Radiological evaluation of the reversal of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
-
摘要: 以肝活组织检查组织学评分为参照金标准,非创伤性肝纤维化评估方法已获得较广泛验证。阐述了多种影像学方法在肝纤维化评估中的应用及其评估肝纤维化逆转的应用前景。影像学方法评估肝纤维化逆转主要集中在瞬时弹性成像技术,通过肝硬度监测提示抗肝纤维化的改善情况,但肝硬度降低程度与肝纤维化组织学改善之间的相关性仍未完全明确。Abstract: Noninvasive methods for the evaluation of liver fibrosis have been widely validated with liver biopsy as the gold standard. This article elaborates on the application of various imaging methods in the evaluation of liver fibrosis and their prospects in evaluating the reversal of liver fibrosis. Transient elastography is the main imaging method for evaluating the reversal of liver fibrosis and can show the improvement in liver fibrosis via liver stiffness measurement, but the association between the reduction in liver stiffness measurement and the improvement of liver fibrosis remains unclear.
-
Key words:
- liver cirrhosis /
- diagnostic imaging
-
肝细胞癌(HCC)是我国最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。国家癌症中心最新数据显示,我国每年新发肝癌约37万人,约32.6万人死于肝癌,其中94.7%与慢性HBV感染有关[1-2]。早期发现、早期诊断和早期治疗是改善原发性肝癌预后的关键。然而目前尚缺乏原发性肝癌高敏感度和高特异度的诊断指标。自噬是细胞自我吞噬胞内长寿蛋白或受损细胞器并通过溶酶体途径进行的分解代谢过程,从而维持细胞稳态[3]。近年研究[4-7]显示自噬在HBV感染和HCC的发生发展起重要作用。但目前关于自噬相关蛋白在HBV相关HCC(HBV-HCC)患者血清中的表达及意义鲜有报道。本研究通过分析HBV-HCC、非HBV相关HCC(nonHBV-HCC)、慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)和健康对照者血清自噬相关蛋白7(ATG7)的表达水平,探讨ATG7对HBV-HCC的诊断价值。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2018年6月—2020年12月于本院住院的HCC患者89例。HCC的诊断标准符合《原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2017年版)》[8]并经病理确认。排除标准如下:病理类型为肝内胆管癌或HCC-肝内胆管癌混合型者;已接受过肝移植术、局部消融、肝动脉化疗栓塞术、放化疗等抗肿瘤治疗者;继发性HCC患者;同时伴有其他肿瘤患者。CHB诊断符合《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)》[9]。根据血清是否检出HBsAg和/或HBV DNA分为HBV-HCC组及nonHBV-HCC组。选取同期50例CHB患者(CHB组)和20例健康体检者作为对照组(HC组)。
1.2 资料收集
收集研究对象性别和年龄,总蛋白(TP)、白蛋白(Alb)、TBil、DBil、ALT、AST、GGT和ALP等实验室指标。另收集HBV-HCC组患者的BCLC分期和肿瘤直径等病理资料。
1.3 血清ATG7检测
所有研究对象清晨空腹肘静脉采血,采血后1 h内送实验室,3000 r/min离心10 min分离血清,-80 ℃冰箱保存。ATG7检测前4 h室温下复溶。使用上海江莱生物技术有限公司人ATG7酶联免疫吸附测定试剂盒(批号:Aug 2020)进行检测,严格按试剂盒说明书操作,在加入终止液15 min内用PHOMO酶标仪(安图生物,合肥)在450 nm波长测定各孔光密度(OD值),用WPS表格以标准品的浓度为纵坐标,OD值为横坐标绘制标准曲线并取得多项式公式,根据多项式公式计算每个样本的ATG7浓度。
1.4 伦理学审查
本研究方案经由福建医科大学孟超肝胆医院伦理委员会审批,批号:科审2020-029-01。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0进行统计分析。非正态分布的计量资料以M(P25~P75)表示,多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,2组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验;计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验;采用Spearman进行相关性分析。运用GraphPad Prism7.0绘制散点图,采用Medcalc18.11.3绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)并比较不同指标曲线下面积(AUC)。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
HCC、CHB及HC 3组比较,男女比例差异无统计学意义,其余指标差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.01)(表 1)。89例HCC患者中,67例(75.28%)血清HBsAg和/或HBV DNA阳性,纳入HBV-HCC组;剩余22例(24.72%)纳入nonHBV-HCC组,包括5例酒精性肝硬化,8例非酒精性脂肪肝,1例慢性丙型肝炎,2例肝硬化(病因未明),6例慢性肝炎(病因未明)。HBV-HCC组血清TBil水平及具有肝硬化背景病例数高于nonHBV-HCC组,而nonHBV-HCC组的血清AST水平和最大肿瘤直径高于HBV-HCC组,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05),其余参数差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)(表 2)。
表 1 3组人口学和实验室特征比较参数 HCC组(n=89) CHB组(n=50) HC组(n=20) χ2值 P值 年龄(岁) 56.0(48.0~66.5) 42.0(32.8~52.5) 37.5(30.0~48.8) 38.807 <0.001 男性[例(%)] 77(86.52) 38(76.00) 13(65.00) 5.480 0.076 TBil(μmol/L) 19.30(12.65~26.10) 19.55(12.78~29.28) 12.15(9.48~18.63) 10.478 0.005 DBil(μmol/L) 7.60(4.70~10.85) 4.45(2.20~7.05) 5.30(4.15~6.35) 17.168 <0.001 TP(g/L) 61.0(54.5~67.5) 66.5(60.8~73.3) 72.0(70.0~77.0) 34.168 <0.001 Alb(g/L) 34.0(31.0~38.5) 37.5(34.0~41.0) 44.0(41.0~47.0) 42.516 <0.001 ALT(U/L) 115.0(62.0~218.5) 87.5(26.5~206.8) 19.0(12.3~26.5) 37.212 <0.001 AST(U/L) 149.0(54.0~286.0) 57.0(31.5~110.5) 17.0(14.3~20.0) 54.345 <0.001 GGT(U/L) 52.0(34.0~110.5) 68.5(29.3~112.0) 17.0(14.3~24.5) 31.527 <0.001 ALP(U/L) 81.0(60.5~103.0) 102.0(82.5~117.0) 66.5(52.8~88.3) 21.160 <0.001 AFP(ng/mL) 37.90(5.00~712.32) 7.20(3.05~241.27) 2.85(2.18~4.48) 33.048 <0.001 ATG7(ng/mL) 21.11(17.76~22.73) 19.21(16.65~20.82) 13.82(8.70~17.82) 33.134 <0.001 表 2 HBV-HCC组与nonHBV-HCC组生化和病理特征比较参数 HBV-HCC组(n=67) nonHBV-HCC组(n=22) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 55.0(46.0~ 65.0) 63.5(50.8~71.8) U=535.000 0.055 男/女(例) 58/9 19/3 χ2=0.001 0.981 TBil(μmol/L) 20.60(13.30~27.40) 16.00(11.15~21.48) U=524.500 0.043 DBil(μmol/L) 7.70(4.80~10.90) 7.15(3.80~9.65) U=602.500 0.201 TP(g/L) 61.0(50.0~67.0) 58.5(51.3~68.3) U=638.500 0.348 Alb(g/L) 34.0(31.0~38.0) 33.0(30.3~39.0) U=709.500 0.793 ALT(U/L) 95.0(54.0~198.0) 152.0(89.8~268.0) U=557.000 0.087 AST(U/L) 136.0(37.0~240.0) 236.5(93.8~348.8) U=523.000 0.042 GGT(U/L) 51.0(30.0~111.0) 58.0(35.0~113.3) U=658.000 0.452 ALP(U/L) 76.0(60.0~99.0) 92.0(62.8~127.8) U=575.500 0.124 AFP(ng/mL) 58.00(7.10~945.80) 18.28(2.48~405.33) U=536.500 0.057 BCLC(A/B/C/D,例) 51/4/12/0 12/5/5/0 χ2=5.229 0.073 最大肿瘤直径(cm) 3.95(2.50~7.70) 8.00(3.70~11.00) U=520.000 0.047 肝硬化[例(%)] 55(82.09) 9(40.91) χ2=13.904 <0.001 2.2 HBV-HCC血清ATG7表达水平升高
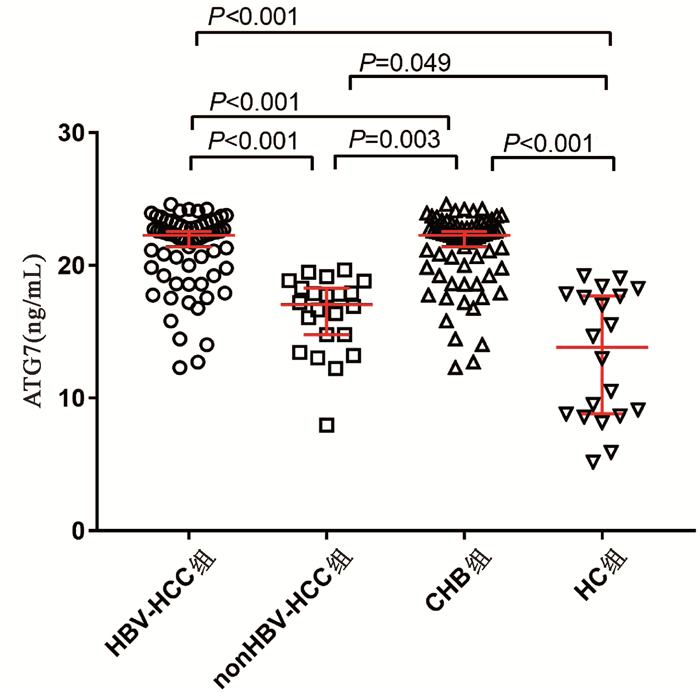
HBV- HCC组、nonHBV-HCC组、CHB组和HC组血清ATG7水平分别为22.88(19.79~23.04)ng/mL、17.06(14.45~19.40)ng/mL、19.21(16.65~20.82)ng/mL和13.82(8.70~17.82)ng/mL,差异有统计学意义(χ2=65.144,P<0.001)。两两比较显示HBV-HCC组血清ATG7不仅高于CHB组(U=758.5,P<0.001)和HC组(U=94.0,P<0.001),也高于nonHBV-HCC组(U=142.0,P<0.001);而nonHBV-HCC组血清ATG7水平不仅低于HBV-HCC组,也低于CHB组(U=311.0,P=0.003),仅稍高于HC组(U=142.0,P=0.049)(图 1)。此外,在67例HBV-HCC患者中,有肝硬化背景和无肝硬化背景患者的血清ATG7水平分别为22.32 (19.79~22.99)ng/mL和20.89(19.40~23.37)ng/mL,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.3 血清ATG7表达水平和血清AFP水平的相关性
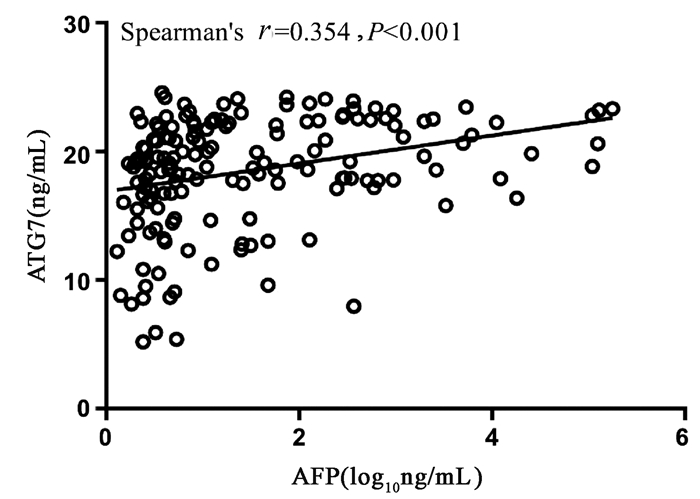
Spearman相关性分析显示,血清ATG7表达水平和血清AFP水平呈正相关,但相关性较弱(r=0.354,95%CI:0.205~0.486,P<0.001)(图 2)。
2.4 ATG7在HBV-HCC中的诊断性能
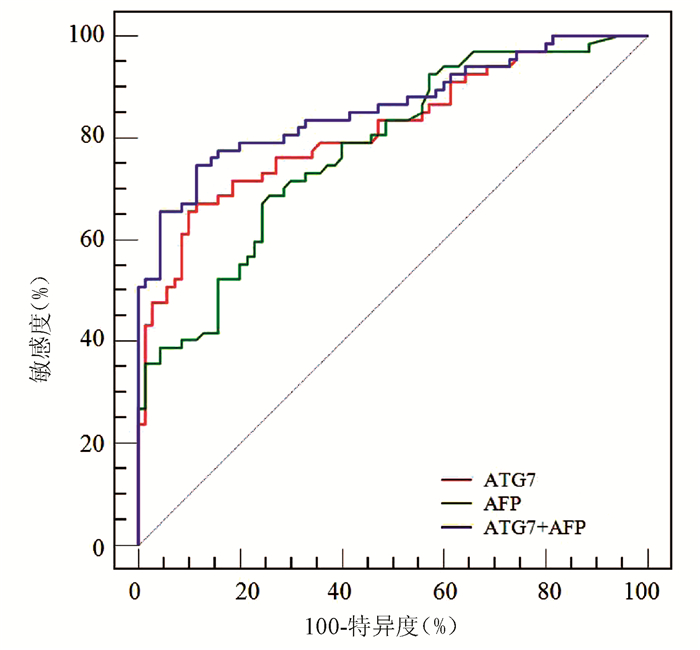
ROC曲线分析显示,ATG7诊断HBV-HCC的AUC为0.818(95% CI:0.743~0.879),稍高于AFP(AUC=0.777,95%CI:0.698~0.843),但二者差异无统计学意义(Z=0.852,P=0.394)(图 3);ATG7诊断HBV-HCC的cut-off值为20.08 ng/mL,敏感度和特异度分别为71.64%和77.14%,均略高于AFP(68.66%和74.29%)。ATG7联合AFP的二元logistic回归预测概率的AUC为0.859 (95%CI:0.790~0.913),显著高于ATG7(Z=2.192,P=0.028)和AFP(Z=2.076,P=0.038)(图 3, 表 3)。
表 3 ATG7、AFP及其联合检测诊断HBV-HCC的性能项目 AUC cut-off值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) AFP 0.777 12.20 ng/mL 68.66 74.29 71.9 71.2 ATG7 0.818 20.08 ng/mL 71.64 77.14 75.0 74.0 ATG7+AFP 0.859 0.56 74.63 88.57 86.2 78.5 3. 讨论
本研究通过ELISA技术检测HCC患者血清ATG7表达水平,结果显示HBV-HCC患者血清ATG7显著升高,血清ATG7是诊断HBV-HCC的良好标志物,ATG7与AFP联合诊断可显著提高HBV-HCC的诊断效率。
ATG7作为一种泛素样修饰物激活酶,通过激活ATG8和ATG12调节自噬体的延伸,是自噬体形成过程的关键蛋白之一[10]。近年研究[11-12]提示ATG7及自噬在HBV-HCC发生发展中发挥重要作用。首先,HBV感染或HBV病毒蛋白的表达可诱导ATG7表达及自噬反应。本研究中CHB组血清ATG7显著高于健康对照组,印证了自噬与HBV感染有关。其次,多项研究[13-14]显示包括ATG7在内的多种自噬相关蛋白在HCC组织表达显著提高。近年的分子细胞学试验进一步揭示多种分子可通过ATG7调节自噬促进HCC发生发展[15-17]。研究[15]显示长链非编码RNA HOX转录反义RNA(HOTAIR)可通过上调ATG7表达激活自噬促进HCC细胞系增殖。癌性锚蛋白重复序列可直接与胞质中的ATG7蛋白相互作用诱导自噬从而促进HCC细胞进展[16]。肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白8(TNFAIP8)则通过与ATG3-ATG7复合物相互作用调节自噬促进HCC细胞增殖[17]。相反,靶向敲减ATG7可抑制自噬,从而促进细胞凋亡、延缓细胞周期及抑制HCC细胞增殖[13]。上述研究结果表明ATG7与HBV-HCC密切相关。本研究数据显示HBV-HCC患者血清ATG7显著高于CHB和健康对照组,进一步证实了自噬与HBV-HCC的相关性,提示血清ATG7是一种潜在HBV-HCC标志物。而且HBV-HCC患者血清ATG7也显著高于nonHBV-HCC,提示不同病因的HCC发病机制不同,其血清标志物也可不同。
虽然AFP已在临床应用数十年,但诊断敏感度不高。最近的一项系统综述[18]显示,AFP诊断HCC的合并敏感度仅为63.9%。与此相符,本研究中AFP诊断HBV-HCC的敏感度、特异度和AUC分别为68.66%、74.29%和0.777。虽然ATG7的敏感度与AFP相仿,但其特异度较高,总体诊断性能较好。此外,ATG7和AFP相关性较弱,提示二者联合检测可有效提高诊断性能。早前有学者[19]提出应用logistic回归分析有助于提高多指标联合诊断效率。本研究结果显示ATG7联合AFP的二元logistic回归预测模型对HBV-HCC的整体诊断性能较好,AUC及诊断敏感度和特异度均显著高于ATG7及AFP。
总之,本研究显示ATG7是HBV-HCC的良好标志物,与AFP有较好的互补性,二者联合检测可显著提高HBV-HCC的诊断效率。然而本研究为单中心横断面研究,纳入研究病例有限,因此其诊断性能仍有待进一步扩大样本的多中心临床验证。
-
[1]EUGENE R, SCHIFF, MICHAEL F. Schiff's hepatology[M].1th, HUANG ZQ. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2006:263. (in Chinese) Eugene R, Schiff, Michael F.希夫肝脏病学[M]. 1版, 黄志强, 译.北京:化学工业出版社, 2006:263. [2]ALLAN R, THOIRS K, PHILLIPS M. Accuracy of ultrasound to identify chronic liver disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16 (28) :3510-3520. [3]CHEN YP, DAI L, WANG JL, et al. Model consisting of ultrasonographic and simple blood indexes accurately identify compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2008, 23 (8) :1228-1234. [4]HUNG CH, LU SN, WANG JH, et al. Correlation between ultrasonographic and pathologic diagnoses of hepatitis B and C virus-related cirrhosis[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2003, 38 (2) :153-157. [5]MOON KM, KIM G, BAIK SK, et al. Ultrasonographic scoring system score versus liver stiffness measurement in prediction of cirrhosis[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2013, 19 (4) :389-398. [6]BARR RG, FERRAIOLI G, PALMERI ML, et al. Elastography assessment of liver fibrosis, society of radiologists in ultrasound consensus conference statement[J]. Ultrasound Q, 2016, 32 (2) :94-107. [7]FERRAIOLI G, WONG VWS, CASTERA L, et al. Liver Ultrasound elastography:An update to the world federation for ultrasound in medicine and biology guideline and recommendation[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2018, 44 (12) :2419-2440. [8]FRAQUELLI M, RIGAMONTI C, CASAZZA G, et al. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Gut, 2007, 56:968-973. [9]CHEN YP, PENG J, HOU JL. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatol Int, 2013, 7 (2) :356-368. [10]Review Panel for Liver Stiffness Measurement. Recommendations for the clinical application of transient elastography in liver fibrosis assessment[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2013, 21 (6) :420-424. (in Chinese) 肝脏硬度评估小组.瞬时弹性成像技术诊断肝纤维化专家意见[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2013, 21 (6) :420-424. [11]LIANG XE, CHEN YP, ZHANG Q, et al. Dynamic evaluation paralleled with bilirubin and ALT normalization to improve diagnostic accuracy of Fibroscan in patients with hepatitis B exacerbation[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2011, 18 (12) :884-891. [12] CHAN HL, WONG GL, CHOI PC, et al. Alanine aminotransferase-based algorithms of liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography (Fibroscan) for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2009, 16 (1) :36-44. [13]CHEN YP, LIANG XE, DAI L, et al. Improving transient elastography performance for detecting hepatitis B cirrhosis[J].Dig Liver Dis, 2012, 44 (1) :61-66. [14]CHEN YP, LIANG XE, ZHANG Q, et al. Larger biopsies evaluation of transient elastography for detecting advanced fibrosis in patients with compensated chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 27 (7) :1219-1226. [15]HALL TJ, MILKOWSKI A, GARRA B, et al. RSNA/QIBA:Shear wave speed as a biomarker for liver fibrosis staging[J]. Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS) , 2013, 2013:397-400. [16]FRIEDRICH-RUST M, NIERHOFF J, LUPSOR M, et al. Performance of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis:A pooled meta-analysis[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2012, 19 (2) :e212-e219. [17]BOTA S, HERKNER H, SPOREA I, et al. Meta-analysis:ARFI elastography versus transient elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33 (8) :1138-1147. [18]HUANG Z, ZHENG J, ZENG J, et al. Normal liver stiffness in healthy adults assessed by real-time shear wave elastography and factors that influence this method[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2014, 40 (11) :2549-2555. [19]LEUNG VY, SHEN J, WONG VW, et al. Quantitative elastography of liver fibrosis and spleen stiffness in chronic hepatitis B carriers:Comparison of shear-wave elastography and transient elastography with liver biopsy correlation[J]. Radiology, 2013, 269 (3) :910-918. [20]CASSINOTTO C, LAPUYADE B, MOURIES A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis with impulse elastography:Comparison of supersonic shear imaging with ARFI and FibroScan[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 61 (3) :550-557. [21]MANNING DS, AFDHAL NH. Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134 (6) :1670-1681. [22]HOODESHENAS S, YIN M, VENKATESH SK. Magnetic resonance elastography of liver:Current update[J]. Top Magn Reson Imaging, 2018, 27 (5) :319-333. [23]SINGH S, VENKATESH SK, WANG Z, et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis:A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13 (3) :440-451. e6. [24] WANLESS IR, NAKASHIMA E, SHERMAN M, et al. Regression of human cirrhosis. Morphologic features and the genesis of incomplete septal cirrhosis[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2000, 12490 (11) :1599-1607. [25]HYTIROGLOU P, THEISE ND. Regression of human cirrhosis:An update, 18 years after the pioneering article by Wanless et al[J]. Virchows Archiv, 2018, 473 (1) :15-22. [26]ENOMOTO M, MORI M, OGAWA T, et al. Usefulness of transient elastography for assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B:Regression of liver stiffness during entecavir therapy[J]. Hepatol Res, 2010, 40 (9) :853-861. [27]WONG GL, WONG VW, CHOI PC, et al. On-treatment monitoring of liver fibrosis with transient elastography in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Antivir Ther, 2011, 16 (2) :165-172. [28]DONG XQ, WU Z, LI J, et al. Declining in liver stiffness can not indicate fibrosis regression in patients with chronic hepatitis B:A 78-week prospective study[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018.[Epub ahead of print] [29]LIANG X, TAN D, XIE Q, et al. Interpretation of liver stiffness measurement-based approach for the monitoring of hepatitis B patients with antiviral therapy:A 2-year prospective study[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25 (3) :296-305. [30]CHAN HL, WONG GL, CHOI PC, et al. Alanine aminotransferasebased algorithms of liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography (Fibroscan) for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2009, 16 (1) :36-44. [31] SUN Y, ZHOU J, WANG L, et al. New classification of liver biopsy assessment for fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients before and after treatment[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65 (5) :1438-1450. [32]KONG Y, SUN Y, ZHOU J, et al. Early steep decline of liver stiffness predicts histological reversal of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with entecavir[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2019.[Epub ahead of print] [33]MAURO E, CRESPO G, MONTIRONI C, et al. Portal pressure and liver stiffness measurements in the prediction of fibrosis regression after sustained virological response in recurrent hepatitis C[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67 (5) :1683-1694. [34]HARTL J, EHLKEN H, SEBODE M, et al. Usefulness of biochemical remission and transient elastography in monitoring disease course in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68 (4) :754-763. [35]European Association for the Study of the Liver, Asociación Latinoamericana parael Estudio del Hígado. EASL-ALEH clinical practice guidelines:Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63:237-264. [36]PINZANI M. Liver fibrosis in the post-HCV era[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2015, 35 (2) :157-165. [37]WU S, KONG Y, PIAO H, et al. On-treatment changes of liver stiffness at week 26 could predict 2-year clinical outcomes in HBV-related compensated[J]. Liver Int, 2018, 38 (6) :1045-1054. [38]HEZODE C, CASTERA L, ROUDOT-THORAVAL F, et al. Liver stiffness diminishes with antiviral response in chronic hepatitis C[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 34 (6) :656-663. [39]KIM SU, PARK JY, KIM DY, et al. Non-invasive assessment of changes in liver fibrosis via liver stiffness measurement in patients with chronic hepatitis B:Impact of antiviral treatment on fibrosis regression[J]. Hepatol Int, 2010, 4 (4) :673-680. [40]D’AMBROSIO R, AGHEMO A, FRAQUELLI M, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of Fibroscan for cirrhosis is influenced by liver morphometry in HCV patients with a sustained virological response[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59 (2) :251-256. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 郭佳佳,张文果,王文秀,张晓丽,马徜徉. 血清Nox2、ATG7水平对新生儿窒息心肌损伤的评估价值. 安徽医药. 2024(09): 1791-1795 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 蔡卓玮,胡刚峰,章波. miR-203在乙型肝炎病毒相关肝细胞癌诊断及预后中的意义. 广西医科大学学报. 2022(11): 1773-1780 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1987 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1987 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: