胰高血糖素样肽1受体激动剂在非酒精性脂肪性肝病治疗中的作用及相关机制
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.043
作者贡献声明:俞晓菡负责课题设计,资料分析,撰写论文;王雨露、许笑阳参与收集数据;平键、赵长青负责拟定写作思路,修改论文,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and related mechanism
-
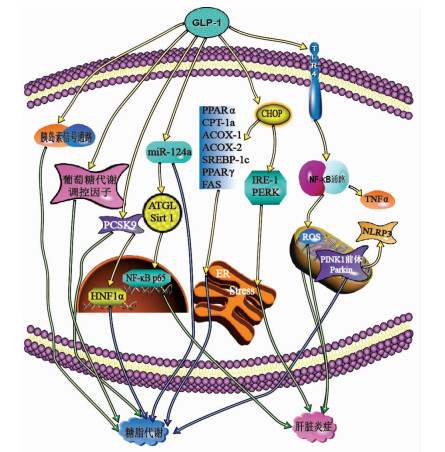
摘要: 非酒精性脂肪性肝病在全球发病率持续上升,由于其复杂的发病机制,尚未开发出有效的治疗药物。该病若未得到及时治疗,可能加剧糖尿、高血脂等相关代谢性疾病发生的风险,严重会导致肝纤维化,甚至发生肝硬化。胰高血糖素样肽-1是小肠L型细胞分泌的一种激素,具有调节葡萄糖依赖性的胰岛素分泌刺激,减少胃排空,抑制食物摄取等作用。综述了胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂对非酒精性脂肪性肝病的治疗作用及其相关机制。
-
关键词:
- 非酒精性脂肪性肝病 /
- 胰高血糖素样肽-1受体 /
- 药理作用分子作用机制
Abstract: The incidence rate of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) continues to rise around the world, and due to its complex pathogenesis, there is still a lack of effective treatment drugs. If NAFLD is not treated in time, it may increase the risk of related metabolic diseases such as diabetes and hyperlipidemia and even lead to liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis. Glucagon-like peptide-1 is a hormone secreted by L-shaped cells of the small intestine and can regulate glucose-dependent stimulation of insulin secretion, reduce gastric emptying, and inhibit food intake. This article reviews the effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in the treatment of NAFLD and related mechanism. -
[1] ESLAM M, SANYAL AJ, GEORGE J, et al. MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(7): 1999-2014. e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312 [2] IQBAL U, PERUMPAIL BJ, AKHTAR D, et al. The epidemiology, risk profiling and diagnostic challenges of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Medicines (Basel), 2019, 6(1): 41. [3] ATHYROS VG, POLYZOS SA, KOUNTOURAS J, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; new kids on the block[J]. Curr Vasc Pharmacol, 2020, 18(2): 172-181. DOI: 10.2174/1570161117666190405164313 [4] YANG Z, FU BS. Research status of liver transplantation in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Ogran Transplantation, 2020, 11(3): 419-423. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2020.03.017杨洲, 傅斌生. 肝移植治疗非酒精性脂肪性肝病的研究现状[J]. 器官移植, 2020, 11(3): 419-423. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2020.03.017 [5] ZHOU F, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4): 1119-1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702 [6] LIU Q, NIU CY. From "two hit theory" to "multiple hit theory": Implications of evolution of pathogenesis concepts for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2019, 27(19): 1171-1178. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXHB201919001.htm刘勤, 牛春燕. 由"二次打击"到"多重打击":发病机制的演变带给非酒精性脂肪性肝病的治疗启示[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2019, 27(19): 1171-1178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXHB201919001.htm [7] GAO X. New thoughts about renaming nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(6): 1201-1204. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.06.001高鑫. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病更名带来的新思考[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(6): 1201-1204. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.06.001 [8] ZHOU Q, SU J, JI MY. Progress in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. China Med Herald, 2020, 17(6): 26-29. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202006008.htm周谦, 苏娟, 季梦遥. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的治疗研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2020, 17(6): 26-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202006008.htm [9] MVLLER TD, FINAN B, BLOOM SR, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)[J]. Mol Metab, 2019, 30: 72-130. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.09.010 [10] BAGGIO LL, DRUCKER DJ. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP[J]. Gastroenterology, 2007, 132(6): 2131-2157. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.054 [11] BULLOCK BP, HELLER RS, HABENER JF. Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor[J]. Endocrinology, 1996, 137(7): 2968-2978. DOI: 10.1210/endo.137.7.8770921 [12] RICHARDS P, PARKER HE, ADRIAENSSENS AE, et al. Identification and characterization of GLP-1 receptor-expressing cells using a new transgenic mouse model[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(4): 1224-1233. DOI: 10.2337/db13-1440 [13] CANTINI G, MANNUCCI E, LUCONI M. Perspectives in GLP-1 Research: New targets, new receptors[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 27(6): 427-438. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.017 [14] XIAO C, BANDSMA RH, DASH S, et al. Exenatide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, acutely inhibits intestinal lipoprotein production in healthy humans[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2012, 32(6): 1513-1519. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.246207 [15] HSIEH J, LONGUET C, BAKER CL, et al. The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor is essential for postprandial lipoprotein synthesis and secretion in hamsters and mice[J]. Diabetologia, 2010, 53(3): 552-561. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1611-5 [16] SHARMA D, VERMA S, VAIDYA S, et al. Recent updates on GLP-1 agonists: Current advancements & challenges[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 108: 952-962. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.088 [17] KHOO J, HSIANG J, TANEJA R, et al. Comparative effects of liraglutide 3 mg vs structured lifestyle modification on body weight, liver fat and liver function in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot randomized trial[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2017, 19(12): 1814-1817. DOI: 10.1111/dom.13007 [18] ARMSTRONG MJ, HULL D, GUO K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 decreases lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(2): 399-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.038 [19] PETIT JM, CERCUEIL JP, LOFFROY R, et al. Effect of liraglutide therapy on liver fat content in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: the lira-NAFLD study[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2017, 102(2): 407-415. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=19d6760c2234e3c8576ae4a3f8dbe431 [20] SHAO N, KUANG HY, HAO M, et al. Benefits of exenatide on obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with elevated liver enzymes in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2014, 30(6): 521-529. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.2561 [21] ARMSTRONG MJ, GAUNT P, AITHAL GP, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10019): 679-690. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X [22] EGUCHI Y, KITAJIMA Y, HYOGO H, et al. Pilot study of liraglutide effects in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with glucose intolerance in Japanese patients (LEAN-J)[J]. Hepatol Res, 2015, 45(3): 269-278. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12351 [23] SEKO Y, SUMIDA Y, TANAKA S, et al. Effect of 12-week dulaglutide therapy in Japanese patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Hepatol Res, 2017, 47(11): 1206-1211. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12837 [24] RAHMAN K, LIU Y, KUMAR P, et al. C/EBP homologous protein modulates liraglutide-mediated attenuation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Lab Invest, 2016, 96(8): 895-908. DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.61 [25] LAKOSKI SG, LAGACE TA, COHEN JC, et al. Genetic and metabolic determinants of plasma PCSK9 levels[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2009, 94(7): 2537-2543. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2009-0141 [26] YANG SH, LI S, ZHANG Y, et al. Positive correlation of plasma PCSK9 levels with HbA1c in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2016, 32(2): 193-199. DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.2712 [27] DONG B, SINGH AB, AZHAR S, et al. High-fructose feeding promotes accelerated degradation of hepatic LDL receptor and hypercholesterolemia in hamsters via elevated circulating PCSK9 levels[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2015, 239(2): 364-374. DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.01.013 [28] YANG SH, XU RX, CUI CJ, et al. Liraglutide downregulates hepatic LDL receptor and PCSK9 expression in HepG2 cells and db/db mice through a HNF-1a dependent mechanism[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2018, 17(1): 48. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-018-0689-9 [29] FANG QH, SHEN QL, LI JJ, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-124a attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through upregulation of adipose triglyceride lipase and the effect of liraglutide intervention[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49(7): 743-757. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30861258 [30] CHIKKA MR, MCCABE DD, TYRA HM, et al. C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) contributes to suppression of metabolic genes during endoplasmic reticulum stress in the liver[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(6): 4405-4415. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432344 [31] SZEGEZDI E, LOGUE SE, GORMAN AM, et al. Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis[J]. EMBO Rep, 2006, 7(9): 880-885. DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400779 [32] RUTKOWSKI DT, WU J, BACK SH, et al. UPR pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators[J]. Dev Cell, 2008, 15(6): 829-840. DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.015 [33] YU X, HAO M, LIU Y, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis activation via mitophagy[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 864: 172715. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172715 [34] SATHYANARAYAN A, MASHEK MT, MASHEK DG. ATGL promotes autophagy/lipophagy via SIRT1 to control hepatic lipid droplet catabolism[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 19(1): 1-9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28380348/ [35] SAAD ZA, KHODEER DM, ZAITONE SA, et al. Exenatide ameliorates experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats via suppression of toll-like receptor 4/NFκB signaling: Comparison to metformin[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 253: 117725. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117725 -



 PDF下载 ( 2390 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2390 KB)

 下载:
下载:


