肠-脑轴神经免疫通信在肝性脑病发病机制中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241224
利益冲突声明:本文不存在任何利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:林镛、毛德文负责课题设计,拟定写作思路;李炯汾、李飞燕、杜沅沁和刘美燕参与资料分析;林镛负责撰写论文;林镛、王明刚、王娜负责修改论文;毛德文、龙富立指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Role of neuroimmune communication via the gut-brain axis in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy
-
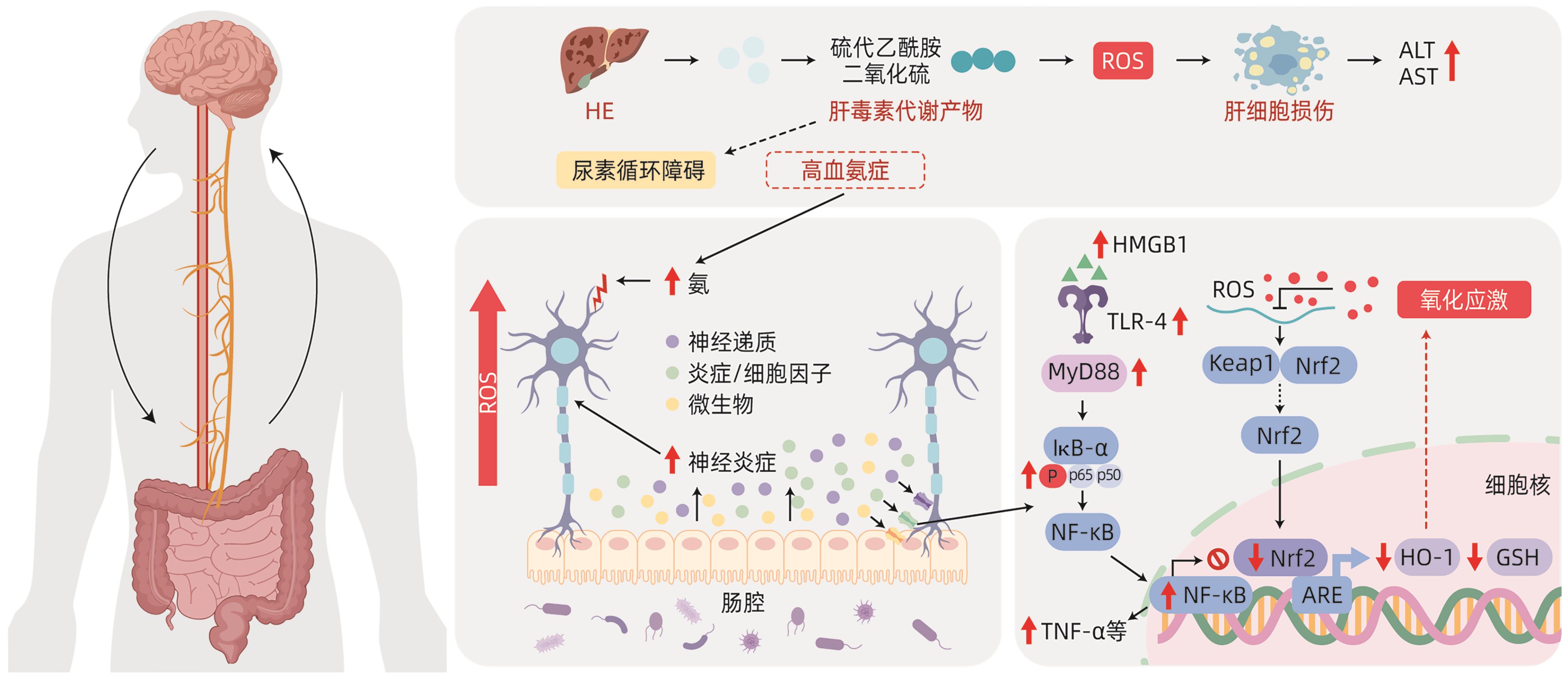
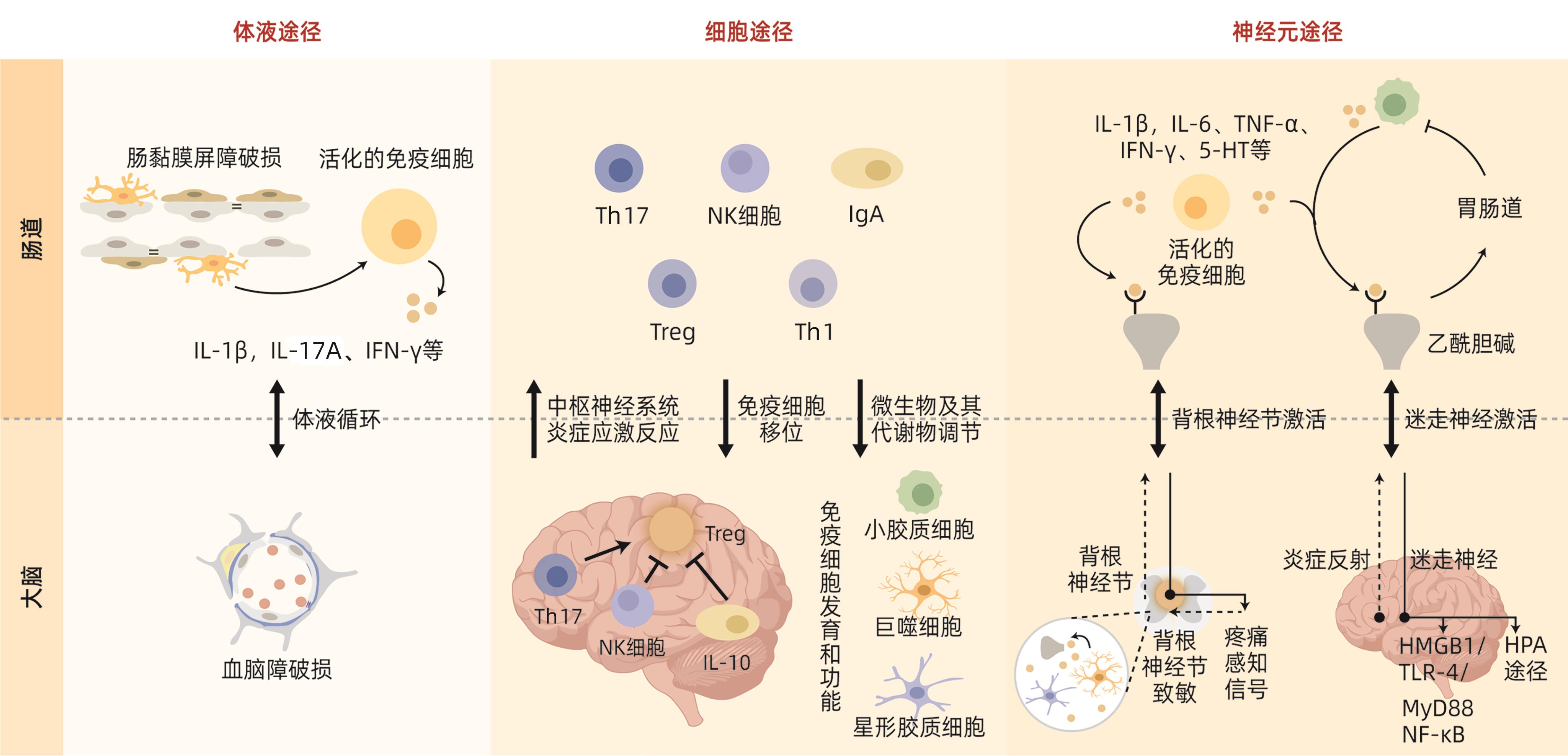
摘要: 肝性脑病(HE)是临床常见的严重肝病症候群,属内科危急重症之一。当前,在确诊显性HE的肝衰竭患者中,超过50%的存活时间不足1年。全面解析HE的复杂发病机制,形成具备循证医学证据的诊疗技术方案,对于缓解其造成临床上高医疗资源消耗、高医疗费用与高死亡率、高发病率叠加的严峻态势具有重要意义。最新研究发现,肠道与中枢神经系统可通过“肠-脑轴”进行双向、连续的交互反应和信号传递,并调节炎症信号、分子、细胞和器官功能状态,即神经免疫通信,与HE的主要病理特征高度一致。本文针对HE的神经免疫通信机制,总结了肠-脑轴炎症信号传导与神经递质调节的关系,以及其在HE神经免疫通信中的作用,为HE的临床诊疗和药物研发提供新思路。Abstract: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a common severe liver disease syndrome in clinical practice and is one of the critical and severe diseases in internal medicine, and more than half of liver failure patients diagnosed with overt HE have a survival time of less than 1 year. A comprehensive analysis of the complex pathogenesis of HE and the development of diagnosis and treatment regimens based on evidence-based medicine are of great importance for alleviating high medical resource consumption, high medical expenses, and high incidence and mortality rates in clinical practice. The latest studies have shown that the intestinal tract and the central nervous system can perform bidirectional continuous interaction and signal transmission and regulate the function of inflammation signals, molecules, cells, and organs, which is known as neuroimmune communication and is highly consistent with the main pathological features of HE. With a focus on the mechanism of neuroimmune communication in HE, this article reviews the association between inflammation signal transduction via the gut-brain axis and neurotransmitter regulation and its role in neuroimmune communication in HE, which provides new ideas for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of HE and the research and development of related drugs.
-
[1] RUDLER M, WEISS N, BOUZBIB C, et al. Diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2021, 25( 2): 393- 417. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2021.01.008. [2] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [3] ELSAID MI, RUSTGI VK. Epidemiology of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2020, 24( 2): 157- 174. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.01.001. [4] LIN Y, YAN GJ, FENG F, et al. Association between cholesterol and liver regeneration and its significance and potential value in clinical treatment of liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 3): 708- 713. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.044.林镛, 颜耿杰, 冯逢, 等. 胆固醇与肝再生关系及其在肝衰竭治疗中的意义和潜在价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 3): 708- 713. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.044. [5] DU YQ, WANG M, HUANG GC, et al. Therapeutic effect of retention enema with compound rhubarb decoction on a rat model of minimal hepatic encephalopathy based on bile acid metabolomics[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 10): 2348- 2357. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.10.012.杜沅沁, 王萌, 黄国初, 等. 基于胆汁酸代谢组学探讨复方大黄煎剂保留灌肠对轻微型肝性脑病大鼠模型的治疗作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2023, 39( 10): 2348- 2357. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.10.012. [6] European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 3): 807- 824. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.06.001. [7] PUN CK, HUANG HC, CHANG CC, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy: From novel pathogenesis mechanism to emerging treatments[J]. J Chin Med Assoc, 2023, 87( 3): 245- 251. DOI: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000001041. [8] RONALDSON PT, DAVIS TP. Regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity by microglia in health and disease: A therapeutic opportunity[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2020, 40( 1_suppl): S6- S24. DOI: 10.1177/0271678X20951995. [9] OCHOA-SANCHEZ R, TAMNANLOO F, ROSE CF. Hepatic encephalopathy: From metabolic to neurodegenerative[J]. Neurochem Res, 2021, 46( 10): 2612- 2625. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-021-03372-4. [10] COOPER AJ, PLUM F. Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia[J]. Physiol Rev, 1987, 67( 2): 440- 519. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.2.440. [11] AGIRMAN G, YU KB, HSIAO EY. Signaling inflammation across the gut-brain axis[J]. Science, 2021, 374( 6571): 1087- 1092. DOI: 10.1126/science.abi6087. [12] VIDAL-CEVALLOS P, CHÁVEZ-TAPIA NC, URIBE M. Current approaches to hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2022, 27( 6): 100757. DOI: 10.1016/j.aohep.2022.100757. [13] ORZEŁ-GAJOWIK K, MILEWSKI K, ZIELIŃSKA M. miRNA-ome plasma analysis unveils changes in blood-brain barrier integrity associated with acute liver failure in rats[J]. Fluids Barriers CNS, 2023, 20( 1): 92. DOI: 10.1186/s12987-023-00484-7. [14] SCOTT SA, FU JJ, CHANG PV. Microbial tryptophan metabolites regulate gut barrier function via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2020, 117( 32): 19376- 19387. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2000047117. [15] KHALIL HMA, ELIWA HA, EL-SHIEKH RA, et al. Ashwagandha(Withania somnifera) root extract attenuates hepatic and cognitive deficits in thioacetamide-induced rat model of hepatic encephalopathy via induction of Nrf2/HO-1 and mitigation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 277: 114141. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114141. [16] ALI SA, DATUSALIA AK. Protective effects of Tinospora cordifolia miers extract against hepatic and neurobehavioral deficits in thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats via modulating hyperammonemia and glial cell activation[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 323: 117700. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117700. [17] CRYAN JF, O’RIORDAN KJ, COWAN CSM, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis[J]. Physiol Rev, 2019, 99( 4): 1877- 2013. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00018.2018. [18] XU CL, LEE SK, ZHANG DC, et al. The gut microbiome regulates psychological-stress-induced inflammation[J]. Immunity, 2020, 53( 2): 417- 428. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.025. [19] LOUVEAU A, HERZ J, ALME MN, et al. CNS lymphatic drainage and neuroinflammation are regulated by meningeal lymphatic vasculature[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2018, 21( 10): 1380- 1391. DOI: 10.1038/s41593-018-0227-9. [20] JAMESON KG, OLSON CA, KAZMI SA, et al. Toward understanding microbiome-neuronal signaling[J]. Mol Cell, 2020, 78( 4): 577- 583. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.006. [21] JIA W, RAJANI C, KADDURAH-DAOUK R, et al. Expert insights: The potential role of the gut microbiome-bile acid-brain axis in the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease and hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Med Res Rev, 2020, 40( 4): 1496- 1507. DOI: 10.1002/med.21653. [22] LIU T, ZHANG LY, JOO D, et al. NF-κB signaling in inflammation[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2017, 2: 17023. DOI: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23. [23] ESSAM RM, SAADAWY MA, GAMAL M, et al. Lactoferrin averts neurological and behavioral impairments of thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats via modulating HGMB1/TLR-4/MyD88/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2023, 236: 109575. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109575. [24] KIGERL KA, LAI WM, WALLACE LM, et al. High mobility group box-1(HMGB1) is increased in injured mouse spinal cord and can elicit neurotoxic inflammation[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2018, 72: 22- 33. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.11.018. [25] YOU XH, WANG LX, FENG DC. Relationship of the intestinal flora and irritable bowel syndrome sub-typing with the functional changes in the neuroendocrine axis[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2022, 21( 15): 1667- 1670. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.15.027.游先辉, 王利霞, 冯大超. 肠道菌群和肠易激综合征分型与神经内分泌轴功能变化的关系研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21( 15): 1667- 1670. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.15.027. [26] PENNY HA, DOMINGUES RG, KRAUSS MZ, et al. Rhythmicity of intestinal IgA responses confers oscillatory commensal microbiota mutualism[J]. Sci Immunol, 2022, 7( 75): eabk2541. DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abk2541. [27] ROJAS OL, PRÖBSTEL AK, PORFILIO EA, et al. Recirculating intestinal IgA-producing cells regulate neuroinflammation via IL-10[J]. Cell, 2019, 176( 3): 610- 624. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.035. [28] BONAZ B, BAZIN T, PELLISSIER S. The vagus nerve at the interface of the microbiota-gut-brain axis[J]. Front Neurosci, 2018, 12: 49. DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00049. [29] BLUTHÉ RM, MICHAUD B, KELLEY KW, et al. Vagotomy blocks behavioural effects of interleukin-1 injected via the intraperitoneal route but not via other systemic routes[J]. Neuroreport, 1996, 7( 15-17): 2823- 2827. DOI: 10.1097/00001756-199611040-00083. [30] MCVEY NEUFELD KA, BIENENSTOCK J, BHARWANI A, et al. Oral selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors activate vagus nerve dependent gut-brain signalling[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9( 1): 14290. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-50807-8. [31] MORAIS LH, SCHREIBER HL 4th. MAZMANIAN SK The gut microbiotabrain axis in behaviour and brain disorders[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2021, 19( 4): 241- 255. DOI: 10.1038/s41579-020-00460-0. [32] MARTÍNEZ-LOZADA Z, ORTEGA A. Glutamatergic transmission: A matter of three[J]. Neural Plast, 2015, 2015: 787396. DOI: 10.1155/2015/787396. [33] CABRERA-PASTOR A, LLANSOLA M, MONTOLIU C, et al. Peripheral inflammation induces neuroinflammation that alters neurotransmission and cognitive and motor function in hepatic encephalopathy: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications[J]. Acta Physiol(Oxf), 2019, 226( 2): e13270. DOI: 10.1111/apha.13270. [34] KOSENKOV AM, GAIDIN SG, SERGEEV AI, et al. Fast changes of NMDA and AMPA receptor activity under acute hyperammonemia in vitro[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2018, 686: 80- 86. DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.08.054. [35] CAULI O, GONZÁLEZ-USANO A, CABRERA-PASTOR A, et al. Blocking NMDA receptors delays death in rats with acute liver failure by dual protective mechanisms in kidney and brain[J]. NeuroMolecular Med, 2014, 16( 2): 360- 375. DOI: 10.1007/s12017-013-8283-5. [36] KULLMANN DM, RUIZ A, RUSAKOV DM, et al. Presynaptic, extrasynaptic and axonal GABAA receptors in the CNS: Where and why?[J]. Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 2005, 87( 1): 33- 46. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2004.06.003. [37] FRIED DE, WATSON RE, ROBSON SC, et al. Ammonia modifies enteric neuromuscular transmission through glial γ-aminobutyric acid signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2017, 313( 6): G570- G580. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00154.2017. [38] MA FH, YANG L, SUN ZR, et al. Neurotransmitter-derived lipidoids(NT-lipidoids) for enhanced brain delivery through intravenous injection[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6( 30): eabb4429. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb4429. [39] TERSTAPPEN GC, MEYER AH, BELL RD, et al. Strategies for delivering therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2021, 20( 5): 362- 383. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-021-00139-y. -



 PDF下载 ( 1541 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1541 KB)

 下载:
下载: