嗜酸性粒细胞在不同肝脏疾病中的作用
DOI: 10.12449/JCH250735
-
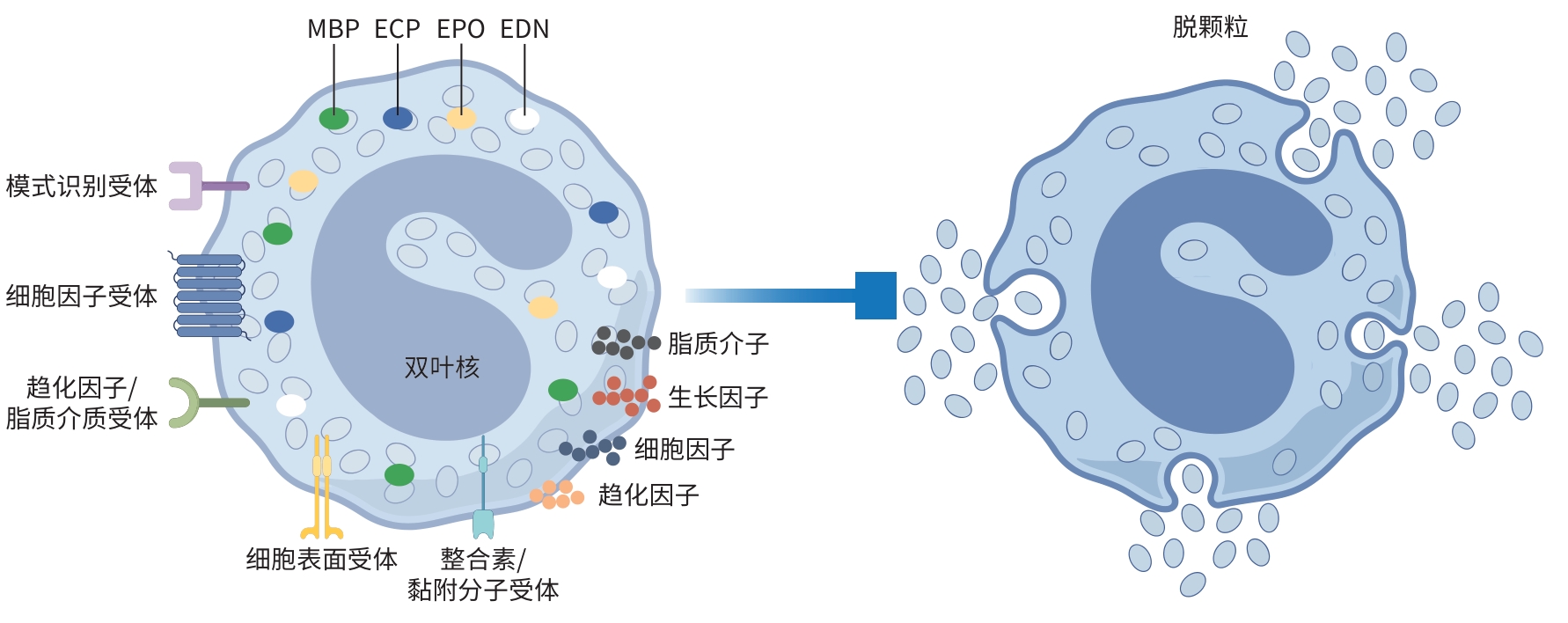
摘要: 肝脏疾病在全球范围内具有较高的患病率,且长期临床预后较差,已成为全球疾病负担和死亡的主要原因之一,对公共卫生构成了严峻挑战。嗜酸性粒细胞(Eos)是一类在进化上高度保守的多效性免疫细胞,在过敏性疾病中发挥关键的效应功能。近年来,越来越多的证据表明,Eos在肝脏疾病的发病机制中扮演重要角色,其在不同的肝脏疾病中表现出保护性或有害性作用,已成为该领域的研究热点。本文旨在阐述Eos在不同肝脏疾病中的作用及其潜在机制,为深入探究肝脏疾病发病机制提供新的视角,同时为开发针对Eos的治疗策略奠定基础。Abstract: Liver diseases have a high prevalence rate worldwide with relatively poor long-term clinical outcomes and have become one of the leading causes of disease burden and death around the world, which poses significant challenges to public health. Eosinophils (Eos) are a class of highly conserved multifunctional immune cells that play critical effector roles in allergic diseases. In recent years, an increasing amount of evidence has shown that Eos plays an important role in the pathogenesis of liver diseases, exerting a protective or harmful effect in different liver diseases, which has become a research hotspot in this field. This article elaborates on the role and potential mechanism of action of Eos in liver diseases, in order to provide a new perspective for in-depth research on the pathogenesis of liver diseases and lay the foundation for developing therapeutic strategies targeting Eos.
-
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- Granulocytes /
- Oxyphil Cells
-
表 1 Eos在不同肝脏疾病中的作用及机制
Table 1. Role and mechanism of EOS in different liver diseases
肝脏
疾病动物模型/
研究对象作用机制 效应 参考
文献DILI 氟烷模型 CCL11和CCL24介导 Eos肝脏浸润 促炎 [20] DILI APAP模型 IL-33通过激活Eos分泌IL-4,刺激巨噬细胞产生CCL24,促进更多Eos向肝脏募集 抗炎 [21] DILI APAP模型 Eos通过p38MAPK/COX/NF-κB信号轴诱导IL-4/IL-13的产生 抗炎 [22] HIRI 小鼠模型 Eos通过分泌IL-4,经IL-4受体α信号传导,激活肝脏巨噬细胞产生肝素结合性表皮生长因子 促修复 [23] HIRI 小鼠模型 IL-33通过ST2受体刺激Eos产生IL-13,抑制中性粒细胞浸润 抗炎 [24] HIRI 小鼠模型 ILC2通过促进IL-13依赖的抗炎巨噬细胞诱导和IL-5依赖的嗜酸性粒细胞升高 抗炎 [25] AILD ConA模型 IL-15减少了NKT衍生的IL-4、IL-5和TNF-α的产生,导致Eos的浸润减少 促炎 [26] AILD ConA模型 辅助性T1和辅助性T2细胞因子产生减少以及Eos积累减少有关 促炎 [27] HCV 临床患者样本 Eos浸润与肝纤维化进展相关(机制未明确) 促纤维化 [28] HCC 临床/动物模型 Eos通过活性氧、颗粒蛋白、TNF-α和NKG 2D介导的机制杀伤肿瘤细胞 抗肿瘤 [29] 注:DILI,药物性肝损伤;CCL,C-C基序趋化因子配体;APAP,对乙酰氨基酚;HIRI,肝缺血再灌注损伤;ILC2,2型先天淋巴细胞;AILD,自身免疫性肝病;NKT,自然杀伤T细胞;Con A,刀豆球蛋白A;TNF-α,肿瘤坏死因子-α;HCC,肝细胞癌。
-
[1] GRIFFIN C, AGBIM U, RAMANI A, et al. Underestimation of cirrhosis-related mortality in the medicare eligible population, 1999-2018[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21( 1): 223- 225. e 3. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.10.036. [2] DEVARBHAVI H, ASRANI SK, ARAB JP, et al. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 79( 2): 516- 537. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.03.017. [3] WECHSLER ME, MUNITZ A, ACKERMAN SJ, et al. Eosinophils in health and disease: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2021, 96( 10): 2694- 2707. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.04.025. [4] XIE LX, ZHANG HJ, XU L. The role of eosinophils in liver disease[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2025, 19( 2): 101413. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.101413. [5] QIAN YH, ZHAO J, WU HL, et al. Innate immune regulation in inflammation resolution and liver regeneration in drug-induced liver injury[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2025, 99( 1): 115- 126. DOI: 10.1007/s00204-024-03886-0. [6] NI HM, LOPEZ-PASCUAL A. Eosinophils: A novel therapeutic target to promote liver regeneration in acute liver injury?[J]. Gut, 2024, 73( 9): 1409- 1411. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332692. [7] DOROSZ A, GROSICKI M, DYBAS J, et al. Eosinophils and neutrophils-molecular differences revealed by spontaneous Raman, CARS and fluorescence microscopy[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 9): 2041. DOI: 10.3390/cells9092041. [8] AOKI A, HIRAHARA K, KIUCHI M, et al. Eosinophils: Cells known for over 140 years with broad and new functions[J]. Allergol Int, 2021, 70( 1): 3- 8. DOI: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.09.002. [9] KLION AD, ACKERMAN SJ, BOCHNER BS. Contributions of eosinophils to human health and disease[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2020, 15: 179- 209. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032756. [10] RODRIGO-MUÑOZ JM, GIL-MARTÍNEZ M, SASTRE B, et al. Emerging evidence for pleiotropism of eosinophils[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22( 13): 7075. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22137075. [11] GRISARU-TAL S, ITAN M, KLION AD, et al. A new dawn for eosinophils in the tumour microenvironment[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20( 10): 594- 607. DOI: 10.1038/s41568-020-0283-9. [12] VALENT P, DEGENFELD-SCHONBURG L, SADOVNIK I, et al. Eosinophils and eosinophil-associated disorders: Immunological, clinical, and molecular complexity[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2021, 43( 3): 423- 438. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-021-00863-y. [13] JACOBSEN EA, JACKSON DJ, HEFFLER E, et al. Eosinophil knockout humans: Uncovering the role of eosinophils through eosinophil-directed biological therapies[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2021, 39: 719- 757. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-093019-125918. [14] SIDDIQUI S, BACHERT C, BJERMER L, et al. Eosinophils and tissue remodeling: Relevance to airway disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2023, 152( 4): 841- 857. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.06.005. [15] COAKLEY G, WANG H, HARRIS NL. Intestinal eosinophils: Multifaceted roles in tissue homeostasis and disease[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2021, 43( 3): 307- 317. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-021-00851-2. [16] XU JY, XIONG YY, TANG RJ, et al. Interleukin-5-induced eosinophil population improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2022, 118( 9): 2165- 2178. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvab237. [17] LIU J, YANG CZ, LIU TX, et al. Eosinophils improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11( 1): 6396. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19297-5. [18] LOPEZ-PEREZ D, PRADOS-LOPEZ B, GALVEZ J, et al. Eosinophils in colorectal cancer: Emerging insights into anti-tumoral mechanisms and clinical implications[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25( 11): 6098. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25116098. [19] SHAH K, IGNACIO A, MCCOY KD, et al. The emerging roles of eosinophils in mucosal homeostasis[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2020, 13( 4): 574- 583. DOI: 10.1038/s41385-020-0281-y. [20] PROCTOR WR, CHAKRABORTY M, CHEA LS, et al. Eosinophils mediate the pathogenesis of halothane-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57( 5): 2026- 2036. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26196. [21] XU L, YANG Y, WEN YK, et al. Hepatic recruitment of eosinophils and their protective function during acute liver injury[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 2): 344- 352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.02.024. [22] XU L, YANG Y, JIANG JL, et al. Eosinophils protect against acetaminophen-induced liver injury through cyclooxygenase-mediated IL-4/IL-13 production[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77( 2): 456- 465. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32609. [23] YANG Y, XU L, ATKINS C, et al. Novel IL-4/HB-EGF-dependent crosstalk between eosinophils and macrophages controls liver regeneration after ischaemia and reperfusion injury[J]. Gut, 2024, 73( 9): 1543- 1553. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2024-332033. [24] WANG YC, YANG Y, WANG M, et al. Eosinophils attenuate hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice through ST2-dependent IL-13 production[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2021, 13( 579): eabb6576. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb6576. [25] CAO Q, WANG RF, NIU ZG, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells are protective against hepatic ischaemia/reperfusion injury[J]. JHEP Rep, 2023, 5( 10): 100837. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100837. [26] LI BF, SUN R, WEI HM, et al. Interleukin-15 prevents concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice via NKT cell-dependent mechanism[J]. Hepatology, 2006, 43( 6): 1211- 1219. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21174. [27] KREMER M, PERRY AW, MILTON RJ, et al. Pivotal role of Smad3 in a mouse model of T cell-mediated hepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47( 1): 113- 126. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21956. [28] TARANTINO G, CABIBI D, CAMMÀ C, et al. Liver eosinophilic infiltrate is a significant finding in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2008, 15( 7): 523- 530. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2008.00976.x. [29] KATAOKA S, KONISHI Y, NISHIO Y, et al. Antitumor activity of eosinophils activated by IL-5 and eotaxin against hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2004, 23( 9): 549- 560. DOI: 10.1089/dna.2004.23.549. [30] Committee on DILI Prevention and Management, Chinese Medical Biotechnology Association; Study Group of Drug⁃Induced Liver Disease, Chinese Medical Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Chinese guideline for diagnosis and management of drug⁃induced liver injury(2023 Version)[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol, 2023, 28( 7): 397- 431. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230419-00176.中国医药生物技术协会药物性肝损伤防治技术专业委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会药物性肝病学组. 中国药物性肝损伤诊治指南(2023年版)[J]. 胃肠病学, 2023, 28( 7): 397- 431. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230419-00176. [31] LI ZL, CHEN LY, CHU HK, et al. Estrogen alleviates hepatocyte necroptosis depending on GPER in hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. J Physiol Biochem, 2022, 78( 1): 125- 137. DOI: 10.1007/s13105-021-00846-5. [32] FELD JJ, HEATHCOTE EJ. Epidemiology of autoimmune liver disease[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2003, 18( 10): 1118- 1128. DOI: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.2003.03165.x. [33] LOUIS H, LE MOINE A, FLAMAND V, et al. Critical role of interleukin 5 and eosinophils in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2002, 122( 7): 2001- 2010. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2002.33620. [34] MARTINELLO M, SOLOMON SS, TERRAULT NA, et al. Hepatitis C[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402( 10407): 1085- 1096. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(23)01320-x. [35] LI F, LI B, ZHU QY. Research progress on the epidemiological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatitis C in China[J]. Int J Virol, 2023, 30( 6): 509- 511. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2023.06.014.黎锋, 李博, 朱秋映. 中国丙肝流行特征与诊断研究进展[J]. 国际病毒学杂志, 2023, 30( 6): 509- 511. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4092.2023.06.014. [36] BRAY F, LAVERSANNE M, SUNG H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74( 3): 229- 263. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21834. [37] XIA CF, DONG XS, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2022, 135( 5): 584- 590. DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002108. [38] WANG QH, ZHANG ZX, ZHOU H, et al. Eosinophil-associated genes are potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis[J]. J Cancer, 2024, 15( 17): 5605- 5621. DOI: 10.7150/jca.95138. [39] TOSHIDA K, ITOH S, YOSHIYA S, et al. Pretreatment eosinophil count predicts response to atezolizumab plus bevacizumab therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024, 39( 3): 576- 586. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.16441. -



 PDF下载 ( 864 KB)
PDF下载 ( 864 KB)

 下载:
下载:


