二维剪切波弹性成像评价肝脾硬度对乙型肝炎肝硬化食管静脉曲张的预测价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.021
利益冲突声明:本研究不存在研究者、伦理委员会成员、受试者监护人以及与公开研究成果有关的利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王雪梅、杨学平负责课题设计,资料分析,撰写论文;王玥、王米雪参与收集数据;张瑶负责指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Clinical value of two-dimensional shear wave elastography in predicting esophageal varices in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis by evaluating liver and spleen stiffness
-
摘要:
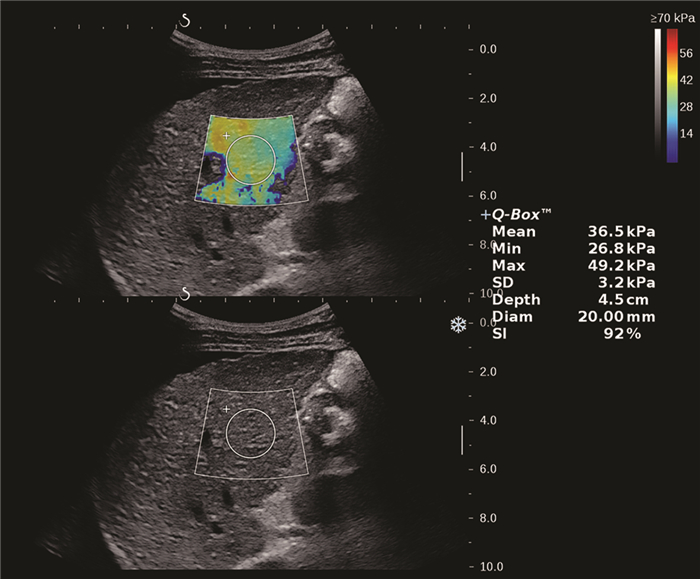
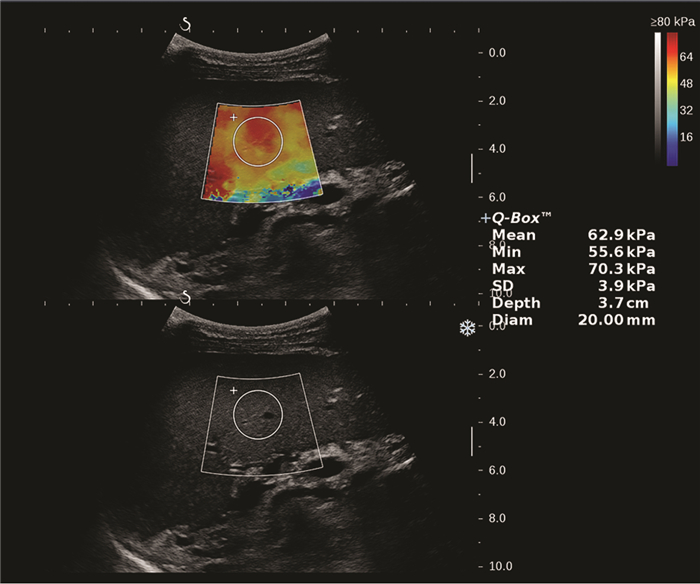
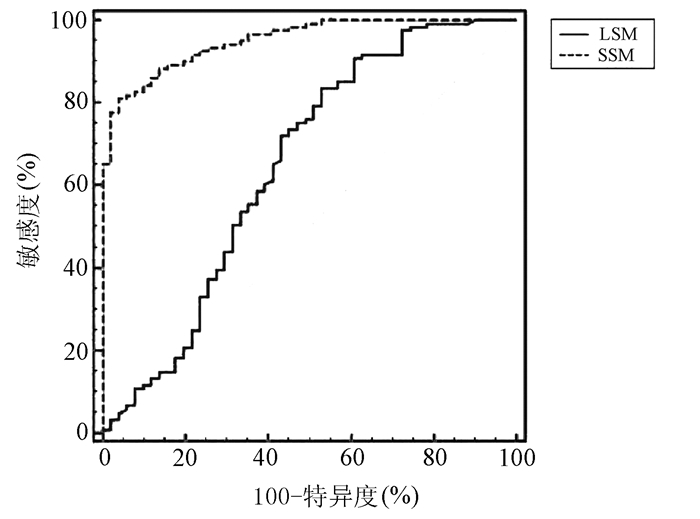
目的 应用二维剪切波弹性成像(2D-SWE)技术测量肝脾硬度(LSM/SSM),无创性评估乙型肝炎肝硬化患者是否存在食管静脉曲张(EV)。 方法 前瞻性研究2019年4月—2020年2月首都医科大学附属北京地坛医院临床诊断为乙型肝炎肝硬化的患者172例,根据胃镜结果分为两组:无EV组和EV组,比较两组患者脾脏厚径(SD)、长径(ST)、LSM及SSM值。正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用独立样本t检验;非正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。应用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价LSM、SSM诊断EV的价值,并利用Z检验比较两者的诊断准确性。 结果 EV组患者121例,无EV组51例,两组间ST(t=8.143,P<0.001)、SD(t=7.363,P<0.001)、LSM(Z=3.024,P=0.002)、SSM(t=15.142,P<0.001),有无腹水(χ2=22.101,P<0.001)差异均有统计学意义。LSM诊断EV的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.646(95%CI: 0.570~0.718),取最佳截断值13.16时,敏感度(Se)、特异度(Sp)、阳性预测值(PPV)及阴性预测值(NPV)分别为83.47%、47.06%、78.9%、54.5%;SSM诊断EV的AUC为0.951(95%CI: 0.907~0.978),取最佳截断值38.08时,Se、Sp、PPV、NPV分别为80.99%、96.08%、98.0%、68.1%。SSM诊断准确性优于LSM(Z=6.096,P<0.001)。 结论 LSM、SSM可用于预测乙型肝炎肝硬化患者有无EV,SSM具有更高的准确性,可为临床提供准确的诊断信息。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) in the noninvasive evaluation of the presence or absence of esophageal varices (EV) in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis by liver stiffness measurement (LSM) and spleen stiffness measurement (SSM). Methods A total of 172 patients who were diagnosed with hepatitis B cirrhosis in Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, from April 2019 to February 2020 were enrolled in a prospective study, and according to the results of gastroscopy, they were divided into non-EV group and EV group. The two groups were compared in terms of spleen thickness (ST), spleen diameter (SD), LSM, and SSM. The independent samples t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between two groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between two groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to investigate the value of LSM and SSM in the diagnosis of EV, and the Z test was used to compare the diagnostic accuracy of LSM and SSM. Results There were 121 patients in the EV group and 51 patients in the non-EV group. There were significant differences between the two groups in ST (t=8.143, P < 0.001), SD (t=7.363, P < 0.001), LSM (Z=3.024, P=0.002), SSM (t=15.142, P < 0.001), and presence or absence of ascites (χ2=22.101, P < 0.001). LSM had an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.646 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.570-0.718) in the diagnosis of EV, with a sensitivity (Se) of 83.47%, a specificity (Sp) of 47.06%, a positive predictive value (PPV) of 78.9%, and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 54.5% at the optimal cut-off value of 13.16. SSM had an AUC of 0.951 (95% CI: 0.907-0.978) in the diagnosis of EV, with an Se of 80.99%, an Sp of 96.08%, a PPV of 98.0%, and an NPV of 68.1% at the optimal cut-off value of 38.08. SSM had a better diagnostic accuracy than LSM (Z=6.096, P < 0.001). Conclusion LSM and SSM can be used to predict the presence or absence of EV in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis. SSM has a higher accuracy than LSM and can provide accurate diagnostic information for clinical practice. -
表 1 EV组与无EV组患者主要临床数据比较
变量 无EV组(n=51) 有EV组(n=121) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 32/19 90/31 χ2=2.236 0.125 年龄(岁) 52.25±12.21 48.96±10.45 t=1.795 0.074 ST(cm) 41.59±8.84 55.08±10.34 t=8.143 <0.001 SD(cm) 129.24±27.29 169.29±34.54 t=7.363 <0.001 LSM(kPa) 14.14(8.54~24.38) 19.94(14.50~26.90) Z=3.024 0.002 SSM(kPa) 26.57±7.47 48.41±10.92 t=15.142 <0.001 腹水(有/无,例) 8/43 66/55 χ2=22.101 <0.001 -
[1] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Endoscopy, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会内镜学分会. 肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002. [2] AI ZL, HONG S, HU JL, et al. Establishment and evaluation of a predictive model for rebleeding after endoscopic treatment of esophageal and gas-tric varices[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(9): 1954-1957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.014.艾正琳, 洪珊, 胡居龙, 等. 食管胃静脉曲张治疗后再出血预测模型的建立与评价[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(9): 1954-1957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.014. [3] GIUFFRÈ M, MACOR D, MASUTTI F, et al. Spleen stiffness probability index (SSPI): A simple and accurate method to detect esophageal varices in patients with compensated liver cirrhosis[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2020, 19(1): 53-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.aohep.2019.09.004. [4] European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(2): 406-460. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024. [5] SINGH S, FUJⅡ LL, MURAD MH, et al. Liver stiffness is associated with risk of decompensation, liver cancer, and death in patients with chronic liver diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 11(12): 1573-1584. e1-2; quiz e88-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.07.034. [6] KONDO R, KAGE M, ⅡJIMA H, et al. Pathological findings that contribute to tissue stiffness in the spleen of liver cirrhosis patients[J]. Hepatol Res, 2018, 48(12): 1000-1007. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13195. [7] CASTERA L, PINZANI M, BOSCH J. Non invasive evaluation of portal hypertension using transient elastography[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56(3): 696-703. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.07.005. [8] LI Y, SUN CY, ZHOU Y. Non-invasive diagnosis of esophageal varices in patients with cirrhosis induced by viral hepatitis[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2013, 6(3): 144-147. DOI: 10.3760/ cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2013.03.005.李焱, 孙长宇, 周言. 非侵入性检查对病毒性肝炎肝硬化食管静脉曲张的评估[J]. 中华临床感染病杂志, 2013, 6(3): 144-147. DOI: 10.3760/ cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2013.03.005. [9] ZHAO F, ZHAO J, CHEN J, et al. Comparison of diagnostic value of Fibroscan and ARFI on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2019, 11(2): 71-75. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2019.02.015.赵帆, 赵娟, 陈静, 等. Fibroscan和ARFI对慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化诊断价值比较[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(2): 71-75. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2019.02.015. [10] COSGROVE D, PISCAGLIA F, BAMBER J, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: Clinical applications[J]. Ultraschall Med, 2013, 34(3): 238-253. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1335375. [11] CASSINOTTO C, LAPUYADE B, MOURIES A, et al. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis with impulse elastography: Comparison of supersonic shear imaging with ARFI and FibroScan®[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 61(3): 550-557. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.044. [12] HU N, OU XJ. Correlation between spleen stiffness measured by FibroTouch and the parameters of liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension[J/CD]. Chin J Clin (Electronic Edition), 2016, 10(4): 468-470. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2016.04.004.胡娜, 欧晓娟. FibroTouch评价脾脏硬度与肝硬化门静脉高压参数的相关性分析[J/CD]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2016, 10(4): 468-470. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2016.04.004. [13] CASTÉRA L, GARCÍA-TSAO G. When the spleen gets tough, the varices get going[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(1): 19-22. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.11.015. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 穆亚娟,高晓霞,王蒙,贺亚妮. 维生素D3辅助阿德福韦酯及拉米夫定治疗乙型肝炎肝硬化对患者肝纤维化指标、细胞免疫的影响. 中国基层医药. 2024(06): 858-862 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2305 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2305 KB)

 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

