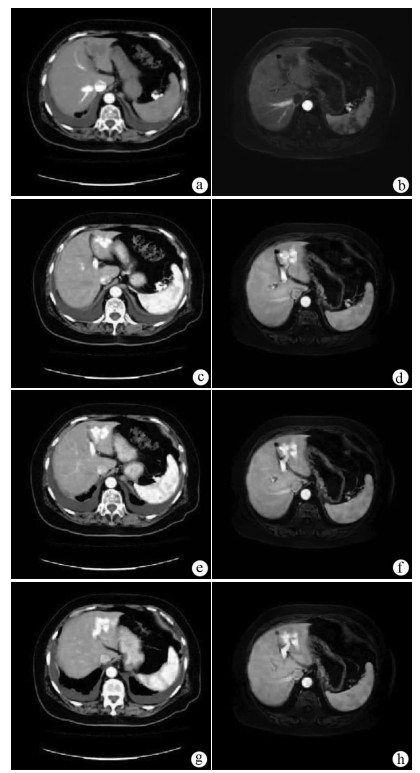
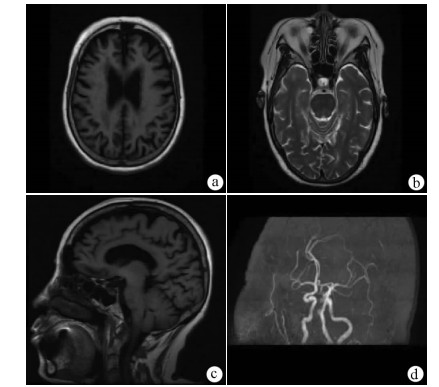
高龄先天性肝内门体分流合并肝性脑病1例报告
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.040
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:张俊君负责课题设计,资料分析,撰写论文;高欣、吴莹、程翌参与收集数据,修改论文;徐维田负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
A case of congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt with hepatic encephalopathy in the elderly
-
[1] STRINGER MD. The clinical anatomy of congenital portosystemic venous shunts[J]. Clin Anat, 2008, 21(2): 147-157. DOI: 10.1002/ca.20574. [2] OHNISHI Y, UEDA M, DOIH, et al. Successful liver transplantation for congenital absence of the portal vein complicated by intrapulmonary shunt and brain abscess[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2005, 40(5): e1-e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.02.011. [3] HOU YL, ZHENG B, YAN JY, et al. Analysis of color Doppler ultrasonographic findings of congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt[J]. Chin Imag J Integr Tradit Western Med, 2019, 17(6): 650-652. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0512.2019.06.033霍亚玲, 郑彬, 闫加勇, 等. 先天性肝内门-体静脉分流的彩色多普勒超声表现分析[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2019, 17(6): 650-652. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0512.2019.06.033 [4] PARK JH, CHA SH, HAN JK, et al. Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1990, 155(3): 527-528. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.155.3.2117349. [5] ZHU LL, LYU ZB. Diagnosis and treatment of common portal vein malformations in children[J]. Chin J Pediatr Surg, 2010, 31(8): 627-629. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3006. 2010.08.016.朱琳琳, 吕志葆. 常见儿童门静脉畸形的诊治现状[J]. 中华小儿外科杂, 2010, 31(8): 627-629. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3006.2010.08.016. [6] LIN ZY, CHEN SC, HSIEH MY, et al. Incidence and clinical significance of spontaneous intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts detected by sonography in adults without potential cause[J]. J Clin Ultrasound, 2006, 34(1): 22-26. DOI: 10.1002/jcu.20176. [7] TAKAHASHI S, YOSHIDA E, SAKANISHI Y, et al. Congenital multiple intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: An autopsy case[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7(1): 425-431. [8] BERNARD O, FRANCHI-ABELLA S, BRANCHEREAU S, et al. Congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Recognition, evaluation, and management[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2012, 32(4): 273-287. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1329896. [9] FRANCHI-ABELLA S, BRANCHEREAU S, LAMBERT V, et al. Complications of congenital portosystemic shunts in children: Therapeutic options and outcomes[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2010, 51(3): 322-330. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181d9cb92. [10] TAKENAGA S, NARITA K, MATSUI Y, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy due to congenital multiple intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts successfully treated by percutaneous transhepatic obliteration[J]. Case Rep Gastroenterol, 2016, 10(3): 701-705. DOI: 10.1159/000452204. [11] ZANG GL, HUANG PT, XU WY, et al. Color doppler ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound model in congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt[J]. Chin J Ultrasonogr, 2012, 21(12): 1043-1047. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2012.12.011.臧国礼, 黄品同, 许伟莹, 等. 先天性肝内门体分流的彩色多普勒超声和超声造影模式研究[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2012, 21(12): 1043-1047. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477. 2012.12. 011. [12] ZANG GL, HUANG PT, ZHOU WP. Routine ultrasound and contrast-enhanced ultrasound findings of congenital hepatic portal venous fistula[J]. Chin J Ultrasonogr, 2010, 19(9): 821-823. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2010.09.032.臧国礼, 黄品同, 周维平. 先天性肝静脉门静脉瘘的常规超声及超声造影表现[J]. 中华超声影像学杂志, 2010, 19(9): 821-823. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4477.2010.09.032. [13] PLESTED MJ, ZWINGENBERGER AL, BROCKMAN DJ, et al. Canine intrahepatic portosystemic shunt insertion into the systemic circulation is commonly through primary hepatic veins as assessed with CT angiography[J]. Vet Radiol Ultrasound, 2020, 61(5): 519-530. DOI: 10.1111/vru.12892. [14] YI LL, DONG Z, CAI HS, et al. Clinical application of MSCTA in diagnosing congenital intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts[J]. J Clin Radiology. 2015, 34(1): 79-83. DOI: 10.13437/j.cnki.jcr.2015.01.025.衣利磊, 董帜, 蔡华崧, 等. MSCTA诊断先天性肝内门-体静脉分流[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2015, 34(1): 79-83. DOI: 10.13437/j.cnki.jcr.2015.01.025. [15] GU XH, SHAO H, SUN AM, et al. Application value of DSA in the clinical classification and treatment of children's congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts[J]. China Med Devic, 2017, 32(7): 60-63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2017.07.017.顾小红, 邵虹, 孙爱敏, 等. DSA在儿童先天性肝外门体静脉分流的临床分型及治疗中的应用价值[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2017, 32(7): 60-63. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2017.07.017. [16] PAPAMICHAIL M, PIZANIAS M, HEATON N. Congenital portosystemic venous shunt[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 2018, 177(3): 285-294. DOI: 10.1007/s00431-017-3058-x. [17] LI XF, WU QQ, WANG L, et al. Ultrasound diagnosis of congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shuns in fetal stage and postpartum: Case report[J]. Chin J Perinat Med, 2016, 19(11): 833-835. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-9408.2016.11.009.李晓菲, 吴青青, 王莉, 等. 先天性肝内门体静脉分流胎儿期及产后超声诊断1例[J]. 中华围产医学杂志, 2016, 19(11): 833-835. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-9408.2016.11.009. [18] LAUTZ TB, TANTEMSAPYA N, ROWELL E, et al. Management and classification of type Ⅱ congenital portosystemic shunts[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2011, 46(2): 308-314. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.11.009. [19] BRADER RA, KIM KR. Transhepatic embolization of a congenital intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in a noncirrhotic patient using Amplatzer vascular plug device[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2017, 12(2): 318-322. DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2016.12.006. [20] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(10): 2076-2089. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.007.中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化肝性脑病诊疗指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(10): 2076-2089. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.007. [21] LI XK, WANG S, LI ZG, et al. Updated key points of Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1485-1488. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.012.李小科, 王姗, 李志国, 等. 2018年《肝硬化肝性脑病诊疗指南》更新要点解读[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1485-1488. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.012. -



 PDF下载 ( 2160 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2160 KB)

 下载:
下载: