Value of HBsAg level in dynamic monitoring of disease progression in patients with chronic HBV infection
-
摘要: 目的探讨HBsAg水平在慢性HBV感染者疾病进展监测中的临床价值。方法收集2011年5月-2015年12月在安徽医科大学第二附属医院门诊及住院时未进行抗病毒治疗的1107例不同临床阶段的慢性HBV感染者的临床资料,并根据疾病状态分为HBeAg阳性慢性乙型肝炎组(HBeAg阳性CHB组,n=356)、HBeAg阴性慢性乙型肝炎组(HBeAg阴性CHB组,n=264)、乙型肝炎肝硬化代偿期组(LC-C组,n=116)、乙型肝炎肝硬化失代偿期组(LC-D组,n=201)、原发性肝癌组(PLC组,n=170),比较不同临床阶段患者之间HBsAg表达水平的差异及HBsAg水平与临床特征的相关性。计量资料多组间比较采用方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验;两组间比较采用t检验。计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验。相关性分析采用Pearson检验。结果HBeAg阳性CHB组、HBeAg阴性CHB组、LC-C组、LC-D组、PLC组之间患者血清HBsAg、HBV DNA水平比较,差异均有统计学意义(F值分别为100.45、86.26,P值均<0.001)。502例HBeAg阳性患者的HBsAg、...Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical value of HBsAg level in dynamic monitoring of disease progression in patients with chronic HBV infection. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 1107 patients with different clinical stages of chronic HBV infection who had not received antiviral therapy at the time of hospitalization in The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University from May 2011 to December 2015, and according to the disease status, they were divided into HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B ( CHB) group ( n = 356) , HBeAg-negative CHB group ( n = 264) , compensated liver cirrhosis group ( LC-C group, n = 116) , decompensated liver cirrhosis group ( LC-D group, n = 201) , and primary liver cancer ( PLC) group ( n = 170) . These groups were compared in terms of HBsAg expression and the association between HBsAg and clinical features. An analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between any two groups; the t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups. The chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between these groups. Pearson correlation analysis was also performed. Results There were significant differences in serum HBsAg and HBV DNA level between the HBeAg-positive CHB group, HBeAg-negative CHB group, LC-C group, LC-D group, and PLC group ( F =100. 45 and 86. 26, both P < 0. 001) . The HBeAg-positive CHB group ( n = 502) had significantly higher levels of HBsAg and HBV DNA than the HBeAg-negative CHB group ( n = 605) ( t = 16. 67 and 16. 22, both P < 0. 001) . There were significant differences in HBsAg and HBV DNA levels between the HBeAg-positive CHB group, LC-C group, LC-D group, and PLC group ( F = 42. 92 and 27. 38, both P <0. 001) , as well as between the HBeAg-negative CHB group, LC-C group, LC-D group, and PLC group ( F = 6. 04 and 4. 10, both P <0. 05) . HBV DNA level was significantly different across patients with different HBsAg levels ( < 1000 IU/ml, 1000-20 000 IU/ml, and> 20 000 IU/ml) ( F = 189. 51, P < 0. 001) . In the HBeAg-positive CHB group, HBeAg-negative CHB group, LC-C group, and LC-D group, serum HBsAg level was positively correlated with HBV DNA level ( r = 0. 554, 0. 501, 0. 320, and 0. 432, all P < 0. 001) .Conclusion HBsAg level gradually decreases with disease progression and is closely associated with HBV DNA level. Dynamic monitoring of HBsAg level helps to evaluate disease progression after HBV infection.
-
Key words:
- hepatitis B virus /
- hepatitis B surface antigens /
- viral load
-
原发性肝癌的发病率持续增长, 已居恶性肿瘤死亡率的第四位[1], 尽管目前肝癌治疗水平已有较大提高[2], 但其预后依然不容乐观[3]。探索肝癌侵袭转移的分子机制及寻找有效的肝癌治疗靶点仍是肝癌研究的重要内容。已有研究[4-5]表明, 中性胆固醇酯水解酶1(neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1, NCEH1)在侵袭性前列腺癌细胞中高表达, 抑制NCEH1的表达则可降低前列腺癌细胞的增殖、转移和侵袭能力, 提示NCEH1是一促癌基因。然而截至目前, NCEH1在肝癌中的表达及作用均尚不清楚。本研究旨在了解NCEH1在肝癌组织及细胞系中的表达情况并探讨其对肝癌细胞增殖、凋亡、转移及侵袭能力的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 NCEH1基因样本
选取2013年1月—2019年6月在暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院手术治疗的32例肝癌患者标本及对应的癌旁组织。所有标本离体后立即存放在液氮罐中, 然后于-80 ℃深低温箱中保存。采用实时荧光定量PCR检测NCEH1基因的相对表达量。同时从ICGC数据库(https://daco.icgc.org)下载截至2020年9月日本人群的肝癌基因表达数据(包含240个肝癌样本和220个正常肝组织样本)作为验证组, 应用R软件(4.0.2版本)中的limma、beeswarm包对NCEH1基因表达数据进行Wilcoxon秩和检验并做散点差异图进行可视化[6]。
1.2 细胞培养
HL7702正常人肝脏细胞系和SMMC-7721、Bel-7402、HepG2和Hep3B人肝癌细胞系均购自中国科学院上海生命科学研究院生物化学与细胞生物学研究所, 293T细胞购自上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司, 细胞置于37 ℃、5% CO2细胞培养箱中, 以含10%胎牛血清(FBS)的高糖DMEM培养基培养, 按常规进行传代。
1.3 实时荧光定量PCR
提取细胞总RNA并逆转录, 在荧光定量PCR仪(TP800, 日本TAKARA公司)上行PCR检测, 反应条件为: 95 ℃预变性15 s, 然后95 ℃变性5 s, 60 ℃退火延伸30 s, 共进行45个循环, 每次在延伸阶段读取吸光值。NCEH1引物为: 上游5′- CCTGCCGTCCTTCCTTCTTC-3′; 下游5′-CCGTGGTGCCCTGTATCATTA -3′。以管家基因GAPDH(甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶)为内参基因, 引物序列为: 上游5′- TGACTTCAACAGCGACACCCA -3′; 下游5′-CACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAA -3′。以2-ΔΔCT法分析各细胞系中NCEH1基因的相对于内参基因的表达水平。若肝癌组织中的NCEH1基因表达水平高于相应的癌旁组织, 则为NCEH1表达上调。
1.4 慢病毒介导的小干扰RNA(siRNA)
慢病毒质粒GV122、包装质粒pGC-LV、pHelper 1.0和pHelper2.0均购自上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司。设计针对NCEH1基因的shRNA序列如下, 正义链: 5′-CCGGATCCAGGCAGAATTTGCATTTCTCGAGAAATGCAAATTCTGCCTGGATTTTTTG-3′, 反义链: 5′AATTCAAAAAATCCAGGCAGAATTT-GCATTTCTCGAGAAATGCAAATTCTG- CCTGGAT-3′; 阴性对照组序列为, 正义链: 5′-CCGGTTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTTTCAA- GAGAA-CGTGACACGTTCGGAGAATTTTTG-3′, 反义链: 5′-AATTCAAAAATTCTCCGA- ACGTGTCACGTTCTCTTGAAACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAA-3′。上述序列由上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司合成, 将其所形成的双链DNA分别连接到siRNA慢病毒质粒GV122, 再将上述质粒分别与pGC-LV、pHelper1.0和pHelper2.0 3个包装质粒共转染至293T细胞, 上述两种慢病毒各自感染的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞系即被分别命名为NCEH1敲减组(KD组)和阴性对照组(NC组)。采用荧光倒置显微镜(micropublisher 3.3RTV, 日本奥林帕斯公司)观察两组细胞的慢病毒感染效率, 并采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测两组细胞中NCEH1基因的相对表达水平, 以检测NCEH1基因的敲减率。
1.5 MTT实验检测肝癌细胞生长增殖能力
将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞培养于6孔板中, 完全培养基重悬成细胞悬液, 选取5块96孔板, 分别标记为1、2、3、4、5 d; 每组设置3个复孔, 每孔加入100 μl细胞悬液, 每板分别铺3组细胞。从铺板后第2天开始, 培养终止前4 h加入20 μl 5 mg/ml的MTT于孔中。4 h后完全吸去培养液, 加100 μl DMSO溶解甲瓒颗粒。振荡器振荡2~5 min, 酶标仪490/570 nm检测光密度(OD)值。
1.6 Annexin V-APC单染法检测肝癌细胞凋亡率
将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞培养于6孔板中, 完全培养基重悬成细胞悬液, 与上清细胞收集于同一5 ml离心管中。然后1300 r/min离心5 min, 弃上清, 4 ℃预冷的PBS洗涤细胞沉淀。1×binding buffer洗涤细胞沉淀一次, 1300 r/min离心3 min, 收集细胞, 200 μl 1×binding buffer重悬细胞沉淀, 加入10 μl Annexin V-APC染色, 室温避光10~15 min。根据细胞量, 补加400~800 μl 1×binding buffer, 上机检测。
1.7 划痕愈合实验检测肝癌细胞迁移能力
将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞培养于6孔板中, 完全培养基重悬成细胞悬液, 根据细胞大小决定铺板细胞密度。置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养。第2天使用划痕仪对准96孔板的上端中央部位, 向上轻推形成划痕。使用PBS轻轻漂洗2~3遍, 加入含1% FBS血清培养基, 0 h扫板。再次于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养, 根据愈合程度选择合适时间用Celigo扫板, 用Celigo分析迁移面积并计算迁移率。
1.8 Transwell转移和侵袭实验
将Transwell小室置于新的24孔板中, 上室加100 μl无FBS培养基, 37 ℃培养箱中放置1 h。将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞加入每个小室, 下室内加入含30% FBS的培养基600 μl, 5% CO2、37 ℃孵育48 h。倒扣小室于吸水纸上以去除培养基, 用棉拭子轻轻移去小室内非转移细胞, 将小室置于4%多聚甲醛固定液中固定30 min后捞出, 用吸水纸吸干小室表面固定液, 滴1~2滴染色液到膜的下表面染色转移细胞1~3 min后, 将小室浸泡冲洗数次, 空气晾干。在显微镜下拍照并计算各组转移细胞数。如将Transwell小室先铺Matrigel胶再重复上述实验步骤即为Transwell侵袭实验。
1.9 伦理学审查
本研究通过暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院伦理委员会审核, 批号: 穗红院医伦审2019-028-01。所有标本采集前均已获患者知情同意。
1.10 统计学方法
应用SPSS 23.0软件进行统计学分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示, 两组间比较采用t检验。采用配对样本比较的Wilcoxon符号秩检验对32例肝癌组织和对应癌旁中的NCEH1相对表达量进行比较, 两个独立样本比较的Wilcoxon秩和检验对ICGC数据库中肝癌和正常肝组织中的NCEH1表达量进行比较。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。统计图采用Graphpad Prism 8.0软件(美国Graphpad软件公司)绘制。
2. 结果
2.1 肝癌组织中NCEH1的表达
实时荧光定量PCR检测结果显示, 在32例患者标本中, 有22例肝癌组织中的NCEH1基因表达上调, NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的平均表达量高于相应的癌旁组织(Z=2.263, P=0.024)(图 1a)。下载ICGC数据库中日本人群的肝癌标本(包含240个肝癌样本, 202个正常肝组织样本), 筛选出每个样本中NCEH1基因表达量进行分析。结果显示, NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的表达水平明显高于正常肝组织(U=18 768, P<0.001)(图 1b)。
2.2 NCEH1在肝癌细胞系中的相对表达水平
t检验结果显示, NCEH1在中等侵袭转移潜能的SMMC-7721和Bel-7402细胞系中的相对表达量较低或无侵袭转移潜能的HepG2(0.004 2±0.000 2 vs 0.002 9±0.000 4, t=4.651, P=0.01;0.003 9±0.000 3 vs 0.002 9±0.000 4, t=3.218, P=0.03)和Hep3B细胞系高(0.004 2±0.000 2 vs 0.002 7±0.000 2, t=9.496, P=0.001;0.003 9±0.000 3 vs 0.002 7±0.000 2, t=3.218, P=0.005);而NCEH1在低或无侵袭转移潜能的HepG2和Hep3B细胞系中的相对表达量较正常HL-7702肝细胞系高(0.002 9±0.000 4 vs 0.001 5±0.000 1, t=5.682, P=0.005; 0.002 7±0.000 2 vs 0.001 5±0.000 1, t=11.302, P=0.000 3)。
2.3 慢病毒的感染效率及NCEH1基因敲减效率
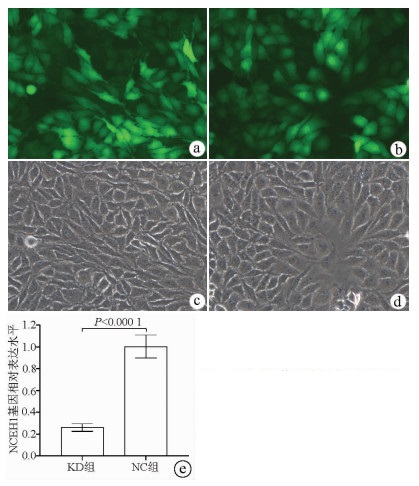
荧光显微镜观察结果显示, KD组及NC组慢病毒对肝癌细胞的感染效率均达到80%以上, KD组SMMC-7721细胞中NCEH1基因的相对表达量仅为NC组细胞的26.0%(0.260±0.035 vs 1.004±0.106, t=11.578, P=0.000 3), 即NCEH1基因在SMMC-7721人肝癌细胞系中的敲减效率达到了74.0%(图 2)。
2.4 NCEH1敲减对肝癌细胞生长增殖能力的影响
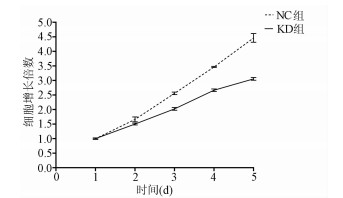
MTT检测结果显示, KD组SMMC-7721肝癌细胞生长速度较NC组明显减缓(第5天相对增殖倍数为3.055±0.046 vs 4.462±0.060, t=32.100, P=0.000 006), 提示NCEH1基因敲减明显抑制了肝癌细胞的生长增殖(图 3)。
2.5 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞凋亡的影响
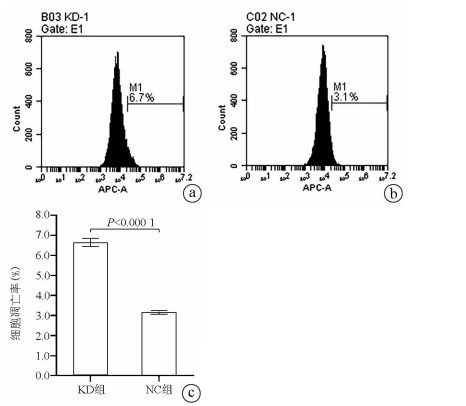
Annexin V-APC单染法流式细胞仪检测显示, KD组SMMC- 7721肝癌细胞凋亡率明显高于NC组(6.650%±0.203% vs 3.150%±0.090%, t=27.303, P=0.000 01), 提示敲减NCEH1基因可促进细胞凋亡(图 4)。
2.6 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞迁移能力的影响
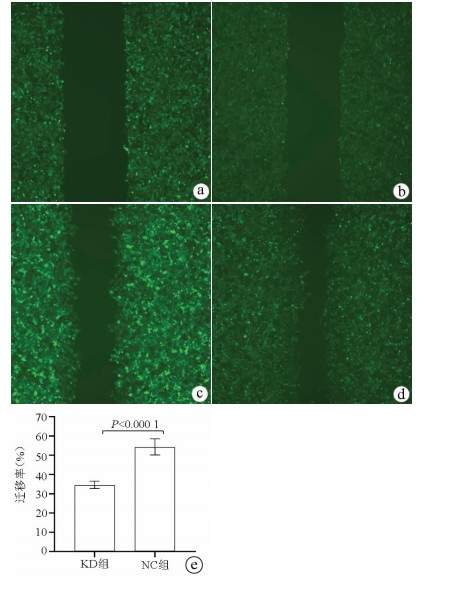
划痕愈合实验结果显示, KD组的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞迁移率明显低于NC组(34.68%±1.89% vs 54.37%±4.23%, t=9.51, P=0.000 01), 提示敲减NCEH1基因可明显抑制肝癌细胞的迁移能力(图 5)。
2.7 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞转移能力的影响
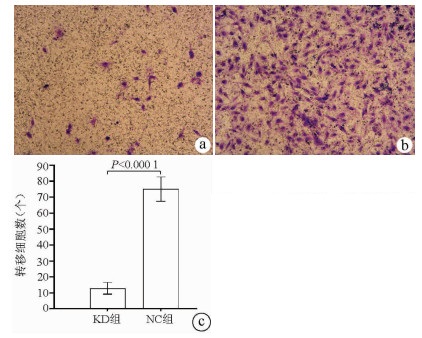
Transwell实验结果显示, KD组SMMC-7721肝癌细胞的转移细胞数明显低于NC组(12.89±3.63 vs 75.04±7.65, t=38.123, P<0.000 1), 提示NCEH1基因敲减可明显抑制肝癌细胞的转移能力(图 6)。
2.8 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞侵袭能力的影响
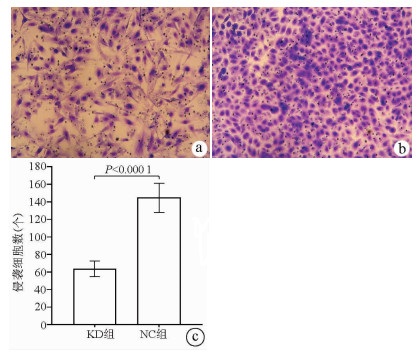
Transwell侵袭实验结果显示, KD组的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞侵袭数明显低于NC组(63.67±8.86 vs 144.52±16.60, t=22.331, P<0.000 1), 提示NCEH1基因敲减可明显抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭能力(图 7)。
3. 讨论
肝癌在全球的发病率和死亡率较高, 据估计2015年全球肝癌死亡人数约为80万[7], 而在全球每年新增肝癌病例中, 约一半发生在我国, 已成为最致命的癌症之一[8]。尽管针对肝癌的治疗手段众多, 手术切除仍然是治疗肝癌的首选方案, 但由于肝癌术后复发率相对较高, 导致肝癌术后5年无复发生存率仅为38%, 严重限制了肝癌的总体治疗效果[9-10]。因此, 探索肝癌侵袭转移的机制以获得有效的肝癌治疗靶点已成为肝癌研究的重点。
近年来的研究表明, 脂代谢异常可能是促进癌症发生发展的一个重要因素, Jiang等[11]通过蛋白质组学分析发现, 改变细胞内胆固醇的分布, 可有效抑制肝细胞癌的增殖和转移。Lin等[12]通过脂质组学分析发现, 脂质代谢的改变与肿瘤侵袭性、生长和增殖密切相关, 目前也已发现多个脂质代谢过程中的关键酶在肿瘤细胞中过表达[13-14], 这为肝癌治疗提供了一个新思路。NCEH1是一个蛋白质编码基因, 定位于人染色体3q26.31, 大小为80 970 bp。NCEH1基因编码的蛋白由408个氨基酸组成, 大小为45.808 kD, 是一种丝氨酸水解酶, 在巨噬细胞和中枢神经细胞中有较高表达[15-16], 并在调节胆固醇代谢过程中发挥重要作用[4]。已有研究[17-18]发现, NCEH1表达产物可作为乙醚脂质信号网络中连接血小板活化因子和溶血磷脂酸的中心节点, 抑制NCEH1表达产物可降低癌细胞中的醚脂质代谢并抑制肿瘤细胞迁移和生长。Chang等[5]的研究则发现, 选择性NCEH1抑制剂可明显降低人前列腺癌细胞系的迁移、侵袭、存活及增殖能力, 提示NCEH1可能与肿瘤的侵袭、迁移及增殖相关, 但NCEH1在肝癌中的表达水平及作用目前均不清楚。
为此, 本研究首先通过对本院32例肝癌及对应癌旁标本进行分析发现, NCEH1在肝癌组织中的表达明显高于对应的癌旁组织, 然后分析ICGC数据库中日本人群的肝癌基因表达数据发现, NCEH1在肝癌组织中的表达明显高于正常肝组织, 与本研究结果一致, 提示NCEH1在肝癌组织中的表达上调。继而, 本研究采用实时荧光定量PCR技术分析发现, NCEH1在所有肝癌细胞系中的表达均高于正常肝细胞系, 这与其在肝癌组织中表达上调的结果一致。更重要的是, NCEH1在侵袭转移潜能较高的肝癌细胞系中的表达明显高于低侵袭转移潜能的肝癌细胞系, 这与Chang等[5]在前列腺癌细胞系中的结果一致, 提示NCEH1与肝癌细胞的侵袭转移相关。本研究采用慢病毒介导的siRNA技术敲减NCEH1在SMMC-7721肝癌细胞系(该细胞系的NCEH1表达水平在笔者检测的4株肝癌细胞系中为最高)中的表达, 结果显示, NCEH1基因的敲减效率高达74.0%, NCEH1基因敲减的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞系得以成功建立。接下来, 本研究采用MTT生长曲线、细胞流式检测及Transwell转移和侵袭实验等一系列细胞功能实验观察NCEH1在肝癌细胞中的功能, 结果显示, NCEH1基因敲减可明显降低肝癌细胞系的增殖、转移及侵袭能力并促进凋亡, 这些结果也均与Chang等[5]在前列腺癌细胞中获得的结果一致, 提示NCEH1可能是一个潜在的肝癌治疗靶点。
对于NCEH1表达及发挥作用的分子调控机制的研究相对较少, Cheung等[19]发现在牛皮癣皮肤的皮下脂肪组织中miR-26b-5p高度上调, 而NCEH1是miR-26b-5p的直接靶点之一, miR-26b-5p可靶向下调NCEH1的表达。现有的研究显示, miR-26b-5p在不同肿瘤组织中均起着抑癌作用[20], 其在肝癌细胞系中明显下调, 且与肝癌的侵袭和转移密切相关[21-22]。而miRNA被认为可调控60%蛋白质编码基因, 并参与几乎所有细胞过程的调控[18, 23]。笔者据此推测miR-26b-5p在肝癌中也可能存在对NCEH1基因表达的负向调控, 即miR-26b-5p的下调可能促使NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的表达上调, 并因此增强了肝癌细胞的增殖、凋亡、转移及侵袭能力。然而, NCEH1在肝癌中表达升高及发挥生物学作用的具体分子机制均尚有待于进一步研究阐明。
综上所述, 本研究结果发现, NCEH1基因在肝癌组织及细胞系中的表达明显升高, 体外实验中可以促进肝癌细胞增殖、侵袭转移并抑制凋亡, 提示其可能是一个潜在的肝癌治疗靶点。
-
[1]TSENG TC, KAO JH.Clinical utility of quantitative HBs Ag in natural history and nucleos (t) ide analogue treatment of chronic hepatitis B:new trick of old dog[J].J Gastroenterol, 2013, 48 (1) :13-21. [2]YANG S, XING H, WANG Y, et al.HBs Ag and HBe Ag in the prediction of a clinical response to peginterferonα-2b therapy in Chinese HBe Ag-positive patients[J].Virol J, 2016, 13 (1) :180. [3]CHUAYPEN N, SRIPRAPUN M, PRAIANANTATHAVORN K, et al.Kinetics of serum HBs Ag and intrahepatic ccc DNA during pegylated interferon therapy in patients with HBe Ag-positive and HBe Ag-negative chronic hepatitis B[J].J Med Virol, 2017, 89 (1) :130-138. [4] Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association.The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2010 version) [J].J Clin Hepatol, 2011, 27 (1) :Ⅰ-ⅩⅥ. (in Chinese) 中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南 (2010年版) [J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2011, 27 (1) :Ⅰ-ⅩⅥ. [5]Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China.Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (V2011) [J].J Clin Hepatol, 2011, 27 (11) :1141-1159. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国卫生部.原发性肝癌诊疗规范 (2011年版) [J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2011, 27 (11) :1141-1159. [6] PEI YZ, HAN T, MA XY, et al.The discrepancy of HBs Ag titre and HBV DNA in patients with chronic hepatitis B, HBV-related liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Chin J Hepatol, 2011, 19 (10) :743-746. (in Chinese) 裴彦祯, 韩涛, 马晓艳, 等.HBs Ag及HBV DNA定量水平在慢性乙型肝炎、肝硬化和肝癌患者中的变化[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2011, 19 (10) :743-746. [7]KARRA VK, CHOWDHURY SJ, RUTTALA R, et al.Clinical significance of quantitative HBs Ag titres and its correlation with HBV DNA levels in the natural history of hepatitis B virus infection[J].J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2016, 6 (3) :209-215. [8]CHAN HL, WONG VW, WONG GL, et al.A longitudinal study on the natural history of serum hepatitis B surface antigen changes in chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology, 2010, 52 (4) :1232-1241. [9]GUPTA E, KUMAR A, CHOUDHARY A, et al.Serum hepatitis B surface antigen levels correlate with high serum HBV DNA levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B:a cross-sectional study[J].Indian J Med Microbiol, 2012, 30 (2) :150-154. [10] GAO YF, ZOU GZ, YE J, et al.Relationship between hepatitis B surface antigen, HBV DNA quantity and liver fibrosis severity[J].Chin J Hepatol, 2015, 23 (4) :254-257. (in Chinese) 郜玉峰, 邹桂舟, 叶珺, 等.HBs Ag和HBV DNA定量水平与肝纤维化程度的关系[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2015, 23 (4) :254-257. [11]CHEN XF, CHEN XP, MA XJ, et al.Relationship between serum HBs Ag level and liver histological features in chronic HBV infection patients with low ALT levels[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31 (10) :1688-1691. (in Chinese) 陈学福, 陈小苹, 马晓军, 等.低ALT水平的慢性HBV感染者血清HBs Ag水平与肝组织学的相关性[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31 (10) :1688-1691. [12]WANG XL, ZOU GZ, YE J, et al.Quantitation value of HBs Ag in different clinical stages of chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J].J Pract Med, 2014, 30 (17) :2765-2767. (in Chinese) 王晓琳, 邹桂舟, 叶珺, 等.乙肝表面抗原在慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染临床不同阶段的变化[J].实用医学杂志, 2014, 30 (17) :2765-2767. [13]CHEN W, WU F, DOU XG, et al.Analysis of related factors for intrahepatic HBV ccc DNA level in patients with chronic HBV infection[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2013, 29 (6) :434-437. (in Chinese) 陈嵬, 吴峰, 窦晓光, 等.慢性HBV感染者肝脏HBV ccc DNA含量相关因素分析[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2013, 29 (6) :434-437. [14] HAN XY, CHEN XJ, YAN ZQ, et al.Correlation among HBs Ag and HBV DNA levels with liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis B[J].Int J Virol, 2016, 23 (1) :50-52, 56. (in Chinese) 韩晓颖, 陈秀记, 闫泽强, 等.血清HBs Ag与HBV DNA水平与乙肝患者肝纤维化程度的相关性分析[J].国际病毒学杂志, 2016, 23 (1) :50-52, 56. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李晶津,王佳玉,金泽宁. 昼夜节律对肝脏胆固醇代谢的影响. 中西医结合肝病杂志. 2022(12): 1110-1113 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1755 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1755 KB)


 下载:
下载:






 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: