肝细胞癌仑伐替尼耐药的分子机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH241225
Molecular mechanism of lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
-
摘要: 肝细胞癌是肝脏最常见的恶性肿瘤,给中国乃至全球带来了严重的卫生负担。然而,大部分肝细胞癌患者就诊时已处于晚期阶段,手术机会较少,治疗选择有限。近年来,分子靶向治疗的进展为晚期肝细胞癌患者提供了新的希望。其中,仑伐替尼是美国食品药品监督管理局继索拉非尼之后批准的第二个用于晚期肝细胞癌治疗的一线药物,因其强大的抗肿瘤特性获得广泛关注。然而,仑伐替尼的疗效受到其耐药性的严重限制。本文主要针对仑伐替尼在肝细胞癌中耐药的分子机制研究进展进行综述,讨论可能改善仑伐替尼耐药的方法,以期能提高其疗效。Abstract: Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common malignancy of the liver and poses serious health burdens on China and the whole world. However, most patients with hepatocellular carcinoma are already in the advanced stage at the time of diagnosis, with fewer opportunities for surgery and limited treatment options. In recent years, the advances in molecular targeted therapies have brought new hope for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Among these therapies, lenvatinib is the second first-line drug after sorafenib approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, and it has attracted widespread attention for its powerful anti-tumor properties. However, the efficacy of lenvatinib is severely limited by its drug resistance. This article reviews the research advances in the molecular mechanisms of lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma and discusses possible ways to improve the efficacy of lenvatinib, so as to improve its efficacy.
-
Key words:
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular /
- Lenvatinib /
- Drug Resistance, Neoplasm
-
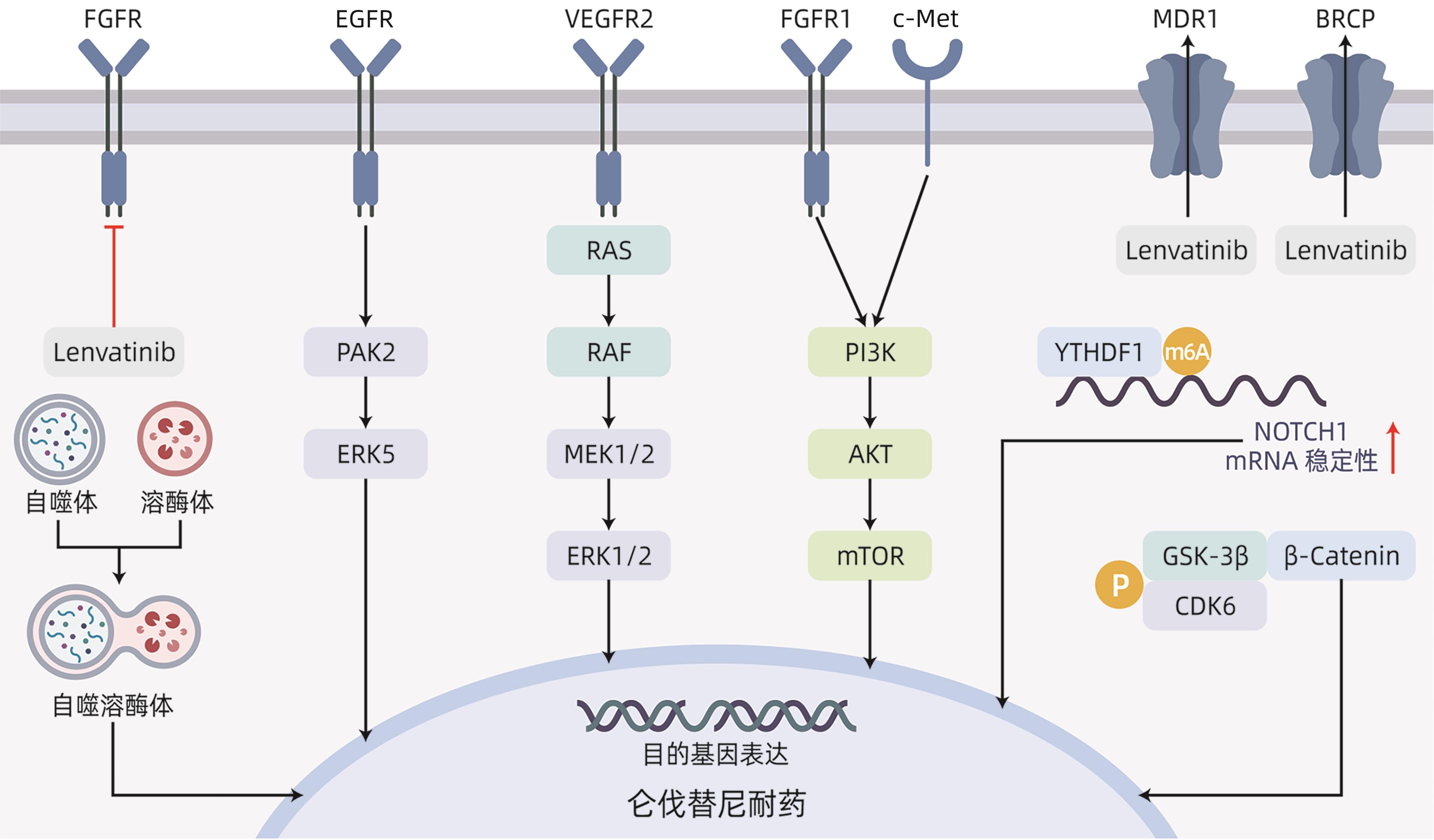
表 1 仑伐替尼耐药机制
Table 1. Lenvatinib resistance mechanism
耐药通路 耐药靶点 耐药模型细胞系 具体耐药机制 逆转耐药策略 EGFR EGFR SNU449 EGFR-PAK2-ERK1/2;
EGFR-PAK2-ERK5[6]
联用吉非替尼;
联用厄洛替尼
VEGFR2 VEGFR2 Huh7;
HepG2
VEGFR2-RAS-MEK-ERK[10] FGFR FGFR1 Hep3B;
HepG2
FGFR1-AKT-mTOR;
FGFR1-ERK[12]
氧化槐果碱 MDR1/BCRP
转运体
MDR1/BCRP
转运体
Huh7 促进仑伐替尼外排[16] 联用依克立达 自噬 LAPTM5 Huh7;HCC-LM3;
SNU449
LAPTM5-自噬体-溶酶体融合-
自噬溶酶体形成-耐药[20]
联用羟氯喹 Wnt/β-catenin
信号通路
IRF2;FZD10;CDK6 HepG2;Huh7;SNU398;Hep3B;PLC/PRF/5 IRF2-β-catenin-抑制凋亡[25];
FZD10-β-catenin-c-Jun-MEK-ERK[26];
CDK6-GSK3β-Wnt/β-catenin[27]
联用帕博西尼 Notch
信号通路
YTHDF1;TM4SF1 Huh7;MHCC97H;LM3;Hep3B;类器官 YTHDF1-m6A-NOTCH1[30];
TM4SF1-MYH9-NOTCH[32]
联用DAPT MAPK/ERK
信号通路
DUSP4;NF1 Huh7;HepG2;
PLC/PRF/5
DUSP4缺陷-MAPK/ERK[34];
NF1缺失-MAPK/ERK[36]
联用司美替尼;
联用曲美替尼
c-Met miR-128-3p SMMC-7721;
MHCC97-L;Huh7
miR-128-3p-c-Met-EMT[39] 联用c-MET抑制剂PHA-665752 铁死亡 Nrf2 Huh7;Hep3B Nrf2-脂质ROS低水平-抑制铁死亡[41] ncRNA lncRNA XIST;
lncRNA AC026401.3;lncRNA MT1JP;circMED27
HepG2;MHCC97-L;
SMMC-7721;Huh7;
PLC/PRF/5;HCCLM3
lncRNA XIST-EZH2-NOD2-ERK[42];
lncRNA AC026401.3-OCT1-E2F2[43];
lncRNA MT1JP-miR-24-3p-BCL2L2[44];
circRNA circMED27-miR-655-3p-USP28[45];
-
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. [2] REHMAN O, JAFERI U, PADDA I, et al. Overview of lenvatinib as a targeted therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2021, 7( 3): 249- 257. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2021.109312. [3] KUDO M, FINN RS, QIN SK, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391( 10126): 1163- 1173. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1. [4] MATSUKI M, HOSHI T, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. Lenvatinib inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fibroblast growth factor signaling pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7( 6): 2641- 2653. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1517. [5] OGASAWARA S, MIHARA Y, KONDO R, et al. Antiproliferative effect of lenvatinib on human liver cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39( 11): 5973- 5982. DOI: 10.21873/anticanres.13802. [6] JIN HJ, SHI YP, LV YY, et al. EGFR activation limits the response of liver cancer to lenvatinib[J]. Nature, 2021, 595( 7869): 730- 734. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03741-7. [7] HE XP, HIKIBA Y, SUZUKI Y, et al. EGFR inhibition reverses resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12( 1): 8007. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12076-w. [8] WANG LN, YANG QX, ZHOU QY, et al. METTL3-m6A-EGFR-axis drives lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2023, 559: 216122. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216122. [9] HUANG ML, LONG JT, YAO ZJ, et al. METTL1-mediated m7G tRNA modification promotes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83( 1): 89- 102. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0963. [10] ZHAO ZW, ZHANG DK, WU FZ, et al. Sophoridine suppresses lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma growth by inhibiting RAS/MEK/ERK axis via decreasing VEGFR2 expression[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25( 1): 549- 560. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16108. [11] BYRON SA, CHEN HB, WORTMANN A, et al. The N550K/H mutations in FGFR2 confer differential resistance to PD173074, dovitinib, and ponatinib ATP-competitive inhibitors[J]. Neoplasia, 2013, 15( 8): 975- 988. DOI: 10.1593/neo.121106. [12] ZHAO ZW, SONG JJ, ZHANG DK, et al. Oxysophocarpine suppresses FGFR1-overexpressed hepatocellular carcinoma growth and sensitizes the therapeutic effect of lenvatinib[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 264: 118642. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118642. [13] WANG JQ, WU ZX, YANG YQ, et al. ATP-binding cassette(ABC) transporters in cancer: A review of recent updates[J]. J Evid Based Med, 2021, 14( 3): 232- 256. DOI: 10.1111/jebm.12434. [14] SHUMAKER RC, ALURI J, FAN J, et al. Effect of rifampicin on the pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib in healthy adults[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2014, 34( 9): 651- 659. DOI: 10.1007/s40261-014-0217-y. [15] SHUMAKER R, ALURI J, FAN J, et al. Effects of ketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib(E7080) in healthy participants[J]. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev, 2015, 4( 2): 155- 160. DOI: 10.1002/cpdd.140. [16] SUN DW, LIU J, WANG YF, et al. Co-administration of MDR1 and BCRP or EGFR/PI3K inhibitors overcomes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 944537. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.944537. [17] ONORATI AV, DYCZYNSKI M, OJHA R, et al. Targeting autophagy in cancer[J]. Cancer, 2018, 124( 16): 3307- 3318. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.31335. [18] HU FQ, SONG D, YAN YM, et al. IL-6 regulates autophagy and chemotherapy resistance by promoting BECN1 phosphorylation[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12( 1): 3651. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23923-1. [19] XU WP, LIU JP, FENG JF, et al. MiR-541 potentiates the response of human hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib treatment by inhibiting autophagy[J]. Gut, 2020, 69( 7): 1309- 1321. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318830. [20] PAN JM, ZHANG M, DONG LQ, et al. Genome-Scale CRISPR screen identifies LAPTM5 driving lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Autophagy, 2023, 19( 4): 1184- 1198. DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2117893. [21] ZHANG YX, ZHANG YJ, TAO HS, et al. Targeting LINC01607 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to lenvatinib via suppressing mitophagy[J]. Cancer Lett, 2023, 576: 216405. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216405. [22] FERNÁNDEZ-PALANCA P, PAYO-SERAFÍN T, SAN-MIGUEL B, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma cells loss lenvatinib efficacy in vitro through autophagy and hypoxia response-derived neuropilin-1 degradation[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2023, 44( 5): 1066- 1082. DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-01021-2. [23] WANG BJ, TIAN T, KALLAND KH, et al. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling for cancer immunotherapy[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 39( 7): 648- 658. DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.008. [24] RUSSELL JO, MONGA SP. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in liver development, homeostasis, and pathobiology[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2018, 13: 351- 378. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-020117-044010. [25] GUO YR, XU J, DU Q, et al. IRF2 regulates cellular survival and Lenvatinib-sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) through regulating β-catenin[J]. Transl Oncol, 2021, 14( 6): 101059. DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101059. [26] WANG JH, YU HM, DONG W, et al. N6-methyladenosine-mediated up-regulation of FZD10 regulates liver cancer stem cells’ properties and lenvatinib resistance through WNT/β-catenin and hippo signaling pathways[J]. Gastroenterology, 2023, 164( 6): 990- 1005. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.01.041. [27] LEUNG CON, YANG Y, LEUNG RWH, et al. Broad-spectrum kinome profiling identifies CDK6 upregulation as a driver of lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14( 1): 6699. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42360-w. [28] VENKATESH V, NATARAJ R, THANGARAJ GS, et al. Targeting Notch signalling pathway of cancer stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Investig, 2018, 5: 5. DOI: 10.21037/sci.2018.02.02. [29] TAKEBE N, MIELE L, HARRIS PJ, et al. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2015, 12( 8): 445- 464. DOI: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.61. [30] ZHANG XY, SU TH, WU YF, et al. N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF1 promotes stemness and therapeutic resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing NOTCH1 expression[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84( 6): 827- 840. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1916. [31] FENG WQ, ZHANG HX, YU Q, et al. Study on the mechanism of Notch pathway mediates the role of lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma based on organoids[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2024. DOI: 10.2174/0115665240268201231213095302.[ Online ahead of print] [32] YANG SB, ZHOU ZH, LEI J, et al. TM4SF1 upregulates MYH9 to activate the NOTCH pathway to promote cancer stemness and lenvatinib resistance in HCC[J]. Biol Direct, 2023, 18( 1): 18. DOI: 10.1186/s13062-023-00376-8. [33] MOON H, RO SW. MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13( 12): 3026. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13123026. [34] HUANG SZ, MA ZY, ZHOU Q, et al. Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screening identified that DUSP4 deficiency induces lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18( 11): 4357- 4371. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.69969. [35] CHEN HF, CHUANG HC, TAN TH. Regulation of dual-specificity phosphatase(DUSP) ubiquitination and protein stability[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20( 11): 2668. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20112668. [36] LU YG, SHEN HM, HUANG WJ, et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in hepatocellular carcinoma with lenvatinib resistance[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2021, 7( 1): 359. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00747-y. [37] MOOSAVI F, GIOVANNETTI E, SASO L, et al. HGF/MET pathway aberrations as diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers in human cancers[J]. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 2019, 56( 8): 533- 566. DOI: 10.1080/10408363.2019.1653821. [38] FU RD, JIANG ST, LI JY, et al. Activation of the HGF/c-MET axis promotes lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells with high c-MET expression[J]. Med Oncol, 2020, 37( 4): 24. DOI: 10.1007/s12032-020-01350-4. [39] XU X, JIANG WJ, HAN P, et al. MicroRNA-128-3p mediates lenvatinib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating c-met[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2022, 9: 113- 126. DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S349369. [40] JIANG XJ, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22( 4): 266- 282. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8. [41] ISEDA N, ITOH S, TOSHIDA K, et al. Ferroptosis is induced by lenvatinib through fibroblast growth factor receptor-4 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Sci, 2022, 113( 7): 2272- 2287. DOI: 10.1111/cas.15378. [42] DUAN AQ, LI H, YU WL, et al. Long noncoding RNA XIST promotes resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via epigenetic inhibition of NOD2[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 4537343. DOI: 10.1155/2022/4537343. [43] WANG Y, TAN K, HU W, et al. LncRNA AC026401.3 interacts with OCT1 to intensify sorafenib and lenvatinib resistance by activating E2F2 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2022, 420( 1): 113335. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113335. [44] YU T, YU JJ, LU L, et al. MT1JP-mediated miR-24-3p/BCL2L2 axis promotes Lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting apoptosis[J]. Cell Oncol, 2021, 44( 4): 821- 834. DOI: 10.1007/s13402-021-00605-0. [45] ZHANG PF, SUN HX, WEN PH, et al. circRNA circMED27 acts as a prognostic factor and mediator to promote lenvatinib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2022, 27: 293- 303. DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.12.001. -



 PDF下载 ( 1034 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1034 KB)

 下载:
下载:


