Clinical management guidelines for acute fatty liver of pregnancy in China (2022)
-
摘要: 妊娠期急性脂肪肝(AFLP)是一种罕见但病情危急的产科特有疾病,致死率高,对母儿安全构成严重威胁。为规范临床管理,改善母儿结局,特制订本指南。基于前期多次的临床问卷调查环节,指南制订小组确定了临床医师最关注的9个临床问题,并对其逐一给出了推荐意见,包括:AFLP的门诊筛查、诊断、术前风险评估、分娩方式选择、麻醉方式选择、围产期并发症、人工肝治疗的指征、预后的评估及治疗期间如何监测,涵盖了AFLP诊治相关的热点问题。Abstract: Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) is a rare but critical obstetric disease with a high mortality rate, and it poses a serious threat to the safety of the mother and the child. The guidelines are developed to standardize clinical management and improve the outcome of the mother and the child. Based on multiple previous clinical questionnaire surveys, the guideline development group identified the nine clinical issues that clinicians are most concerned with and gave recommendations for each issue, including the outpatient screening for AFLP, diagnosis, preoperative risk assessment, selection of mode of delivery, selection of anesthesia method, perinatal complications, indication for artificial liver therapy, evaluation of prognosis, and monitoring during treatment, which covers the hot topics associated with the diagnosis and treatment of AFLP.
-
Key words:
- Fatty Liver /
- Pregnant Women /
- Clinical Governance /
- Pratice Guidelines As Topic
-
表 1 证据质量与推荐强度的GRADE分级表
Table 1. GRADE classification table of evidence quality and recommended strength
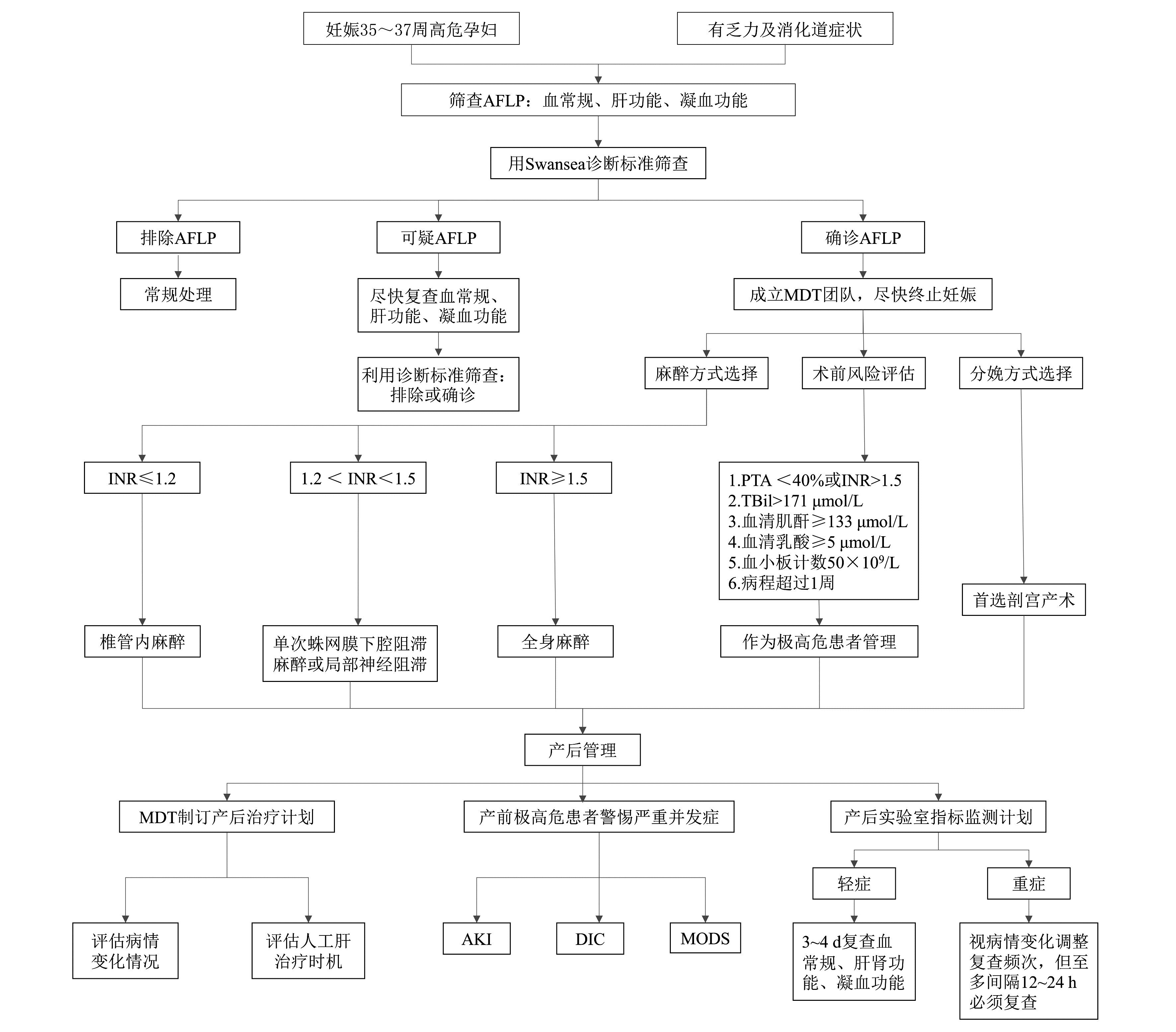
类别 分级 具体描述 证据质量分级 高(A) 非常有把握观察值接近真实值 中(B) 对观察值有中等把握:观察值有可能接近真实值,但也有可能差别很大 低(C) 对观察值的把握有限:观察值可能与真实值有很大差别 极低(D) 对观察值几乎没有把握:观察值与真实值可能有极大差别 推荐强度分级 强(1) 明确显示干预措施利大于弊或弊大于利 弱(2) 利弊不确定或无论质量高低的证据均显示利弊相当 GPS 基于非直接证据或专家意见、经验形成的推荐 注:GRADE表示推荐意见的分级评估、制订和评价;GPS表示良好实践声明。 表 2 文献中AFLP孕妇的临床特征、实验室及超声检查的异常率
Table 2. Clinical characteristics, laboratory and ultrasound bnormalities of AFLP pregnant women in the literature
类别 朱特选等[9] (中国湖南,n=78) Gao等[10] (中国多中心,n=133) Nelson等[4] (美国,n=51) Knight等[11] (英国,n=57) 孕周[x或x±s(范围)] 35.6(29.0~42.0) 36.1±2.7(21.0~41.0) 37.0±2.6(31.7~40.9) 36.0(22.0~40.0) 临床表现(%) 恶心呕吐 64.1 42.9 57.0 60.0 上腹不适 24.4 30.8 53.0 56.0 黄疸 79.5 47.4 33.0 - 肝性脑病 26.9 28.6 16.0 9.0 烦渴或多尿 21.8 - - 12.0 实验室检查(%) 白细胞计数升高 88.5 77.4 98.0 98.0 血小板计数减少 - 42.1 69.0 65.0 转氨酶升高 93.6 91.7 100.0 100.0 高胆红素血症 98.7 93.2 100.0 100.0 PT延长或凝血功能障碍 87.0 69.2 48.0 87.0 血氨升高 43.3 - - 50.0 血肌酐升高 80.8 60.9 96.0 58.0 血糖异常 34.7(低血糖) 57.1(低血糖),9.8(高血糖) 18.0(低血糖) 78.0(低血糖或高血糖) 超声检查(%) 明亮肝或腹水 83.1 57.1 27.0 27.0 注:-无此项;AFLP表示妊娠期急性脂肪肝;PT表示凝血酶原时间。 类别 诊断标准 临床症状 呕吐 腹痛 烦渴或多尿 肝性脑病 生化指标 胆红素>14 μmol/L(0.8 mg/dL) 血糖 < 4 mmol/L(72 mg/dL) 尿酸>340 μmol/L(5.7 mg/dL) 白细胞计数>11×109/L 转氨酶>42 U/L 血氨>47 μmol/L(27.5 mg/dL) 血清肌酐>150 μmol/L(1.7 mg/dL) PT>14 s或APTT>34 s 超声检查 腹水或明亮肝 肝组织活检 微泡性脂肪变性 注:表中所有指标的异常以检测实验室所定标准进行界定,符合6个及以上的条目诊断为AFLP;AFLP表示妊娠期急性脂肪肝;PT表示凝血酶原时间;APTT表示部分凝血活酶时间。 -
[1] MA K, BERGER D, REAU N. Liver diseases during pregnancy[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2019, 23(2): 345-361. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2018.12.013. [2] DEY M, REEMA K. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. N Am J Med Sci, 2012, 4(11): 611-612. DOI: 10.4103/1947-2714.103339. [3] ALLEN AM, KIM WR, LARSON JJ, et al. The epidemiology of liver diseases unique to pregnancy in a US community: A population-based study[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 14(2): 287-294. e1-e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.08.022. [4] NELSON DB, YOST NP, CUNNINGHAM FG. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: Clinical outcomes and expected duration of recovery[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2013, 209(5): 456. e1-e7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.07.006. [5] LIU J, GHAZIANI TT, WOLF JL. Acute fatty liver disease of pregnancy: Updates in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2017, 112(6): 838-846. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2017.54. [6] WANG HY, JIANG Q, SHI H, et al. Effect of caesarean section on maternal and foetal outcomes in acute fatty liver of pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 28826. DOI: 10.1038/srep28826. [7] World Health Organization. WHO handbook for guideline development, 2nd edition[EB/OL]. (2014-12-18)[2021-09-07]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241548960. [8] JIANG ZM, ZHAN SY, JIA XW, et al. Basic methods and procedures for formulating / revising clinical diagnosis and treatment guidelines[J]. Natl Med J China, 2016, 96(4): 250-253. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.04.004.蒋朱明, 詹思延, 贾晓巍, 等. 制订/修订《临床诊疗指南》的基本方法及程序[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(4): 250-253. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.04.004. [9] ZHU TX, LI Q, ZHANG WS, et al. Screening time and schedule for outpatients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. J Cent South Univ(Med Sci), 2015, 40(7): 748-753. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2015.07.008.朱特选, 李琪, 张卫社, 等. 妊娠期急性脂肪肝患者门诊筛查时机和筛查方案的探讨[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2015, 40(7): 748-753. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2015.07.008. [10] GAO Q, QU X, CHEN X, et al. Outcomes and risk factors of patients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy: A multicentre retrospective study[J]. Singapore Med J, 2018, 59(8): 425-430. DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2018001. [11] KNIGHT M, NELSON-PIERCY C, KURINCZUK JJ, et al. A prospective national study of acute fatty liver of pregnancy in the UK[J]. Gut, 2008, 57(7): 951-956. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2008.148676. [12] GOEL A, RAMAKRISHNA B, ZACHARIAH U, et al. How accurate are the Swansea criteria to diagnose acute fatty liver of pregnancy in predicting hepatic microvesicular steatosis?[J]. Gut, 2011, 60(1): 138-139; author reply 139-140. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2009.198465. [13] LAMPRECHT A, MORTON A, LAURIE J, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy and concomitant medical conditions: A review of cases at a quaternary obstetric hospital[J]. Obstet Med, 2018, 11(4): 178-181. DOI: 10.1177/1753495X18764816. [14] JOUEIDI Y, PEOC'H K, LE LOUS M, et al. Maternal and neonatal outcomes and prognostic factors in acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2020, 252: 198-205. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.06.052. [15] CH'NG CL, MORGAN M, HAINSWORTH I, et al. Prospective study of liver dysfunction in pregnancy in Southwest Wales[J]. Gut, 2002, 51(6): 876-880. DOI: 10.1136/gut.51.6.876. [16] LI CS, WANG XQ, XIONG HF, et al. Consistency of Swansea diagnostic criteria and domestic diagnostic criteria in the diagnosis of acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2019, 11(4): 73-76. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2019.04.011.李传胜, 王雪晴, 熊号峰, 等. 妊娠急性脂肪肝Swansea诊断标准与国内诊断标准一致性研[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(4): 73-76. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2019.04.011. [17] TRAN TT, AHN J, REAU NS. ACG clinical guideline: Liver disease and pregnancy[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2016, 111(2): 176-194; quiz 196. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2015.430. [18] LAU HH, CHEN YY, HUANG JP, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy in a Taiwanese tertiary care center: A retrospective review[J]. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol, 2010, 49(2): 156-159. DOI: 10.1016/S1028-4559(10)60033-2. [19] ZHANG YP, KONG WQ, ZHOU SP, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: A retrospective analysis of 56 cases[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2016, 129(10): 1208-1214. DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.181963. [20] GAO Q, MA Y, ZHANG J, et al. Risk factors assessment in patients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy treated without plasma exchange or renal replacement therapy[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2020: 1-5. DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1777267. [21] WANG S, LI SL, CAO YX, et al. Noninvasive Swansea criteria are valuable alternatives for diagnosing acute fatty liver of pregnancy in a Chinese population[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2017, 30(24): 2951-2955. DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2016.1269316. [22] FU LH, ZHANG LJ, YI N, et al. Clinical diagnosis and treatment analysis of 23 cases of acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2015, 7(2): 40-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2015.02.008.付丽华, 张丽菊, 伊诺, 等. 23例妊娠急性脂肪肝临床诊疗分析[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2015, 7(2): 40-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2015.02.008. [23] ZHU TX, ZHANG WS, LI Q, et al. Prognostic value of different factors to predict death of acute fatty liver of pregnancy cases[J]. Chin J Clinl Med, 2016, 23(2): 152-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYX201602006.htm朱特选, 张卫社, 李琪, 等. 妊娠期急性脂肪肝患者预后相关危险因素分析及预测模型建立[J]. 中国临床医学, 2016, 23(2): 152-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCYX201602006.htm [24] GUO YH, FU XD, HOU QH. Clinical features and maternal and infant outcomes of 36 cases of acute fatty liver during pregnancy[J]. Prog Obstet Gynecol, 2016, 25(10): 781-783, 786. DOI: 10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2016.10.016.郭燕华, 傅晓冬, 侯清华. 36例妊娠期急性脂肪肝的临床特征及母婴结局[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2016, 25(10): 781-783, 786. DOI: 10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2016.10.016. [25] CHEN G, HUANG K, JI B, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy in a Chinese Tertiary Care Center: A retrospective study[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2019, 300(4): 897-901. DOI: 10.1007/s00404-019-05259-w. [26] MENG J, WANG S, GU Y, et al. Prenatal predictors in postpartum recovery for acute fatty liver of pregnancy: Experiences at a tertiary referral center[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2016, 293(6): 1185-1191. DOI: 10.1007/s00404-015-3941-5. [27] XU WT, LI J, JIA MW, et al. Clinical analysis of 63 cases of acute fatty liver during pregnancy[J]. J Shandong Univ (Health Sciences), 2019, 57(5): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYB201905020.htm徐文婷, 李静, 贾明旺, 等. 63例妊娠期急性脂肪肝临床分析[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2019, 57(5): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYB201905020.htm [28] CHANG L, WANG M, LIU H, et al. Pregnancy outcomes of patients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy: A case control study[J]. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth, 2020, 20(1): 282. DOI: 10.1186/s12884-020-02980-2. [29] DROLZ A, HORVATITS T, RUTTER K, et al. Lactate improves prediction of short-term mortality in critically ill patients with cirrhosis: A multinational study[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(1): 258-269. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30151. [30] REYES H, SANDOVAL L, WAINSTEIN A, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: A clinical study of 12 episodes in 11 patients[J]. Gut, 1994, 35(1): 101-106. DOI: 10.1136/gut.35.1.101. [31] PAN H, ZHANG LJ, XIA AB. The risk factors on prognosis in acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. J Int Obstet Gynecol, 2017, 44(2): 225-227. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1870.2017.02.026.潘华, 张丽娟, 夏爱斌. 影响妊娠期急性脂肪肝预后的危险因素分析[J]. 国际妇产科学杂志, 2017, 44(2): 225-227. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1870.2017.02.026. [32] LONG Y, TANG H, CHEN Y, et al. Clinical study of 7 cases of vaginal delivery with acute fatty liver during pregnancy[J]. J Guangxi Med Univ, 2014, 31(6): 958-961. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2014.06.025.龙禹, 唐卉, 陈悦, 等. 妊娠期急性脂肪肝阴道分娩7例临床探讨[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2014, 31(6): 958-961. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2014.06.025. [33] NAOUM EE, LEFFERT LR, CHITILIAN HV, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: Pathophysiology, anesthetic implications, and obstetrical management[J]. Anesthesiology, 2019, 130(3): 446-461. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002597. [34] SENTILHES L, MERLOT B, MADAR H, et al. Postpartum haemorrhage: Prevention and treatment[J]. Expert Rev Hematol, 2016, 9(11): 1043-1061. DOI: 10.1080/17474086.2016.1245135. [35] TANG SW. Analysis of the clinical features of the acute fatty liver of pregnancy and assessment of the impact of the time of termination on the prognosis of the mother and child[J]. Med Recapitulate, 2013, 19(18): 3412-3414. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2013.18.052.唐圣魏. 妊娠期急性脂肪肝的临床特点及终止妊娠时间对母儿预后的影响评价[J]. 医学综述, 2013, 19(18): 3412-3414. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2013.18.052. [36] LI SY, LI H, NI J. Study on anesthesia methods for termination of pregnancy with acute fatty liver during pregnancy[J]. J Clin Anesthesiol, 2016, 32(8): 811-812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMZ201608030.htm李淑英, 李慧, 倪娟. 妊娠期急性脂肪肝终止妊娠麻醉方式的探讨[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2016, 32(8): 811-812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCMZ201608030.htm [37] HORLOCKER TT, WEDEL DJ, BENZON H, et al. Regional anesthesia in the anticoagulated patient: Defining the risks (the second ASRA Consensus Conference on Neuraxial Anesthesia and Anticoagulation)[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2003, 28(3): 172-197. DOI: 10.1053/rapm.2003.50046. [38] QU YY, ZENG H, GUO XY, et al. Retrospective analysis of anesthetic and perioperative management in patients of acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. Natl Med J China, 2017, 97(24): 1878-1882. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.24.008.曲音音, 曾鸿, 郭向阳, 等. 妊娠期急性脂肪肝患者的麻醉管理及围手术期处理方式分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2017, 97(24): 1878-1882. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.24.008. [39] HADI Y, KUPEC J. Fatty liver in pregnancy[M]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls, 2021. [40] YU J, XU B, HE XY, et al. Clinical analysis of six cases of acute fatty liver in pregnancy[J]. Chin J Obstet Gynecol, 2002, 37(6): 363-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHFC200206014.htm余江, 徐兵, 何晓宇, 等. 妊娠急性脂肪肝六例临床分析[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2002, 37(6): 363-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHFC200206014.htm [41] MARTIN JN Jr, BRIERY CM, ROSE CH, et al. Postpartum plasma exchange as adjunctive therapy for severe acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. J Clin Apher, 2008, 23(4): 138-143. DOI: 10.1002/jca.20168. [42] YIN HY, GUO R, FENG P, et al. Clinical significance of blood purification in the treatment of acute fatty liver in pregnancy[J]. J Inter Intens Med, 2018, 24(2): 146-147. DOI: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20180217.殷红岩, 郭蕊, 冯萍, 等. 血液净化治疗妊娠急性脂肪肝的临床意义[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2018, 24(2): 146-147. DOI: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20180217. [43] REBAHI H, STILL ME, EL ADIB AR. A successful use of therapeutic plasma exchange in a fulminant form of acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod, 2019, 48(2): 133-137. DOI: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2018.10.001. [44] PAN Y. Effect of early plasma exchange on clinical outcome of acute fatty liver in pregnancy[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2018.潘烨. 早期血浆置换对妊娠期急性脂肪肝的临床结局的影响[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2018. [45] HARTWELL L, MA T. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy treated with plasma exchange[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(9): 2076-2080. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-014-3328-7. [46] JIN F, CAO M, BAI Y, et al. Therapeutic effects of plasma exchange for the treatment of 39 patients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. Discov Med, 2012, 13(72): 369-373. [47] DING J, HAN LP, LOU XP, et al. Effectiveness of combining plasma exchange with plasma perfusion in acute fatty liver of pregnancy: A retrospective analysis[J]. Gynecol Obstet Invest, 2015, 79(2): 97-100. DOI: 10.1159/000368752. [48] HOU HY. Application of plasma exchange in acute fatty liver during pregnancy[J/CD]. Chin J Obstetr Emerg(Electronic Edition), 2014, 3(3): 180-182. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3259.2014.03.007.侯红瑛. 血浆置换在妊娠期急性脂肪肝中的应用[J/CD]. 中华产科急救电子杂志, 2014, 3(3): 180-182. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3259.2014.03.007. [49] WANG QQ, BAI XY, HOU HY. Clinical value of plasma exchange in treating patients with acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J/CD]. Chin J Obstetr Emerg(Electronic Edition), 2014, 3(3): 196-199. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3259.2014.03.012.王青青, 白小艺, 侯红瑛. 血浆置换在治疗妊娠期急性脂肪肝中的应用价值[J/CD]. 中华产科急救电子杂志, 2014, 3(3): 196-199. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3259.2014.03.012. [50] ZHOU M, LUO XD, YANG Y. Analysis of changes in clinical characteristics and laboratory indexes of 54 cases of acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2019, 27(8): 638-642. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.08.010.周敏, 罗小东, 杨洋. 54例妊娠急性脂肪肝患者临床特点和实验室指标变化分析[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2019, 27(8): 638-642. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.08.010. -



 PDF下载 ( 2822 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2822 KB)

 下载:
下载:


