胆道结石与胆源性胰腺炎的关系
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241031
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:李玮佳、李振方、赵琦负责课题设计,资料分析,撰写论文;张倩、李聪、王凤娇参与收集数据,修改论文;赵琦负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
-
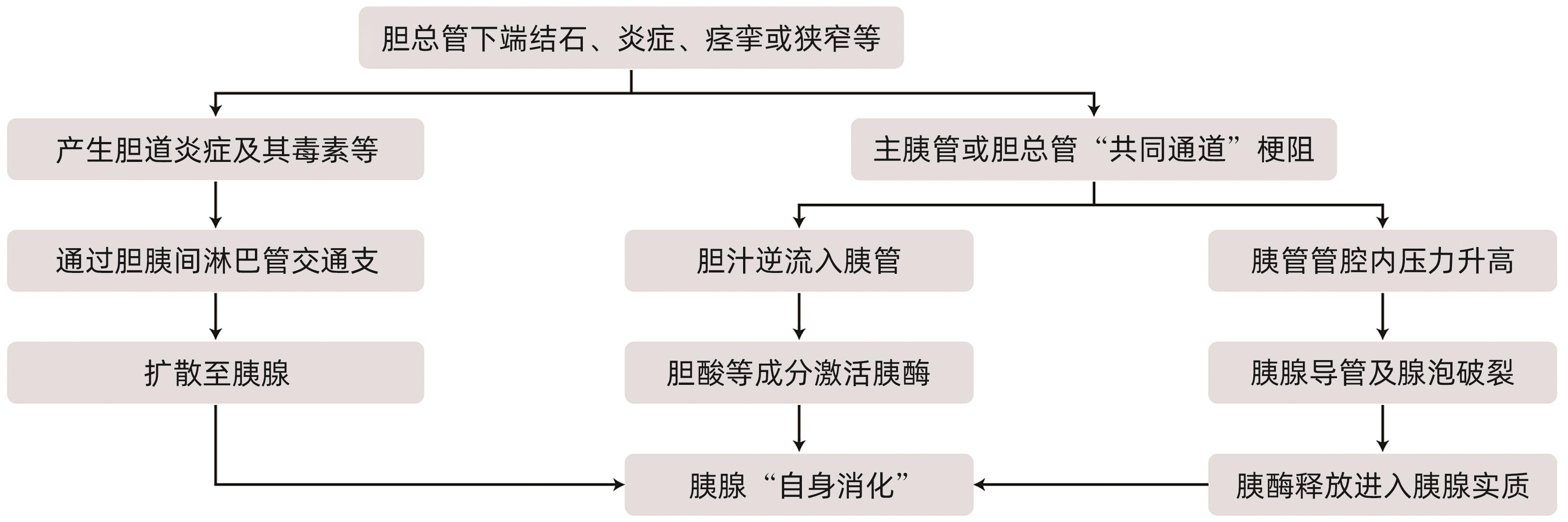
摘要: 急性胰腺炎是临床上最常见的急腹症之一,胆道疾病、酒精、胰管疾病、代谢障碍如高甘油三酯血症和高钙血症、过度进食、十二指肠降段疾病如十二指肠乳头旁憩室等是急性胰腺炎的常见病因。根据病因将急性胰腺炎分为胆源性胰腺炎、高脂血症性胰腺炎等。胆源性胰腺炎的致病因素很多,在全球范围内,胆道结石等胆系疾病仍是胆源性胰腺炎最主要的病因。各种病因导致的胆胰管排流不畅及压力异常、胆汁向胰管反流、胰液引流受阻、胰酶异常活化是导致胆源性胰腺炎发生的中心环节。胆道结石所在部位、结石大小、质地、数目、形状等与胆源性胰腺炎的发病率及严重程度一定的关系。Abstract: Acute pancreatitis is one of the most common acute abdominal diseases in clinical practice, and the common etiologies of acute pancreatitis include biliary diseases, alcohol, pancreatic duct diseases, metabolic disorders (hypertriglyceridemia and hypercalcemia), excessive eating, and diseases of the descending duodenum (periampullary duodenal diverticula). According to the etiology, acute pancreatitis is classified into biliary pancreatitis and hyperlipidemic pancreatitis, and although there are various pathogenic factors for biliary pancreatitis, biliary diseases including bile duct stones remain the most important etiology of biliary pancreatitis. Obstructed biliopancreatic duct drainage and abnormal pressure due to various causes, bile reflux into the pancreatic duct, obstruction of pancreatic juice drainage, and abnormal activation of pancreatic enzymes are the central links in the development of biliary pancreatitis. The location, size, texture, number and shape of bile duct stones are associated with the incidence rate and severity of biliary pancreatitis to a certain degree.
-
Key words:
- Pancreatitis /
- Abdomen, Acute /
- Gallstones
-
[1] LEPPÄNIEMI A, TOLONEN M, TARASCONI A, et al. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. World J Emerg Surg, 2019, 14: 27. DOI: 10.1186/s13017-019-0247-0. [2] RAMAI D, HEATON J, ABOMHYA A, et al. Frailty is independently associated with higher mortality and readmissions in patients with acute biliary pancreatitis: A nationwide inpatient study[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2023, 68( 6): 2196- 2203. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-023-07830-7. [3] KUNDUMADAM S, FOGEL EL, GROMSKI MA. Gallstone pancreatitis: General clinical approach and the role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography[J]. Korean J Intern Med, 2021, 36( 1): 25- 31. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2020.537. [4] LI JL, YUE P, ZHANG XZ, et al. Risk factors of acute biliopancreatic complications in patients of pregnancy combined with gallbladder stone and construction of prediction model[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 7): 899- 908. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20230608-00270.李建龙, 岳平, 张先卓, 等. 妊娠合并胆囊结石发生急性胆胰并发症的危险因素分析及预测模型构建[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22( 7): 899- 908. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20230608-00270. [5] TRAN QT, TRAN VH, SENDLER M, et al. Role of bile acids and bile salts in acute pancreatitis: From the experimental to clinical studies[J]. Pancreas, 2021, 50( 1): 3- 11. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001706. [6] YANG YM, XIE XH. Status and progress of the diagnosis and treatment of biliary pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2020, 40( 11): 1240- 1242, 1246. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.11.03.杨尹默, 谢学海. 胆源性胰腺炎诊治现状与进展[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40( 11): 1240- 1242, 1246. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.11.03. [7] SUGIMOTO M, SONNTAG DP, FLINT GS, et al. Biliary stenosis and gastric outlet obstruction: Late complications after acute pancreatitis with pancreatic duct disruption[J]. Pancreas, 2018, 47( 6): 772- 777. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001064. [8] ROSE M, LAPUEBLA A, LANDMAN D, et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of a novel antisense peptide nucleic acid compound against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii[J]. Microb Drug Resist, 2019, 25( 7): 961- 965. DOI: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0179. [9] ZHENG ZX, BI JT, CAI X, et al. The clinical significance of body mass index in the early evaluation of acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8( 12): e12003. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12003. [10] SUGIYAMA M, ATOMI Y. Risk factors for acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2004, 60( 2): 210- 212. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5107(04)01552-4. [11] COHEN ME. Gallstone size and risk for pancreatitis[J]. Arch Intern Med, 1998, 158( 5): 543- 544. DOI: 10.1001/archinte.158.5.543. [12] FRATANTONI ME, GIUFFRIDA P, MENNO JD, et al. Prevalence of persistent common bile duct stones in acute biliary pancreatitis remains stable within the first week of symptoms[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 25( 12): 3178- 3187. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-021-05068-0. [13] XIAO LN, GENG C, LI X, et al. Comparable safety of ERCP in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with common bile duct stones: A propensity-matched analysis[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2021, 56( 1): 111- 117. DOI: 10.1080/00365521.2020.1853222. [14] YOU QJ, ZOU XQ, ZHANG RH, et al. Morphological characteristics of gallstones and the relationship between plasma lipopolysaccharide level and acute biliary pancreatitis in patients with gallstones[J]. Prog Mod Biomed, 2019, 19( 16): 3098- 3101. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2019.16.018.游起军, 邹夏芹, 张仁虎, 等. 胆囊结石患者结石形态学特征及血浆脂多糖水平与急性胆源性胰腺炎的关系研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2019, 19( 16): 3098- 3101. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2019.16.018. [15] CHEN DW. Study on related risk factors of cholelithiasis complicated with acute biliary pancreatitis[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2022.陈大伟. 胆石症并发急性胆源性胰腺炎的相关危险因素研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2022. [16] COX DRA, FONG J, LIEW CH, et al. Emergency presentations of acute biliary pain: Changing patterns of management in a tertiary institute[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2018, 88( 12): 1337- 1342. DOI: 10.1111/ans.14898. [17] MAEKAWA T, FUKAYA R, TAKAMATSU S, et al. Possible involvement of Enterococcus infection in the pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis and cancer[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 506( 4): 962- 969. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.169. [18] CHATILA AT, BILAL M, GUTURU P. Evaluation and management of acute pancreatitis[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2019, 7( 9): 1006- 1020. DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i9.1006. [19] HOGAN WJ. Gallstone size and risk of pancreatitis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 1998, 47( 5): 427- 428. [20] KIM SB, KIM TN, CHUNG HH, et al. Small gallstone size and delayed cholecystectomy increase the risk of recurrent pancreatobiliary complications after resolved acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2017, 62( 3): 777- 783. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-016-4428-3. [21] KAMISAWA T, SUYAMA M, FUJITA N, et al. Pancreatobiliary reflux and the length of a common channel[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2010, 17( 6): 865- 870. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-010-0282-4. [22] BOXHOORN L, VOERMANS RP, BOUWENSE SA, et al. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396( 10252): 726- 734. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31310-6. [23] YANG K, YAO BM, ZENG N. Clinical features of acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Guangdong Med J, 2023, 44( 8): 981- 984. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.20225318.杨凯, 姚兵明, 曾宁. 急性胆源性胰腺炎的临床特征[J]. 广东医学, 2023, 44( 8): 981- 984. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.20225318. [24] WANG WZ. Discussion of the clinical relationship between gallstone type and gallstone pancreatitis[J]. Chin Community Dr, 2014, 30( 31): 23- 23, 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2014.31.12.王稳忠. 胆石类型与胆源性胰腺炎的临床关系探讨[J]. 中国社区医师, 2014, 30( 31): 23- 23, 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2014.31.12. [25] YE LP, ZHANG Y, MAO XL, et al. Association of common bile duct stone with acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Dig, 2009, 29( 12): 808- 810. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2009.12.005.叶丽萍, 张玉, 毛鑫礼, 等. 胆总管结石与胆源性胰腺炎的相关性研究[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2009, 29( 12): 808- 810. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2009.12.005. [26] WANG M, SHEN YZ, WANG LZ, et al. A study of the correlation between the calculous of bile duct and acute pancreatitis and its edoscopic treatment[J]. Chin J Clin Gastroenterol, 2006, 18( 6): 364- 366. DOI: 10.3870/j.issn.1005-541X.2006.06.015.王枚, 沈云志, 汪良芝, 等. 急性胰腺炎与胆管结石相关因素探讨及内镜治疗[J]. 临床消化病杂志, 2006, 18( 6): 364- 366. DOI: 10.3870/j.issn.1005-541X.2006.06.015. [27] SUN JM, YU H, LIU MZ, et al. The relationship between the morphology of gallstones and the pathogenesis of acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Pract Clin Med, 2015, 1( 1): 49- 50, 58.孙建明, 余华, 刘明忠, 等. 胆囊结石形态与急性胆源性胰腺炎发病的关系[J]. 实用临床医学, 2015, 1( 1): 49- 50, 58. [28] ZHANG P, YU CH. Clinical analysis of relationship between gallstone morphology and biliary pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2014, 30( 1): 46- 47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.01.015.张鹏, 于聪慧. 胆囊结石形态与胆源性胰腺炎关系的临床分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2014, 30( 1): 46- 47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2014.01.015. [29] ALBERT AR, VALENCIA R, SMERECK JA. Acute hepatitis B with pancreatitis and cholecystitis leading to acute liver failure and death[J]. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med, 2018, 2( 4): 304- 308. DOI: 10.5811/cpcem.2018.7.38344. [30] CHEN TH, WANG JJ. Niacin pretreatment attenuates ischemia and reperfusion of pancreas-induced acute pancreatitis and remote lung injury through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation and activation of SIRT1[J]. Transplant Proc, 2018, 50( 9): 2860- 2863. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.03.052. [31] LU YC, HUANG JS, XU HX, et al. Analysis of influencing factors for acute biliary pancreatitis in patients with cholecystolithiasis and construction of nomogram prediction model[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2023, 32( 8): 1199- 1207. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2023.08.008.陆颖超, 黄锦山, 徐红星, 等. 胆囊结石患者并发急性胆源性胰腺炎的影响因素分析及列线图预测模型构建[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2023, 32( 8): 1199- 1207. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2023.08.008. [32] ZHANG ZH, DING YX, WU YD, et al. A meta-analysis and systematic review of percutaneous catheter drainage in treating infected pancreatitis necrosis[J]. Medicine, 2018, 97( 47): e12999. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012999. [33] WANG XP, MENG XZ. Risk factors for gallstones complicated by acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 8): 1728- 1732. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.08.027.王宪鹏, 孟宪志. 胆囊结石并发急性胆源性胰腺炎的危险因素分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34( 8): 1728- 1732. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.08.027. [34] NIE YQ, XIE B, LI YY. Relationship between gallstone size and acute pancreatitis[J]. Guangdong Med J, 2003, 24( 4): 405- 407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2003.04.034.聂玉强, 谢飚, 李瑜元. 胆结石大小与急性胰腺炎的关系[J]. 广东医学, 2003, 24( 4): 405- 407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2003.04.034. [35] NEOPTOLEMOS JP, OYUNBIYI O, WILSON PG, et al. Etiology, pathogenesis, natural history and treatment of biliary acute pancreatitis[M]//BEGER HG, WARSHAW AL. Pancreas. Blackwell Science Ltd, 1998: 521- 547. [36] ACOSTA JM, RUBIO GALLI OM, ROSSI R, et al. Effect of duration of ampullary gallstone obstruction on severity of lesions of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 1997, 184( 5): 499- 505. [37] DOLAY K, HASBAHÇECI M, HATIPOĞLU E, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of biliary obstruction due to acute cholangitis and acute pancreatitis secondary to Fasciola hepatica infection[J]. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg, 2018, 24( 1): 71- 73. DOI: 10.5505/tjtes.2017.89490. [38] KAISER AM, SALUJA AK, STEER ML. Repetitive short-term obstructions of the common bile-pancreatic duct induce severe acute pancreatitis in the opossum[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 1999, 44( 8): 1653- 1661. DOI: 10.1023/a:1026687632370. [39] FENG BX, HUANG B, ZHAI CB, et al. Pancreatic duct occlusion plays an important role in inducing acute hemorrhagic necrotizing pancreatitis in dog[J]. Shanxi Med J, 1999( 4): 289- 290.冯变喜, 黄博, 翟春宝, 等. 胰管持续梗阻促进急性胰腺炎的发展[J]. 山西医药杂志, 1999( 4): 289- 290. [40] SHI CX, YU J, YANG XH, et al. Effects of pancreatic duct pressure on pancreatic blood flow, pancreatic enzyme release and pancreatic tissue in dogs[J]. Guizhou Med J, 1996( 3): 138- 139.石承先, 余舰, 杨新华, 等. 胰管压力对犬胰血流量、胰酶释放及胰组织的影响[J]. 贵州医药, 1996( 3): 138- 139. [41] FANG CF, SHI CX, JU YL. The correlation of pancreatic duct pressure with the pathologic type of acute biliary pancreatitis in cats[J]. Guizhou Med J, 2003, 27( 1): 37- 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2003.01.015.方传发, 石承先, 剧永乐. 猫胰管压力与急性胆源性胰腺炎病理类型的关系[J]. 贵州医药, 2003, 27( 1): 37- 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2003.01.015. [42] QIU ZJ, LI BH, HUA TF, et al. Effect of duration of pancreatic duct obstruction on the severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 1998, 4( 5): 332. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.1998.05.132.裘正军, 李宝华, 花天放, 等. 胰管梗阻持续时间对急性胰腺炎损伤严重程度的影响[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 1998, 4( 5): 332. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-8118.1998.05.132. -



 PDF下载 ( 996 KB)
PDF下载 ( 996 KB)

 下载:
下载:


