GGT/Alb比值对慢性HBV感染者肝纤维化的无创诊断价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.019
Value of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase/albumin ratio in the noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
-
摘要:
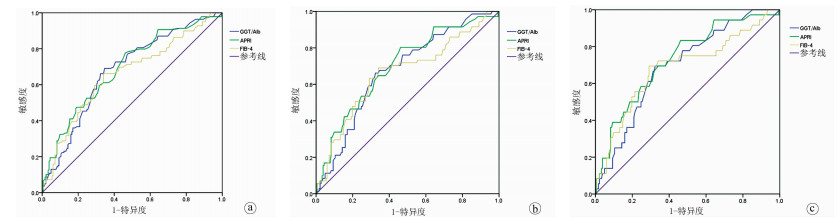
目的 评价GGT/Alb比值对慢性HBV感染者肝纤维化程度的无创诊断价值。 方法 回顾分析2018年1月—2020年3月安徽医科大学附属巢湖医院经肝穿刺活检的慢性HBV感染者资料。根据肝穿刺病理检查结果,将322例患者按照肝纤维化程度分为S0~1(183例)、S2(68例)、S3(35例)、S4(36例)。收集患者的血常规、病毒学、血生化等临床指标。正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,非正态分布的计量资料多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H秩和检验; 计数资料采用χ2检验。采用Spearman等级相关分析评估3种无创模型GGT/Alb比值、APRI评分和FIB-4指数与肝纤维化程度的相关性。绘制GGT/Alb比值的受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)评价其诊断价值。 结果 随着肝纤维化程度的加重,患者的Alb(F=7.351)、HBV DNA(χ2=2.820)和PLT(F=6.182)逐渐降低,而年龄(χ2=3.145)、GGT(χ2=6.149)、GGT/Alb比值(χ2=7.064)、APRI评分(χ2=9.022)和FIB-4指数(χ2=8.254)逐渐升高,差异有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。Spearman等级相关性分析得出,GGT/Alb比值与肝纤维化分期呈正相关(r=0.396,P<0.01),其相关系数高于APRI评分(r=0.327,P<0.01)和FIB-4指数(r=0.370,P<0.01)。ROC曲线结果显示,在显著肝纤维化、严重肝纤维化和肝硬化患者中,GGT/Alb比值的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)(分别为0.680、0.676、0.695)与APRI评分(AUC分别为0.692、0.698、0.728)和FIB-4指数(AUC分别为0.659、0.661、0.684)相当,差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。GGT/Alb比值分别以0.435、0.465和0.465为截断值,其用于诊断显著肝纤维化、严重肝纤维化和肝硬化患者的灵敏度分别为69.1%、66.2%和69.0%,特异度分别为65.4%、65.9%和67.0%。 结论 与APRI评分和FIB-4指数一样,GGT/Alb比值是一种简单、实用的肝纤维化无创诊断模型,可以对慢性HBV感染者肝纤维程度的诊断提供参考价值。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)/albumin (Alb) ratio in the noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis degree in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 322 patients with chronic HBV infection who underwent liver biopsy in Chaohu Hospital of Anhui Medical University from January 2018 to March 2020, and according to liver fibrosis degree based on liver biopsy, the 322 patients were divided into S0-S1 group with 183 patients, S2 group with 68 patients, S3 group with 35 patients, and S4 group with 36 patients. The clinical indices of routine blood test, virology, and blood biochemistry were collected. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data. A Spearman rank correlation analysis was used to investigate the correlation of the three noninvasive models GGT/Alb ratio, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) score, and fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index with liver fibrosis degree. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted for GGT/Alb ratio to evaluate its diagnostic value. Results With the aggravation of liver fibrosis degree, there were gradual reductions in Alb (F=7.351, P < 0.05), HBV DNA (χ2=2.820, P < 0.05), and platelet count (F=6.182, P < 0.05) and gradual increases in age (χ2=3.145, P < 0.05), GGT (χ2=6.149, P < 0.05), GGT/Alb ratio (χ2=7.064, P < 0.05), APRI score (χ2=9.022, P < 0.05), and FIB-4 index (χ2=8.254, P < 0.05). The Spearman rank correlation analysis showed that GGT/Alb ratio was positively correlated with liver fibrosis stage (r=0.396, P < 0.01), with a significantly higher correlation coefficient than APRI score (r=0.327, P < 0.001) and FIB-4 index (r=0.370, P < 0.001). The ROC curve analysis showed that in the patients with significant liver fibrosis, severe liver fibrosis, and liver cirrhosis, GGT/Alb ratio had similar areas under the ROC curve to APRI score and FIB-4 index (0.680/0.676/0.695 vs 0.692/0.698/0.728 and 0.659/0.661/0.684, all P > 0.05). At the optimal cut-off values of 0.435, 0.465, 0.465, respectively, GGT/Alb ratio had sensitivities of 69.1%, 66.2%, and 69.0%, respectively, and specificities of 65.4%, 65.9%, and 67.0%, respectively, in the diagnosis of significant liver fibrosis, severe liver fibrosis, and liver cirrhosis. Conclusion Like APRI score and FIB-4 index, GGT/Alb ratio is a simple and practical noninvasive model for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and can provide a reference for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis degree in patients with chronic HBV infection. -
Key words:
- Hepatitis B, Chronic /
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- gamma-Glutamyltransferase /
- Albumin
-
表 1 不同肝纤维化分期临床指标的比较
临床指标 S0~1(n=183) S2(n=68) S3(n=35) S4(n=36) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 123/60 47/21 24/11 26/10 χ2=0.378 0.954 HBeAg(阳性/阴性, 例) 121/62 48/20 23/12 25/11 χ2=0.565 0.904 年龄(岁) 35(27~45) 38(30~47) 40(36~48) 48(41~54) χ2=3.145 0.025 PLT(109/L) 176.89±48.96 165.86±52.54 157.05±48.11 140.27±53.17 F=6.182 <0.001 ALT(U/L) 28(23~35) 42(25~60) 40(25~52) 40(25~56) χ2=5.202 0.002 AST(U/L) 28(23~35) 35(28~43) 36(26~40) 35(27~40) χ2=6.457 <0.001 GGT(U/L) 16(11~30) 27(17~40) 28(15~36) 29(16~40) χ2=6.149 <0.001 Alb(g/L) 46.65±2.82 45.18±2.96 40.09±2.87 35.00±3.16 F=7.351 <0.001 HBV DNA(lg IU/ml) 5.03(3.74~5.77) 4.60(3.74~6.09) 4.34(3.53~5.71) 3.78(3.13~5.11) χ2=2.820 0.039 GGT/Alb 0.34(0.24~0.62) 0.49(0.28~0.73) 0.60(0.33~0.79) 0.71(0.46~0.97) χ2=7.064 <0.001 APRI 0.41(0.31~0.55) 0.56(0.42~0.84) 0.61(0.44~0.89) 1.18(0.82~1.67) χ2=9.022 <0.001 FIB-4 1.24(0.91~1.79) 1.55(0.94~2.61) 1.72(0.96~2.59) 1.95(1.11~2.64) χ2=8.254 <0.001 表 2 GGT/Alb比值、APRI评分和FIB-4指数对慢性HBV感染者肝纤维化程度的预测价值
指标 显著肝纤维化(n=139) 严重肝纤维化(n=71) 肝硬化(n=36) GGT/Alb APRI FIB-4 GGT/Alb APRI FIB-4 GGT/Alb APRI FIB-4 截断值 0.435 0.425 1.560 0.465 0.425 1.560 0.465 0.425 1.67 AUC 0.680 0.692 0.659 0.676 0.698 0.661 0.695 0.728 0.684 95% CI 0.621~0.738 0.634~0.750 0.598~0.719 0.605~0.747 0.626~0.770 0.583~0.739 0.607~0.782 0.639~0.817 0.581~0.787 敏感度(%) 69.1 77.7 66.2 66.2 80.3 69.0 69.0 83.3 69.4 特异度(%) 65.4 53.8 65.9 65.9 53.8 65.9 67.0 53.8 70.9 阳性似然比 2.00 1.68 1.94 2.04 1.74 2.03 2.14 1.81 2.38 阴性似然比 0.47 0.41 0.51 0.50 0.37 0.47 0.45 0.31 0.43 约登指数 0.344 0.315 0.321 0.338 0.341 0.349 0.370 0.372 0.403 -
[1] LIU XD, WU JL, LIANG J, et al. Globulin-platelet model predicts minimal fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis B virus infected patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012, 18(22): 2784-2792. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2784. [2] CUI Y, JIA J. Update on epidemiology of hepatitis B and C in China[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28(Suppl 1): 7-10. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12220. [3] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006.中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. [4] de LEDINGHEN V, VERGNIOL J, BARTHE C, et al. Noninvasive tests for fibrosis and liver stiffness predict 5-year survival of patients chronically infected with hepatitis B virus[J]. Aliment Pharm Ther, 2013, 37(10): 979-988. DOI: 10.1111/apt.12307. [5] COSKUN BD, ALTINKAYA E, SEVINC E, et al. The diagnostic value of a globulin/platelet model for evaluating liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2015, 107(12): 740-744. DOI: 10.17235/reed.2015.3851/2015. [6] ZHENG SQ, WANG QZ. Current status and prospects of research on noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 197-200. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001- 5256.2019.01.043.郑少秋, 王启之. 无创肝纤维化诊断研究现状与前景[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(1): 197-200. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001- 5256.2019.01.043. [7] ZHAO F, ZHAO J, CHEN J, et al. Comparison of diagnostic value of Fibroscan and ARFI on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2019, 11(2): 71-75. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2019.02.015.赵帆, 赵娟, 陈静, 等. Fibroscan和ARFI对慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化诊断价值比较[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(2): 71-75. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2019.02.015. [8] LEMOINE M, SHIMAKAWA Y, NAYAGAM S, et al. The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio (GPR) predicts significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic HBV infection in West Africa[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(8): 1369-1376. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309260. [9] ZHANG Z, WANG G, KANG K, et al. The diagnostic accuracy and clinical utility of three noninvasive models for predicting liver fibrosis in patients with HBV infection[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0152757. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152757. [10] WANG H, XUE L, YAN R, et al. Comparison of FIB-4 and APRI in Chinese HBV-infected patients with persistently normal ALT and mildly elevated ALT[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2013, 20(4): e3-e10. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12010. [11] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn. 1001-5256.2019.12.007中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn. 1001-5256.2019.12.007 [12] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of hepatic fibrosis(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007. [13] JIN CT, GUO LW, LIANG WF. Research progress on non-invasive serum markers for liver fibrosis assessment in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J/CD]. Chin J Exp Clin infect Dis(Electronic Edition), 2018, 12(1): 11-14. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2018.01.003.金彩婷, 郭利伟, 梁伟峰. 慢性乙型病毒性肝炎肝纤维化无创性血清诊断指标研究进展[J/CD]. 中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版), 2018, 12(1): 11-14. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-1358.2018.01.003. [14] XU LM, LIU P, SHEN XZ, et al. Guidelines for integrated Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis (2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007.徐列明, 刘平, 沈锡中, 等. 肝纤维化中西医结合诊疗指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007. [15] MUELLER S, SEITZ HK, RAUSCH V. Non-invasive diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(40): 14626-14641. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14626. [16] SILVA IS, FERRAZ ML, PEREZ RM, et al. Role of gamma-glutamyl transferase activity in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2004, 19(3): 314-318. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2003.03256.x. [17] EVERHART JE, WRIGHT EC. Association of γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) activity with treatment and clinical outcomes in chronic hepatitis C (HCV)[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57(5): 1725-1733. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26203. [18] YANG JG, HE XF, HUANG B, et al. Rule of changes in serum GGT levels and GGT/ALT and AST/ALT ratios in primary hepatic carcinoma patients with different AFP levels[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2018, 21(4): 743-746. DOI: 10.3233/CBM-170088. [19] LEE J, KIM MY, KANG SH, et al. The gamma-glutamyl transferase to platelet ratio and the FIB-4 score are noninvasive markers to determine the severity of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. Br J Biomed Sci, 2018, 75(3): 128-132. DOI: 10.1080/09674845.2018.1459147. 期刊类型引用(20)
1. 秦鹏,李树森,刘皓,吴广迎. 胃冠状静脉栓塞术在门脉高压性上消化道出血经颈静脉肝内门腔静脉分流术患者中的临床疗效. 血管与腔内血管外科杂志. 2022(09): 1130-1134 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 高绍,王宏亮,聂春晖,张岳林,周坦洋,余子牛,杨月,孙军辉. 对比TIPS联合胃冠状静脉栓塞术与单独TIPS治疗肝硬化门静脉高压伴上消化道出血的中远期疗效:Meta分析. 中国介入影像与治疗学. 2022(11): 673-677 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 张大维,吴东辉,孙兴安. TIPS对肝硬化并发上消化道出血患者近期肝肾功能和远期疗效的影响. 当代医学. 2021(35): 129-130 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 林纲毅,马洺远,蔡宗洋. 超声引导下门静脉穿刺导引经颈静脉肝内门体分流术联合曲张静脉栓塞治疗食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血的临床效果. 中国当代医药. 2020(07): 113-116 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 王宁,林芳明,吕明. TIPS联合GCVE用于门静脉高压并发上消化道大出血的应用价值. 肝脏. 2020(09): 952-954 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 韩志强. 肝硬化上消化道出血37例外科临床治疗效果观察. 世界最新医学信息文摘. 2019(05): 95+102 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 张明礼. PTVE联合PSE治疗肝硬化门脉高压并上消化道出血的观察. 实用中西医结合临床. 2019(05): 24-26 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 孙允涛. 肝硬化门静脉高压并发上消化道出血的相关危险因素分析. 中国民康医学. 2019(10): 81-83 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 孙巧玉,赖雪珍,河源媛. 门脉高压合并上消化道出血采用PTVE联合PSE手术的效果分析. 现代消化及介入诊疗. 2019(08): 837-841+846 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 杨荣焕. TIPS和PTVE介入方法治疗肝硬化门静脉高压引起的上消化道出血的优劣差异. 黑龙江医学. 2019(09): 1012-1013+1016 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 武和平. 不同介入途径胃冠状静脉栓塞术治疗肝硬化门静脉高压出血的临床疗效观察. 现代消化及介入诊疗. 2018(02): 208-210 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 李广忠. 分析肝硬化门脉高压症下食管静脉曲张破裂出血的危险因素. 智慧健康. 2018(07): 91-92+126 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 李贤圣,董勤勇,张乐,夏侨,贺军. 经颈静脉门静脉分流术介入治疗门静脉高压引起上消化道出血的疗效分析. 浙江创伤外科. 2018(02): 272-273 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 赵晓飞,林栋栋,李宁,臧运金,郭庆良,武聚山. 门静脉高压患者脾切断流术后曲张静脉再出血的危险因素分析. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2018(10): 2182-2185 .  本站查看
本站查看15. 吴笋. 经颈静脉肝内门体静脉分流术加胃冠状静脉栓塞术治疗门脉高压症初探. 现代医用影像学. 2018(05): 1522-1523+1528 .  百度学术
百度学术16. 田广俊,池晓玲,常钢,孟凡喆,曹敏玲,黎英贤,徐浩祥,梁宏才,赵朋涛,吴晓菊,萧焕明. 中药灌肠防治TIPS治疗肝硬化门静脉高压伴上消化道出血术后肝性脑病临床观察. 新中医. 2018(12): 87-91 .  百度学术
百度学术17. 樊春燕,叶晓丽,戴晓婷,吴宇清. 肝硬化门静脉高压并发上消化道出血的相关性分析研究. 血管与腔内血管外科杂志. 2018(05): 381-385 .  百度学术
百度学术18. 彭虹. 肝硬化门静脉高压并发上消化道出血的相关危险因素分析. 中国继续医学教育. 2017(31): 58-59 .  百度学术
百度学术19. 张志勇. 不同手术方案治疗肝硬化门脉高压症的临床对比. 临床医药文献电子杂志. 2017(46): 8924-8925 .  百度学术
百度学术20. 向平,张川,张亮科,唐瑞强,叶继彬. 1例上消化道出血病人护理体会. 世界最新医学信息文摘. 2016(14): 247 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2489 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2489 KB)

 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

