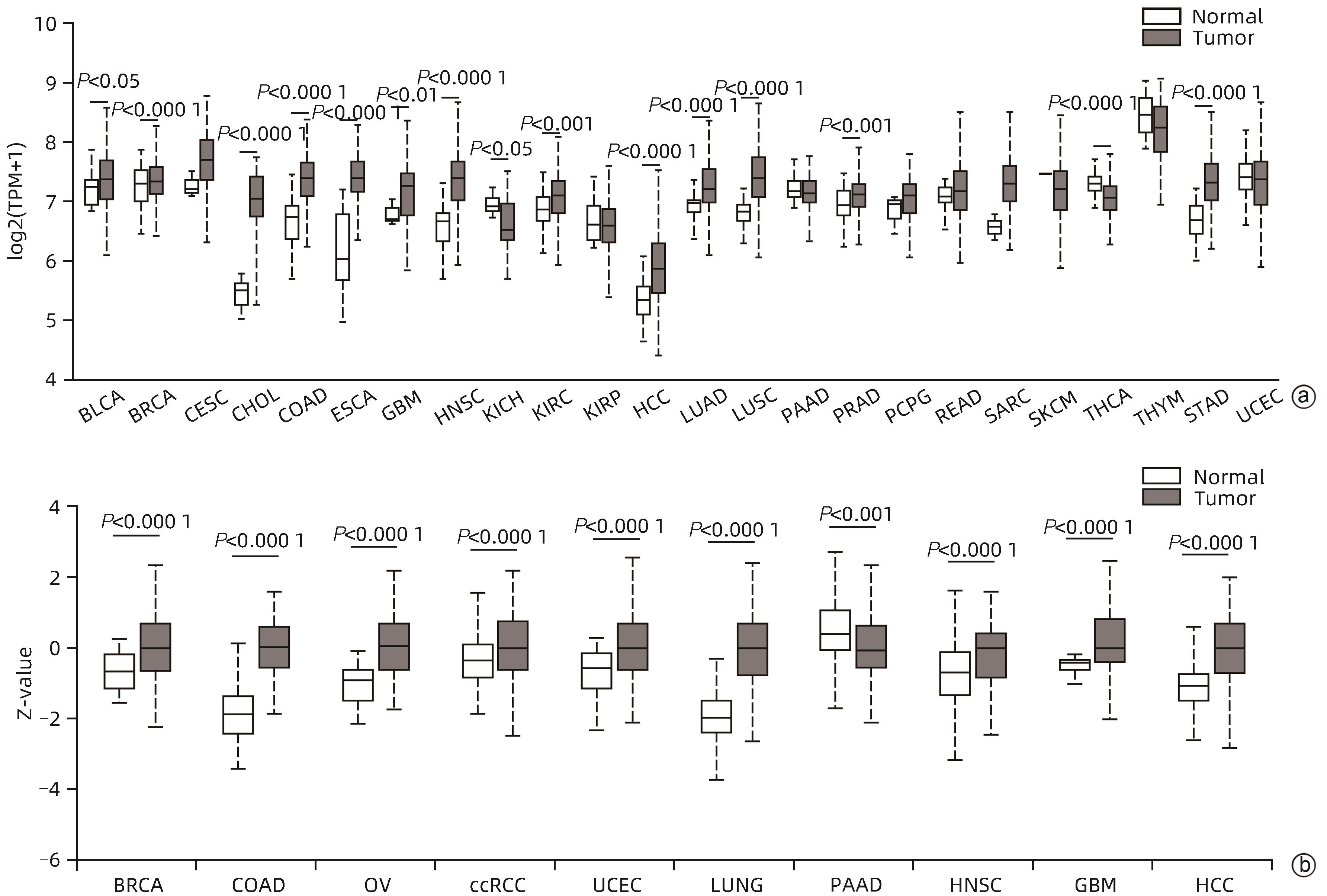
目的 探究AU富集元件RNA结合蛋白1(AUF1)对肝癌细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移能力的影响及可能机制,阐明AUF1在肝细胞癌(HCC)进展中发挥的作用及分子机制。 方法 利用UALCAN和TCGA-HCC数据库分析AUF1在泛癌中的表达以及AUF1表达水平与HCC患者临床病理学特征和预后的相关性;利用CCK-8、细胞凋亡、Transwell小室迁移等实验在细胞水平探究AUF1的功能;利用RNA-seq分析AUF1敲减后肝癌细胞转录组变化。计量资料两组间比较采用t检验,Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,Log-rank检验评估生存率差异。 结果 相较于正常组织,AUF1的mRNA和蛋白水平在多种肿瘤组织中呈异常表达(P值均<0.05)。AUF1的mRNA水平与HCC恶性程度以及早期肝癌的不良预后呈正相关(P值均<0.05)。与对照组相比,过表达外源AUF1促进肝癌细胞的增殖、抑制肝癌细胞的凋亡及迁移。而AUF1敲减则抑制肝癌细胞增殖、促进肝癌细胞凋亡及迁移。RNA-seq分析发现,AUF1敲减主要影响Wnt/β-cateinin通路,并下调β-catenin蛋白水平。 结论 AUF1的异常表达与早期肝癌的预后有关,AUF1的促癌作用可能与其激活Wnt信号通路有关。 -
关键词:
- 癌, 肝细胞 /
- 核不均一核糖核蛋白D /
- Wnt信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of AU-rich element RNA-binding factor 1 (AUF1) on the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration abilities of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and possible mechanisms, and to clarify the role and molecular mechanism of AUF1 in the progression of HCC. Methods The UALCAN and TCGA-HCC databases were used to analyze the expression of AUF1 in pan-cancer and investigate the association of the expression level of AUF1 with the clinicopathological features and prognosis of HCC patients. CCK-8 assay, cell apoptosis assay, and Transwell chamber assay were used to investigate the function of AUF1 at the cellular level, and RNA-seq assay was used to investigate transcriptome changes in HCC cells after AUF1 knockdown. The t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups; the Kaplan-Meier method was used to plot survival curves, and the log-rank test was used for comparison of survival rates. Results There were abnormal mRNA and protein expression levels of AUF1 in various tumor tissues compared with normal tissue (P<0.05). The mRNA expression level of AUF1 was positively correlated with the degree of HCC malignancy and the poor prognosis of early-stage HCC (P<0.05). Compared with the control group, the overexpression of exogenous AUF1 in HCC cells promoted the proliferation of HCC cells and inhibited the apoptosis and migration of HCC cells, while AUF1 knockdown inhibited HCC cell proliferation and promoted the apoptosis and migration of HCC cells. The RNA-seq analysis showed that AUF1 knockdown mainly affected the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and downregulated the protein expression level of β-catenin. Conclusion The abnormal expression of AUF1 is associated with the prognosis of early-stage HCC, and AUF1 may exert an oncogenic effect by activating the Wnt signaling pathway. -
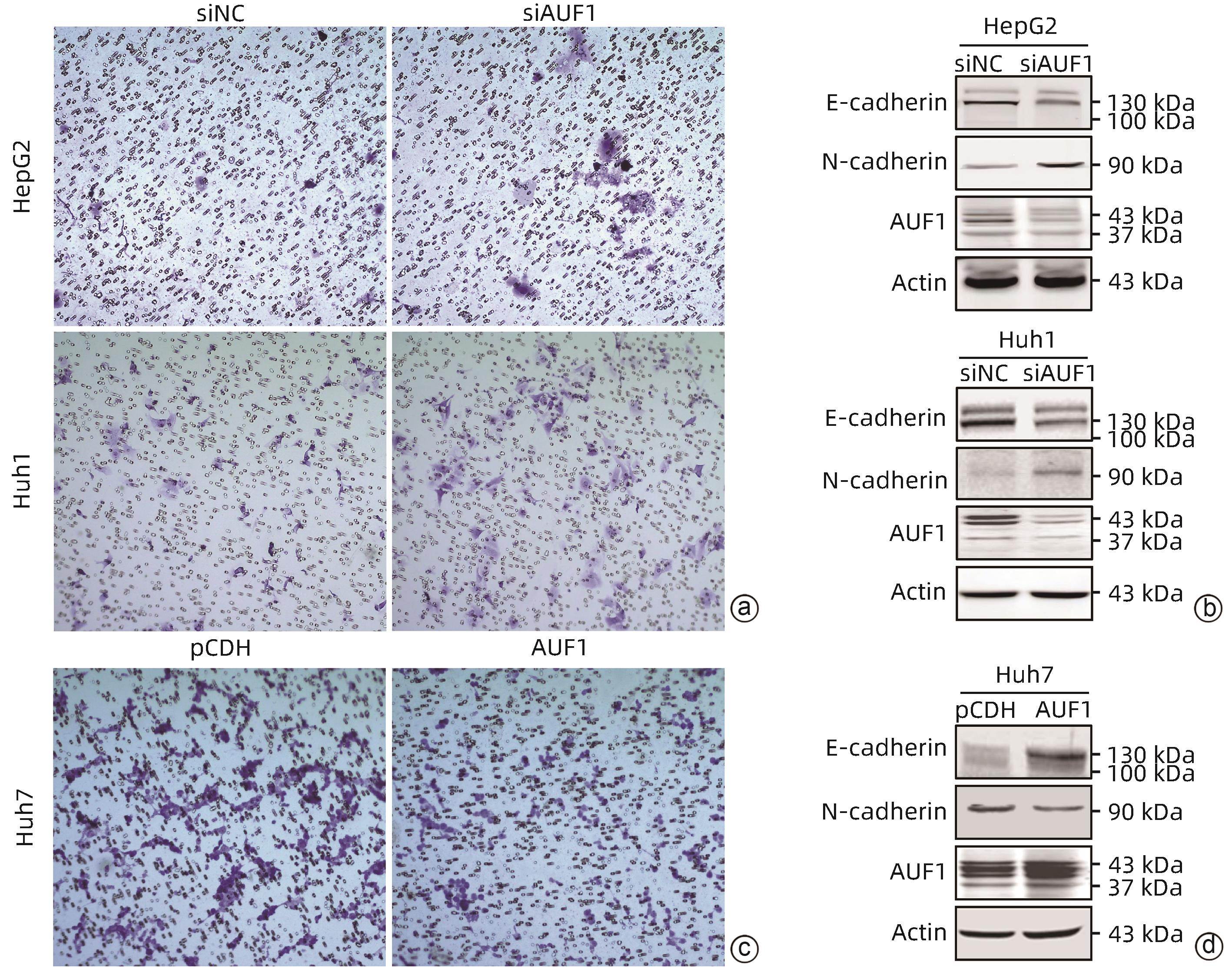
注: a,Transwell实验检测AUF1敲减对细胞迁移能力的影响(结晶紫染色,×20);b,Western Blot检测AUF1敲减对E-cadherin和N-cadherin水平的影响;c,Transwell实验检测AUF1过表达对细胞迁移能力的影响(结晶紫染色,×20);d,Western Blot检测AUF1过表达对E-cadherin和N-cadherin水平的影响。
图 5 AUF1对肝癌细胞迁移能力的影响
Figure 5. The effect of AUF1 on the migration ability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
-
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [2] BLECHACZ B, MISHRA L. Hepatocellular carcinoma biology[J]. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2013, 190: 1- 20. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-16037-0_1. [3] CHEN CY, SHYU AB. AU-rich elements: Characterization and importance in mRNA degradation[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 1995, 20( 11): 465- 470. DOI: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89102-1. [4] LIU H, ZHENG W, SONG Z. circDlgap4 alleviates cerebral ischaemic injury by binding to AUF1 to suppress oxidative stress and neuroinflammation[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2022, 59( 5): 3218- 3232. DOI: 10.1007/s12035-022-02796-5. [5] CHEN LY, LINGNER J. AUF1/HnRNP D RNA binding protein functions in telomere maintenance[J]. Mol Cell, 2012, 47( 1): 1- 2. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.06.031. [6] ULLMER W, SEMLER BL. Direct and indirect effects on viral translation and RNA replication are required for AUF1 restriction of enterovirus infections in human cells[J]. mBio, 2018, 9( 5): e01669- e01618. DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01669-18. [7] MOORE AE, CHENETTE DM, LARKIN LC, et al. Physiological networks and disease functions of RNA-binding protein AUF1[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2014, 5( 4): 549- 564. DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1230. [8] WU QC, LI JH, WANG B, et al. Significance of the expression levels of GPC-3 and AUF1 in cancer tissue in the evaluation of pathological stage and prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer[J]. Clin Misdiagnosis Mistherapy, 2023, 9( 10): 44- 48.吴其琛, 李俊海, 王博, 等. 癌组织中GPC-3、AUF1表达水平对食管癌患者病理分期及预后评估的意义[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2023, 9( 10): 44- 48. [9] CHANDRASHEKAR DS, BASHEL B, BALASUBRAMANYA SAH, et al. UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses[J]. Neoplasia, 2017, 19( 8): 649- 658. DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002. [10] CHANDRASHEKAR DS, KARTHIKEYAN SK, KORLA PK, et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform[J]. Neoplasia, 2022, 25: 18- 27. DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001. [11] ZHANG T, GUAN GW, ZHANG J, et al. E2F1-mediated AUF1 upregulation promotes HCC development and enhances drug resistance via stabilization of AKR1B10[J]. Cancer Sci, 2022, 113( 4): 1154- 1167. DOI: 10.1111/cas.15272. [12] KIM D, PERTEA G, TRAPNELL C, et al. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions[J]. Genome Biol, 2013, 14( 4): R36. DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36. [13] LIAO Y, SMYTH GK, SHI W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30( 7): 923- 930. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. [14] ROBINSON MD, MCCARTHY DJ, SMYTH GK. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26( 1): 139- 140. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [15] YANG YZ, KANG P, GAO J, et al. AU-binding factor 1 expression was correlated with metadherin expression and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35( 3): 2747- 2751. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-013-1362-2. [16] DANG H, TAKAI A, FORGUES M, et al. Oncogenic activation of the RNA binding protein NELFE and MYC signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2017, 32( 1): 101- 114. e 8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.06.002. [17] JUNG YS, STRATTON SA, LEE SH, et al. TMEM9-v-ATPase activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling via APC lysosomal degradation for liver regeneration and tumorigenesis[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 2): 776- 794. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31305. [18] LACHENMAYER A, ALSINET C, SAVIC R, et al. Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by sorafenib[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18( 18): 4997- 5007. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2322. [19] QU JY, LIU XT, LI J, et al. AKR1B10 promotes proliferation of breast cancer cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 35( 12): 1094- 1100.屈佳肴, 刘香婷, 李佳, 等. 醛酮还原酶家族1成员B10(AKR1B10)通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进乳腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 1094- 1100. -



 PDF下载 ( 4247 KB)
PDF下载 ( 4247 KB)

 下载:
下载: