肝移植供肝动脉变异与重建方式对术后早期动脉并发症的影响
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.08.030
Influence of arterial variation and reconstruction of the donor hepatic artery in liver transplantation on early postoperative arterial complications
-
表 1 415例肝移植患者临床资料
项目 所有患者
(n=415)变异组
(n=68)非变异组
(n=347)统计值 P值 男/女(例) 333/82 56/12 277/70 χ2=0.09 0.75 年龄(岁) 51.7±10.0 50.9±10.5 51.9±9.9 t=0.70 0.48 BMI(kg/m2) 24.41±7.28 24.59±3.61 24.38±3.84 t=0.43 0.67 MELD评分 9.0(4.1~15.0) 9.8(5.7~15.5) 8.4(3.6~15.0) Z=0.27 0.27 冷缺血(min) 371.4±133.8 398.4±158.2 365.3±131.5 t=1.51 0.13 手术时间(min) 517.9±129.6 519.7±99.7 517.0±135.5 t=0.15 0.88 手术方式(例) χ2=1.03 0.31 经典肝移植术 366 57 309 背驮式肝移植术 49 11 38 原发病(例) χ2=10.21 0.08 原发性肝癌 216 35 181 肝炎后肝硬化 125 18 107 酒精性肝硬化 23 1 22 自身免疫性肝病 26 5 21 其他1) 25 9 16 注:1)包括急性肝衰竭、肝小静脉闭塞综合征、布加综合征、药物性肝硬化、多囊肝、肝移植术胆道并发症、多囊肝、肝豆状核变性。 表 2 415例供肝动脉的解剖分型术中动脉具体重建方式
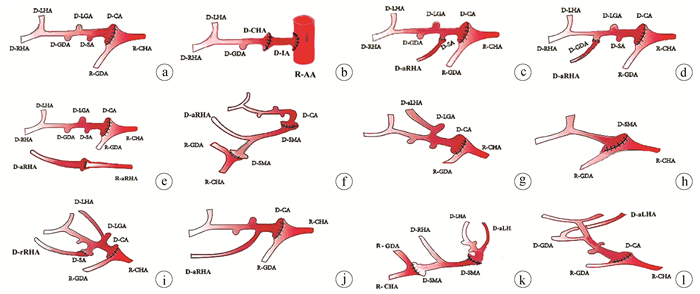
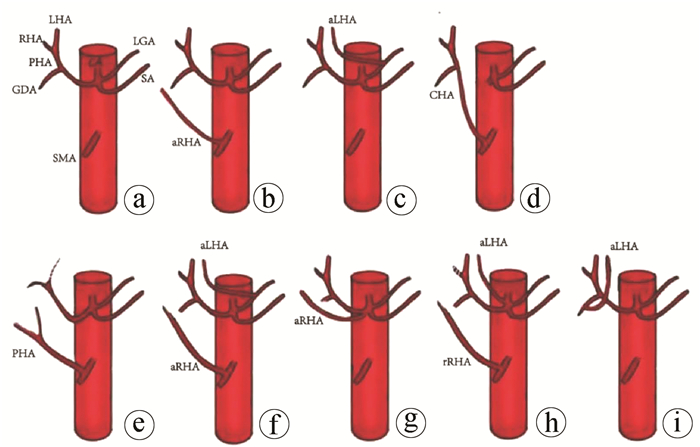
解剖类型 例(%) HIATT分型 重建方式 正常型 347(83.61) Ⅰ 将供肝CT或将SA和CHA分叉修整成袖片与受者GDA及CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2a);
使用供体髂动脉(Iliac artery,ⅠA)架桥,一端与受者腹主动脉(Abdominal aorta,AA)吻合,另一端与供肝CHA吻合3例(图 2b)aRHA发自SMA 41(9.88) Ⅲ 将供体aRHA与供肝SA或GDA端端吻合, 再将供肝CT与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2c、2d);
供受体均有aRHA,将其端端吻合,再将供肝CT与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2e);
将供肝SMA一端与供肝CT端端吻合,另一端与受者GDA和CHA分叉端端吻合(图 2f)aLHA发自LGA 8(1.93) Ⅱ 将供肝CT与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2g) CHA发自SMA 4(0.96) Ⅴ 将肝动脉与SMA分叉修整成袖片,与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2h) PHA发自SMA 5(1.20) Ⅴ aRHA发自SMA并aLHA发自LGA 6(1.45) Ⅳ 将供肝aRHA与供肝SA做端端吻合,再将供肝CT与受者GDA及CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2i) aRHA发自CT 2(0.48) Ⅲ 将供肝CT与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2j) rRHA发自SMA并aLHA发自CT 1(0.24) Ⅳ 将供肝SMA远端与供肝CT作端端吻合,再将供肝SMA近端与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端缝合(图 2k) aLHA发自GDA 1(0.24) Ⅱ 将供肝CT与受者GDA和CHA分叉做端端吻合(图 2l) 注:aRHA,副肝右动脉;SMA,肠系膜上动脉;aLHA, 副肝左动脉;rRHA,替代肝右动脉。 表 3 不同重建方式与动脉并发症的关系
并发症 供体侧重建方式 受体侧重建方式 复杂重建
(n=50)普通重建
(n=365)P值 CT或CHA/SA分叉(n=395) CHA或PHA
(n=20)P值 CHA/GDA分叉
(n=391)CHA
(n=15)RHA/LHA分叉
(n=9)P值 有 10 1 0.40 10 1 0 0.48 3 8 0.13 无 385 19 381 14 9 47 357 -
[1] LI MX, PENG GZ, YE QF. Progress of hepatic artery complications after liver transplantation[J]. J Hepatopancreatobiliary Surg, 2016, 28(3): 251-254. DOI: 10.11952/j.issn.1007-1954.2016.03.024.李明霞, 彭贵主, 叶啟发. 肝移植术后肝动脉并发症研究进展[J]. 肝胆胰外科杂志, 2016, 28(3): 251-254. DOI: 10.11952/j.issn.1007-1954.2016.03.024. [2] KARAKOYUN R, ROMANO A, YAO M, et al. Impact of hepatic artery variations and reconstructions on the outcome of orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. World J Surg, 2020, 44(6): 1954-1965. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-020-05406-4. [3] WARNER P, FUSAI G, GLANTZOUNIS GK, et al. Risk factors associated with early hepatic artery thrombosis after orthotopic liver transplantation univariable and multivariable analysis[J]. Transpl Int, 2011, 24(4): 401-408. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2010.01211.x. [4] SOLIMAN T, BODINGBAUER M, LANGER F, et al. The role of complex hepatic artery reconstruction in orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl, 2003, 9(9): 970-975. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2003.50167. [5] HERRERO A, SOUCHE R, JOLY E, et al. Early hepatic artery thrombosis after liver transplantation: What is the impact of the arterial reconstruction type?[J]. World J Surg, 2017, 41(8): 2101-2110. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-017-3989-4. [6] SOLIMAN T, BODINGBAUER M, LANGER F, et al. The role of complex hepatic artery reconstruction in orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl, 2003, 9(9): 970-975. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2003.50167. [7] ZHANG H, GU LH, XIA Q. Application and progress of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of complications after liver transplantation[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2017, 22(1): 72-75. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2017.01.024.张赫, 顾莉红, 夏强. 超声造影在肝移植术后并发症诊断中的应用及进展[J]. 肝脏, 2017, 22(1): 72-75. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2017.01.024. [8] FUJIKI M, HASHIMOTO K, PALAIOS E, et al. Probability, management, and long-term outcomes of biliary complications after hepatic artery thrombosis in liver transplant recipients[J]. Surgery, 2017, 162(5): 1101-1111. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2017.07.012. [9] XUE Z, CHEN M, ZHANG X, et al. Analysis of early hepatic artery thrombosis after liver transplantation[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2018, 88(3): 172-176. DOI: 10.1111/ans.13911. [10] SONG S, KWON CH, MOON HH, et al. Single-center experience of consecutive 522 cases of hepatic artery anastomosis in living-donor liver transplantation[J]. Transplant Proc, 2015, 47(6): 1905-1911. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.06.014. [11] YANG Y, ZHAO JC, YAN LN, et al. Risk factors associated with early and late HAT after adult liver transplantation[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(30): 10545-10552. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10545. [12] ALGARNI AA, MOURAD MM, BRAMHALL SR. Anticoagulation and antiplatelets as prophylaxis for hepatic artery thrombosis after liver transplantation[J]. World J Hepatol, 2015, 7(9): 1238-1243. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i9.1238. [13] CHENG YF, OU HY, YU CY, et al. Interventional radiology in living donor liver transplant[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(20): 6221-6225. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6221. [14] TRONINA O, MIKOȽAJCZYK N, PIETRZAK B, et al. Pregnancy in a patient with hepatic artery thrombosis after liver transplantation: A case report[J]. Transplant Proc, 2014, 46(8): 2929-2931. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.09.021. [15] CHEN C, GAO J, HU LB. Interventional diagnosis and treatment of hepatic artery complications after liver transplantation[J]. China Med, 2015, 10(10): 1478-1480. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2015.10.019.陈尘, 高建, 胡立宝. 肝移植术后肝动脉并发症的介入诊断与治疗[J]. 中国医药, 2015, 10(10): 1478-1480. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4777.2015.10.019. [16] RINALDI P, INCHINGOLO R, GIULIANI M, et al. Hepatic artery stenosis in liver transplantation: Imaging and interventional treatment[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2012, 81(6): 1110-1115. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.02.055. -



 PDF下载 ( 2761 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2761 KB)

 下载:
下载: