Diagnostic value of serum cystatin C and urotensin II for hepatorenal syndrome in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis
-
摘要:
目的探讨胱抑素C(CysC)、血浆尾加压素Ⅱ(uⅡ)在失代偿期肝硬化合并肝肾综合征(HRS)患者中的诊断价值。方法收集2011年2月-2011年11月于常州市第一人民医院消化内科住院的失代偿期肝硬化患者50例,计算其校正内生肌酐清除率(Ccr),并根据Ccr分为单纯肝硬化组、亚临床HRS组及HRS组,以15例健康体检者为对照组,检测ALT、AST、总胆汁酸(TBA)、Alb、血清肌酐(Scr)、CysC、uⅡ浓度,比较各组上述指标的差异,若数据成正态分布且方差齐,进行单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA),两组间比较采用t检验;否则,多组间进行非参数秩和检验(Kruskall-Wallis H test),两组间比较使用Mann-Whjtney U检验。相关分析采用Spearman相关检验。并通过绘制CysC、uⅡ浓度判断肝硬化合并亚临床HRS及HRS的ROC曲线,获得其曲线下面积(AUC)及最佳临界值。结果肝硬化病例组与正常对照组ALT、AST、TBA、Alb、Scr、Cysc、uⅡ比较差异有统计学意义。单纯肝硬化组、亚临床HRS组及HRS组CysC、uⅡ浓度均呈升高趋势,差异...
-
关键词:
- 半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂 /
- 尿紧张素类 /
- 肝肾综合征 /
- 肝硬化 /
- 诊断
Abstract:Objective To evaluate the relation of serum cystatin C (CysC) and urotensin II (uII) levels with presence of hepatorenal syndrome in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis to determine the diagnostic potential for these serum markers in order to facilitate early detection of hepatorenal syndrome at subclinical stages.Methods A total of 50 patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis were recruited for study and divided into three groups according to creatinine elimination rate (Ccr) : simple liver cirrhosis, ≥80 ml/min (n=22) ;subclinical hepatorenal syndrome, 40≤Ccr<80 ml/min (n=19) ;and hepatorenal syndrome, ≤40 ml/min (n=9) .Fifteen healthy individuals were recruited for use as controls.Fasting blood samples were collected from all cases and controls for measurements of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) , aspartate aminotransferase (AST) , total bile acid (TBA) , albumin (Alb) , serum creatinine (Scr) , CysC, and uII.For normally distributed data, single-factor analysis was carried out by One-Way ANOVA and pairwise comparisons were carried out by the Student′s t-test;for non-normally distributed data, the Kruskall-Wallis H test and Mann-Whitney U test were used, respectively.Correlation analysis was carried out with the Spearman′s rank correlation coefficient.Diagnostic accuracy was assessed by generating a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and using the area under the curve (AUC) to select the optimal threshold for diagnosing subclinical hepatorenal syndrome and hepatorenal syndrome in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis.Results Compared to the healthy controls, the cirrhosis cases had significantly higher levels of ALT, AST, TBA, ALB, Scr, CysC, and uII (all P<0.05) .However, among the cirrhotic patients, those with subclinical hepatorenal syndrome and hepatorenal syndrome had slightly, but significantly, higher levels of CysC and uII than the patients with simple cirrhosis (both P<0.05) .For subclinical hepatorenal syndrome, the AUCs of CysC and uII were 0.91 and 0.867 and the optimal thresholds were 1.40 mg/L and 299.06 pg/ml respectively.For hepatorenal syndrome, the AUCs of CysC and uII were 0.942 and 0.901 and the optimal thresholds were 2.22 mg/L and 321 pg/ml respectively.Conclusion Enhanced levels of serum CysC and uII can reflect hepatorenal damage in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis, even when serum creatinine levels are within normal range, suggesting that these two serum markers may have diagnostic value for detecting subclinical hepatorenal syndrome and hepatorenal syndrome at early stages in this patient population.
-
Key words:
- cysteine proteinase inhibitors /
- urotensins /
- hepatorenal syndrome /
- liver cirrhosis /
- diagnosis
-
胰腺癌(pancreatic cancer,PC)是一种恶性程度极高的消化系统肿瘤,其在我国发病率上升至第9位,死亡率位居第6位,5年生存率仅为7.2%[1-2]。由于PC发病隐匿和早期诊断困难等因素,约80%的患者确诊时已为晚期,错过最佳手术机会[3-4]。对于无法手术治疗及术后转移的晚期患者,化疗是主要的治疗方式,但化疗引起的不良反应导致患者生存质量严重下降[5]。因此,寻找具有良好抗肿瘤活性、较强组织渗透性和毒副作用小的抗PC药物是临床亟待解决的重要问题。
可利霉素(Carrimycin)是我国首次利用合成生物学技术自主研发的基因工程药物,拥有完全自主知识产权,于2019年6月批准上市[6]。最新研究[7]发现,可利霉素中的主要成分异戊螺旋霉素Ⅰ可抑制肝癌细胞的肿瘤生长,并初步揭示其通过下调细胞程序性死亡配体1表达抑制肝癌增殖、转移的分子机制。Liang等[8]的研究结果也显示,可利霉素在体内和体外均能抑制口腔鳞状细胞癌的细胞生物学活性。但其在PC恶性进展中是否发挥类似的抗癌作用仍有待阐释。为此,本研究旨在探究可利霉素对PC细胞生物学功能的影响,从而为其在PC中的治疗提供实验基础和理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 细胞株
PC细胞株MIA PaCa-2、BxPC-3、Panc-1和PATU 8988均由延边大学肿瘤研究中心提供。
1.1.2 主要试剂
DMEM液体培养基(C11330500BT)、胎牛血清(10100147)和胰蛋白酶(25200-072)均购自美国GIBCO公司;可利霉素(国药准字号:H20190029)购自上海同联制药有限公司;青霉素/链霉素(15140-122)购自美国GIBCO公司;超敏ExPlus ECL化学发光检测试剂盒(ZD310A)购自庄盟生物科技有限公司;EdU(5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine)试剂盒(C10310)购自广州锐博生物技术有限公司;二甲基亚砜(dimethyl sulfoxide,DMSO)(D8371)与四甲基偶氮唑盐[3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide,MTT](M8180)购自北京索莱宝生物科技有限公司;BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(CW0014)购自北京康为世纪生物科技有限公司;兔抗上皮钙黏素(E-cadherin)(ab15148)抗体购自美国Abcam公司;兔抗锌指转录因子(Snail)(sc-271977)购自美国Santa-Cruz公司;小鼠抗波形蛋白(Vimentin)(V6389)抗体购自美国Millipore公司;小鼠β-肌动蛋白(CW0096M)抗体购自康为世纪生物科技有限公司;细胞周期依赖性蛋白激酶抑制因子1A(P21)(28248-1-AP)购自美国Proteintech公司;HRP标记的山羊抗兔二抗(ZB-2301)和HRP标记的山羊抗小鼠二抗(ZB-2305)购自北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司;山羊抗兔荧光二抗Alexa Fluor 488(A-11034)和山羊抗小鼠荧光二抗Alexa Fluor 568(A-11004)购自美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司。
1.1.3 仪器
CO2恒温培养箱(FormaTM系列Ⅱ3110)购自美国Thermo公司;台式微量冷冻离心机(CT15RE)购自日本日立公司;全波长多功能酶标仪(Spark)购自瑞士Tecan公司;光学倒置显微镜(IX71)购自日本Olympus公司;荧光正置显微镜(BX53)购自日本Olympus公司;垂直电泳仪(PowerPac系列)购自美国BioRad公司;电转仪(全能型蛋白转印系统1704150)购自美国BioRad公司;ChemiDoc成像系统(1708280)购自美国BioRad公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
将MIA PaCa-2、BxPC-3、Panc-1和PATU 8988细胞培养在含100 mL/L胎牛血清、100 IU/mL青霉素和100 μg/mL链霉素的DMEM液体培养基中,置于37 ℃、5% CO2的恒温培养箱中孵育,当细胞长至90%时,以1: 3的比例进行传代,待细胞处于对数生长期时进行后续实验。
1.2.2 MTT实验
将细胞常规消化、离心后以MIA PaCa-2每孔5×103个/100 μL、BxPC-3每孔2×103个/100 μL、Panc-1每孔3×103个/100 μL和PATU 8988每孔5×103个/100 μL的细胞数种植于96孔板中,每孔补充培养基至200 μL,待细胞贴壁后,加入浓度为0、2、4、8和16 μmol/L的可利霉素,每个药物浓度设置5个平行复孔。分别培养24、48和72 h后,每孔加入20 μL(5 mg/mL)MTT溶液,置于培养箱中孵育4 h后弃去上清液,每孔内加入100 μL的DMSO,震荡10 min之后,使用全波长酶标仪于570 nm波长测定各培养孔的吸光值(A)。根据公式计算细胞生存率(%)=(可利霉素处理组吸光值/对照组吸光值)×100%,并绘制细胞增殖曲线计算半数抑制浓度(IC50)值。
1.2.3 细胞分组
取对数生长期MIA PaCa-2、BxPC-3、Panc-1和PATU 8988细胞加入不同浓度可利霉素组,进行MTT实验筛选细胞株。依据MTT实验结果选择BxPC-3和MIA PaCa2两种细胞系在4、8和16 μmol/L用药浓度和48 h用药时间进行后续实验。
1.2.4 EdU细胞增殖检测实验
将生长对数期细胞常规消化、离心后以MIA PaCa-2每孔1×104个/100 μL、BxPC-3每孔5×103个/100 μL的细胞数种植于96孔板中,待细胞贴壁后分别加入0、4、8和16 μmol/L的可利霉素处理细胞48 h,然后每孔加入100 μL 50 μmol/L EdU,在37 ℃、5% CO2恒温培养箱内孵育2 h。PBS洗涤细胞2次,加入50 μL 4%多聚甲醛室温固定30 min,每孔加入50 μL 2 mg/mL甘氨酸溶液摇床孵育5 min,PBS洗涤5 min,再加入100 μL 0.5% Triton X-100摇床孵育10 min。再次洗涤细胞后每孔加入100 μL 1×Apollo染色反应液后室温避光摇床孵育30 min,弃染色反应液。洗涤细胞后每孔加入1×Hoechst33342反应液100 μL,室温避光孵育30 min。再次洗涤后每孔加入100 μL PBS,最后在荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.2.5 集落形成实验
常规消化细胞后接种于6孔板,每孔接种1000个细胞,分别加入浓度为0、4、8和16 μmol/L的可利霉素处理细胞继续培养2周,当细胞生长至肉眼可见的细胞集落时,终止培养。吸去培养液,预冷PBS清洗2次,4%多聚甲醛固定细胞20 min,苏木素染色30 min,弃苏木素,蒸馏水返蓝后于室温下干燥,计数每孔集落形成数目。
1.2.6 细胞周期检测
取对数生长期且生长良好的MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞,常规消化制成单细胞悬液接种于6孔板中,待细胞贴壁后,分别加入浓度为0(对照组)、4、8和16 μmol/L的可利霉素处理细胞48 h后常规消化,收集细胞悬液,用预冷PBS洗涤2次,再加入预冷的70%乙醇,4 ℃固定过夜。次日细胞离心、预冷PBS重悬后,每管加入1.5 mL PI染色液轻轻重悬均匀,37 ℃水浴锅中避光孵育30 min后上机检测。
1.2.7 细胞划痕愈合实验
常规消化细胞并等量接种于6孔板中,细胞密度达到80%时,使用无菌枪头在单层细胞上垂直划痕。用PBS清洗漂浮的细胞后,分别加入浓度为0、4、8和16 μmol/L的可利霉素处理细胞,分别培养0、12、24和48 h后观察并拍照。
1.2.8 免疫蛋白印迹法(Western blot)
用药处理结束后,收集细胞,加入裂解液提取总蛋白。使用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒测定各组蛋白的浓度。各组蛋白取30 μg样本进行凝胶电泳、转膜、5%脱脂牛奶封闭1 h后,与一抗在4 ℃孵育过夜。次日用TBS-T洗膜,TBS-T稀释二抗,于低速摇床上室温孵育2 h后,用ECL法显影、曝光,最后用Image J统计结果并分析。
1.2.9 免疫荧光染色实验
将细胞置于6孔板中培养48 h后,依次进行PBS洗涤、多聚甲醛固定、Triton-100透化、胎牛血清封闭后,以1: 100的比例稀释兔抗E-cadherin抗体、小鼠抗Vimentin抗体。一抗4 ℃孵育过夜。次日,PBS洗涤后,以1: 400的比例稀释山羊抗兔荧光二抗或山羊抗小鼠荧光二抗,室温避光孵育2 h。PBS洗涤后,滴入含DAPI的封片剂封片。于荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.3 统计学方法
本实验的结果均采用Graphpad Prism 8.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料数据以x±s表示,多组间比较采用方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。所有实验均重复3次或3次以上。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 可利霉素抑制PC细胞的增殖活性
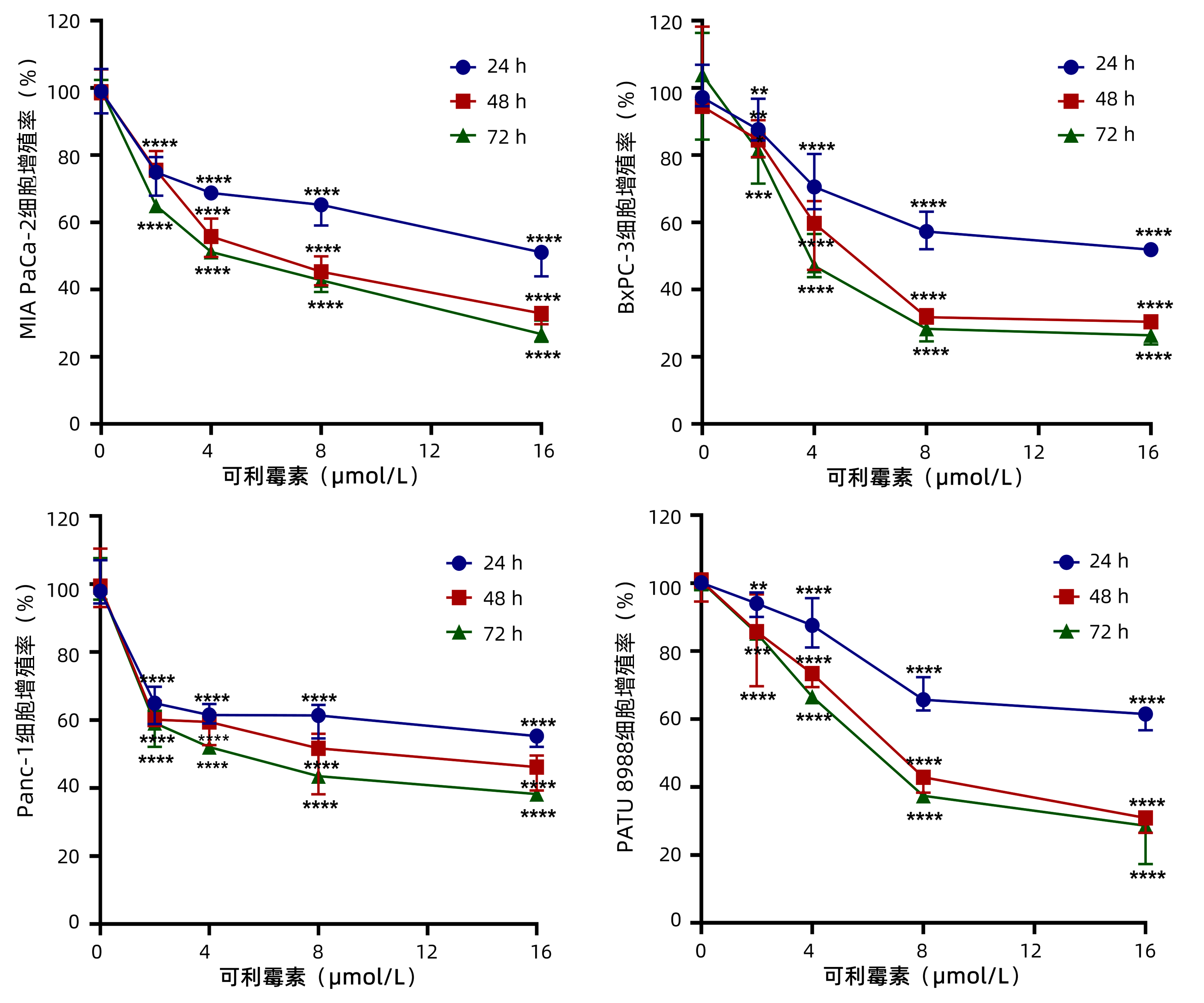
为了观察可利霉素对PC细胞增殖活性的影响,MTT实验检测以0、2、4、8和16 μmol/L的可利霉素处理PC细胞MIA PaCa-2、BxPC-3、Panc-1和PATU 8988于24、48和72 h后细胞的增殖活力,结果显示:可利霉素可抑制PC细胞的增殖活性,且随着药物浓度的升高和用药时间的延长,细胞活性逐渐降低,并呈药物浓度与时间依赖性(P值分别<0.01、<0.001、<0.0001)(图 1);应用Graphpad Prism 8.0软件计算得出可利霉素处理PC细胞48 h后MIA PaCa-2细胞的IC50值为6.67 μmol/L;BxPC-3细胞的IC50值为5.76 μmol/L;Panc-1细胞的IC50值为8.62 μmol/L;PATU 8988细胞的IC50值为7.47 μmol/L。根据这一结果,将选取MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞,0、4、8和16 μmol/L用药浓度和48 h用药时间进行后续实验。
2.2 可利霉素抑制PC细胞的增殖和克隆形成能力
EdU细胞增殖实验结果(图 2a)显示:4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素分别与对照组比较,可显著降低PC细胞MIA PaCa-2(t值分别为2.378、4.984、18.970,P值分别为<0.05、<0.01、<0.000 1)及BxPC-3(t值分别为4.879、6.089、9.521,P值分别为<0.01、<0.001、<0.000 1)的DNA复制能力;集落形成实验结果(图 2b)表明,4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理PC细胞14 d后,分别与对照组比较,MIA PaCa-2(t值分别为5.889、11.240、15.840,P值分别为<0.001、<0.000 1、<0.000 1)和BxPC-3(t值分别为6.717、15.800、18.850,P值分别为<0.001、<0.000 1、<0.000 1) 细胞的集落形成能力随着药物浓度的增加而明显减少。以上结果提示,可利霉素能够抑制PC细胞的增殖能力。
 图 2 EdU及集落形成实验检测不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞增殖的抑制作用注:a,EdU实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3的DNA复制能力的影响;b,集落形成实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3克隆形成能力的影响。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.000 1。Figure 2. The inhibitory effects of different concentrations of Carrimycin on the proliferation of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells were detected by EdU and colony formation assay
图 2 EdU及集落形成实验检测不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞增殖的抑制作用注:a,EdU实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3的DNA复制能力的影响;b,集落形成实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3克隆形成能力的影响。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.000 1。Figure 2. The inhibitory effects of different concentrations of Carrimycin on the proliferation of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells were detected by EdU and colony formation assay2.3 可利霉素促进PC细胞周期阻滞
通过流式细胞术分析可利霉素是否通过调控细胞周期抑制PC细胞的增殖,结果(图 3a)显示:与对照组比较,4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后MIA PaCa-2细胞G1期比例(t值分别为9.071、12.280、19.360,P值均<0.000 1)及BxPC-3细胞G1期比例(t值分别为3.06 1、4.962、8.868,P值分别为<0.05、<0.01、<0.000 1)均增加,MIA PaCa-2细胞S期比例(t值分别为2.316、4.165、5.562,P值分别为<0.05、<0.01、<0.001)及BxPC-3细胞S期比例(t值分别为2.424、3.264、5.744,P值分别为<0.05、<0.05、<0.001)均降低。Western blot实验(图 3b)进一步证实,与对照组比较,周期相关蛋白P21在MIA PaCa-2(t值分别为5.437、6.453、8.799,P值分别为<0.001、<0.001、<0.000 1)和BxPC-3细胞(t值分别为25.13、44.75、52.96,P值均<0.000 1)中的表达水平随可利霉素用药浓度增加而逐渐上调。上述结果表明,可利霉素促进G1期细胞周期阻滞、上调P21表达抑制PC细胞的增殖。
 图 3 细胞周期和Western Blot实验检测不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞周期的影响注:a,细胞周期实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞周期的影响;b,Western blot实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3中P21蛋白的表达量。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.0001。Figure 3. Cell cycle and Western Blot experiments were performed to examine the effects of different concentrations of Carrimycin on the cell cycle of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells
图 3 细胞周期和Western Blot实验检测不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞周期的影响注:a,细胞周期实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞周期的影响;b,Western blot实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3中P21蛋白的表达量。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.0001。Figure 3. Cell cycle and Western Blot experiments were performed to examine the effects of different concentrations of Carrimycin on the cell cycle of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells2.4 可利霉素抑制PC细胞的迁移和上皮细胞-间充质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)进程
划痕愈合实验结果(图 4a、b和表 1)显示,0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理12、24和48 h PC细胞MIA PaCa-2(P值分别为<0.05、<0.01、<0.001、<0.000 1)及BxPC-3(P值分别为<0.05、<0.001、<0.000 1)的横向迁移能力明显减弱。Western Blot实验结果(图 4c)显示,与对照组比较,4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后MIA PaCa-2(t值分别为2.388、4.899、5.819,P值分别<0.05、<0.01、<0.001)及BxPC-3细胞(t值分别为2.533、5.836、6.774,P值分别<0.05、<0.001、<0.001)中上皮标志物E-cadherin的表达明显上调,同样地,4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后MIA PaCa-2 (t值分别为12.440、14.830、16.800,P值均<0.000 1)及BxPC-3细胞(t值分别为5.039、5.893、7.725,P值分别为<0.01、<0.001、<0.000 1)中间质标志物Snail的表达水平显著下调,4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后MIA PaCa-2 (t值分别为3.105、7.752、11.200,P值分别为<0.05、<0.000 1、<0.000 1)及BxPC-3细胞(t值分别为2.555、4.883、9.153,P值分别为<0.05、<0.01、<0.000 1)中间质标志物Vimentin的表达水平也显著下调;与上述结果一致,免疫荧光结果(图 4d)进一步亦证实,可利霉素处理组的E-cadherin荧光信号明显增强,而Vimentin的荧光信号则明显减弱。这些结果表明,可利霉素通过EMT进程抑制PC细胞的迁移。
 图 4 不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞迁移及EMT进程的影响注:a,划痕愈合实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3迁移能力的影响;b,0、4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPc-3细胞伤口愈合率;c,Western blot实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3中EMT相关蛋白E-cadherin、Snail和Vimentin的表达水平;d,免疫荧光实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3中E-cadherin和Vimentin的表达水平。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.000 1。Figure 4. Effects of different concentrations of Carrimycin on migration and EMT progression of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells表 1 不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2细胞和BxPC-3细胞迁移的影响Table 1. Effect of carrimycin at different concentrations on the migration of MIA PaCa-2 cells and BxPC-3 cells migration
图 4 不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3细胞迁移及EMT进程的影响注:a,划痕愈合实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素对PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3迁移能力的影响;b,0、4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPc-3细胞伤口愈合率;c,Western blot实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3中EMT相关蛋白E-cadherin、Snail和Vimentin的表达水平;d,免疫荧光实验检测0和4、8、16 μmol/L可利霉素处理后PC细胞MIA PaCa-2和BxPC-3中E-cadherin和Vimentin的表达水平。*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001,****P<0.000 1。Figure 4. Effects of different concentrations of Carrimycin on migration and EMT progression of MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells表 1 不同浓度的可利霉素对MIA PaCa-2细胞和BxPC-3细胞迁移的影响Table 1. Effect of carrimycin at different concentrations on the migration of MIA PaCa-2 cells and BxPC-3 cells migration组别 对照组 4 μmol/L 8 μmol/L 16 μmol/L MIA PaCa-2细胞 12 h 15.23±2.84 11.97±1.90 8.58±1.05 2.53±0.64 24 h 25.08±1.98 21.11±2.23 14.08±2.48 5.36±1.49 48 h 28.31±1.53 23.63±2.06 17.93±1.12 12.06±1.79 BxPC-3细胞 12 h 18.15±2.15 14.54±1.91 7.61±2.01 5.80±1.53 24 h 38.28±1.74 31.80±3.45 19.50±2.64 15.08±1.14 48 h 50.75±2.35 39.71±2.64 29.50±2.47 24.89±2.31 3. 讨论
在肿瘤治疗过程中,随着抗癌药物的广泛应用,肿瘤细胞对其产生不可忽视的耐药性,致使人们对不同药物重新定位,挖掘潜在的临床价值。令人鼓舞的是,许多临床批准的非癌症药物在生物学实验中甚至临床上都显示出较好的抗肿瘤活性,其中关于大环内酯类药物的相关研究较多。例如,大环内酯类药物雷帕霉素能抑制PC、肝癌、肺癌等多种肿瘤细胞的增殖、迁移及侵袭能力,并能促进细胞周期阻滞,诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,从而抑制肿瘤形成[9]。有研究[10-12]报道显示,大环内酯类化合物埃博霉素与微管蛋白结合,影响肿瘤细胞的有丝分裂过程,进而抑制肿瘤生长。可利霉素作为一种大环内酯类抗生素新药,不仅具有良好的抗菌效果,还具有抑制肿瘤细胞增殖及其转移的作用[13]。后续研究[7]发现,可利霉素可通过抑制PI3K/mTOR信号通路,降低IL-6和IL-8水平,抑制肿瘤细胞细胞程序性死亡-配体1的表达,从而抑制调节性T淋巴细胞特异性活化,继而发挥抑癌作用,还具备诱导M2型巨噬细胞向M1型巨噬细胞转化的功能。但其具体抑癌机制尚不明确。为此,本研究主要探讨大环内酯类抗生素可利霉素对PC细胞体外增殖及转移能力是否有抑制作用,并进一步研究其可能的机制,为今后治疗PC提供新思路。
肿瘤细胞异常增殖是促进癌细胞发生发展进程中的重要因素,因此,抑制肿瘤细胞增殖能有效调控癌细胞发生发展过程。本研究利用浓度和时间梯度可利霉素处理PC细胞,观测可利霉素对PC细胞活力、增殖及细胞周期的影响。研究结果显示,可利霉素随着药物浓度的增加和用药时间的延长能有效抑制PC细胞的体外增殖、集落形成能力及DNA复制能力并诱导PC细胞周期阻滞于G1期,进一步的Western Blot实验证实了细胞周期相关标志蛋白P21的表达随可利霉素用药浓度增加而逐渐上调,上述结果均可表明可利霉素能够抑制PC细胞的增殖能力。这与Jin等[7]和Liang等[8]的研究结果相一致。
有报道[14]证实EMT进程是参与胰腺炎向PC转变以及PC转移的重要机制。当肿瘤细胞EMT进程得到促进时,下调上皮标志物E-cadherin蛋白和过量表达间质标志物Snail与Vimentin蛋白,导致肿瘤细胞的运动能力变强,进而在宏观上表现为癌症全身转移扩散,从而加剧了肿瘤的治疗难度[15-17]。因此,在肿瘤的发生发展过程中,抑制或逆转EMT进程对帮助肿瘤患者抑制疾病和治疗疾病等均起着重要作用。于是通过划痕愈合实验、Western Blot和免疫荧光实验研究可利霉素对PC细胞侵袭转移能力的影响。结果显示,与对照组相比,可利霉素呈浓度和时间依赖性的方式抑制PC细胞的迁移,同时上调上皮标志物E-cadherin的表达,下调间质标志物Snail和Vimentin的表达水平,提示可利霉素可通过逆转EMT进程抑制PC细胞的迁移能力。而PC的侵袭转移是一个多基因参与、多因素影响的多步骤复杂过程[18],对于EMT进程在侵袭转移中的机制及可能存在的其他与转移相关的信号通路还有待进一步发掘和探讨。
综上所述,可利霉素可通过有效抑制PC细胞的增殖和迁移等生物学进程发挥其抗肿瘤的生物学活性。并且深入探究可利霉素在PC发生与发展过程中的作用及机制,可为PC的治疗进一步提供基础研究和新的希望,但可利霉素抑制PC细胞可能涉及多条信号通路,其具体的作用机制和临床应用仍需更深入地研究探讨。
-
[1]ZHENG XL, WANG LZ.Crrent diagnosis and treatment of hepatorenalsyndrome[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2011, 27 (1) :107-109. (in Chinese) 郑晓丽, 汪良芝.肝肾综合征诊治现状[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2011, 27 (1) :107-109. [2]Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases and Parasitology and ChineseSociety of Hepatology of Chinese Medical Association.Preventionand treatment of viral hepatitis[J].Chin J Hepatol, 2000, 8 (6) :324-329. (in Chinese) .中华医学会传染病与寄生虫病学分会、肝病学分会.病毒性肝炎防治方案[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2000, 8 (6) :324-329. [3]SALERNO F, GERBES A, GINES P, et al.Diagnosis, preventionand treatment of hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis[J].Gut, 2007, 56 (9) :1310-1318. [4]COULOUAM Y, LITU-MEMN I, JEGOU S, et al.Cloning of eD-NA encoding the urotensinⅡprecurmr in frog and human reveals in-tense expression of the urotensinⅡgene in motoneurons of the spi-nal cord[J].Prec Natl Acad Sci USA, 1998, 95 (26) :158-163. [5]LUO JF, GONG YS.Novel progress in research on urotensinⅡ[J].Int J Endocrinol Metabol, 2005, 32 (10) :10-13. (in Chi-nese) 骆健峰, 龚永生.尾加压素II研究新进展[J].国外医学.内科学分册, 2005, 32 (10) :10-13. [6]HELLER J, SCHEPKE M, NEFF M, et al.Increased urotensin IIplasma levels in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension[J].J Hepatol, 2002, 37 (6) :767-772. [7]TASAKI K, HORI M, OZAKI H, et al.Mechanism of human uro-tensin II induced contraction in rat aorta[J].Pham Acol Sci, 2004, 94 (4) :3762-3764. [8]TOTSUNE K, TAKAHASHI K, ARIHARA Z, et al.Role of uro-tensin II in patients on dialysis[J].Lancet, 2001, 358 (9284) :810-811. [9]JOHN GT, FLEMING JJ, TALAULIKAR GS, et al.Measurementof renal function in kidney donors using serum eystatin C and beta (2) mieroglobulin[J].Ann Clin Biochem, 2003, 40 (6) :656-658. [10]DHARNIDHARKA VR, KWON C, STEVENS G.Serum cystatin Cis superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function:a ma-ta analysis[J].Am Kidney Dis, 2002, 40 (2) :221-226. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 周佳,邱智东,林喆,律广富,许佳明,林贺,王可欣,王雨辰,黄晓巍. 白屈菜红碱对人卵巢癌SKOV3细胞迁移、侵袭和上皮-间质转化的影响. 吉林大学学报(医学版). 2024(01): 25-32 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 778 KB)
PDF下载 ( 778 KB)


 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: