NCEH1基因在肝癌组织与细胞系中的表达及生物学作用
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.023
Expression and biological role of the neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 gene in liver cancer tissue and cell lines
-
摘要:
目的 了解中性胆固醇酯水解酶1(neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1, NCEH1)基因在肝癌组织及人肝癌细胞系中表达水平, 观察NCEH1基因敲减对SMMC-7721人肝癌细胞系增殖、凋亡、侵袭及转移能力的影响。 方法 选取2013年1月—2019年6月在暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院手术治疗的32例肝癌患者标本及对应的癌旁组织, 采用实时荧光定量PCR方法检测NCEH1基因的相对表达量。从ICGC数据库下载截至2020年9月份的肝癌样本基因表达数据, 应用R软件整理数据, 筛选出每个样本中NCEH1基因表达量, 分别采用配对Wilcoxon符号秩检验和Wilcoxon秩和检验分析肝癌与癌旁组织间的差异。采用实时荧光定量PCR方法检测NCEH1基因在SMMC-7721、Bel-7402、HepG2、Hep3B人肝癌细胞系和HL7702正常人肝细胞系中的表达水平。通过慢病毒介导的小干扰RNA(siRNA)技术构建NCEH1基因敲减的SMMC-7721人肝癌细胞系, 分为NCEH1敲减组(KD组)和阴性对照组(NC组), 以实时荧光定量PCR法检测NCEH1基因的敲减效率, 再以MTT检测实验、Annexin V-APC单染法流式细胞仪检测、划痕愈合实验、Transwell实验和Transwell侵袭小室实验检测2组SMMC-7721肝癌细胞的增殖、凋亡、转移和侵袭能力, 采用t检验对两组间数据进行统计学分析。 结果 NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的平均表达量高于癌旁组织(本院标本Z=2.263, P=0.024, ICGC数据库U=18 768, P<0.001)。NCEH1基因在中等侵袭转移潜能的SMMC-7721细胞系中的表达量最高; 在低侵袭转移潜能的Bel-7402和HepG2细胞系中的表达水平次之, 在无侵袭转移潜能的Hep3B细胞系中的表达水平最低。KD组SMMC-7721细胞中NCEH1基因的表达水平明显低于NC组(t=11.578, P=0.000 3), NCEH1基因的敲减效率高达74.0%。较之NC组, KD组细胞生长速度明显减缓(t=32.10, P<0.001);细胞凋亡率明显升高(t=27.303, P<0.001);迁移率、转移和侵袭细胞数均明显降低(t值分别为9.51、38.123、22.331, P值均<0.001)。 结论 NCEH1基因在肝癌组织及细胞系中的表达明显升高, 且可促进肝癌细胞的生长增殖及侵袭转移并抑制凋亡, 提示其可能是一个潜在的肝癌治疗靶点。 -
关键词:
- 癌, 肝细胞 /
- 中性胆固醇酯水解酶1 /
- RNA, 小分子干扰
Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression of the neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 (NCEH1) gene in liver cancer tissue and human hepatoma cell lines and the effect of NCEH1 gene knockdown on the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis abilities of human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Methods Liver cancer tissue samples and adjacent tissue samples were collected from 32 patients with liver cancer who underwent surgical treatment in Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University from January 2013 to June 2019, and quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the relative expression level of the NCEH1 gene. Gene expression data of liver cancer samples up to September 2020 were downloaded from the ICGC database, and R software was used to analyze the data and obtain the expression level of the NCEH1 gene in each sample. The paired Wilcoxon signed-rank test and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test were used to investigate the differences between liver cancer tissue and adjacent tissue. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the expression level of the NCEH1 gene in human hepatoma SMMC-7721, Bel-7402, HepG2, and Hep3B cells and normal human HL7702 liver cells. The lentivirus-mediated small interfering RNA (siRNA) technique was used to establish a human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cell line with NCEH1 gene knockdown, and the cells were divided into NCEH1 knockdown group (KD group) and negative control group (NC group); quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the knockdown efficiency of the NCEH1 gene, and then MTT assay, flow cytometry with Annexin V-APC single staining, wound healing assay, Transwell assay, and Transwell chamber invasion assay were used to measure the proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, and invasion abilities of SMMC-7721 cells in both groups. The t-test was used for statistical analysis of data between the two groups. Results The mean expression level of the NCEH1 gene in liver cancer tissue was significantly higher than that in adjacent tissue (specimens from our hospital: Z=2.263, P=0.024; ICGC database: U=18 768, P < 0.001). SMMC-7721 cell line with moderate potential of invasion and metastasis had the highest expression level of the NCEH1 gene, followed by BEL-7402 and HepG2 cell lines with low potential of invasion and metastasis, and Hep3B cell line without the potential of invasion and metastasis had the lowest expression level. The KD group had a significantly lower expression level of the NCEH1 gene than the NC group (t=11.578, P=0.000 3), and the knockdown efficiency of the NCEH1 gene was as high as 74.0%. Compared with the NC group, the KD group had a significant reduction in cell growth rate, a significant increase in apoptosis rate, and significant reductions in migration rate and the number of metastatic and invasive cells (t=32.100, 27.303, 9.51, 38.123, and 22.331, all P < 0.001). Conclusion There is a significant increase in the expression of the NCEH1 gene in liver cancer tissue and cell lines, and the NCEH1 gene can promote the growth, proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of hepatoma cells and inhibit their apoptosis, suggesting that it may be a potential therapeutic target for liver cancer. -
原发性肝癌的发病率持续增长, 已居恶性肿瘤死亡率的第四位[1], 尽管目前肝癌治疗水平已有较大提高[2], 但其预后依然不容乐观[3]。探索肝癌侵袭转移的分子机制及寻找有效的肝癌治疗靶点仍是肝癌研究的重要内容。已有研究[4-5]表明, 中性胆固醇酯水解酶1(neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1, NCEH1)在侵袭性前列腺癌细胞中高表达, 抑制NCEH1的表达则可降低前列腺癌细胞的增殖、转移和侵袭能力, 提示NCEH1是一促癌基因。然而截至目前, NCEH1在肝癌中的表达及作用均尚不清楚。本研究旨在了解NCEH1在肝癌组织及细胞系中的表达情况并探讨其对肝癌细胞增殖、凋亡、转移及侵袭能力的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 NCEH1基因样本
选取2013年1月—2019年6月在暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院手术治疗的32例肝癌患者标本及对应的癌旁组织。所有标本离体后立即存放在液氮罐中, 然后于-80 ℃深低温箱中保存。采用实时荧光定量PCR检测NCEH1基因的相对表达量。同时从ICGC数据库(https://daco.icgc.org)下载截至2020年9月日本人群的肝癌基因表达数据(包含240个肝癌样本和220个正常肝组织样本)作为验证组, 应用R软件(4.0.2版本)中的limma、beeswarm包对NCEH1基因表达数据进行Wilcoxon秩和检验并做散点差异图进行可视化[6]。
1.2 细胞培养
HL7702正常人肝脏细胞系和SMMC-7721、Bel-7402、HepG2和Hep3B人肝癌细胞系均购自中国科学院上海生命科学研究院生物化学与细胞生物学研究所, 293T细胞购自上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司, 细胞置于37 ℃、5% CO2细胞培养箱中, 以含10%胎牛血清(FBS)的高糖DMEM培养基培养, 按常规进行传代。
1.3 实时荧光定量PCR
提取细胞总RNA并逆转录, 在荧光定量PCR仪(TP800, 日本TAKARA公司)上行PCR检测, 反应条件为: 95 ℃预变性15 s, 然后95 ℃变性5 s, 60 ℃退火延伸30 s, 共进行45个循环, 每次在延伸阶段读取吸光值。NCEH1引物为: 上游5′- CCTGCCGTCCTTCCTTCTTC-3′; 下游5′-CCGTGGTGCCCTGTATCATTA -3′。以管家基因GAPDH(甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶)为内参基因, 引物序列为: 上游5′- TGACTTCAACAGCGACACCCA -3′; 下游5′-CACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAAA -3′。以2-ΔΔCT法分析各细胞系中NCEH1基因的相对于内参基因的表达水平。若肝癌组织中的NCEH1基因表达水平高于相应的癌旁组织, 则为NCEH1表达上调。
1.4 慢病毒介导的小干扰RNA(siRNA)
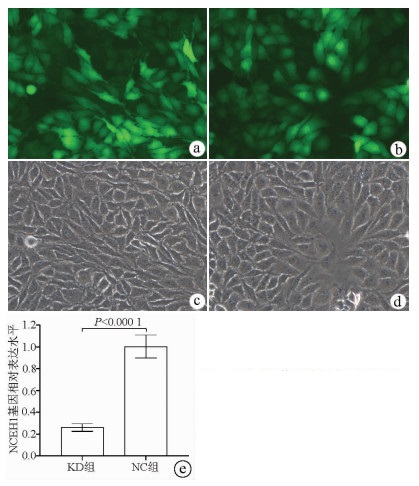
慢病毒质粒GV122、包装质粒pGC-LV、pHelper 1.0和pHelper2.0均购自上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司。设计针对NCEH1基因的shRNA序列如下, 正义链: 5′-CCGGATCCAGGCAGAATTTGCATTTCTCGAGAAATGCAAATTCTGCCTGGATTTTTTG-3′, 反义链: 5′AATTCAAAAAATCCAGGCAGAATTT-GCATTTCTCGAGAAATGCAAATTCTG- CCTGGAT-3′; 阴性对照组序列为, 正义链: 5′-CCGGTTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTTTCAA- GAGAA-CGTGACACGTTCGGAGAATTTTTG-3′, 反义链: 5′-AATTCAAAAATTCTCCGA- ACGTGTCACGTTCTCTTGAAACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAA-3′。上述序列由上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司合成, 将其所形成的双链DNA分别连接到siRNA慢病毒质粒GV122, 再将上述质粒分别与pGC-LV、pHelper1.0和pHelper2.0 3个包装质粒共转染至293T细胞, 上述两种慢病毒各自感染的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞系即被分别命名为NCEH1敲减组(KD组)和阴性对照组(NC组)。采用荧光倒置显微镜(micropublisher 3.3RTV, 日本奥林帕斯公司)观察两组细胞的慢病毒感染效率, 并采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测两组细胞中NCEH1基因的相对表达水平, 以检测NCEH1基因的敲减率。
1.5 MTT实验检测肝癌细胞生长增殖能力
将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞培养于6孔板中, 完全培养基重悬成细胞悬液, 选取5块96孔板, 分别标记为1、2、3、4、5 d; 每组设置3个复孔, 每孔加入100 μl细胞悬液, 每板分别铺3组细胞。从铺板后第2天开始, 培养终止前4 h加入20 μl 5 mg/ml的MTT于孔中。4 h后完全吸去培养液, 加100 μl DMSO溶解甲瓒颗粒。振荡器振荡2~5 min, 酶标仪490/570 nm检测光密度(OD)值。
1.6 Annexin V-APC单染法检测肝癌细胞凋亡率
将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞培养于6孔板中, 完全培养基重悬成细胞悬液, 与上清细胞收集于同一5 ml离心管中。然后1300 r/min离心5 min, 弃上清, 4 ℃预冷的PBS洗涤细胞沉淀。1×binding buffer洗涤细胞沉淀一次, 1300 r/min离心3 min, 收集细胞, 200 μl 1×binding buffer重悬细胞沉淀, 加入10 μl Annexin V-APC染色, 室温避光10~15 min。根据细胞量, 补加400~800 μl 1×binding buffer, 上机检测。
1.7 划痕愈合实验检测肝癌细胞迁移能力
将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞培养于6孔板中, 完全培养基重悬成细胞悬液, 根据细胞大小决定铺板细胞密度。置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养。第2天使用划痕仪对准96孔板的上端中央部位, 向上轻推形成划痕。使用PBS轻轻漂洗2~3遍, 加入含1% FBS血清培养基, 0 h扫板。再次于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养, 根据愈合程度选择合适时间用Celigo扫板, 用Celigo分析迁移面积并计算迁移率。
1.8 Transwell转移和侵袭实验
将Transwell小室置于新的24孔板中, 上室加100 μl无FBS培养基, 37 ℃培养箱中放置1 h。将KD组及NC组SMMC-7721细胞加入每个小室, 下室内加入含30% FBS的培养基600 μl, 5% CO2、37 ℃孵育48 h。倒扣小室于吸水纸上以去除培养基, 用棉拭子轻轻移去小室内非转移细胞, 将小室置于4%多聚甲醛固定液中固定30 min后捞出, 用吸水纸吸干小室表面固定液, 滴1~2滴染色液到膜的下表面染色转移细胞1~3 min后, 将小室浸泡冲洗数次, 空气晾干。在显微镜下拍照并计算各组转移细胞数。如将Transwell小室先铺Matrigel胶再重复上述实验步骤即为Transwell侵袭实验。
1.9 伦理学审查
本研究通过暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院伦理委员会审核, 批号: 穗红院医伦审2019-028-01。所有标本采集前均已获患者知情同意。
1.10 统计学方法
应用SPSS 23.0软件进行统计学分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示, 两组间比较采用t检验。采用配对样本比较的Wilcoxon符号秩检验对32例肝癌组织和对应癌旁中的NCEH1相对表达量进行比较, 两个独立样本比较的Wilcoxon秩和检验对ICGC数据库中肝癌和正常肝组织中的NCEH1表达量进行比较。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。统计图采用Graphpad Prism 8.0软件(美国Graphpad软件公司)绘制。
2. 结果
2.1 肝癌组织中NCEH1的表达
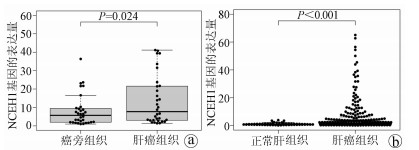
实时荧光定量PCR检测结果显示, 在32例患者标本中, 有22例肝癌组织中的NCEH1基因表达上调, NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的平均表达量高于相应的癌旁组织(Z=2.263, P=0.024)(图 1a)。下载ICGC数据库中日本人群的肝癌标本(包含240个肝癌样本, 202个正常肝组织样本), 筛选出每个样本中NCEH1基因表达量进行分析。结果显示, NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的表达水平明显高于正常肝组织(U=18 768, P<0.001)(图 1b)。
2.2 NCEH1在肝癌细胞系中的相对表达水平
t检验结果显示, NCEH1在中等侵袭转移潜能的SMMC-7721和Bel-7402细胞系中的相对表达量较低或无侵袭转移潜能的HepG2(0.004 2±0.000 2 vs 0.002 9±0.000 4, t=4.651, P=0.01;0.003 9±0.000 3 vs 0.002 9±0.000 4, t=3.218, P=0.03)和Hep3B细胞系高(0.004 2±0.000 2 vs 0.002 7±0.000 2, t=9.496, P=0.001;0.003 9±0.000 3 vs 0.002 7±0.000 2, t=3.218, P=0.005);而NCEH1在低或无侵袭转移潜能的HepG2和Hep3B细胞系中的相对表达量较正常HL-7702肝细胞系高(0.002 9±0.000 4 vs 0.001 5±0.000 1, t=5.682, P=0.005; 0.002 7±0.000 2 vs 0.001 5±0.000 1, t=11.302, P=0.000 3)。
2.3 慢病毒的感染效率及NCEH1基因敲减效率
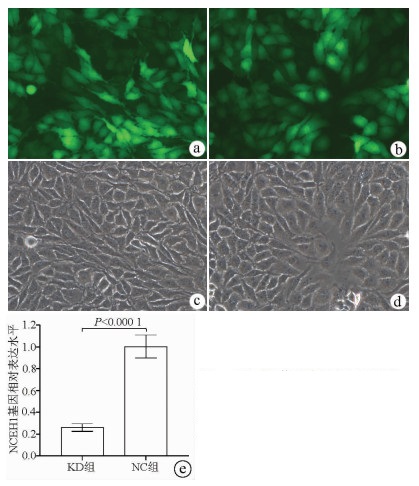
荧光显微镜观察结果显示, KD组及NC组慢病毒对肝癌细胞的感染效率均达到80%以上, KD组SMMC-7721细胞中NCEH1基因的相对表达量仅为NC组细胞的26.0%(0.260±0.035 vs 1.004±0.106, t=11.578, P=0.000 3), 即NCEH1基因在SMMC-7721人肝癌细胞系中的敲减效率达到了74.0%(图 2)。
2.4 NCEH1敲减对肝癌细胞生长增殖能力的影响
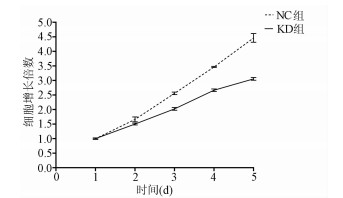
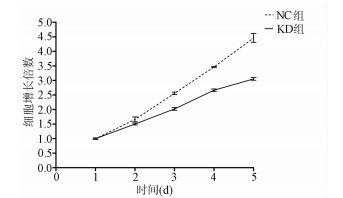
MTT检测结果显示, KD组SMMC-7721肝癌细胞生长速度较NC组明显减缓(第5天相对增殖倍数为3.055±0.046 vs 4.462±0.060, t=32.100, P=0.000 006), 提示NCEH1基因敲减明显抑制了肝癌细胞的生长增殖(图 3)。
2.5 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞凋亡的影响
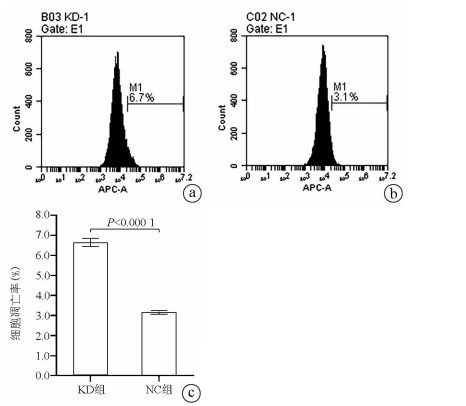
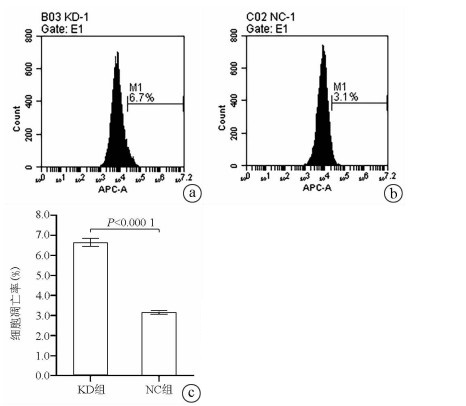
Annexin V-APC单染法流式细胞仪检测显示, KD组SMMC- 7721肝癌细胞凋亡率明显高于NC组(6.650%±0.203% vs 3.150%±0.090%, t=27.303, P=0.000 01), 提示敲减NCEH1基因可促进细胞凋亡(图 4)。
2.6 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞迁移能力的影响
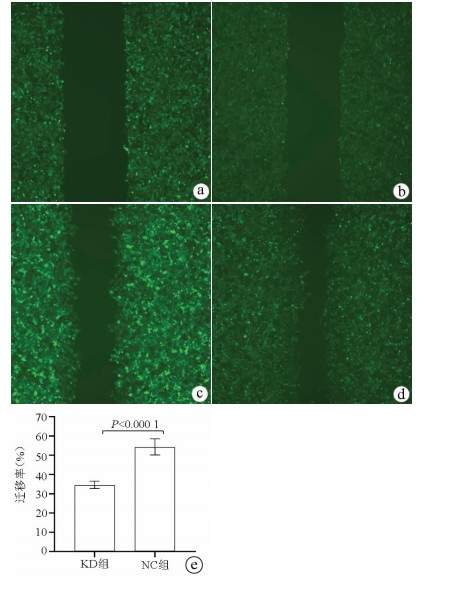
划痕愈合实验结果显示, KD组的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞迁移率明显低于NC组(34.68%±1.89% vs 54.37%±4.23%, t=9.51, P=0.000 01), 提示敲减NCEH1基因可明显抑制肝癌细胞的迁移能力(图 5)。
2.7 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞转移能力的影响
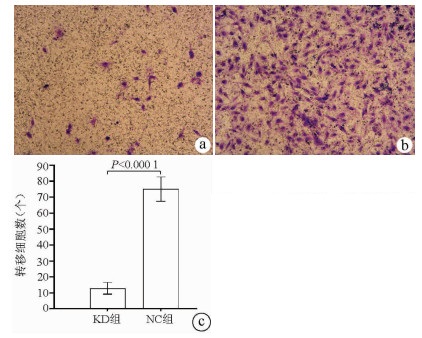
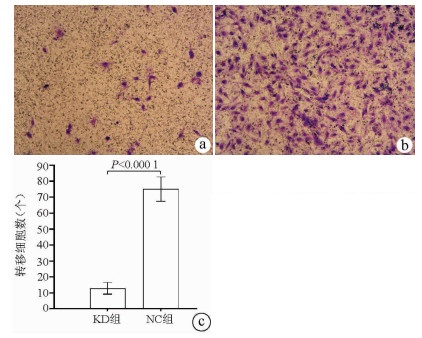
Transwell实验结果显示, KD组SMMC-7721肝癌细胞的转移细胞数明显低于NC组(12.89±3.63 vs 75.04±7.65, t=38.123, P<0.000 1), 提示NCEH1基因敲减可明显抑制肝癌细胞的转移能力(图 6)。
2.8 敲减NCEH1基因对肝癌细胞侵袭能力的影响
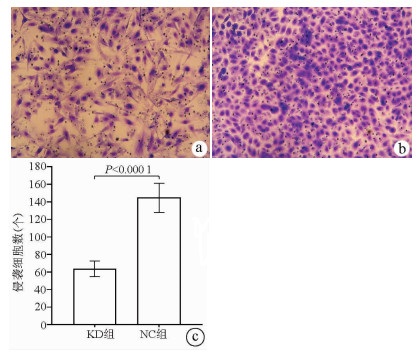
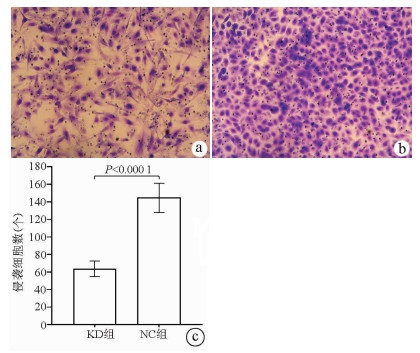
Transwell侵袭实验结果显示, KD组的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞侵袭数明显低于NC组(63.67±8.86 vs 144.52±16.60, t=22.331, P<0.000 1), 提示NCEH1基因敲减可明显抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭能力(图 7)。
3. 讨论
肝癌在全球的发病率和死亡率较高, 据估计2015年全球肝癌死亡人数约为80万[7], 而在全球每年新增肝癌病例中, 约一半发生在我国, 已成为最致命的癌症之一[8]。尽管针对肝癌的治疗手段众多, 手术切除仍然是治疗肝癌的首选方案, 但由于肝癌术后复发率相对较高, 导致肝癌术后5年无复发生存率仅为38%, 严重限制了肝癌的总体治疗效果[9-10]。因此, 探索肝癌侵袭转移的机制以获得有效的肝癌治疗靶点已成为肝癌研究的重点。
近年来的研究表明, 脂代谢异常可能是促进癌症发生发展的一个重要因素, Jiang等[11]通过蛋白质组学分析发现, 改变细胞内胆固醇的分布, 可有效抑制肝细胞癌的增殖和转移。Lin等[12]通过脂质组学分析发现, 脂质代谢的改变与肿瘤侵袭性、生长和增殖密切相关, 目前也已发现多个脂质代谢过程中的关键酶在肿瘤细胞中过表达[13-14], 这为肝癌治疗提供了一个新思路。NCEH1是一个蛋白质编码基因, 定位于人染色体3q26.31, 大小为80 970 bp。NCEH1基因编码的蛋白由408个氨基酸组成, 大小为45.808 kD, 是一种丝氨酸水解酶, 在巨噬细胞和中枢神经细胞中有较高表达[15-16], 并在调节胆固醇代谢过程中发挥重要作用[4]。已有研究[17-18]发现, NCEH1表达产物可作为乙醚脂质信号网络中连接血小板活化因子和溶血磷脂酸的中心节点, 抑制NCEH1表达产物可降低癌细胞中的醚脂质代谢并抑制肿瘤细胞迁移和生长。Chang等[5]的研究则发现, 选择性NCEH1抑制剂可明显降低人前列腺癌细胞系的迁移、侵袭、存活及增殖能力, 提示NCEH1可能与肿瘤的侵袭、迁移及增殖相关, 但NCEH1在肝癌中的表达水平及作用目前均不清楚。
为此, 本研究首先通过对本院32例肝癌及对应癌旁标本进行分析发现, NCEH1在肝癌组织中的表达明显高于对应的癌旁组织, 然后分析ICGC数据库中日本人群的肝癌基因表达数据发现, NCEH1在肝癌组织中的表达明显高于正常肝组织, 与本研究结果一致, 提示NCEH1在肝癌组织中的表达上调。继而, 本研究采用实时荧光定量PCR技术分析发现, NCEH1在所有肝癌细胞系中的表达均高于正常肝细胞系, 这与其在肝癌组织中表达上调的结果一致。更重要的是, NCEH1在侵袭转移潜能较高的肝癌细胞系中的表达明显高于低侵袭转移潜能的肝癌细胞系, 这与Chang等[5]在前列腺癌细胞系中的结果一致, 提示NCEH1与肝癌细胞的侵袭转移相关。本研究采用慢病毒介导的siRNA技术敲减NCEH1在SMMC-7721肝癌细胞系(该细胞系的NCEH1表达水平在笔者检测的4株肝癌细胞系中为最高)中的表达, 结果显示, NCEH1基因的敲减效率高达74.0%, NCEH1基因敲减的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞系得以成功建立。接下来, 本研究采用MTT生长曲线、细胞流式检测及Transwell转移和侵袭实验等一系列细胞功能实验观察NCEH1在肝癌细胞中的功能, 结果显示, NCEH1基因敲减可明显降低肝癌细胞系的增殖、转移及侵袭能力并促进凋亡, 这些结果也均与Chang等[5]在前列腺癌细胞中获得的结果一致, 提示NCEH1可能是一个潜在的肝癌治疗靶点。
对于NCEH1表达及发挥作用的分子调控机制的研究相对较少, Cheung等[19]发现在牛皮癣皮肤的皮下脂肪组织中miR-26b-5p高度上调, 而NCEH1是miR-26b-5p的直接靶点之一, miR-26b-5p可靶向下调NCEH1的表达。现有的研究显示, miR-26b-5p在不同肿瘤组织中均起着抑癌作用[20], 其在肝癌细胞系中明显下调, 且与肝癌的侵袭和转移密切相关[21-22]。而miRNA被认为可调控60%蛋白质编码基因, 并参与几乎所有细胞过程的调控[18, 23]。笔者据此推测miR-26b-5p在肝癌中也可能存在对NCEH1基因表达的负向调控, 即miR-26b-5p的下调可能促使NCEH1基因在肝癌组织中的表达上调, 并因此增强了肝癌细胞的增殖、凋亡、转移及侵袭能力。然而, NCEH1在肝癌中表达升高及发挥生物学作用的具体分子机制均尚有待于进一步研究阐明。
综上所述, 本研究结果发现, NCEH1基因在肝癌组织及细胞系中的表达明显升高, 体外实验中可以促进肝癌细胞增殖、侵袭转移并抑制凋亡, 提示其可能是一个潜在的肝癌治疗靶点。
-
-
[1] CHEN H, JIA W. Progress in hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma and peri-operation management[J]. Genes Dis, 2020, 7(3): 320-327. DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.02.001. [2] ALI ES, RYCHKOV GY, BARRITT GJ. Deranged hepatocyte intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Calcium, 2019, 82: 102057. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.102057. [3] ALY SM, FETAIH HA, HASSANIN A, et al. Protective effects of garlic and cinnamon oils on hepatocellular carcinoma in albino rats[J]. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst), 2019, 2019: 9895485. DOI: 10.1155/2019/9895485. [4] IGARASHI M, OSUGA J, UOZAKI H, et al. The critical role of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 in cholesterol removal from human macrophages[J]. Circ Res, 2010, 107(11): 1387-1395. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.226613. [5] CHANG JW, NOMURA DK, CRAVATT BF. A potent and selective inhibitor of KIAA1363/AADACL1 that impairs prostate cancer pathogenesis[J]. Chem Biol, 2011, 18(4): 476-484. DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.02.008. [6] SHI WJ, LI XC, WEN HX, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of AL360181.1 regulating the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer[J]. J Xi'an Univ (Med Sci), 2020, 41(5): 731-737. DOI: 10.7652/jdyxb202005018.史维俊, 李欣灿, 温贺新, 等. 基因AL360181.1调节结直肠癌进展及预后的生物信息学分析[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2020, 41(5): 731-737. DOI: 10.7652/jdyxb202005018. [7] YE Z, WANG S, CHEN W, et al. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein promotes the tumorigenesis and development of liver cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(2): 1409-1417. DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11673. [8] LI P, LIU Y. Effect of hepatitis B x gene on the expression of major histocompatibility complex class Ⅰ chain-related gene A-A5.1, invasion, and migration of HepG2.2.15 cells[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(4): 808-812. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.020.李沛, 刘宇. HBx基因对HepG2.2.15细胞MICA-A5.1表达及侵袭、迁移的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(4): 808-812. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.020. [9] HO SY, HSU CY, LIU PH, et al. Albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade-based nomogram to predict tumor recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2019, 45(5): 776-781. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.10.541. [10] YUAN SX, ZHOU WP. Progress and hot spots of comprehensive treatment for primary liver cancer[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(2): 163-170. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20201211-00776.袁声贤, 周伟平. 原发性肝癌综合治疗的进展和热点[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20(2): 163-170. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20201211-00776. [11] JIANG Y, SUN A, ZHAO Y, et al. Proteomics identifies new therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nature, 2019, 567(7747): 257-261. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-0987-8. [12] LIN L, DING Y, WANG Y, et al. Functional lipidomics: Palmitic acid impairs hepatocellular carcinoma development by modulating membrane fluidity and glucose metabolism[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(2): 432-448. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29033. [13] POPE ED 3rd, KIMBROUGH EO, VEMIREDDY LP, et al. Aberrant lipid metabolism as a therapeutic target in liver cancer[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2019, 23(6): 473-483. DOI: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1615883. [14] NAKAGAWA H, HAYATA Y, KAWAMURA S, et al. Lipid metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2018, 10(11): 447. DOI: 10.3390/cancers10110447. [15] CHISTIAKOV DA, BOBRYSHEV YV, OREKHOV AN. Macrophage-mediated cholesterol handling in atherosclerosis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2016, 20(1): 17-28. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12689. [16] LUCAS EK, DOUGHERTY SE, MCMEEKIN LJ, et al. PGC-1α provides a transcriptional framework for synchronous neurotransmitter release from parvalbumin-positive interneurons[J]. J Neurosci, 2014, 34(43): 14375-14387. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1222-14.2014. [17] CHIANG KP, NIESSEN S, SAGHATELIAN A, et al. An enzyme that regulates ether lipid signaling pathways in cancer annotated by multidimensional profiling[J]. Chem Biol, 2006, 13(10): 1041-1050. DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.08.008. [18] NOMURA DK, FUJIOKA K, ISSA RS, et al. Dual roles of brain serine hydrolase KIAA1363 in ether lipid metabolism and organophosphate detoxification[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2008, 228(1): 42-48. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.11.021. [19] CHEUNG L, FISHER RM, KUZMINA N, et al. Psoriasis skin inflammation-induced microRNA-26b targets NCEH1 in underlying subcutaneous adipose tissue[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2016, 136(3): 640-648. DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2015.12.008. [20] ZHOU A, PAN H, SUN D, et al. miR-26b-5p inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human papillary thyroid cancer in a β-catenin-dependent manner[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 1593-1603. DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S236319. [21] WANG Y, SUN B, ZHAO X, et al. Twist1-related miR-26b-5p suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion by targeting SMAD1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(17): 24383-24401. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8328. [22] KHOSLA R, HEMATI H, RASTOGI A, et al. miR-26b-5p helps in EpCAM+cancer stem cells maintenance via HSC71/HSPA8 and augments malignant features in HCC[J]. Liver Int, 2019, 39(9): 1692-1703. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14188. [23] GUPTA M, CHANDAN K, SARWAT M. Role of microRNA and long non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2020, 26(4): 415-428. DOI: 10.2174/1381612826666200115093835. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李晶津,王佳玉,金泽宁. 昼夜节律对肝脏胆固醇代谢的影响. 中西医结合肝病杂志. 2022(12): 1110-1113 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3035 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3035 KB)


 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术