致命性医源性胆道出血的影像学特征和治疗对策
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241022
-
摘要:
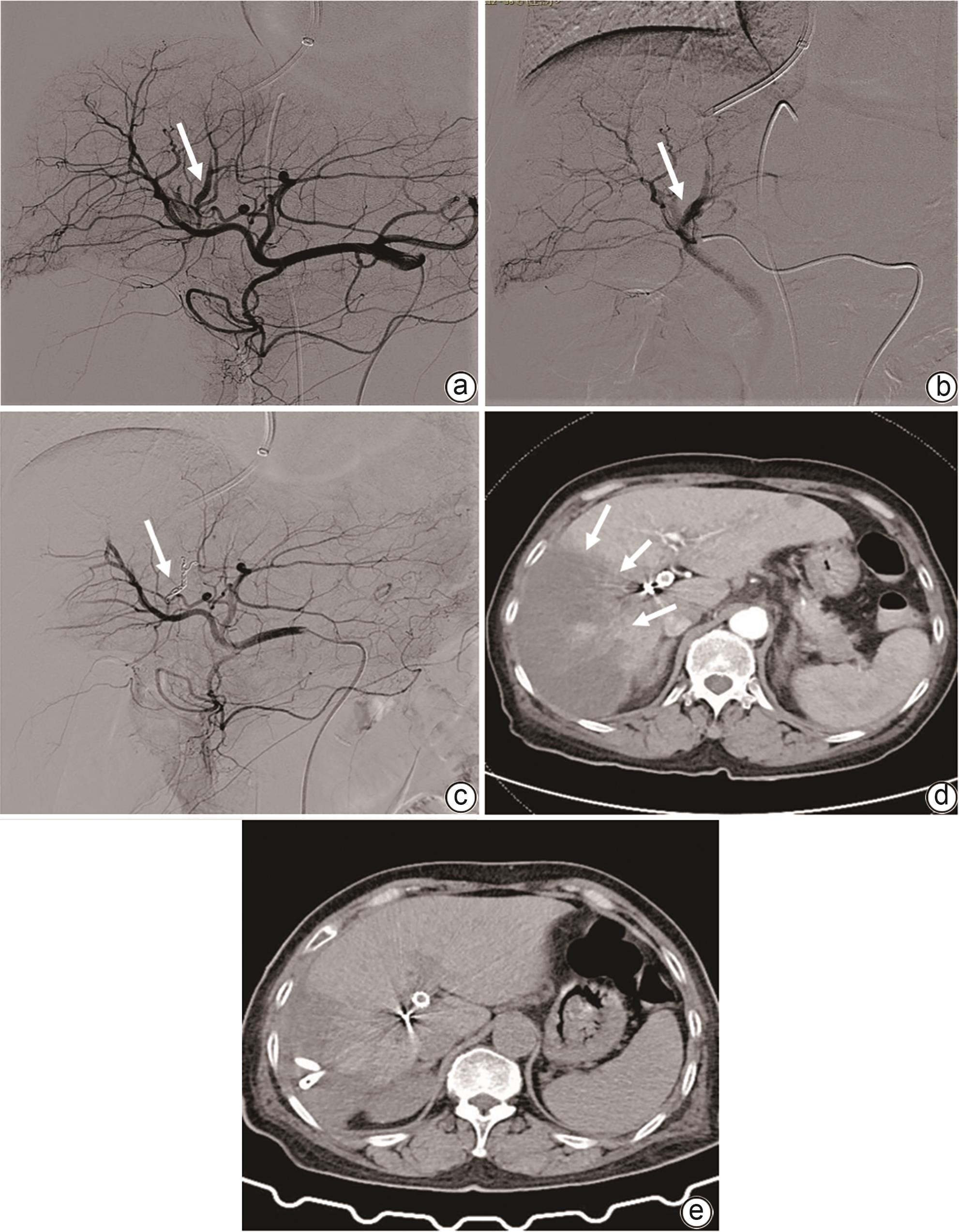
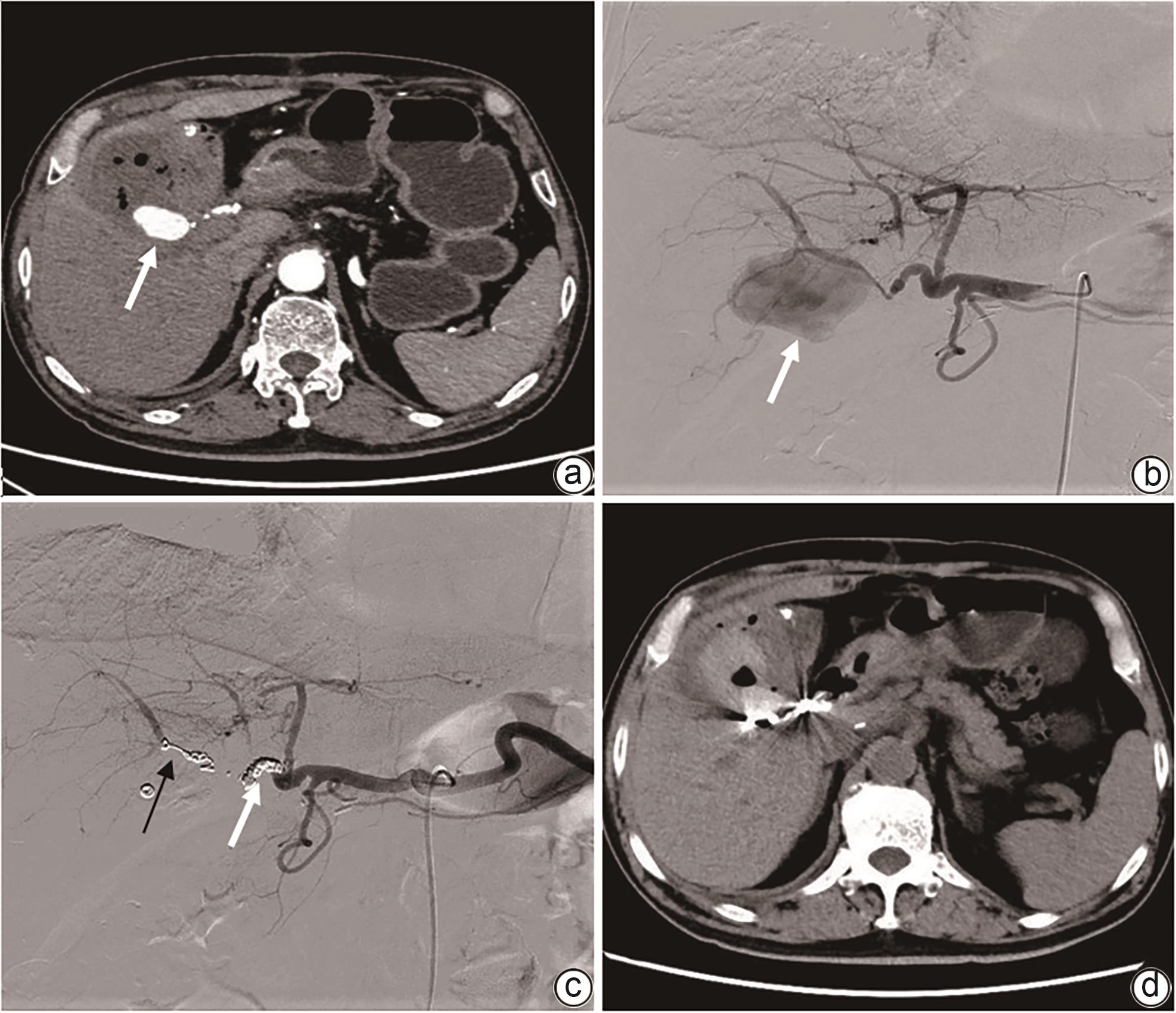
目的 分析致命性医源性胆道出血(LIH)的影像学特征和发病机制,评价经动脉腔内治疗LIH的价值。 方法 收集2009年8月—2023年7月南京医科大学第一附属医院收治的上消化道出血住院患者269例,对其中确诊为LIH并得到治疗的24例患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析,包括LIH的医源性原因、血管造影结果和动脉腔内治疗方法。23例患者使用明胶海绵颗粒和弹簧圈进行动脉栓塞(TAE),1例患者使用覆膜支架进行隔离。评估疗效的主要标准是手术技术成功率、相关并发症和长期疗效的临床随访。 结果 12例LIH是由介入手术引起,12例是由肝胆胰外科手术所致。主要表现为显著的血压或持续血红蛋白下降(n=13)和上消化道出血(n=18)。2例患者在手术期间即出现症状,4例患者在24 h内出现症状,18例患者在24 h后出现症状。血管造影术显示出血阳性率为100%(24/24)。表现为假性动脉瘤(n=15)、肝动脉截断(n=3)、造影剂外渗(n=5)、肝动脉胆道瘘(n=3)。23例患者行TAE,1例患者行支架置入术。23例患者成功止血,技术成功率为95.8%(23/24)。4例TAE术后出现肝坏死和脓肿。治疗止血后无再出血复发。 结论 多种肝内外医源性损伤均可引起致命性胆道出血且临床及影像学表现多样。综合影像诊断联合动脉腔内治疗是LIH最佳的有效救命措施。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the imaging features and pathogenesis of lethal iatrogenic hemobilia (LIH) and the value of transarterial intervention in the treatment of LIH. Methods A total of 269 patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding who were admitted to The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from August 2009 to July 2023 were enrolled, among whom 24 had a confirmed diagnosis of LIH and received treatment, and a retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of these 24 patients, including the iatrogenic causes, angiographic findings, and arterial interventions of LIH. Among the 24 patients, 23 received transarterial embolization (TAE) with gelatin sponge particles and coils, and 1 received a covered stent for isolation. The main criteria for assessing treatment outcome included the technical success rate of surgery, procedure-related complications, and long-term clinical follow-up. Results Among the 24 patients with LIH, 12 had LIH caused by interventional procedures, and 12 had LIH caused by hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery. The main clinical manifestations included a significant reduction in blood pressure or a persistent reduction in hemoglobin in 13 patients and upper gastrointestinal bleeding in 18 patients. Among the 24 patients, 2 developed symptoms during surgery, 4 developed symptoms within 24 hours, and 18 developed symptoms after 24 hours. Angiography showed a positive bleeding rate of 100% (24/24), and imaging findings included pseudoaneurysms in 15 patients, hepatic artery truncation in 3 patients, extravasation of contrast medium in 5 patients, and hepatic arteriobiliary fistula in 3 patients. Among the 24 patients, 23 received TAE and 1 received stent implantation. Successful hemostasis was achieved for 23 patients, with a technical success rate of 95.8% (23/24). Four patients developed hepatic necrosis and abscess after TAE, and there was no rebleeding or recurrence after hemostatic treatment. Conclusion Various iatrogenic injuries may result in LIH with diverse clinical and imaging findings, and integrated diagnostic imaging combined with transarterial intervention is the best effective life-saving measure for LIH. -
表 1 24例LIH患者的临床资料
Table 1. Overview of clinical features, management and outcome in 24 patients with LIH
项目 数值 年龄(岁) 64(40~90) 男/女(例) 16/8 LIH病因(例) PLB/PTCD/TIPS/ERCP 1/9/1/1 PPPD/胆道探查/胆囊切除术/胆道镜检查/胆总管空肠吻合术/OLT 4/2/3/1/1/1 LIH发病时间(例) 医源性创伤后即刻 2 24 h内 4 24 h以上 18 CT/彩超/减影血管造影(例) 15/21/24 假性动脉瘤 15 肝动脉分支截断 3 造影剂外渗 5 动静脉-胆管瘘 3 动脉腔内手术(例) 动脉栓塞 23 支架移植物隔绝术 1 技术成功率(例) 止血成功 23 止血失败 1 并发症 4 注:PLB,经皮肝活检;PTCD,经皮肝胆管引流术;TIPS,经颈静脉肝内门体分流术;ERCP,内镜逆行胰胆管造影;PPPD,保留幽门的胰十二指肠切除术;OLT,原位肝移植。
-
[1] CURET P, BAUMER R, ROCHE A, et al. Hepatic hemobilia of traumatic or iatrogenic origin: Recent advances in diagnosis and therapy, review of the literature from 1976 to 1981[J]. World J Surg, 1984, 8( 1): 2- 8. DOI: 10.1007/BF01658356. [2] CZERNIAK A, THOMPSON JN, HEMINGWAY AP, et al. Hemobilia:A disease in evolution[J]. Arch Surg, 1988, 123( 6): 718- 721. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400300064010. [3] MUKUND A, RANA S, CHOUDHURY A, et al. Outcome of percutaneous transhepatic biliary interventions in the management of biliary enteric anastomotic strictures with hepatolithiasis[J]. Clin Radiol, 2023, 78( 1): e6- e12. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2022.08.125. [4] KIM KH, KIM TN. Etiology, clinical features, and endoscopic management of hemobilia: A retrospective analysis of 37 cases[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2012, 59( 4): 296- 302. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2012.59.4.296. [5] THAI BINH N, TRA MY TT, LAN OANH DT, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic endoscopic thulium laser vaporesection for management of severe and focal benign biliary strictures[J]. Clin Ter, 2023, 174( 4): 360- 364. DOI: 10.7417/CT.2023.2451. [6] LIU TT, HOU MC, LIN HC, et al. Life-threatening hemobilia caused by hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: A rare complication of chronic cholangitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2003, 9( 12): 2883- 2884. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2883. [7] NAVULURI R. Hemobilia[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2016, 33( 4): 324- 331. DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1592321. [8] BERRY R, HAN J, GIROTRA M, et al. Hemobilia: Perspective and role of the advanced endoscopist[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2018, 2018: 3670739. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3670739. [9] ZHORNITSKIY A, BERRY R, HAN JY, et al. Hemobilia: Historical overview, clinical update, and current practices[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39( 8): 1378- 1388. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14111. [10] CATHCART S, BIRK JW, TADROS M, et al. Hemobilia: An uncommon but notable cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2017, 51( 9): 796- 804. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000876. [11] YASUDA M, SATO H, KOYAMA Y, et al. Late-onset severe biliary bleeding after endoscopic pigtail plastic stent insertion[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23( 4): 735- 739. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.735. [12] PUNTEL G, PUPPINI G, PERANDINI S, et al. Diagnosis and management of iatrogenic hemobilia secondary to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedure[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12( 4): e7629. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.7629. [13] KURNIAWAN K, WIBAWA IDN, SOMAYANA G, et al. Massive hemobilia caused by rupture of gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm, a delayed complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2021, 15( 1): 331. DOI: 10.1186/s13256-021-02915-1. [14] ABIKO T, EBIHARA Y, TAKEUCHI M, et al. Hemobilia-a rare complication after laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J]. Surg Case Rep, 2020, 6( 1): 91. DOI: 10.1186/s40792-020-00837-6. [15] VACHHANI PG, COPELAN A, REMER EM, et al. Iatrogenic hepatopancreaticobiliary injuries: A review[J]. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2015, 32( 2): 182- 194. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1549377. [16] HU XW, LI T. Diagnosis and treatment of common biliary complications after orthotopic liver transplantation in adults[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2022, 13( 5): 569- 576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.05.004.胡鑫文, 李亭. 成人原位肝移植术后常见胆道并发症的诊疗[J]. 器官移植, 2022, 13( 5): 569- 576. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.05.004. [17] LEE YT, LIN H, CHEN KY, et al. Life-threatening hemobilia caused by hepatic pseudoaneurysm after T-tube choledochostomy: Report of a case[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2010, 10: 81. DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-10-81. [18] HU Y, GAO Q, ZHANG X, et al. Effect of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography combined with lithotomy and laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the treatment of bile duct stones[J]. J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2023, 39( 10): 1146- 1149. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.10.018.胡勇, 高琦, 张翔, 等. 经内镜逆行胰胆管造影联合取石术与腹腔镜胆囊切除术治疗胆管结石的效果[J]. 长春中医药大学学报, 2023, 39( 10): 1146- 1149. DOI: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2023.10.018. [19] VULTAGGIO F, MORÈRE PH, CONSTANTIN C, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding and obstructive jaundice: Think of hepatic artery aneurysm[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2016, 8( 6): 467- 471. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i6.467. [20] QUENCER KB, TADROS AS, MARASHI KB, et al. Bleeding after percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage: Incidence, causes and treatments[J]. J Clin Med, 2018, 7( 5): 94. DOI: 10.3390/jcm7050094. [21] BERRY R, HAN JY, KARDASHIAN AA, et al. Hemobilia: Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Liver Res, 2018, 2( 4): 200- 208. DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2018.09.007. [22] SINGH P, SCIBELLI N, GOSAL K, et al. Hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm presenting as gastrointestinal hemorrhage[J]. Cureus, 2021, 13( 3): e14190. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14190. [23] KHOT R, MORGAN MA, NAIR RT, et al. Radiologic findings of biliary complications post liver transplantation[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY), 2023, 48( 1): 166- 185. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-022-03714-y. [24] WEN F, DONG Y, LU ZM, et al. Iatrogenic hemobilia: Imaging features and management with transcatheter arterial embolization in 30 patients[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2016, 22( 4): 371- 377. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2016.15295. -



 PDF下载 ( 2026 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2026 KB)

 下载:
下载: