肝包虫病影像学诊断专家共识
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.04.014
Expert consensus on the imaging diagnosis of hepatic echinococcosis
-
摘要: 包虫病是呈全球性分布的人畜共患性疾病,已成为严重危害全世界公共卫生健康的问题。影像学技术在肝包虫病的早期诊断、术前评价及疗效监测方面发挥着至关重要的作用。目前包虫病影像诊断缺乏统一共识,不利于影像专业人员学习培训以及临床对于包虫病的规范诊断与治疗,为此由首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院和新疆医科大学第一附属医院联合多家医院的感染与炎症放射学专家,在充分学习国际指南、文献以及国内外最新研究成果的基础上,结合循证医学对建立指南及标准的方法学要求,针对肝包虫病影像学诊断依据、诊断原则、诊断标准和鉴别诊断形成共识,为临床医师在肝包虫病影像学临床应用中提供明确的诊断依据。Abstract: Echinococcosis is a zoonotic disease with global distribution and has become an issue seriously affecting public health around the world. Imaging technology plays an important role in the early diagnosis, preoperative evaluation, and treatment outcome monitoring of hepatic echinococcosis. At present, no consensus has been reached on the imaging diagnosis of echinococcosis, which brings difficulties in the learning and training of imaging professionals and the standard diagnosis and treatment of echinococcosis in clinical practice. For this reason, Beijing YouAn Hospital, Capital Medical University, and The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University organized the radiologists engaged in infection and inflammation from several hospitals to reach a consensus on the basis, principles, and criteria for the imaging diagnosis of echinococcosis and the differential diagnosis of echinococcosis, with reference to international guidelines, related articles, the latest research findings in China and globally, and the methodological requirements for the establishment of guidelines and standards in evidence-based medicine, so as to provide a clear diagnostic basis for clinicians in the clinical application of hepatic echinococcosis imaging.
-
Key words:
- Echinococcosis, Hepatic /
- Diagnosis /
- Consensus
-
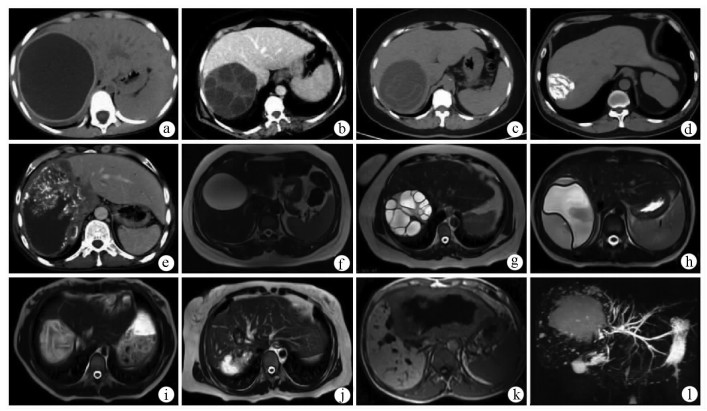
图 1 肝包虫病影像学表现
注:a为CE1型,CT平扫显示肝右叶类圆形水样密度病灶,囊壁较厚伴钙化; b为CE2型,CT增强静脉期显示多子囊型包虫囊肿呈“囊内囊”“轮辐征”; c为CE3型,CT平扫显示包虫囊肿内囊壁塌陷并漂浮在囊液中呈“飘带征”; d为CE5型,CT平扫显示囊壁及囊内容物全部钙化; e为AE,CT增强静脉期显示肝右叶不均质的实性肿块,病灶内可见小囊泡和钙化,中心可见液化坏死区,共同构成“地图征”样外观; f为CE1型,T2WI显示肝右叶边缘光滑的囊性病灶,信号均匀;囊壁呈厚薄均匀一致的低信号; g为CE2型,T2WI显示多子囊型包虫囊肿呈“囊内囊”“玫瑰花瓣征”; h为CE3型,T2WI显示塌陷的内囊悬浮于囊液中形成“飘带征”; i为CE4型,T2WI显示包虫囊肿内部信号不均匀,塌陷皱缩的内囊显示为脑回状稍低T2信号; j为CE5型,T2WI显示肝右前叶上段类圆形病灶,囊壁或囊内容物的钙化部分显示为低信号; k为AE,T1WI显示肝左叶病灶以低信号为主,病灶内的液化坏死区表现为“熔洞征”或“地图征”; l为AE,MRCP显示病灶实质内特征性的高信号“小囊泡”结构。
表 1 GRADE分级系统证据等级及推荐强度
GRADE分级系统 说明 证据级别 Ⅰ 基于横断面研究设计的诊断试验(与公认的金标准进行独立盲法的比较)的系统评价或Meta分析 Ⅱ 单个的横断面研究设计的诊断试验(与公认的金标准进行独立盲法的比较) Ⅲ 单个横断面研究设计的诊断试验(未与公认的金标准进行独立盲法的比较)或非连续性研究 Ⅳ 病例对照研究 Ⅴ 基于机制的推理或专家经验及共识 推荐强度 强 能明确显示所有病变和对疾病的定性诊断提供确切的依据支持,临床可行性强 弱 无法全部明确显示病变和对疾病的定性诊断,无法提供确切的依据支持 -
[1] QIAN MB, ZHOU XN. Walk together to combat echinococcosis[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2018, 18(9): 946. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30466-3. [2] FLISSER A. Eliminating cystic echinococcosis in the 21st century[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2018, 18(7): 703-704. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30299-8. [3] DEPLAZES P, RINALDI L, ALVAREZ ROJAS CA, et al. Global distribution of alveolar and cystic echinococcosis[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017, 95: 315-493. DOI: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.11.001. [4] LI HJ. Radiology of infectious disease: Volume 2[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2016. [5] LI HJ. Radiology of parasitic diseases[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016.李宏军. 寄生虫病影像学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. [6] PICCOLI L, BAZZOCCHI C, BRUNETTI E, et al. Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus in south-eastern Romania: Evidence of G1-G3 and G6-G10 complexes in humans[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2013, 19(6): 578-582. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03993.x. [7] WEN H, VUITTON L, TUXUN T, et al. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2019, 32(2). DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00075-18. [8] BHUTANI N, KAJAL P. Hepatic echinococcosis: A review[J]. Ann Med Surg (Lond), 2018, 36: 99-105. DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2018.10.032. [9] KERN P, MENEZES DA SILVA A, AKHAN O, et al. The echinococcoses: Diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017, 96: 259-369. DOI: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.09.006. [10] CASULLI A, BARTH T, TAMAROZZI F. Echinococcus multilocularis[J]. Trends Parasitol, 2019, 35(9): 738-739. DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.05.005. [11] GOTTSTEIN B, SOBOSLAY P, ORTONA E, et al. Immunology of alveolar and cystic echinococcosis (AE and CE)[J]. Adv Parasitol, 2017, 96: 1-54. DOI: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.09.005. [12] FENG X, WEN H, ZHANG Z, et al. Dot immunogold filtration assay (DIGFA) with multiple native antigens for rapid serodiagnosis of human cystic and alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Acta Trop, 2010, 113(2): 114-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.10.003. [13] CHEN X, CHEN X, LU X, et al. The production and comparative evaluation of native and recombinant antigens for the fast serodiagnosis of cystic echinococcosis with dot immunogold filtration assay[J]. Parasite Immunol, 2015, 37(1): 10-15. DOI: 10.1111/pim.12151. [14] ZHANG W, WEN H, LI J, et al. Immunology and immunodiagnosis of cystic echinococcosis: An update[J]. Clin Dev Immunol, 2012, 2012: 101895. DOI: 10.1155/2012/101895. [15] CISAK E, SROKA J, WÓJCIK-FATLA A, et al. Evaluation of reactivity to Echinococcus spp. among rural inhabitants in Poland[J]. Acta Parasitol, 2015, 60(3): 525-529. DOI: 10.1515/ap-2015-0074. [16] TERRACCIANO L, BROZEK J, COMPALATI E, et al. GRADE system: New paradigm[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2010, 10(4): 377-383. DOI: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32833c148b. [17] CONRATHS FJ, PROBST C, POSSENTI A, et al. Potential risk factors associated with human alveolar echinococcosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2017, 11(7): e0005801. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005801. [18] CAI DM, WANG HY, WANG XL, et al. Ultrasonographic findings of small lesion of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Acta Trop, 2017, 174: 165-170. DOI: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.01.030. [19] LIU W, DELABROUSSE É, BLAGOSKLONOV O, et al. Innovation in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis imaging: Best use of old tools, and necessary evaluation of new ones[J]. Parasite, 2014, 21: 74. DOI: 10.1051/parasite/2014072. [20] STOJKOVIC M, ROSENBERGER K, KAUCZOR HU, et al. Diagnosing and staging of cystic echinococcosis: How do CT and MRI perform in comparison to ultrasound?[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2012, 6(10): e1880. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001880. [21] ZHENG J, WANG J, ZHAO J, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI for the initial viability evaluation of parasites in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: Comparison with positron emission tomography[J]. Korean J Radiol, 2018, 19(1): 40-46. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.40. [22] KANTARCI M, PIRIMOGLU B. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging findings in a growing problem: Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2014, 83(10): 1991-1992. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.07.013. [23] BULAKÇ M, KARTAL MG, Y LMAZ S, et al. Multimodality imaging in diagnosis and management of alveolar echinococcosis: An update[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2016, 22(3): 247-256. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2015.15456. [24] LI J, DONG J, YANG L, et al. Comparison of[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for evaluation of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis activity[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2018, 44(11): 2199-2208. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.06.010. [25] GHARBI HA, HASSINE W, BRAUNER MW, et al. Ultrasound examination of the hydatic liver[J]. Radiology, 1981, 139(2): 459-463. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.139.2.7220891. [26] KERN P, WEN H, SATO N, et al. WHO classification of alveolar echinococcosis: Principles and application[J]. Parasitol Int, 2006, 55 Suppl: s283-s287. DOI: 10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.041. [27] WEN H, LUAN MX, YANG WG, et al. Study on standard classification and clinical significance for hepatic echinococcosis[J]. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 2002, 25(2): 129-130. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5551.2002.02.005. [28] KODAMA Y, FUJITA N, SHIMIZU T, et al. Alveolar echinococcosis: MR findings in the liver[J]. Radiology, 2003, 228(1): 172-177. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2281020323. -



 PDF下载 ( 2065 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2065 KB)

 下载:
下载:


