中药单体调控氧化应激抗肝纤维化的机制和价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.09.039
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:周志文负责文章思路设计,撰写论文;李姗负责课题设计,修改论文;李宁宁、刘湘花、孙宁负责文献检索,整理参考文献;禄保平负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章及最后定稿。
Research advances in monomers of Chinese herbs in treatment of liver fibrosis by regulating oxidative stress
-
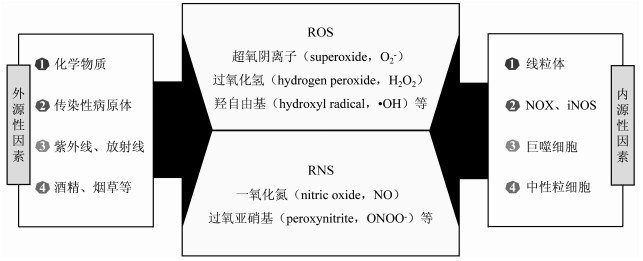
摘要: 肝纤维化是诸多类型慢性肝病的共同病理过程,是由慢性肝损伤后细胞外基质的过度沉积所致。越来越多的证据表明,氧化应激与肝纤维化的发生发展密切相关,在多种病因所致的肝纤维化病理过程中都有氧化应激的参与。中药单体成分天然、结构明确,在近年来抗肝纤维化的研究中已经取得了显著成效。就中药单体调控氧化应激相关信号通路抗肝纤维化的研究进展进行阐述。Abstract: Liver fibrosis, a common pathological process of most types of chronic liver diseases, is caused by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins after chronic liver injury. An increasing number of evidence has shown that oxidative stress is closely associated with the development and progression of liver fibrosis and is involved in the pathological process of liver fibrosis caused by various factors. With natural constituents and a clear structure, Chinese herbal monomers herbs have achieved a marked clinical effect in the treatment of liver fibrosis. This article reviews the research advances in monomers of Chinese herbs in the treatment of liver fibrosis by regulating oxidative stress-related signaling pathways.
-
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- CHEMICAL PRINCIPLES (TCD) /
- Oxidative Stress /
- Signal Transduction
-
表 1 中药单体或活性成分干预氧化应激的信号通路
单体/活性成分 靶细胞/组织/动物模型 信号通路 参考文献 芒果苷 肝组织 TGFβ/Smad [20] 黄芪甲苷 肝纤维化小鼠 TGFβ/Smad [21] 夏枯草总三萜 肝纤维化大鼠 TGFβ/Smad [22] 狗肝菜多糖 肝纤维化大鼠 MAPK [26] 柴胡皂苷 大鼠HSC-T6细胞 MAPK [24] 熊果酸 大鼠HSC-T6细胞 PI3K/Akt [28] 麦芽酚 肝纤维化小鼠 PI3K/Akt [29] 熊果酸 HSC细胞 NF-κB [34] 红景天苷 肝纤维化小鼠及HSC-T6细胞 NF-κB [35] 水飞蓟宾 酒精性肝纤维化大鼠 Wnt/β-catenin [36] 沙苑子黄酮 肝纤维化小鼠 Wnt/β-catenin [37] -
[1] CHEN YP. Brief analysis of the current situation of liver fibrosis treatment[J]. Mod, Pract Med, 2018, 30(3): 281-283. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2018.03.001.陈永平. 浅析肝纤维化治疗现状[J]. 现代实用医学, 2018, 30(3): 281-283. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2018.03.001. [2] Liver Disease Committee, Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine. Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis with integrative medicine[J]. J Chin Integr Med, 2006, 4(6): 551-555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD201907009.htm中国中西医结合学会肝病专业委员会. 肝纤维化中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 中西医结合学报, 2006, 4(6): 551-555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD201907009.htm [3] LI S, HONG M, TAN HY, et al. Insights into the role and interdependence of oxidative stress and inflammation in liver diseases[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 4234061. DOI: 10.1155/2016/4234061. [4] GÄBELE E, BRENNER DA, RIPPE RA. Liver fibrosis: Signals leading to the amplification of the fibrogenic hepatic stellate cell[J]. Front Biosci, 2003, 8: d69-d77. DOI: 10.2741/887. [5] TRAUTWEIN C, FRIEDMAN SL, SCHUPPAN D, et al. Hepatic fibrosis: Concept to treatment[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62(1 Suppl): s15-s24. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.039. [6] WU FR, NING LJ, ZHOU R. Protective effects of Xiaochaihu Decoction on chemical hepatic fibrosis in mice[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 25(5): 481-488. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2020.05.001.吴芙蓉, 宁丽娟, 周冉. 小柴胡汤对化学性肝纤维化小鼠的保护作用[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2020, 25(5): 481-488. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2020.05.001. [7] GUO Y, LU FM, LIU DP. The pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis and the effect of rhein on hepatic fibrosis[J]. Med Inf, 2020, 33(12): 27-32, 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.12.010.郭冶, 卢凤美, 刘东璞. 肝纤维化发病机制及大黄酸对肝纤维化的作用[J]. 医学信息, 2020, 33(12): 27-32, 39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.12.010. [8] ZHANG XH, ZHU X. ROS produced by NOX mediated signaling pathway and liver fibrosis[J]. Int J Dig Dis, 2011, 31(1): 34-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2011.01.011.张新华, 朱萱. NOX通过ROS介导的信号通路与肝纤维化[J]. 国际消化病杂志, 2011, 31(1): 34-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2011.01.011. [9] LI S, TAN HY, WANG N, et al. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16(11): 26087-26124. DOI: 10.3390/ijms161125942. [10] THANAN R, OIKAWA S, HIRAKU Y, et al. Oxidative stress and its significant roles in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 16(1): 193-217. DOI: 10.3390/ijms16010193. [11] ZHAO J, QI YF, YU YR. Research advances in the role of oxidative stress in the development and progression of liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(9): 2067-2071. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.040.赵杰, 齐永芬, 鱼艳荣. 氧化应激在肝纤维化发生发展中的作用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(9): 2067-2071. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.09.040. [12] de MINICIS S, SEKI E, PAIK YH, et al. Role and cellular source of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in hepatic fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52(4): 1420-1430. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23804. [13] HUANG Y, HUANG C, LI J. Effect of cytokines secreted from Kupffer cell on HSC proliferation, apoptosis in hepatic fibrosis process[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2010, 26(1): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YAOL201001006.htm黄艳, 黄成, 李俊. 肝纤维化病程中Kupffer细胞分泌的细胞因子对肝星状细胞活化增殖、凋亡的调控[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2010, 26(1): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YAOL201001006.htm [14] CAI CN, FANG RJ, LI PP, et al. Effect of PVA with portocaval shunt on iNOS in cirrhotic rat liver[J]. Shandong Med J, 2014, 54(30): 14-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2014.30.005.蔡潮农, 方瑞君, 李培平, 等. PVA加门腔分流术对肝硬化大鼠肝脏组织中iNOS水平的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2014, 54(30): 14-16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2014.30.005. [15] MOLDOGAZIEVA NT, MOKHOSOEV IM, FELDMAN NB, et al. ROS and RNS signalling: Adaptive redox switches through oxidative/nitrosative protein modifications[J]. Free Radic Res, 2018, 52(5): 507-543. DOI: 10.1080/10715762.2018.1457217. [16] LYU YH, WU SS, WANG ZC, et al. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine regulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) against liver fibrosis[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 39(6): 117-121. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.吕艳杭, 吴姗姗, 王振常, 等. 中医药调控活性氧(ROS)抗肝纤维化的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(6): 117-121. DOI: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717. [17] RAMÍREZ A, VÁZQUEZ-SÁNCHEZ AY, CARRIÓN-ROBALINO N, et al. Ion channels and oxidative stress as a potential link for the diagnosis or treatment of liver diseases[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2016, 2016: 3928714. DOI: 10.1155/2016/3928714. [18] ZHANG ZP, QIN YH, REN YX, et al. Advances in research on the oxidative stress response to hepatic fibrosis[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2017, 12(11): 1130-1133. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.171124.张忠佩, 秦元华, 任一鑫, 等. 氧化应激反应对肝纤维化形成研究的进展[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2017, 12(11): 1130-1133. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.171124. [19] YUAN LP, CHEN FH, LU L, et al. Effect of TFB on TGF-β1 signaling pathway in HSC of liver fibrosis rats[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2009, 25(12): 1655-1659. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1978.2009.12.027.袁丽萍, 陈飞虎, 鹿玲, 等. 鬼针草总黄酮对肝纤维化大鼠肝星状细胞TGF-β1信号传导通路的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2009, 25(12): 1655-1659. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1978.2009.12.027. [20] HUANG SJ, XUE XW. Pathogenesis and treatment progress of liver fibrosis[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2019, 46(9): 145-146, 107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2019.09.063.黄素洁, 薛晓文. 肝纤维化的发病机制和治疗进展[J]. 广东化工, 2019, 46(9): 145-146, 107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2019.09.063. [21] MI K, HUANG R. Mechanism of mangiferin on liver fibrosis in rats based on TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Sichuan Med J, 2020, 41(2): 142-146. DOI: 10.16252/j.cnki.issn1004-0501-2020.02.007.米凯, 黄锐. 基于TGF-β/Smad信号通路研究芒果苷对肝纤维化大鼠的作用机制[J]. 四川医学, 2020, 41(2): 142-146. DOI: 10.16252/j.cnki.issn1004-0501-2020.02.007. [22] GUI SY, WEI W, WANG H, et al. Effects and mechanisms of crude astragalosides fraction on liver fibrosis in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2006, 103(2): 154-159. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.07.025. [23] ZHANG SP, HE Y, XU T, et al. Regulatory effects of total triterpenoid of Prunella vulgarisL. on activities of ERK and TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in protecting hepatic fibrosis in rats[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull, 2015, 31(2): 261-266. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2015.02.023.章圣朋, 何勇, 徐涛, 等. 夏枯草总三萜调控ERK、TGF-β1/Smad通路对肝纤维化大鼠的保护作用研究[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2015, 31(2): 261-266. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2015.02.023. [24] TSUKADA S, PARSONS CJ, RIPPE RA. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2006, 364(1-2): 33-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2005.06.014. [25] LIU JK. Effects of Saponin D on the proliferation and activation of HSC-T6 in rat hepatic stellate cells and the expression of estrogen receptor[D]. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University, 2014.刘进锴. 柴胡皂苷d对大鼠肝星状细胞HSC-T6的增殖活化及雌激素受体表达的影响[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2014. [26] YE L, CHEN ZY, YAN MX, et al. Activation of liver MAPKs signaling pathway in rats with liver fibrosis and its significance[J]. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med, 2013, 31(12): 2748-2750. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS201312054.htm叶蕾, 陈芝芸, 严茂祥, 等. 肝纤维化大鼠肝组织MAPKs信号通路的活化及意义[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2013, 31(12): 2748-2750. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYHS201312054.htm [27] ZHANG KF, GAO Y, CAO HK, et al. Study on the mechanism of dicliptera chinensis polysaccharide on anti-hepatic fibrosis in rats based on MAPK signal pathway[J]. J Chin Med Materls, 2017, 40(10): 2424-2427. DOI: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2017.10.042.张可锋, 高雅, 曹后康, 等. 狗肝菜多糖对肝纤维化MAPK信号通路调控作用的研究[J]. 中药材, 2017, 40(10): 2424-2427. DOI: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2017.10.042. [28] ZHU ZH. KIF20A promotes the occurrence and development of fibrosarcoma through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.朱振华. KIF20A通过PI3K-AKT信号通路促进纤维肉瘤发生发展的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020. [29] SHI F, HE WH, ZHU X, et al. Effects of ursolic acid (UA) on NADPH oxidase (NOX) subunit and its regulation on downstream signaling pathways in rat activated hepatic stellate cells (HSC)[J]. Fudan Univ J Med Sci, 2014, 41(3): 328-334, 339. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2014.03.008.施凤, 何文华, 朱萱, 等. 熊果酸(UA)对大鼠活化型肝星状细胞(HSC)的NADPH氧化酶(NOX)亚基及PI3K/Akt、P38MAPK信号通路活化的影响[J]. 复旦学报(医学版), 2014, 41(3): 328-334, 339. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2014.03.008. [30] MI XJ, HOU JG, JIANG S, et al. Maltol mitigates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis through TGF-β1-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(5): 1392-1401. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05943. [31] KARIN M. Nuclear factor-kappa B in cancer development and progression[J]. Nature, 2006, 441(7092): 431-436. DOI: 10.1038/nature04870. [32] LUEDDE T, SCHWABE RF. NF-κB in the liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 8(2): 108-118. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.213. [33] HE X, PU G, TANG R, et al. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in the hepatic stellate cells of mice with schistosomiasis japonica[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e104323. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104323. [34] WANG F, LIU S, DU T, et al. NF-κB inhibition alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis via suppression of activated hepatic stellate cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2014, 8(1): 95-99. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1682. [35] CHEN T, HE WH, HUANG W, et al. Effect of ursolic acid on AP-1 and NF-κB expression in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Guangdong Med J, 2016, 37(17): 2545-2548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GAYX201617006.htm陈涛, 何文华, 黄雯, 等. 熊果酸对肝星状细胞内AP-1、NF-κB表达的影响[J]. 广东医学, 2016, 37(17): 2545-2548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GAYX201617006.htm [36] CHEN L. Anti-fibrosis of salidroside: ROS-related TGF-β1, NF-κB, MMPs/TIMPs and NO pathways[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2013.陈磊. 红景天苷抗肝纤维化: 涉及ROS相关的TGF-β1, NF-κB, MMPs/TIMPs及NO通路[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2013. [37] HUANG J. Experimental study on the protective effect of silybin on alcoholic liver fibrosis model rats through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, 2016.黄静. 水飞蓟宾通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对酒精性肝纤维化模型大鼠的保护作用机制的实验研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学, 2016. [38] SUN LB. Intervention effect of FAC and EGCG on hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl4 in mice and its mechanism[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2019.孙利兵. FAC及EGCG对CCl4致小鼠肝纤维化的干预作用及其机制研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2009. -



 PDF下载 ( 2372 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2372 KB)

 下载:
下载:


